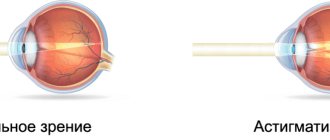
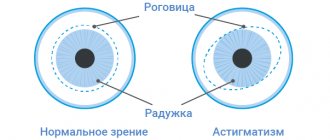
Astigmatism is a visual impairment caused by changes in the shape of the cornea or lens of the eye. This disease is the most common and can be farsighted, nearsighted (myopic) or mixed. The mixed type is characterized by the development of farsightedness along one axis (the main meridian) and myopia along the other axis (the second main meridian). With astigmatism, a person sees objects around him unclearly, often in a distorted form. Depending on the specific meridian, astigmatism is characterized by a difference in refractive power, which causes objects to be distorted horizontally or vertically. There are direct and reverse astigmatism.
Causes
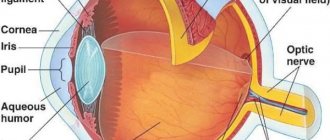
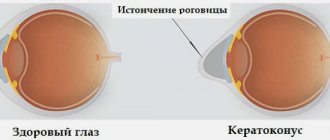
The disease is caused by a violation of the shape of the eye lens or uneven curvature of the cornea. Their configuration is considered normal, close to spherical. With astigmatism, it changes, the eye begins to perceive the image of objects in different planes.
For the most part, astigmatism is hereditary; the pathology of the visual organ is formed at the intrauterine stage. This is caused by genetic predisposition, underdevelopment of the optic nerve of the fetus, and infectious diseases suffered by the woman during pregnancy.
Note! If at least one of the parents has astigmatism, the child should be shown to an ophthalmologist and examined at the earliest possible age.
The acquired form is associated with injuries to the cornea or lens, and the consequences of eye surgery. The development of astigmatism can also be influenced by dystrophic processes (keratoconus - a pathology in which thinning of the cornea occurs and a change in its shape), clouding of the cornea as a result of inflammatory lesions.
Astigmatism can be provoked by the use of incorrectly selected glasses or contact lenses, increased intraocular pressure, and pathologies of the maxillofacial apparatus, in which the structure of the orbit changes and the eyeball is deformed.
Treatment of astymatism
Astigmatism is considered one of the most difficult refractive pathologies to diagnose and treat. That is why, to make a diagnosis, the qualifications of specialists and the ability to conduct an examination using modern, highly informative equipment are of particular importance.
The Moscow Eye Clinic has created all the conditions for rapid diagnosis and effective treatment of all types of this refractive error. Treatments for astigmatism recommended by our specialists may include:
- Contact correction.
- Hardware treatment.
- Microsurgical operation.
In addition, here you can get rid of concomitant ophthalmological pathologies that cause disruption of the refractive powers in the transparent media of the eye: corneal injuries, keratoconus, etc.
In the medical department, everyone can undergo examination using the most modern diagnostic equipment, and based on the results, receive advice from a highly qualified specialist. We are open seven days a week and work daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. Our specialists will help identify the cause of vision loss and provide treatment for identified pathologies. Experienced refractive surgeons, detailed diagnostics and examination, as well as the extensive professional experience of our specialists ensure a favorable outcome for the patient.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure and make an appointment at the Moscow Eye Clinic by calling multi-line phone 8 (daily from 9:00 to 21:00, free for mobile phones and regions of the Russian Federation) or by filling out the online registration form.
Mironova Irina Sergeevna
Classification
Astigmatism is classified according to several different criteria:
| Signs | Form | Explanations |
| By groups | physiological astigmatism | caused by uneven growth of the eyeball; the difference in refraction of the main meridians is from 0.5 to 0.75, no more than 1 diopter; there is no noticeable effect on the quality of vision; in children requires careful monitoring and timely response in case of deterioration of vision |
| pathological | the difference in refraction of the two meridians reaches 1 diopter or more, visual acuity noticeably decreases; medical intervention is required | |
| congenital | hereditary pathology; manifests itself in early childhood (1-2 years) | |
| acquired | The cause of the appearance is injuries, eye surgeries, in some cases malocclusion pathologies, infectious diseases | |
| According to development options | corneal | a common form of congenital changes; the refractive power of the cornea is exceeded in comparison with other elements of the organ of vision |
| lenticular | the configuration of the main lens of the eye changes; most often results from injury; cannot be corrected with lenses; treatment requires surgery or complete lens replacement | |
| By form | correct | simple hypermetropic – farsightedness is observed |
| simple myopic – the disease develops in combination with myopia | ||
| complex hypermetropic – characterized by varying degrees of severity along each of the axes | ||
| complex myopic – there is no coincidence between the retina and the main focus | ||
| mixed - refractive error in combination of farsightedness and myopia in one eye organ | ||
| wrong | different sections of one meridian are distinguished by irregular curvature - in the shape of a horizontal oval; usually caused by injury or surgery | |
| By degree of development | weak | any changes up to 3 diopters, independent of the reasons for the appearance and the mechanism of development; often unnoticeable to the patient; correction is possible with glasses or contact lenses; impact on quality of life is minimal |
| average | changes in refraction 3-6 diopters; conservative treatment is difficult | |
| strong | changes above 6 diopters; difficult to correct; advanced cases are corrected by surgical intervention |
Symptoms (signs)
The disease begins to develop without pronounced symptoms; with refractive errors of up to 0.5-0.7 diopters, a person does not experience major problems with vision. He may associate some discomfort with eye fatigue after working at the computer or watching TV.
Gradually, the clarity of vision decreases, objects appear blurry, and sometimes appear double. A person has difficulty reading texts with small print and looking at miniature objects.
Another characteristic symptom is headaches (eye area, forehead, brow ridges). Signs of “night blindness” appear - vision deteriorates at dusk. The eyes tolerate electric lighting more easily than daylight.
The development of astigmatism is accompanied by a characteristic sensation of “sand” in the eyes without redness of the conjunctiva. The consequences of a severe injury can be expressed by a noticeable distortion of the shape of the eyeball, this is already a reason for urgent surgical intervention, otherwise the eye may become completely blind.
The reason for an ophthalmological examination and diagnosis of the disease may be any of the following factors:
- you are forced to tilt your head to change the optical axes of the eye;
- squint while looking at objects;
- in an attempt to better examine the object, you try to come closer to it or, conversely, move away;
- noticeable fatigue is caused by watching TV, reading, working;
- prolonged attempts to focus your gaze lead to headaches and dizziness;
- general well-being and neuropsychic state are disturbed.
Symptoms in children
It is not easy to determine congenital astigmatism in a child with a weak degree of pathology. Since such children cannot compare their condition with the norm, they do not complain of vision problems. Parents can guess the first symptoms of the disease from the following indirect signs:
- when looking at an object, the child is forced to squint his eyes and tilt his head at different angles;
- he, unlike many healthy children, is reluctant to draw, sculpt, does not even want to look at pictures in a book, fine motor skills are impaired;
- Headaches may appear (most often in the frontal part, in the eyebrow area).
All these manifestations can be attributed to indirect signs, but they also serve as a reason to visit an ophthalmologist.
BLOG OF DMITRY EVTIFEEV
I think that the use of optics, any kind, in the world of cinema and the world of photography is still somewhat different. Photos and videos are different things, besides, filming, by definition, is a thing, that is. initially professional. Ruining a film with illiterate camera work (if only in terms of selection and improper use of the lens) is a disaster. A photographer is usually not within such strict limits. It is clear that professional photographers also cannot joke with optics, but in general I was talking about cinematographers. That’s why I think that “how and how” ordinary photographers can play with vignetting is not suitable for cinematographers. They have other tasks. If in the era of film cinema the permissible deviation of the center from the edges was 30% and this was the world norm, then in the digital era this deviation is already 5%.
Of course, the advent of computer technology and general progress did not bypass the production of lenses. I even heard that it seems like the lens polishing process itself has changed from parallel to concentric. Yes, and photographers have advanced, before in order to examine the frame in detail, in what size should it be printed? Now increase it by at least 1600%) Here, indeed, nothing will go unnoticed.
The value of vignetting is, of course, important. Maybe not so for ordinary amateur photographers, for whom a lens profile or one slider movement in Photoshop is enough. As you rightly noted, he is a “particularly demanding photographer,” and maybe he has such tasks that nothing can be left to chance.
We all, as I believe and hope, are interested in many things) Just in conversations with you, I have heard you mention several times in one context or another about astrophotography and telescopes. From this, in fact, my conclusion followed that this is one of your hobbies or interests. Of course, I cannot have any idea at all about the degree of its depth. But, you see, if a person mentions something similar quite often, then it is remembered, since it is quite obvious that this is not accidental. Well, I know our St. Petersburg latitude and weather firsthand, I’ve lived in this city all my life) Maybe that’s why I didn’t become an astrophotographer) How can one not remember Immanuel Kant, with his probably most famous statement “Two things always fill the soul with something new and that’s all.” with greater surprise and awe, the more often and longer we reflect on them - this is the starry sky above me and the moral law in me.” Although in Konigsberg, in Kant’s homeland, the sky also seems to be not very different from ours, of course, with a discount for centuries)
I understood your analogue example. But I was talking about something else, so I asked again. The word “experienced” for me just means that a person has experience working with different lenses and knows what kind of picture they produce. That is why he does not always need to compare 2 or more lenses with each other. Well, I’ve been shooting all my life, let’s say with a 50mm 1.4 Nikon. Don’t I really know how he shoots at different apertures and distances? And I wanted to buy, say, ZEISS Milvus 50/1.4. Will I really not see the difference? Or is it so small that it can only be detected by parallel shooting with two lenses and a detailed examination of the photos under high magnification? If this is so, then why take another lens at all if the difference is visible only under a microscope?) The same applies to autofocus speed and workmanship. Of course, if a person is not so experienced in working with a lens, then photographing a wall with one lens will not do much for him. Regarding the subjectivity of measurement by photographing walls, I have already expressed my point of view. 2 lenses or 22, for me this is still a qualitatively objective, but quantitatively subjective opinion.
The assessment was about me and no one else. “Can’t I really understand from the test images how well this lens suits me?” Others have nothing to do with it. I spoke only about my personal evaluation criteria for myself and for no one else. Now, if I had said, “Can’t I really understand from the test images how suitable this lens is for Dmitry?”, then it would be a different matter, your comment would be appropriate)
And I completely agree with you; indeed, it would be very good to have TS. lens rating, yes, we have already touched on this issue a little. After all, the range of lenses is very wide, and everyone is probably wondering, but lens A, how much better is it than my lens B? In the end, lenses are bought, in most cases, to improve the quality of the photo) How can I decide which lens to change mine to, if not by comparing mine with other lenses? Actually, here we are in complete agreement. As well as in the assessment visually (from pictures), and quantitatively (from numbers).
About the program. It seems to me that you have greatly complicated everything. Why should I move the target, the tripod, or change the lighting? The target is set, the tripod is set, the head is adjusted, the light is set. Only the lenses change. What could change here? Distance from target to lens? If you are shooting at 50 focal lengths, let’s say the lens is 50mm. Distance 2m 50cm. A few centimeters from 2m 50cm is not so critical for relative tests. By the way, I have asked people many times, where should one measure the distance to the test target? And everyone speaks differently) Moreover, it seems like these people are not new to photography. And why should the light in the apartment change if I use, say, special lighting, photographic? Is the voltage jumping or what is happening to the light? I don't understand this point. I would be grateful if you could clarify for me.
I agree with the focus. But what difference does it make whether I focus in the studio or at home? Does focus work differently in the studio?) Any focus works, both phase and contrast, and manual too. It doesn’t walk manually on its own, of course; it may not be possible to simply set the perfect focus. When I read your articles about testing lenses, I kept wondering how Dmitry manages to focus so accurately manually to see such a small difference in sharpness? Where is his guarantee that he is clearly focused? Yes, you can do a series, this is probably the best thing. I don’t even mention other tricks like remote release and mirror raising. By the way, I watched a video by a photographer here the other day, and he was talking about some lens that if he gets 1 frame out of 10, then that’s normal) I don’t know, I’m an amateur, but I’d probably hang myself with such a lens))
Regarding the results of the program. There's not only lp/mm, I mean MTF Mapper. Of course, I understand your breadth, Dmitry, and I appreciate it, but honestly, I have no desire to show the results of my tests in the program to anyone, since they are done personally for me, regarding my different lenses. They have a relative meaning, not an absolute one. I can relax some test conditions, as long as this relaxation is the same for all my tested lenses. The lenses will still receive their places objectively, although the numbers in which all this will be expressed will be far from absolute values. And why should I go out to people with these numbers if, as you say, “this is achievable only in studio conditions”) Why would I deceive people? But I can, in one way or another, get the lens I need for a while, test it under similar conditions and get numbers that are incorrect in the absolute sense, but correct in the relative sense. In addition, if in relative tests, lens A is better than lens B, then in absolute tests the same will happen. The only difference will be in the numbers.
“To date, not at all.” So I say that this is the whole point, this is what our whole conversation is about, both this one and the earlier ones. Just all for the sake of making at least a “relative how” out of “no way”) There are so many of us, sufferers... the darkness is overwhelming, honor everyone, but things are still there. Of course, I am far from the idea of becoming a benefactor of photohumanity, my scale is not the same, too small for such daring, but still, I would like to at least somehow make progress in solving this problem. "A rolling stone gathers no moss".
Thanks for the links, I'll take a look. Maybe some idea will come to mind. Well, generally useful.
I don’t agree to buy a “pig in a poke”) Waiting is also not my principle. There must be a way out, albeit partial and relative, but it must be.
Diagnostics
The integrated use of various diagnostic methods helps to identify the disease. Visual acuity (visometry) can be checked either without correction or using a trial frame: one eye is covered with an opaque screen, and the gaze of the other is focused through cylindrical lenses of different refractive powers placed in front of it - in this way the ophthalmologist achieves maximum visual acuity.
Refraction is determined using the skiascopy method (shadow test). More complete information is provided by refractometry - a study using a beam of infrared light that is directed through the pupil to the retina. The procedure is performed in a state of mydriasis (pupil dilation).
Inflammatory or degenerative diseases of the cornea are detected using eye biomicroscopy (non-contact diagnosis of eye diseases, which allows examining the intraocular media and the structure of the eye under magnification using a slit lamp).
The examination of the fundus and vitreous body is carried out through ophthalmoscopy - special instruments, an ophthalmoscope or a fundus lens are used, with the help of which the doctor assesses the condition of the retina, optic nerve head, and fundus vessels.
The radius of curvature of the corneal surface is measured using an ophthalmometer and ultrasound of the eye. Computer keratotopography, a non-invasive method that involves the use of laser scanning, allows identifying degenerative non-inflammatory eye diseases in which thinning and changes in the shape of the cornea occur.
Glasses and contact lenses for astigmatism
The selection of glasses for vision correction for astigmatism is preceded by a thorough diagnosis. “Complex” glasses are used, into which special cylindrical lenses are inserted. With a high degree of astigmatism, getting used to them can be accompanied by unpleasant symptoms - dizziness, pain in the eyes, visual discomfort.
In previous years, astigmatism, in addition to glasses, was corrected with rigid gas-permeable contact lenses. Many patients complained about their inconvenience, in addition, they had a bad effect on the cornea. With the advent of modern technology, they were replaced by soft toric lenses. Due to their special geometry, they are well maintained in a stable position without interfering with eye movements.
Note! Starting to wear glasses or contact lenses to correct your vision will not get rid of the disease once and for all.
You should regularly visit an ophthalmologist, because while using glasses or lenses, they may need to be replaced.
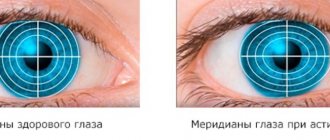
How do astigmatists see?
In the image you can clearly see the difference between healthy vision and pathology. The top photo is how a healthy person sees. The bottom picture is the result of a person with a visual impairment. In the second picture you can clearly see blurry objects that have no outline.
It is known that with astigmatism, focusing of vision on certain objects is impaired. The appearance of the meridians leads to the appearance of several pictures that are displaced. This is the cause of blurry and unclear objects.
With the help of this photo you can understand that the distance of objects does not matter. At any distance, all objects are not clear. The photo on the left provides an example of healthy vision, and on the right - astigmatism.
The degree of damage to the disease depends on how an astigmatist sees. The first stage does not cause major changes. Characteristic symptoms appear when the disorder exceeds the 3D mark.
With normal vision, all objects are clear and do not blur. They are clearly visible from a distance. Astigmatism is accompanied by significant visual impairment. This can be clearly seen above in the comparison photo.
Treatment of astigmatism in children
Vision in children is more plastic than in adults. The earlier their astigmatism is diagnosed, the easier it is to correct the resulting deviations. If treatment is not started on time, there is a risk of developing strabismus and even partial loss of vision.
Until the age of 18, the visual organ continues to grow, so only conservative treatment methods are used, surgical or laser correction is used later.
The most common method of correction is wearing special astigmatic glasses. But first the child will have to get used to them; for some time he may experience discomfort and headaches. If they do not go away within a week, you should visit the doctor again: your glasses may need to be replaced.
To correct vision in children, hard contact lenses are also used to correct the curvature of the cornea. But this method will only help correct weak astigmatism up to 1.5 diopters.
After 18 years, laser correction can be used.
What other methods of correcting astigmatism are there?
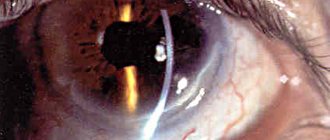
In cases where astigmatism is accompanied by farsightedness or myopia, another surgical method is used as an alternative to laser correction - installing an intraocular contact lens on the lens. Also, in some cases, tangential keratotomy, or correction of corneal pathology by incision, is indicated. Previously, this operation was carried out manually. Nowadays, a universal “scalpel” is used for this in the form of ultrashort laser pulses, which make a cut without heating or damaging surrounding tissues. Tangential keratotomy is the most accessible method of laser correction. In some cases, various implants are also used - astigmatic lenses - and special frames are installed to support the cornea (crosslinking and corneal rings).
What other correction methods are there?
- Intraocular contact lenses.
- Tangential keratotomy.
- Installation of implants (astigmatic lenses).
- Crosslinking and corneal rings.
Remember that only an ophthalmologist can correctly determine the treatment method after conducting a detailed examination of the patient’s visual system. Independently choosing a correction method can lead to worsening vision and serious adverse consequences for the eyes.
In the Ochkov.Net online store you can order high-quality lenses for astigmatism correction from world brands. We guarantee you ease of ordering and fast delivery of goods throughout Russia.
Treatment of astigmatism in adults
When choosing a correction tactic, the doctor takes into account the severity of symptoms, the patient’s age, response to treatment, and the risk of complications.
In adult patients, correction of astigmatism is more difficult than in children, since their visual organs are already formed. But the set of techniques used is the same: mild forms of pathology require the use of special glasses and contact lenses (some of them are recommended to be worn constantly, others - to be worn only at night).
Advanced or traumatic astigmatism requires surgical intervention. As a rule, the problem is solved with the help of laser surgery, but in difficult cases, keratotomy (an operation with a non-through incision of the cornea of the eye with further scarring at the micron level) or keratoplasty (replacement of fragments of the cornea with a donor graft) is used.
Average degree of astigmatism
With an average degree of astigmatism, a person feels very specific difficulties with vision, he is worried about:
- Rapid eye fatigue.
- Poor distance and/or near vision.
- Feeling of “blurred” shapes.
- Distortion of objects
- Headache.
Moderate astigmatism is usually accompanied by decreased visual acuity, which impairs the patient’s performance. Common symptoms are often observed:
- Pressing headache.
- Sensation of a constricting hoop in the back of the head, forehead, temples.
- Dizziness.
- Feeling of instability.
Such symptoms often force the patient to seek help from an ENT doctor or neurologist. But the first on the list of visiting doctors, in this case, should be an ophthalmologist.
Timely correction of moderate astigmatism will help avoid the occurrence of “lazy eye” syndrome, as amblyopia is called, when the functions of one of the retinas are blocked and vision becomes monocular—non-volume. Its sharpness also seriously deteriorates.
Eye exercises for astigmatism
Special eye exercises cannot be considered as an independent method of treating astigmatism; these exercises are used as an addition to the main correction methods.
With the help of specially designed exercises, you can slow down the process of vision loss and relieve fatigue and tension in your eyes. Such charging is considered a good way to prevent ophthalmic pathologies. For astigmatism, it helps to change the curvature of the lens in the desired direction.
Various techniques are used, including gymnastics to relieve eye strain, the Bates and Zhdanov methods. Before you start using them, you should definitely consult an ophthalmologist.
Note! Such exercises should not be done for six months after eye surgery.
Prevention
It is impossible to fight congenital eye pathologies. But basic rules of visual hygiene help prevent the appearance of astigmatism and stop its development. For children, this is, first of all, limiting the load on the eyes; it must correspond to the age of the child.
Try not to overwork your visual analyzer. Normalize your daily routine, if possible, balance your diet, moderate your computer work, and watch TV.
If you are at risk for astigmatism, these simple but effective rules should accompany you throughout your life.
What about surgery?
It seems that there is nothing simpler - you have surgery and goodbye astigmatism, however, there are pitfalls here too: the method does not guarantee 100% reliable scarring, and there is a risk of developing postoperative astigmatism. Even excimer laser therapy for irregular astigmatism does not guarantee a good result. Of all the methods of laser correction of astigmatism, Femto LASIK is the most effective for irregular astigmatism.
Irregular astigmatism is a serious disease. A person sees poorly both near and far, the contours of objects are distorted, it is difficult for him to determine which of them is closer and which is further away. Even with a timely visit to an ophthalmologist, it is very difficult to cure irregular astigmatism. It is much easier to prevent the development of this pathology - to avoid eye injuries and not expose them to toxic substances.