The eyelid, despite its apparent simplicity, has a rather complex structure. In particular, in the inner space of the eyelid there is a number of glands (Meibomian, Zeiss), which produce the “lubricant” necessary for the eye; some of them emerge at the mouths of the eyelashes, others - on the inner, conjunctival mucous membrane of the eyelid.
And although the sebaceous glands of the eyelid are somewhat different from other similar glands on the human body, they are subject to the same problems and risks as any other sebaceous gland. The most common pathology in this case is blockage and cystic suppuration of the gland due to the inflammatory process or its hypersecretory activity (excessive production of functional secretion) as an innate individual characteristic of the body.
This kind of cyst on the eyelid (from the Greek “bubble”), or atheroma, is a benign neoplasm and looks like a ball rolling under the skin. The size of the cyst can vary over a fairly wide range - from a pellet to a pigeon egg and more. In many cases, the patient does not experience any physical discomfort, and if he consults an ophthalmologist, it is only with complaints about a cosmetic defect.
However, sometimes atheroma begins to grow rapidly, fester intensively, and become inflamed; If the size is significant, an optical obstruction to vision may occur. Such (or similar) development will no longer require planned, but urgent ophthalmic surgical intervention.
In addition, there is always a risk behind a “harmless” and painless swelling of missing the onset of a life-threatening malignant tumor process. Hence the quite obvious conclusion: if any tumors, lumps, swellings, or suppurations appear on the skin of the eyelid, self-medication and waiting are strictly contraindicated; Consultation with an ophthalmologist is required.
Causes
Atheroma on the upper eyelid.
Atheroma on the eyelid (lower or upper) usually develops in people 16-60 years of age. There are no exact causes for this condition, but experts have determined what factors can trigger the development of a cyst. A similar disease can develop when:
- hormonal imbalance;
- puberty and menopause;
- impaired functioning of the nervous system, stress;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- weakened immune system;
- some pathologies that occur in a chronic form;
- the presence of other skin diseases (seborrhea, acne, etc.).
Atheroma on the eyelid, causes, treatment, consequences
The human eye is a unique but vulnerable structure.
To preserve it, there are two movable skin coverings on the face - the eyelids. These structures protect and protect human eyes from the harmful effects of the environment (sand, dust, wind, etc.). However, the eyelids, like other components of the human body, are also susceptible to various kinds of diseases.
One of the most common diseases is atheroma of the eyelid. Next, we will talk about this common neoplasm on the face.
What is atheroma of the century according to the ICD?
Atheroma is a cystic skin formation that is localized in the sebaceous gland. It develops in all people, regardless of race, gender and age. It is worth noting that this formation is classified as retention cysts, i.e. they arise due to blockage of the sebaceous ducts located in the thickness of the skin.
Due to the harmful effects of the environment, disruption of metabolic processes in the body, non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, or excessive secretion of sebum, the ducts of the sebaceous glands become blocked or blocked. The sebaceous secretion, unable to find a way out, accumulates in the excretory tract, atheroma is formed, and then a local inflammatory reaction may develop.
The growth can occur in any part of the skin, especially where the hairline is well developed. Mostly sebaceous cysts develop on the scalp, eyelids, skin of the back, neck, and groin area. The only areas of skin where sebaceous cysts do not develop are the skin of the palms and soles.
Causes and mechanism of development of pathology
Atheroma of the eyelid is a benign skin tumor that usually does not pose a threat to health. For purely medical reasons, it is not necessary to remove atheromas. Most patients want benign tumors removed for cosmetic reasons. More than 70% of patients wish to remove atheroma located on the face - near the lips or on the eyelids.
Visually, the cyst quickly catches the eye of the environment, which is unpleasant for many. Atheroma usually does not disappear on its own. Unless the sebaceous gland obstruction goes away again. This is rarely the case with small atheromas, but never with large ones.
The cause of atheroma of the upper or lower eyelid in many cases is blockage of the sebaceous glands. Sebaceous glands typically secrete oil and provide elasticity to the skin and shiny hair.
Dead skin cells or dried sebum can block this excretory duct. Sebum then accumulates because the glands continue to produce oil. However, these are always very small amounts per day, so the atheroma only slowly increases in size.
True atheromas on the upper or lower eyelid occur when cells disperse from the top layer of skin and block the point where hair grows.
Horny cells that regularly form in the skin can no longer come out and accumulate - an epidermal cyst occurs. The more horny material accumulates, the larger the atheroma becomes.
Doctors suggest that there is a genetic basis for these atheromas.
Causes of atheroma on the eyelid
The disease does not develop abruptly, but gradually. Atheroma on the eyelid may not bother a person for many years. After the appearance of obstruction of the sebaceous duct, a gradual accumulation of sebaceous secretion occurs in the lumen of the duct itself.
After the development of atheroma begins, it may stop its growth, but most often the development of the disease continues. Atheroma on the eyelid is a painless subcutaneous formation, palpated as a small mobile spherical structure (from 2 mm to 3 cm or more), painless when pressed.
Most often, it is visually identified as a small, light-colored dot on the eyelid, slightly protruding to the surface. The sebaceous cyst contains a capsule in its structure.
Inside it is filled with a thick whitish or slightly yellow mass, which consists of sebaceous secretions and keratin protein, which is produced in the walls of the sebaceous gland.
Sometimes the atheroma of the eye communicates with the surface of the skin due to a small hole through which masses of a cheesy or liquid nature with a nasty odor can be released. Often, this cyst tends to become inflamed and suppurate, which leads to the development of complications. In this case, opening of the capsule in most cases occurs independently. After a certain period of time they may recur.
The upper eyelid contains twice as many sebaceous glands as the lower eyelid, and therefore, sebaceous cysts develop more often in the upper eyelid.
Preventive recommendations
In order to prevent pathology, it is necessary to regularly consult with your family doctor. If the doctor suspects the onset of the disease, you need to promptly contact a dermatovenerological or surgical hospital.
The patient can prevent complications by leading a healthy lifestyle, eating low-calorie foods, doing moderate exercise, and regularly taking blood tests for biochemical tests.
All these measures will help prevent serious complications for the visual organs.
What is the danger of atheroma of the lacrimal caruncle?
To begin with, it should be noted that a skin lesion cannot become malignant (from benign to malignant). Atheroma is not a tumor! This is a cyst that arises due to the accumulation of lipid secretions in the sebaceous ducts of the skin. According to the ICD (international classification of diseases), atheroma is classified as D23 (other benign skin neoplasms).
Complications of a sebaceous cyst include:
- local inflammatory reaction;
- furuncle;
- abscess;
- phlegmon
Symptoms
Atheroma is a round formation that is displaced by a finger when pressing on the skin of the eyelid. The cyst may become inflamed, red, painful, and swollen.
The inflammation goes away on its own, but more often becomes the cause of a purulent infection. The formation quickly increases in size and opens on its own. When opened, the contents come out of the node.
If the patient does not go to the hospital, blood poisoning occurs - sepsis.
Treatment methods
Actually, diagnosing ocular atheroma is not a difficult task. Patients complain of a tumor-like formation in the eyelid area (often the upper one), round in shape, painless, mobile, the skin over the defect is without any features, but with the development of an inflammatory reaction it can become hyperemic. In advanced forms, complications may develop, which will be discussed below.
It should be remembered that a sebaceous cyst is very easy to confuse with other neoplasms (fibropapillomas, eyelid adenoma, wart, benign eyelid nevus, hygroma, lipoma, etc.).
For differential diagnosis, it may be necessary to take a biopsy specimen and conduct a histological examination.
Therefore, if a tumor is detected on the skin, it is imperative to consult a specialist and choose a rational method of treatment.
Untimely treatment or its absence is fraught with the development of the disease and the appearance of complications!
The following question naturally arises: How to treat this disease? Official medicine recognizes only one method of treating atheromas on the eye - removal. However, there are variations in the method of cyst removal.
There is no need to worry about this. This procedure is not difficult and is painless, most often under local anesthesia.
Despite the presence of several methods for removing a sebaceous cyst, an important point is the removal of the area of skin that is directly associated with the atheroma, as well as resection of the cyst capsule, which is guaranteed to exclude relapses.
- Most often, a surgical incision is made directly above the atheroma, then the neoplasm is removed from the wound or the contents of the membrane are first removed and subsequently the membrane itself. The wound is then sutured.
- There is also photocoagulation of atheroma on the eyelid using a laser. When carrying out this method of treatment, “evaporation of the cyst” occurs and damage to surrounding tissues does not occur.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms indicating atheroma of the eyelid:
- Atheroma appears as a visible bulge on the skin of the face. It can range in size from a few millimeters to centimeters, but can also grow to the size of a chicken egg or a tennis ball.
- The cyst is round, swollen and elastic.
- The touch does not cause pain.
- Large atheromas stretch the skin and cause a feeling of tension.
- Sometimes a dark spot appears on the atheroma; this corresponds to blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland.
- Vision problems occur only with very large tumors.
What does atheroma of the century look like?
Signs of inflamed atheroma of the eyelid:
- pain in atheroma and surrounding tissues;
- skin is sensitive to pressure;
- reddened and swollen skin around the tumor;
- overheating of the skin.
Removal of atheroma from the upper and lower eyelids
In addition to the methods described above, the cystic capsule of the lower or upper eyelid is evaporated using a laser from inside the capsule.
In this case, the cyst is opened using a scalpel, and all the contents of the atheroma are cleaned out. Next, the edges of the skin are moved to the sides and under the action of the laser, the sebaceous cyst shell is evaporated from the inside.
After the manipulation, the wound is sutured and the sutures are removed on the 10th day.
There are a number of contraindications for laser removal of a sebaceous cyst!
These include:
- Diabetes.
- Immunodeficiency states.
- Pregnancy.
- Malignant neoplasms, etc.
The radio wave method allows you to completely avoid relapses after removal of the atheroma; the wound heals without sutures with minimal scars and much faster.
Reviews
About 90% of reviews about atheroma removal are positive. In them, people indicate that the operation is simple, painless and does not cause severe discomfort.
However, after the operation, the wound healing period, which lasts 1–2 weeks, is associated with a certain discomfort, since there is pain, it is necessary to go to dressings and try not to move so that the edges of the incision do not diverge to the sides, but grow together and heal.
In addition, when performing an operation with a scalpel, a noticeable scar almost always remains at the site of the atheroma, which can only be removed by laser resurfacing. It is the scar and discomfort after surgery that are the reasons for negative reviews.
People who regarded the scar and postoperative discomfort as an inevitable but tolerable inconvenience left positive feedback, since the manipulation helped get rid of atheroma.
Prevention of occurrence
Preventive measures include following the rules of personal hygiene, it is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of the skin, in particular the eyelid area, follow a diet to normalize metabolic processes in the body, etc. Following these simple rules significantly reduces the risk of developing this pathology.
Atheroma near the eyelid is a very common pathology that develops as a result of obstruction of the ducts of the sebaceous glands.
Contrary to popular belief, atheroma on the eye is not a tumor, but a cystic formation.
This pathology requires specific treatment, which involves removal of the cyst and subsequent adherence to preventive measures to prevent relapses. The article has been verified by the editors
Source: https://alternativa-mc.ru/glaza-bolezni/ateroma-veka.html
What is the danger of atheroma of the eyelid and lacrimal caruncle?
The main purpose of the lacrimal system is to protect the eyeballs from the negative effects of external factors, as well as the conjunctiva and cornea to avoid drying out.
The pathology is not capable of transforming into a malignant cyst.
A tumor of the lacrimal caruncle is a fairly rare disease that occurs only if a person has fine hairs growing on the lacrimal canaliculi. It is a non-working organ in the human body.
Atheroma of the eye is not capable of transforming into a malignant cyst and does not affect visual function. Although the patient may present the following complaints when visiting a doctor:
Burning sensation in the eye.
- there is a burning sensation in the eye;
- there is a feeling of the presence of a foreign body near the lacrimal caruncle;
- the membranes of the eye are not sufficiently moisturized;
- There is usually no pain;
- There is an increase and hyperemia of the lacrimal caruncle.
The reasons for the formation of a cyst on the eyelid are not known for certain, but doctors say that the development of a cyst can be triggered by:
- eyelashes caught in the eye;
- foreign objects getting into the eyes;
- microtrauma of the eyeball and infection penetrating through it.
Atheroma can cause the following complications in the eye condition:
- suppuration;
- inflammatory process;
- infectious damage to other structures of the visual system.
Experts advise not to wait for complications to form, but to perform an operation to remove such a wen under local anesthesia; for children under 7 years of age, general anesthesia is used.
It should be noted that when purulent contents penetrate the subcutaneous layer, they enter the bloodstream, which can become a source of blood infection. This often causes death.
Symptoms
Atheroma does not have any clinical
, since the neoplasm does not hurt, does not change the structure of the skin in the area of localization, etc. We can say that, apart from an external cosmetic defect in the form of a bulge on the skin, atheroma does not have any symptoms. That is why practicing doctors consider the symptoms of atheroma to be its appearance and structural features, revealed by palpation.
So, the following characteristics are considered symptoms of atheroma:
- A clearly visible limited bulge on the surface of the skin;
- Clear contours of the convexity;
- Normal skin over the bump;
- The structure is dense and elastic to the touch;
- Relative mobility of the formation, allowing it to be moved slightly to the side;
- Visible as a black dot in the center of the atheroma, an enlarged excretory duct of the sebaceous gland.
Thus, the symptoms of atheroma are a set of exclusively external characteristic signs that allow one to simultaneously suspect and diagnose a cyst.
When atheroma becomes inflamed, the following clinical symptoms appear:
- Redness of the skin in the area of atheroma;
- Swelling of the skin in the area of atheroma;
- Soreness of the bulge when palpated;
- Pus breaks out (not always).
Apart from a cosmetic defect, atheroma does not have any symptoms. It does not hurt or cause discomfort, so only its external manifestations are considered signs of a cyst. The diagnosis is made based on examination and palpation of the tumor.
Atheroma is characterized by the following manifestations:
- A bulge above the skin with clear contours.
- Unchanged skin in the area of the cyst, but may acquire a bluish tint.
- It has a dense and elastic structure.
- May move slightly relative to the surface of the skin.
- The sebaceous gland duct is visible on the surface.
But atheroma can become inflamed, then a number of other symptoms are added to the external manifestations:
- Redness and swelling appear in the area of the cyst.
- Soreness.
- In some cases, pus breaks out.
Note! Atheroma in a child is no different from the formation in an adult. Therefore, diagnosis, symptoms and treatment of children are the same as for adults. The only difference is that in children, epidermal cysts are more often congenital.
Removal of atheroma from the upper and lower eyelids
In addition to the methods described above, atheroma on the lower or upper eyelid can be evaporated by exposing the capsule to a laser. During the procedure, the cyst is opened with a scalpel, and it is cleaned of exudate.
Then the skin edges are moved apart, and the capsule shell is evaporated from the inside using a laser. At the end of the operation, the wound is sutured, and the sutures are removed on the 10th day.
A laser is used to evaporate the capsule shell from the inside.
However, laser evaporation of a cystic formation on the eyelid has some contraindications. You cannot carry out such an operation if you have:
- diabetes mellitus;
- immunodeficiency states;
- pregnancy;
- malignant tumors, etc.
Radio wave therapy makes it possible to prevent the re-development of pathology after surgery; the wound is not sutured when using this technique, it heals very quickly, and only a slight scar remains.
Treatment price
The cost of removing atheroma, cysts, papillomas at MGK starts from 5,500 rubles. The figure is calculated individually and will depend on the volume of treatment and diagnostic procedures performed. You can find out the price of a particular procedure by calling a number in Moscow (the call is free for mobile phones and regions of the Russian Federation) or online, you must use the appropriate form on the website, you can also familiarize yourself with the “Prices” section.
Dagaev Adam Huseinovich
Prevention
The sebaceous glands in the eyelid area, as well as elsewhere, can become clogged due to an innate tendency, a weakened immune system, or failure to comply with hygiene requirements. Preventive measures to prevent the development of atheroma of the lacrimal organ are of a general nature, but they are quite effective. The following rules must be observed:
- adhere to sanitary and hygienic requirements (regular bathing, toning and cleansing the skin);
- remove makeup from the face with special means;
- review your own diet - it should be balanced;
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle;
- When working in dusty rooms, wear closed clothing and use personal protective equipment;
- start timely treatment of common diseases, carry out sanitation of acute and chronic foci of infection, especially those localized in the larynx, nose, ears, mouth and teeth;
- if a hormonal imbalance occurs, immediately consult an endocrinologist;
- maintain stool control - prevent the occurrence of diarrhea and constipation.
With the help of such preventive actions, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of atheroma, both in the eye and in another area of the body. They help normalize metabolic processes. The danger of the formation of such a pathology on clean and healthy skin is minimal.
Atheroma does not threaten human health. However, some conditions can provoke the development of an inflammatory process, which brings significant discomfort. In addition, atheroma of the eye organ is a cosmetic defect, so experts advise getting rid of such formation.
Diagnosis and types of atheromas
Atheroma is a collective name for epidermal cysts in the area of hair follicles with various etiologies and histologies. These include epidermal cyst, trichymemal cyst and steatocystoma. The British Association of Dermatologists distinguishes “true” from “false” atheromas.
Epidermal cysts are usually traumatic due to the breakdown of squamous epithelium into subepithelial tissue. The most common complication is rupture with secondary sepsis. Healing with atypical scarring occurs if the cyst is not surgically removed.
Epidermal cysts make up about 70% of all benign skin cysts and are most often seen on the hairless scalp, face, torso, feet and hands. Men suffer more than women. The defeat occurs mainly in the 2-4 decades of life. Epidermal cysts are sliding subcutaneous nodules with a sticky consistency ranging in size from a few millimeters to 2-3 centimeters.
Doctors often use the term "atheroma" very inconsistently. Strictly speaking, the following variants of atheroma can be distinguished. “True” atheromas (epidermal cysts) form on the hair follicles - in the upper part where the hair emerges from the skin. They arise from skin cells and subcutaneous tissue.
The nodes appear spherical, convex and elastic. Epidermal cysts usually do not have an optically recognizable excretory duct. Horny cells and hair accumulate in the cyst; the contents smell unpleasant when the doctor opens the atheroma. True atheromas often occur in families and can be inherited.
“False” atheroma forms in the lower part of the hair follicles. The knots also feel rough, hard, and rubbery. False atheromas occur when one or more sebaceous glands become clogged, such as loose skin cells or dried sebum.
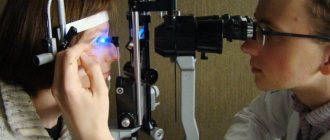
Examination is one of the methods for diagnosing atheroma of the eyelid
Fat does not come out and gradually accumulates in the tissues. The location of a blocked exit passage is sometimes recognized as a black dot. The cyst grows slowly because the sebaceous glands produce only a small amount of oil each day.
Atheroma can occur almost anywhere on the body because hair follicles and sebaceous glands extend throughout the skin. Atheroma on the head, neck, ear, chest, back, neck, face or genital area is not uncommon. However, most dermatologists do not always distinguish between “true” and “false”. Therefore, both forms are often called simply “atheroma.”
Take care of your eyes, do not allow atheroma to appear on the eyelid
Atheroma does not belong to the category of tumors. This is a cyst that forms due to blockage of the sebaceous gland. It forms where there are sebaceous passages, and the eyelid area is no exception.
Neoplasms of the eye
On the eyelid, atheromas are not large, reaching a diameter of 5-10 mm, but sometimes they can be the size of a walnut (up to 2 cm). If the formation is small, then it does not cause inconvenience to a person, but a large atheroma, and even in a visible place, brings many problems to its owner.
But not only in aesthetic terms, a wen can cause harm. If it has grown to an impressive size, then such a formation begins to compress neighboring tissues, blood vessels and nerve endings, causing headaches and dysfunction of those systems and organs that the atheroma has compressed. The person may also feel soreness in this area.
When removing atheroma on the eyelid, the doctor must refer the patient to a consultation with an ophthalmologist .
Causes
The following factors can influence the occurrence of atheroma of the upper and lower eyelids:
- Hormonal disorders in the body, often they occur during adolescence or during menopause in a woman.
- A congenital cyst can occur due to the effect of maternal hormones on the child.
- Due to diseases of the central nervous system or the autonomic nervous system, lipid metabolism may be disrupted.
- Violation of metabolic processes.
- Problems with the adrenal glands.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Seborrheic dermatitis.
Why is a lacrimal caruncle cyst dangerous?
The task of the lacrimal apparatus is to protect the eyes from environmental influences and protect the cornea and conjunctiva in order to maintain normal humidity levels.
A cyst in the area of the lacrimal caruncle is formed extremely rarely and only in those people whose lacrimal canaliculi are covered with thin hairs. This organ is not a working one in the human body.
Fortunately, atheroma of the lacrimal caruncle does not become malignant and does not affect vision . But still, a person experiences the following unpleasant symptoms:
- burning sensation in the eye;
- it feels like there is a foreign body in the area of the lacrimal caruncle;
- dry eye;
- pain is usually absent;
- The lacrimal caruncle may become enlarged and reddened.
For what reason atheroma forms in this part of the eye, scientists will not say with certainty, but the following circumstances can presumably influence it:
- when fallen eyelashes penetrate the eye;
- foreign objects entering the eye;
- microtrauma of the eye and penetration of infection through it.
The following changes in the eye are complications of atheroma of the lacrimal caruncle:
- suppuration;
- inflammation;
- infectious damage to other structures of the organ of vision.
Doctors recommend not to wait for complications and to remove such wen; the operation is performed under local anesthesia; children under 7 years of age receive general anesthesia.
Important! If the purulent contents of the atheroma penetrate the skin, it will enter the bloodstream, and this is fraught with blood poisoning, which most often leads to the death of a person.
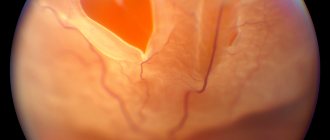
Photo
In the photo below, you can find out what atheroma of the eyelid mucosa looks like:
Treatment
Due to the peculiarity of its structure, the sebaceous gland cyst on the face, including the eyelid, does not resolve on its own . It is useless to use medication or folk treatment; they still won’t help.
The only correct solution is to completely remove the atheroma along with the capsule in which it is located.
It is not recommended to open a cyst on your own , especially if it is located in the eyelid area; in addition to the risk of loss of vision, there are other complications of such a rash step:
- abscess;
- phlegmon;
- sepsis;
- and even blood poisoning.
Thanks to modern technologies, atheroma can be removed without visible scars, pain and subsequent complications.
The doctor chooses the surgical removal tactics based on many circumstances. This is also due to the fact that atheroma of the eyelid can often become inflamed and suppurate . Therefore, it is better to remove it immediately after a small formation appears, and not wait for it to grow.
Inflamed atheromas, even after complete removal, can recur, this is due to the fact that sometimes access to them is limited due to the structure of the eye. And the capsule has no clear boundaries. Therefore, precise removal of the wen is almost impossible.
With a purulent cyst, it is necessary to wait for complete remission. And only then carry out its removal. The recovery period lasts on average 1.5 months, the seam on the eyelid is of minimal size, and therefore is not considered a cosmetic defect.
Regarding the newest techniques, namely laser coagulation or radio wave destruction, the patient must first
consult with an ophthalmologist .
Some doctors combine treatment methods. For example, the atheroma is first removed surgically by cutting it out, and then the removal site is treated with a laser.
Reference . Conservative and alternative treatment is not able to rid a person of a cyst on the eyelid, since even if the atheroma is cleared of pus, it will appear again. It is necessary to get rid of the wen along with the capsule, and this is achieved surgically.
Removal of atheroma
There are and are used various methods for eliminating atheroma; The main ones at the moment are:
- ophthalmic surgery;
- laser removal;
- radio wave destruction.
Any of these methods is highly effective in all aspects. And if in urgent and emergency conditions the patient does not have to choose (the decision is made by the doctor), then during a planned removal it makes sense to study the issue and choose the best option for yourself. Many patients interested in eliminating, first of all, aesthetic discomfort, opt for non-contact methods - laser or radio wave. However, it must be emphasized again that in order to have choice and time to consider options, it is necessary to seek help as early as possible. At the stage of purulent inflammation, multi-stage treatment becomes inevitable, which includes surgical opening of the cyst, cleaning the cavity from pus and then medical support for the postoperative period.
Today, for “quiet” removal of atheroma, combined techniques are often used, including, for example, surgical intervention followed by laser exposure.