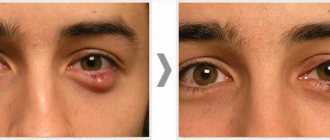
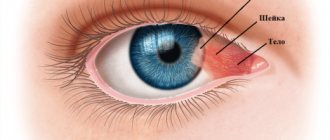
A chalazion is a dense encapsulated accumulation of sebaceous secretion from the meibomian gland inside the lower or upper eyelid. Translated from Greek, the word “chalazion” roughly corresponds to the Russian “gradinka” or “pea”; This means something hard, round and small in size.
Outwardly, this pathology resembles the well-known barley, but there is a difference between them, and a very significant one.
First of all, barley (hordeolum) is an acute purulent infectious-inflammatory process caused in most cases by bacterial pathogens (usually Staphylococcus aureus); In this case, it is not the meibomian gland that becomes inflamed, but another sebaceous gland (Zeiss) or an eyelash follicle. With adequate treatment - or even without it, if the immune response is strong enough - the stye disappears after 5-7 days. Chalazion occurs due to other, non-infectious reasons (although a previous inflammatory process is a direct risk factor), proceeds differently and requires a different approach to treatment.
The meibomian glands, of which there are about seventy on one pair of eyelids (on the upper one a little more than on the lower one), produce a special sebaceous-mucosal secretion designed to lubricate and reduce friction during blinking, on the one hand, and on the other hand, for hydroregulation and prevent too much abundant wetting of the eyelid with tear fluid. The exit tubules are located along the ciliary border of the eyelid, closer to the surface of the eye.
If the exit channel of the gland is blocked, and the secretion continues to be produced, its accumulation in the blocked mouth leads to swelling and inflammation of the meibomian gland, then to the breakthrough of the secretion into the surrounding cartilaginous tissue and encapsulation there in the form of an internal “sac”, which, gradually thickening and hardening, forms characteristic “pellet in the eyelid”. Chalazion occurs in any age category, starting from early childhood, however, some sources indicate that, due to certain age-related characteristics, this disease is somewhat more often diagnosed in patients 30-40 years of age and older. In this same (older) age group, differential diagnosis with other neoplasms is especially important - in particular, with the very dangerous adenocarcinoma of the sebaceous gland.
In itself, a “classic” uncomplicated chalazion does not pose any threat to life and health, does not affect visual acuity, but creates a noticeable cosmetic defect, which sometimes persists for up to a year or more, and tends to recur. Therefore, reasonable measures are necessary for its timely treatment and prevention, as well as to eliminate the most common causes and risk factors (if they are avoidable in a particular case).
Causes
As mentioned above, a previous infectious and inflammatory process (conjunctivitis, blepharitis, hordeolum, etc.) can lead to the development of chalazion. Other reasons include general oily skin (hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands), injuries and burns of the eye, chronic endocrine, gastroenterological, hematological (presumably) disorders - in short, any pathology that can disrupt the functioning of the glands and the composition of their secretion - as well as helminthiasis, immune system weakness, vitamin deficiency. Sometimes chalazions appear almost simultaneously in two eyes or on different eyelids of the same eye. Recurrence in the same place can be caused by undertreatment or incomplete removal of the previous chalazion.
Chalazion - what is it?
Chalazion
(translated as nodule, hailstone) is a chronic aseptic inflammation of the eyelids. An ocular chalazion develops on the eyelids due to blockage and disruption of the outflow of fatty secretions of the meibomian or other sebaceous glands of the conjunctiva of the eyelids. The cause of blockage of the excretory ducts of these glands may be chronic inflammation of the conjunctiva - conjunctivitis, eye injuries, metabolic disorders.
The Meibomian glands are located just behind the eyelashes on the upper and lower eyelids. Accordingly, a person may develop a chalazion of the upper or lower eyelid. However, when treating chalazion, it does not matter much whether the upper or lower eyelid is inflamed - the technique is universal and consists of three main stages.
Symptoms
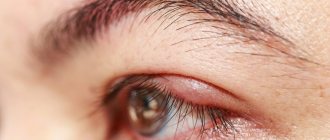
In the initial phase, the eyelid turns red, itches and most often causes “bursting” pain; many patients note a painfully aggravated reaction to bright light, increased lacrimation, and a sensation of a foreign body. Then the pain subsides; a characteristic round compaction forms inside the eyelid, rolling freely under slightly hyperemic skin (on the side of the conjunctiva, hyperemia is more pronounced). The swollen area may have a grayish-white center. In this state, the chalazion, if it does not resolve (spontaneously or as a result of treatment) in 2-4 weeks, can remain for months. It is very likely that it will become secondary to infection and purulent inflammation of the internal capsule; sometimes such a purulent sac opens and the contents leak out. In certain localizations (closer to the inner, mucous surface of the eyelid), mechanical irritation and inflammation of the conjunctiva by friction is also possible.
How to bury correctly
For chalazion, it is important not only to select effective drops, but also to instill them correctly, ensuring maximum penetration of the active components into the eye. In order for the treatment to be effective and recovery to be quick, it is necessary to perform eye drops as follows:
- Before the procedure, you need to wash your hands well with soap.
- The most comfortable position for instilling eye drops is sitting on a chair, leaning on the back. You can also lie down on the sofa.
- Throwing your head back, you need to slightly pull back the lower eyelid and look up, then turn the bottle over and drop 1-2 drops into the eye.
- After this, you need to close your eyes and blot with a cotton swab, removing excess liquid.
- To enhance the effect, it is recommended to sit with your eyes closed for 2-3 minutes, lightly pressing your finger on the inner corner of the eye.
How to use eye drops correctly
During the treatment of chalazion with drops, you should stop wearing lenses or put them on no earlier than after 15 minutes.
Treatment without surgery
Since chalazion seems to be an “understandable” and relatively harmless disease, attempts to self-treat it with folk remedies are widespread. These methods are so numerous and varied that, even if they were effective, humanity should have long ago forgotten about chalazions. However, most patients (at least 75%) sooner or later consult an ophthalmologist. In the early stages of formation, a chalazion is subject to treatment with anti-inflammatory, absorbable and, if indicated, antibiotic ointments, drops, gels, etc., as well as 1% mercury yellow ointment and physiotherapeutic procedures (ultraviolet or ultra-high-frequency heating). At later stages, with a significant volume of chalazion, injections of corticosteroid hormones into the capsule are sometimes successfully practiced.
If all other procedures are ineffective, as well as if the patient is unwilling to put up with a cosmetic defect and/or be subjected to bizarre experiments within the framework of traditional medicine for a long time, surgical removal of the chalazion is prescribed.
List of drugs
Chalazion can become a chronic process, so treatment should not be delayed under any circumstances. The following ointments and liniments help to avoid negative consequences:
Levomekol
Compound:
- chloramphenicol;
- methyluracil;
- polyethylene oxide
Properties: suppresses bacteriological flora, eliminates swelling.
Price: 70 rubles (3g).
The drug is considered a broad-spectrum antibiotic. It is used as a compress (Levomekol is applied to a piece of film and applied to the tumor) or rubbed. In the case where the hailstone is located on the lower eyelid, the ointment is placed under the eyelid.
Blefarogel
Compound:
- hyaluronic acid;
- aloe juice;
- propylene glycol;
- glycerol;
- methylparaben;
- carbomer;
- hemodesis;
- purified water.
Properties: has an antihistamine effect, kills microbes, accelerates the resorption of gland blockage. Effective for the prevention of chalazion.
Price: 189 rubles (15 ml).
Apply the product to the affected eyelid with gentle massaging movements.
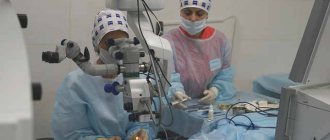
Chalazion removal surgery
First of all, it should be noted that there are no special reasons for preoperative anxiety or, especially, fear in this case: the procedure is quite simple, has been worked out a long time ago, is performed on an outpatient basis and usually lasts about 20 minutes “from entering the manipulation room to leaving the room” (as was said a hundred years ago). At the same time, the professional level of the clinic and the qualifications of the doctor certainly matter, so the choice of an ophthalmic center should be meaningful and justified.
Local, subcutaneous anesthesia: after mandatory antiseptic treatment, an anesthetic is injected with a thin needle (usually a solution of lidocaine or novocaine), which ensures reliable insensitivity of the surgical field. The problem area is fixed using a window clamp; the chalazion capsule is opened (along the suppurating fistula canal, if there is one) and exhumed along with all the contents. Depending on the location, the incision is made either from the outside of the eyelid or from the conjunctival side. Then the surgical field is once again treated with antibacterial agents, drained if necessary and closed with suture material. A relatively tight bandage is applied.
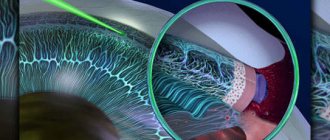
Laser removal methods
Modern medical technologies, primarily using a laser scalpel, in this case have clear advantages over traditional ophthalmic surgery. Laser surgery is much less invasive and virtually bloodless; results are more predictable and accurate. The risk of complications and the duration of postoperative rehabilitation are significantly reduced.
By contacting our ophthalmological center for chalazion removal, you receive an individual approach (the exact method and surgical approach is selected), which guarantees the highest treatment result.
Effective ointments for chalazion
Conservative treatment of the disease can be carried out using eye ointment. One of them is Vishnevsky ointment, which reduces the risk of the disease becoming chronic. The drug not only eliminates the symptoms of the disease, but also helps the resorption of pus.
Very often, during the treatment process, hydrocortisone ointment is used, which eliminates itching, as well as all the symptoms of the inflammatory process.
Tetracycline ointment is considered effective in the treatment of chalazion. Before starting therapy, you need to make sure that there are no contraindications. It is often enough to use the ointment for a week, lubricating the eyelid of the affected eye with it two to three times a day. In advanced cases, a specialist can extend therapy up to two weeks, combining eye ointment with antibacterial drops. Tetracycline can be applied not only to the outside of the eyelid, but also to put a little ointment under it.
Doctors recommend that patients with chalazion apply compresses with Levomekol ointment at night. A little product is applied to the bandage, after which it is tightly attached to the affected area of the eye.
Chalazion is a chronic disease that requires long-term therapy. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. Having detected the disease at the initial stage, it is necessary to carry out conservative treatment. There is no need to advance the disease so that the formation does not have to be removed surgically.
Prices for surgical removal of chalazion
The cost of surgery to remove a chalazion in our ophthalmology center is 7,500 rubles (for 1 eye): the choice of method is determined by the attending physician after consultation. The necessary tests for the operation are collected at the patient’s place of residence. You can check with the administrators for details.
Forecast
A typical chalazion is a benign formation and not prone to malignancy (malignant degeneration). High-quality removal does not leave any cosmetic defects. At the same time, one has to reckon with a fairly high risk of relapse, incl. multiple, therefore, all reasonable and necessary preventive measures should be taken: remediation of chronic background diseases and foci of infection, normalization of nutrition and lifestyle, compliance with eye hygiene rules, etc. In each specific case, these measures are developed and prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
In general, the prognosis is favorable.
Review of hormonal drops
Corticosteroid drugs are usually prescribed to treat inflammation of an allergic nature: they perfectly relieve itching, swelling and other symptoms of inflammation. Therefore, they are sometimes prescribed to prevent inflammatory processes of other etiologies, for example, bacterial eye damage. In this case, hormonal eye drops with the addition of antibiotics are especially good.
Maxitrol
These eye drops contain three active ingredients:
- Neomycin (antibiotic);
- Polymyxin (antibiotic);
- Dexamethasone (hormone).
Antibiotics complement each other's action: if microbes turn out to be resistant to one substance, then another component will help against them. The hormone helps to quickly suppress the inflammatory process.
Contraindications to the use of Maxitrol:
- Hypersensitivity to the composition of the drug;
- Adenoviral and fungal eye infections;
- Herpetic infections;
- Purulent forms of eye diseases;
- Damage to the cornea.
The possibility of using Maxitrol for children, pregnant and lactating women has not been established. Therefore, the drug should be used only in exceptional cases when the expected benefits outweigh the potential risks. The drug is prescribed with caution for glaucoma and cataracts.
Shake the bottle before use. In severe cases of the disease, the medicine is instilled every hour, 1-2 drops. Subsequently, the number of installations is reduced to 4-6 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician. When used for more than 10 days, it is necessary to monitor intraocular pressure (it can increase significantly).
Side effects:
- Itching and swelling of the eyelids;
- Hyperemia of the whites of the eye;
- Glaucoma;
- Slowing down regenerative processes.
The average cost of a bottle of 5 ml drops is 490 rubles. Maxitrol is dispensed strictly according to a doctor's prescription.