Diabetes mellitus is a disease of the endocrine system, in which there is a deficiency in the formation of its own insulin and an increase in blood glucose levels - hyperglycemia. Many eye pathologies also develop in diabetes mellitus. Special drops are used to treat them. Let's talk about the most popular means.
Doctors have long established that diabetes mellitus directly affects the appearance and development of certain eye diseases. Increased blood sugar spreads to the entire vascular system, including the vessels of the eye organs. At the same time, they quickly collapse, and the walls of newly formed capillaries are extremely fragile. This leads to the release of exudate into the eye area. Visual functions may also be impaired, and clouding of the lens occurs.
What ophthalmological diseases occur in diabetes?
Diabetes causes severe eye pathologies, so patients need to constantly monitor their vision and regularly visit an ophthalmologist. These are the disorders the disease provokes.
Diabetic retinopathy is a vascular pathology in which the walls of the capillaries are damaged. As a result, some of them begin to narrow and become clogged, while others expand. Then some dilated vessels burst, and pinpoint hemorrhages appear in the eyes, which gradually merge into hemophthalmos. In the clogged areas, a lack of oxygen begins, the growth of connective tissue begins, and all this leads to detachment of the retina.
Neovascular glaucoma With this disease, intraocular pressure increases, and blood vessels begin to grow into the iris and anterior chamber of the eye, inhibiting the outflow of fluid. This condition leads to optic nerve atrophy. This type of glaucoma is difficult to treat and often results in blindness.
Cataract Due to metabolic disorders, clouding of the lens begins. It is usually a disease of the elderly that develops after age 60, but can occur at a young age in diabetics.
Cataracts and diabetes mellitus
We talked above about the fact that diabetics experience clouding of the lens. Partial or complete clouding of it leads to cataracts. The main symptoms of the disease are blurred vision, double vision, and photosensitivity. If these signs occur, it is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist to determine an accurate diagnosis and treatment. It is performed only surgically. During the operation, the damaged lens is removed and replaced with an artificial one. In the future, for clearer vision, the patient is often prescribed contact lenses or glasses.
What methods are used to treat eye diseases in diabetes?
When eye pathologies are detected in a person with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus, timely therapy can be applied, which will significantly slow down the deterioration of the visual organs. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely get rid of these diseases. For direct treatment, eye drops are usually used. Surgery may be necessary in severe or advanced cases of the disease. The risk group includes absolutely all patients with diabetes. To control the course of the disease, you need to undergo regular examinations with a doctor, monitor your diet, monitor blood glucose levels and take action if they increase. Eye drops for diabetes mellitus are preventive and therapeutic. All of them have a positive effect on blood vessels, increasing their elasticity and strengthening the walls, normalizing blood microcirculation in the organs of vision.
What should a diabetic do to avoid dry eye syndrome and its complications?
Let us give you some advice:
- First, listen to yourself. Any new sensations, and especially visual discomfort, are a reason to see an ophthalmologist. You should not ignore preventive examinations, even if nothing hurts.
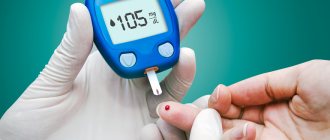
- Secondly, monitor your blood sugar. It needs to be constantly monitored, glycated hemoglobin and other tests taken, and regular visits to the doctor. Uncontrolled “jumps” in sugar gradually disrupt the functioning of all organs, including affecting vision.
- Thirdly, do not play roulette with food and medicine. Only a low-carbohydrate diet, careful taking of medications, and giving up bad habits can help a diabetic keep the disease “in control,” that is, compensate, and not allow complications to develop, including “dry eye” and retinal damage.
Antiglaucoma eye drops for diabetes
The main danger with glaucoma is increased eye pressure, which can lead to optic nerve atrophy. The purpose of the drops is to improve the outflow of fluid from the eyes and reduce its increased amount. Let's look at the most popular drugs.
- "Pilocarpine"
The main active ingredient is pilocarpine hydrochloride. The drops cause a constriction of the pupil, reduce pressure, helping the outflow of intraocular fluid, and also eliminate spasm of accommodation. The drug is effective for up to 14 hours.
- "Timolol"
The active ingredient is timolol maleate. Its effect occurs half an hour after administration and lasts approximately 1.5-2 hours. However, timolol can cause adverse reactions: allergies, blurred vision, etc.
- "Betaxolol"
Prescribed for chronic pathologies of the eyeball against the background of increased blood sugar. Two hours after instillation, intraocular pressure decreases. The medicine may last up to 24 hours. When treating with Betaxolol, you need to pay attention to third-party reactions (lacrimation, photophobia, itching). If they occur, the drug should be stopped immediately. Compliance with the dosage is also important - if it is increased, insomnia or neurosis may occur.
- "Ganfort"
The active ingredients in these drops are timolol and bimatoprost. Their effect allows you to stop clouding of the lens and pathology of the eyeball. However, Ganfort has many contraindications, so it is prescribed with caution.
The principle of using topical medications for glaucoma in diabetes mellitus is approximately the same: 1-2 drops are carefully injected into the conjunctival sac. The effect of the drug begins in approximately 10–30 minutes, depending on the degree and form of glaucoma, as well as on the concentration of active substances in the drug. The procedure must be repeated 1–3 times a day, depending on the doctor’s recommendations.
Glaucoma and diabetes mellitus
Another disease that often accompanies diabetes is glaucoma. Quite often at the initial stage it is asymptomatic, so it is not always possible to guess its presence. Therefore, as a preventative measure, a diabetic needs to visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year, and if vision problems already exist, every six months. Glaucoma is characterized by frequent hemorrhages, eye pain, blurred vision, and high intraocular pressure. Treatment is prescribed either with medication or surgery. The first treatment method involves the use of special eye drops that help normalize intraocular pressure. If there is no improvement after using them, surgery is prescribed.
Drops for eye cataracts in type 2 diabetes mellitus
The main function of the lens is to refract light rays so that they fall directly on the retina. Only in this case does a person have normal vision. This natural lens is naturally clear, but when cataracts occur, it begins to become cloudy. The more severe the diabetes, the cloudier the lens becomes. A radical way to get rid of this is the procedure of lensectomy, that is, replacing the natural lens, which has lost its properties, with an intraocular lens, which will ensure normal functioning of the eye.
But in the early stages of diabetes, timely therapy will stop damage to the lens. In addition, surgical intervention cannot be performed on all people due to the presence of third-party contraindications. These are the drops used to treat cataracts in diabetics.
- "Katalin." They prevent the processes of sedimentation of protein deposits and the formation of insoluble structures in the lens.
- “Potassium iodide” strengthens the local immunity of the organs of vision, promotes the breakdown of protein deposits and has a strong antimicrobial effect.
- "Katachrome". Effectively moisturize the eyes, protect them from negative influences, stimulate metabolic processes, and help remove free radicals from the tissues of the eye structures. The drops protect the lens from destruction and promote the regeneration of its damaged cells, which is important for developing cataracts.
Fungal infection of nails and skin (mycosis) in diabetes mellitus
The source of fungal infection is contact with mycoses on the skin. The weakening of the immune defense in diabetic patients leads to the fact that the fungus begins to actively multiply. Fungal infections in patients with diabetes occur more than 2 times more often than in healthy people.
Mycosis of the nail plate (onychomycosis) is manifested by a change in the color of the nail, its thickening or separation. A thickened nail creates additional pressure on the toe in the shoe, which can result in the formation of a diabetic ulcer. To reduce the thickness of the nail, patients with diabetes regularly undergo mechanical treatment of the plate: grinding with a file or pumice.
Itching, irritation in the folds of the skin or in the interdigital space indicate the presence of a fungal infection of the skin. To prevent the occurrence of skin mycoses, patients can be recommended to use daily cosmetic creams containing fungicidal and antibacterial complexes. Fungal infections can be easily treated with modern medications, both oral and topical, as long as they do not increase moisture between the toes.
Patients with diabetes are characterized by increased sweating and disturbances in thermoregulation, especially in the folds of the skin, resulting in diaper rash. To prevent the development of a fungal infection, it is recommended to treat areas with diaper rash with talc or preventive creams containing zinc oxide.
Drugs for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy
This eye pathology occurs with type 2 diabetes mellitus, which lasts for a long time. In addition, it aggravates the symptoms of the underlying disease and can lead to cataracts or glaucoma. Treatment for retinopathy should be started immediately if it is diagnosed. The first signs are burst blood vessels in the whites of the eyes. Gradually they become thicker, and then merge into noticeable red spots - hemophthalmos.
At an early stage of the disease, vitamin preparations are used to stop progression. They replenish the deficiency of essential nutrients, strengthen the walls of blood vessels, and improve blood circulation. Here is a list of popular eye drops for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy:
- "Taufon". The active ingredients of this product are taurine and various vitamins. They are also used for treatment of glaucoma. The medicine relieves fatigue and eye strain, accelerates metabolic processes. The course of treatment can last up to 1 month, then you should take a break.
- "Riboflavin". The drops eliminate dry mucous membranes, replenish the lack of vitamins A and C, and help cope with inflammatory diseases that diabetics are susceptible to - conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis.
- "Quinax." Their active component, sodium azapentacene polysulfonate, accelerates the work of enzymes in the anterior chamber of the eye. After introducing the drops, a thin film is formed on the surface of the organs of vision, protecting them from external influences.
- "Lakemox" and "Emoxipin" help moisturize the mucous membrane and accelerate the resorption of hemorrhages inside the eye caused by vascular damage.
- “Hilo-chest of drawers” help eliminate the feeling of dryness that occurs due to disturbances in the proper nutrition of eye tissue.
All medications are prescribed by an ophthalmologist, taking into account the degree and severity of the disease, as well as individual contraindications. He will also indicate the recommended time of the therapeutic course. Diabetics should visit a doctor regularly for eye exams to detect eye problems early and begin appropriate treatment.
MagazinLinz.ru team
Signs and complications detected in patients with diabetic ophthalmopathy
Diabetes mellitus is accompanied by disturbances in the microcirculation of the conjunctiva of the eye. When examining the conjunctiva of the eye with a slit lamp in patients with diabetic ophthalmopathy, an increase in the tortuosity of the venules, dilation of the capillaries in the form of aneurysms, destruction of the capillaries and their blockage with blood clots are noted.
A characteristic sign of diabetic ophthalmopathy when examining the iris is sclerosis of the vessels of the iris, neovascularization, i.e. formation of new blood vessels, called rubeosis. At the same time, the iris loses its elasticity and mobility, which impairs the possibility of its expansion with the help of medications. Due to rubeosis and the proliferation of connective tissue at the site of hemorrhages, the outflow of intraocular fluid is disrupted, which leads to increased intraocular pressure and the development of secondary diabetic glaucoma
. Most often, rubeous glaucoma in patients with diabetes mellitus is combined with cataracts, retinal detachment and intraocular hemorrhage.
Patients with diabetes mellitus, due to a decrease in local and general immunity, are more susceptible to the influence of stress factors and pathogens of infectious diseases. This is why diabetic ophthalmopathy often manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the conjunctiva, blepharitis, and erosive lesions of the cornea. Pathological processes do not bypass the lens, the volume of which increases, which leads to a decrease in the depth of the anterior chamber and the development of diabetic cataracts
. In addition, due to disruption of metabolic processes, there is a weakening of the capsular-ligamentous apparatus of the lens, which increases the risk of subluxation.
Signs of diabetes in children
Due to the fact that diabetes mellitus negatively affects the child’s body, in particular the visual analyzer, parents should know the main signs of this disease in order to notice it in time and also begin treatment.
Symptoms of childhood diabetes include:
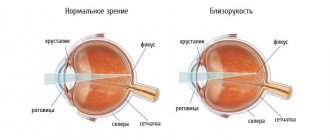
- blurred vision;
- frequent urination;
- increased thirst;
- severe fatigue;
- increased appetite, which results in decreased body weight;
- disturbance of sensitivity (paresthesia, anesthesia) in the extremities;
- long-healing abrasions and scratches;
- feeling of dry mouth;
- frequent bacterial infections associated with reduced immunity.
If parents discover signs of diabetes in their baby, they should immediately visit a pediatrician.
Diabetes eyes
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common endocrine diseases. Eye damage in people with diabetes is one of the main causes of blindness among the population of developed countries. MORE DETAILS
The fear of vision loss haunts these patients throughout their lives. However, the integrated use of surgical and laser methods makes it possible to restore vision to previously incurable patients.
Diagnosis of eye diabetes
Damage to the retina (diabetic retinopathy) is the most serious and common complication of diabetes mellitus. This disease can affect almost every patient, regardless of the type of diabetes and treatment. This process can only be stopped by surgery.
TREATMENT
As a conservative treatment, various medications are used to strengthen the walls of blood vessels, resolve hemorrhages, fat and protein deposits in the retina, improve metabolism and blood supply to the eye. However, as practice shows, numerous medications cannot stop the progression of the disease and should be used as auxiliary measures.
Surgical treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus requires a special approach, since tissue healing is much worse and slower due to disruption of all types of metabolism. It is also important to take into account the characteristics of the disease as a whole, and not to treat one of the eye diseases of diabetes mellitus.
For diabetic retinopathy, a surgical operation is performed - vitrectomy, the purpose of which is to remove the altered vitreous body and scarred tissue from the surface of the retina to eliminate its tension and detachment. In some cases, the removed vitreous is replaced with saline solution. In especially severe cases, the process of scar formation can also affect the inner layers of the retina. Therefore, silicone has to be injected into the eye cavity. This is necessary in order to minimize internal scarring of the retina with further re-detachment. When postoperative observation does not reveal re-scarring of the retina, the silicone is removed.
The operation is performed under general and local anesthesia under an operating microscope. To perform vitreoretinal surgery, operating rooms are equipped with the most modern devices from the best manufacturers.
On the morning of the operation, drops are instilled into the eye to dilate the pupil. You may also be given a mild sedative to help you relax and not worry.
In the operating room you will be accompanied by a surgeon, his assistant, an operating room nurse, an anesthesiologist and a nurse anesthetist.
15 years of experience in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy by MNTK surgeons proves that early removal of the altered vitreous body in case of initial lesions of the retina stops the development of the disease for many years.
The MNTK Eye Microsurgery is constantly developing new methods for treating diabetic eye damage. Many operations are unique, thanks to them an increasing number of people, previously doomed to complete blindness and considered hopeless, are able to see.
REMEMBER: People with diabetes need to visit an ophthalmologist regularly to monitor intraocular pressure and visual field.
Do not forget that diabetic retinopathy and its complications are only a manifestation of a general disease, so it is extremely important to monitor the course of diabetes and control blood sugar levels.