Some expectant mothers complain that their vision decreases during pregnancy. This problem worries 25-45% of women. Most often, visual impairments are caused by hormonal changes in the body and are temporary, i.e. after childbirth everything goes away.
What are the causes of vision problems during pregnancy?
- Loss of moisture from the mucous membranes, their excessive dryness. This occurs due to hormonal imbalance and restructuring of metabolic processes in a woman’s body. Often pregnant women suffer from dry eyes due to the use of contact lenses to correct vision while constantly working on a computer.
- Histoses are pathologies when the body accumulates excess water in cells and tissues, including the cornea. Therefore, the natural shape of the optical structures in the eyes changes and the perception of reality is distorted.
- Development of preeclampsia. This formidable complication occurs not only due to decreased vision during pregnancy, but also due to sudden increases in blood pressure and the formation of extensive swelling on the woman’s body, as well as the appearance of protein in the urine.
Reduced intraocular pressure
During pregnancy, intraocular pressure decreases by 2-3 mm Hg [3] and remains low for several months after birth. Several mechanisms of this phenomenon have been described: increased outflow of aqueous humor; decreased vascular tone, leading to a decrease in episcleral venous pressure; a general increase in tissue elasticity, leading to softening of the sclera; general acidemia. This may be important for women with glaucoma, as their condition has been reported to improve during pregnancy. [1,2]
How to avoid visual impairment during pregnancy?
- Do not miss scheduled visits to the ophthalmologist: the first visit should be made at 10–14 weeks, the last at 32–36 weeks. If problems are identified or there were vision problems before pregnancy, the expectant mother will need more frequent consultations.
- If any negative changes occur, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will determine the degree of refraction, examine the fundus of the eye, and the condition of the retina (there should be no tears on it). A sharp deterioration in these indicators may become an indication for cesarean section.
- Avoid unnecessary physical activity, sharp bends, prevent rapid blood flow to the head, control blood pressure.
- Perform special eye exercises regularly. Such exercises take no more than 10 minutes a day.
- The doctor may additionally prescribe vitamin-mineral complexes with vitamins C, B2, E and Omega-3 to maintain healthy eyes, which do not receive the necessary nutrition during pregnancy.
For example, the Pregnoton Mama complex is designed specifically for pregnant and lactating women and includes 15 vitamins and minerals, including those mentioned above, as well as Omega-3. These substances not only help prevent birth defects and provide micronutrient support to the expectant mother, but also help prevent vision problems.
THIS IS NOT AN ADVERTISING. THE MATERIAL WAS PREPARED WITH THE PARTICIPATION OF EXPERTS.
What should you pay attention to?
During pregnancy, women become very suspicious. At times it may seem that your vision has become poor. It's easy to explain. The fact is that during pregnancy, all the connective tissues of the body become more elastic, and the structure of the eye also undergoes such changes. But, unfortunately, our eyes do not have the ability to recover, that is, vision during pregnancy can actually worsen and fall by one or two diopters.
The peculiar effect of flies flashing before the eyes is usually not dangerous; it can be observed in any person. This is a completely normal process in physiology. Usually, all changes in the eyes go completely unnoticed, which is why they are dangerous. But occasionally, a lightning effect may appear, that is, you may see periodic bright second flashes. If you notice something similar in yourself, immediately contact an ophthalmologist.
Vision problems are quite common these days. Almost every second person suffers from myopia. If you have low vision, you should see your eye doctor every month throughout your pregnancy. At this time, it is better not to wear lenses, but to limit yourself to glasses. Most women at this time experience discomfort when wearing lenses. During this period, the entire body of expectant mothers is rebuilt, the structure of the eye also changes, so lenses that are selected individually may no longer suit you.
Every woman who has vision problems asks the question: how does myopia affect childbirth, whether it will be natural or by caesarean section. A lot of factors influence the final verdict of the ophthalmologist on whether to allow a woman to give birth on her own if she is myopic. Everything is assessed: age, general condition of the body, degree of vision impairment, condition of the retina, etc.
The main reason why an ophthalmologist prohibits natural childbirth is retinal dystrophy. During labor, pushing causes serious changes in intraocular pressure, which can lead to retinal detachment, changes in the fundus and sudden loss of vision.
From a medical point of view, the presence of myopia or other eye diseases only in 10% of cases leads to a cesarean section during pregnancy. If your ophthalmologist's opinion clearly says yes to a cesarean section, don't be discouraged. It is much more important to preserve both the health of the unborn child and your own. Your baby will need you healthy and strong.
At up to 35 weeks, you can have laser vision coagulation. During this procedure, which takes only a few minutes, a kind of “welding” of the retina is performed in the weakened layers. In these places, scarring of the connective tissue occurs and a strong connection between the retina and the choroid is created. This simple procedure will save you from further deterioration of vision and possible caesarean section.
Signs of vision problems
- The appearance of cloudiness and blurriness before the eyes;
- Feeling of dry eyes, burning, itching, “sand”.
- The appearance of floaters or dark spots before the eyes.
- Discomfort from daytime or bright evening light.
- Change in clarity of perception.
- Double vision.
Vision often deteriorates during pregnancy in women with myopia, farsightedness, and astigmatism. In these cases, increased eye strain can cause an exacerbation of individual symptoms or overall progression of the disease.
Visual pathologies can manifest themselves in expectant mothers with diabetes or kidney diseases, in such cases they will be combined with clinical signs of the underlying disease (extreme thirst, sudden weight fluctuations, weakness or increased frequency of urination, false urge to urinate, pain in the lumbar region, decreased volume urine)
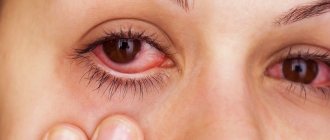
Due to active changes in hormonal levels in the early stages of pregnancy and decreased immunity, expectant mothers can easily catch bacterial or viral infections from others, which manifest as conjunctivitis. Inflammation of the eyes negatively affects visual acuity and manifests itself:
- redness of the mucous membranes;
- severe lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- copious or scanty discharge from the eyes;
- pinpoint hemorrhages in the sclera;
- the appearance of small papules or petechiae on the inner lining of the eyelids;
- severe itching and discomfort.
Pregnancy and the retina
During pregnancy, the main threat to the visual system is the condition of the retina. The retina is a thin layer of nerve tissue located on the inside of the back of the eyeball that absorbs light. It is a complex formation, the main one of which is a thin layer of light-sensitive cells - photoreceptors. The retina of the eye is responsible for perceiving the image that is projected onto it using the cornea and lens, and converting it into nerve impulses, which are then transmitted to the brain. The main problems with the retina are: retinal dystrophy, retinal rupture, retinal detachment.
To prevent possible eye complications during pregnancy and childbirth, it is necessary to determine in advance the state of the visual system of the expectant mother and be sure to check the retina. Ophthalmologists strongly recommend, regardless of how you see and whether you have vision complaints, to undergo an examination at 10-14 weeks of pregnancy .
In addition to a general examination of the visual system, diagnostics of the fundus with a dilated pupil is mandatory. If the diagnostic results do not reveal any abnormalities, then repeating the vision examination closer to the end of pregnancy - at 32-36 weeks . However, if you have myopia, ophthalmologists recommend monitoring your vision monthly. During pregnancy, a woman’s entire body undergoes changes, including her vision. Therefore, the visual system requires special attention from the expectant mother.
Vision decreases during pregnancy - why visiting a doctor is so important
Deterioration of vision during pregnancy most affects those mothers who were already nearsighted or farsighted before conception. Usually, this is a temporary effect, but it is better not to delay consultation with a specialist, as the problem may indicate other complications, such as preeclampsia. If you notice doubling, blurriness, or sudden swelling around the eyes, tell your gynecologist as soon as possible. In the vast majority of cases, vision is completely restored after breastfeeding is completed.
Laser vision correction during pregnancy is not recommended, since the result may be distorted, resulting in progression of the disorder. In addition, after correction, eye drops containing antibiotics and corticosteroids are used, which negatively affect the course of pregnancy. Refusal to use them leads to prolonged healing and sometimes useless results.
If vision deteriorates significantly, doctors recommend a cesarean section. Increased intraocular pressure during labor is normal, but with poor vision, it interferes with recovery after childbirth. Regular visits to an ophthalmologist and following his recommendations will help prevent negative consequences.
Eye changes during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the eyes, their condition and functionality may undergo the following changes:
- Swelling of the eyelids . As a rule, they occur in the morning and are associated with diet. You should increase your intake of liquids (preferably clean, still drinking water or green tea) and reduce your intake of salty foods.
- Dry eyes . Often accompanied by a sensation of a foreign body in the eye, photophobia (increased sensitivity to light). Caused by changes in hormonal levels and a decrease in the secretion of the lacrimal gland. Goes away after childbirth without additional treatment.
- Flashing of “dots”, “spots” . If this becomes a constant phenomenon, then the problem lies in vascular disorders, in spasm of the vessels of the fundus. Requires immediate contact with an ophthalmologist.
- Concentric narrowing . It consists in the fact that a woman ceases to distinguish colors in the periphery of her eyes. This is especially pronounced during long periods of pregnancy. This condition quite often accompanies normal pregnancy and goes away after childbirth.
- Spasm of the accommodative muscle . Symptoms: decreased distance visual acuity and some blurred vision, rapid eye fatigue. This may simply be a temporary change that will stop after childbirth, but may also be a warning sign of myopia. If such changes occur, it is recommended to immediately contact an ophthalmologist to exclude possible complications.
- Discomfort when wearing lenses . It occurs as a result of increased sensitivity of the eye cornea. It is especially pronounced in the last trimester and goes away after childbirth. If the dim comfortable sensations become unbearable, it is recommended to abandon the lenses and replace them with regular glasses.
Various changes are often associated with changes in intraocular pressure - it decreases, especially over long periods. The vessels narrow, which leads to all sorts of discomfort and temporary deterioration in vision function. Most of them do not require special treatment and disappear without a trace after the end of pregnancy. However, pathological changes are also possible, which may result in retinal detachment, partial or complete loss of vision. Therefore, it is recommended to be checked by an ophthalmologist at the beginning, middle and end of pregnancy. If any discomfort, unusual phenomena, etc. occur. You should visit a specialist more often and register if necessary.
Impact on existing diseases
Pregnancy can significantly complicate existing eye diseases. Women with pathologies associated with lesions of the lens, retina, optic nerve, cornea and vascular tract are at risk. To avoid vision loss, it is necessary not only to be regularly observed by an ophthalmologist, but also to take appropriate measures during childbirth. This can be a gentle delivery - the application of obstetric forceps to reduce the period of pushing; in severe cases, a caesarean section is performed.
The most dangerous are optic neuritis and retinitis. Normal childbirth is contraindicated for such pathologies. A caesarean section is performed, and in particularly dangerous cases, pregnancy termination is recommended. For these diseases, constant monitoring by a specialist is necessary, whose testimony will become the decisive factor.