Eye diseases
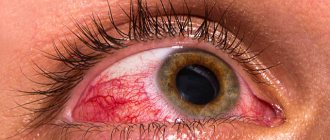
Chronic infectious kerato-conjunctivitis, accompanied by diffuse inflammatory infiltration of the submucosal tissue with the formation of follicles (trachomatous grains) resulting in scarring. The causative agent of trachoma is chlamydia trachoma.
Clinical picture
The incubation period is 7-14 days. The onset of the disease is inconspicuous, less often acute, with symptoms of conjunctivitis, hyperemia and infiltration of the upper transitional fold. As the process progresses, infiltration and the number of follicles increase. The process spreads to the cartilage, the upper eyelid becomes heavy and droops - trachomatous ptosis develops. Subsequently, the process spreads to the conjunctiva of the eyeball, which thickens and becomes cloudy; Possible formation of follicles on the semilunar fold, papillary hyperplasia. All these changes are characteristic of stage I of trachoma. In stage II, the disintegration of follicles and their replacement with connective tissue—the formation of scars—are observed; in stage III - widespread scarring of the conjunctiva in the presence of residual effects of inflammatory infiltration and follicles. The fourth stage is complete scarring of the conjunctiva without inflammatory phenomena, clinical recovery. Trachomatous pannus, a superficial diffuse vascular inflammation of the cornea, is characteristic of trachoma. The process begins with the appearance of infiltrates at the upper edge of the cornea, into which conjunctival vessels grow; the process spreads down, reaches the center of the cornea, and can cover the entire cornea. An outcome with multiple consequences as a result of scarring of the mucous membrane: symblepharon - fusion of the conjunctiva of the eyelid with the conjunctiva of the eyeball, trichiasis - abnormal growth of eyelashes, inversion of the eyelids, curvature of the cartilage. The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture and identification of specific intraepithelial inclusions in scrapings from the conjunctiva.
Treatment
For trachoma of stages I, II and III, 1% tetracycline ointment is applied to the eyelids 4-5 times a day for 2-3 months. When transitioning from stage III to stage IV, the ointment is applied 2 times a day. 1% dibiomycin ointment is applied to the eyelids once a day at night for several months. In persistent cases, local drug treatment is combined with the use of sulfonamide drugs in age-appropriate doses 4 times a day for a week. If the follicles do not tend to develop back, then drug therapy is combined with squeezing out the trachomatous follicles, which is carried out 2-3 weeks after the start of treatment.
Visual analyzer
analyzer
In the human body, as everyone knows, there are six sense organs, with the help of which it is possible to perceive the environment in the broad sense of this concept. The importance of smell, touch, hearing, taste, muscle-joint sense can hardly be overestimated when performing complex professional actions. However, it is even more difficult to overestimate the importance of the visual analyzer when performing a basic reading of a given text, for example. Few people think about the importance of the visual analyzer for its good functioning in the absence of diseases, but it is worth turning off the light in the evening in your own room or trying to leave the house with your eyes closed, or having breakfast with a blindfold, and it will become clear to anyone how important good vision is. The visual analyzer is, in its function, part of the central nervous system. To carry out this function in the body, nature provides several different organs that perform separate subtasks to ensure the highest quality functioning of the organ of vision. Among them are the auxiliary organs of the visual analyzer: eyelids, extraocular muscles, eye socket, lacrimal organs (tear-producing and tear-draining parts); the eyeball itself; optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, subcortical and cortical centers of the brain. All these organs work as a single whole, as a result of which the visual analyzer is a complex optical device with a variable focal length, providing high-quality information in a wide range of brightness and contrast of the observed objects and background, allowing stereoscopic viewing of moving objects in color, including the movement of the person himself. Due to the development of science and technology, today there is not a single device that would have the full range of functional capabilities of the human eye. Any disturbances at any level of the visual analyzer inevitably lead to a deterioration in the quality of vision. Some of them are fully or partially correctable or removable in nature as various options for defocusing (myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism, clouding of optical media) through the use of optical correction means, or surgical interventions, the cure of acute inflammatory diseases or the correction of certain disorders in chronic diseases. Unfortunately, not all diseases and disorders of the visual organ are reversible. In addition, not all diseases in the early stages of their development are noticeable to a sick person. That is why regular, approximately at least once every 12 months, consultations with an ophthalmologist are important.
| Make an appointment | Make an appointment by calling +7 (812) 600-67-67 or filling out the online form - the administrator will contact you to confirm your appointment |
UNION CLINIC guarantees complete confidentiality of your request.
Eye diseases and damage
Unfortunately, eye diseases are widespread. For people over 40 years old, this becomes one of the main problems. In Russia, about 60% of the population has vision problems, and more than 1 million are visually impaired and blind.
Eye diseases include the following:
Myopia
- a disease in which it is difficult for a person to distinguish objects located far away.
For farsightedness
a person has trouble seeing objects at close range.
Astigmatism
- change in the refractive power of the eye. With this eye disease, light rays pass at different angles. The retina does not produce a clear image of an object due to the fact that each point appears blurry.
Glaucoma
characterized by increased intraocular pressure. This can lead to the death of the optic nerve.
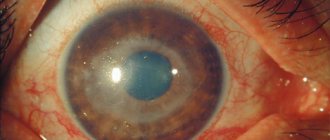
Cataract
occurs as a result of a violation of the transparency of the lens.
Retinal pathologies
. The most common type is retinal detachment.
Strabismus
- impairment of binocular vision. It is expressed in the non-parallelism of the optical axes of the eye. This results in split images.
Inflammatory eye diseases
. For example, conjunctivitis.
Myopia and farsightedness
Cause of myopia
, or myopia, is that a clear image of objects in the surrounding world, passing through the optical system of the eye, is formed “close” in front of the retina. Where does the name of the disease come from?
The causes of myopia may be elongation of the eyeball
or
insufficient functioning of the ciliary muscle
. In the latter case, accommodation is disrupted; the lens does not flatten enough for the required angle of refraction of the rays.
Therefore, myopic people have difficulty seeing distant objects, while being able to clearly distinguish what is nearby.
To correct the defect, glasses with biconcave lenses are used.
There are also special physical exercises for the ciliary muscle that can restore its functions or prevent the progression of myopia.
Farsightedness
to some extent the opposite of myopia. In this case, a clear image is formed behind the retina.
Causes of farsightedness
– shortening of the eyeball (for example, almost all infants are farsighted due to the small size of the eyes), as well as the inability of the lens to accommodate, which increases with age.
As a result, farsighted people, in contrast to nearsighted people, have difficulty distinguishing objects located near their eyes.
In this case, vision correction is achieved using glasses with biconvex lenses.
Thanks to the constant development of medicine, people have learned to deal with many eye diseases.
But the rule that says that a disease is easier to prevent than to treat has not been canceled. To prevent eye disease, you should try to follow the following rules:
Firstly, your eyes need to be protected from pollution.
. It is not recommended to rub or touch them with your hands. If a speck gets into your eye, you should rinse it with cooled boiled water or blink in the water.
When reading and writing, the distance from the book and notebook to the eyes should be 30-35 cm
. Place your hand on your elbow and touch your temple with your fingers. This will help check this distance.
After half an hour of visual work, the eyes need a few minutes of rest.
Organization of the workplace is also very important.
. The light should come from the front on the left side. With proper lighting, human performance increases.
Radiation from TV screens and monitors has a strong impact on the eyes. Therefore, spending time with them should be limited.
It is highly recommended not to read on public transport.
. When shaking, the lens of the eye needs to accommodate almost every second, which leads to severe wear and tear on the ciliary muscle.
During intense visual work, we blink very rarely. As a result, the eye does not receive physiologically necessary hydration. Therefore, you should blink as often and systematically as possible. Or even use drops that additionally moisturize the eye.
Eyes should be protected from ultraviolet radiation
. Despite the well-developed auxiliary apparatus of the eye, which protects the eyeball from external influences, the organ of vision is often injured.
In case of penetrating injury, foreign bodies cannot be removed from the eyeball.
. You need to see a doctor.
If caustic liquids get into the eye, rinse it with running water.
In case of severe bruises or burns, a sterile bandage is applied to the eye and the victim is taken to a doctor.
To prevent such incidents during work, you must follow safety precautions.
Eye exercises that, together with the information above, will allow your visual analyzer to function without failure for as long as possible.
Blink frequently and intensely for a minute.
Blink your eyes closed.
Move your gaze from the tip of your nose (10 seconds) to distant objects (about 30 seconds) for some time. This exercise has a strengthening effect on the ciliary muscle and even helps get rid of myopia.
Massage your eyebrows with light patting movements with your fingertips.
Close your eyes with your palm for one minute.
Types of hereditary diseases
Doctors divide hereditary eye diseases into three categories:
— external defects that do not require special treatment; - congenital pathologies that require surgical intervention to eliminate; - eye abnormalities associated with diseases of other organs.
The causes of such diseases can be various factors: internal and external. Let's look at them in more detail.
- Disruption of the development of normal tissues and their replacement with pathological ones while in the womb, as well as difficult childbirth.
- Hormonal imbalances in the mother's body.
- Age of parents (the risk group includes couples under 16 years of age or, conversely, over 40 years of age).
- Chromosome mutation.
- Consanguineous marriages.
- Incompatibility of the Rh factor of mother and fetus and some others.
The main cause of pathological heredity is gene mutation, which provokes the appearance of hereditary diseases. Doctors and biologists admit that the mechanism of such a change is still not fully understood.