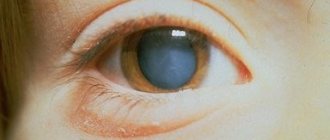
Cataract is a disease in which visual acuity progressively decreases due to clouding of the lens, i.e. natural intraocular focusing lens with variable optical power. The development of cataracts is mainly associated with age: after 45 years, the risk of lens opacification increases. Less commonly, the loss of light transmission of the lens is caused by the action of external pathogenic factors, such as mechanical injuries, burns (thermal, chemical, ultraviolet), concomitant ophthalmological diseases, and endocrine disorders. In addition, the high significance of hereditary predisposition to the development of cataracts has been confirmed. There are also cases of congenital opacity of the lens, caused by disturbances in intrauterine development or the unhealthy lifestyle of a pregnant woman.
Once cataracts have started, they do not develop back and cannot be cured either with folk remedies or spontaneously. There are topical preparations, incl. the latest and quite promising, as well as certain therapeutic regimens that can slow down the progressive opacification, however, they are effective only in the early stages of the disease and in most cases do not completely stop the pathological process. Cataracts are diseases that can only be treated surgically.
The radical solution to the cataract problem is the surgical removal of the incompetent natural lens of the eye with simultaneous implantation of an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Lens replacement today is the only effective (and has already been proven and tested during several million successful operations) method of restoring vision in case of cataracts.
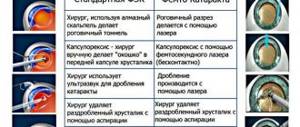
At the present stage of development of medical technologies, removal of the lens by ultrasonic phacoemulsification is considered the safest and most predictable. If treatment is carried out before the cataract is fully “ripened” (which can lead to a catastrophic clinical picture), ultrasonic waves successfully cope with the task of softening it to an emulsion state, due to which the entire volume of the lens substance is evacuated through a microscopic incision without risk to nearby tissues.
The algorithm for replacing a lens with a polymer lens has now been verified to the smallest detail; this is no longer considered a particularly complex procedure and is performed on an outpatient basis. An important component of this technique, however, is the postoperative period. The effectiveness of cataract surgical treatment largely depends on the patient’s compliance with recommendations during the rehabilitation stage. Depending on the patient’s initial condition, the progress and results of the operation, and the presence of concomitant diseases, the recovery period can last from 1 to 3 months. During this period, for maximum therapeutic effect, the patient must comply with the schedule of visits to the ophthalmologist, regularly take medications according to a prescribed strictly individual regimen, as well as limit (in some cases, completely exclude) physical and visual stress.
What is this condition?
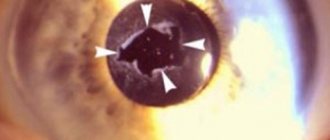
Secondary cataracts are changes that occur in the posterior capsule of the lens, as a result of which it begins to become cloudy. Afterwards it becomes very dense and does not allow light to penetrate. Which can lead to complete loss of vision, as this disease progresses very quickly.
Causes
There are no specific scientific reasons for secondary cataracts. There are only a few suspected factors contributing to the development of this disease:
- various eye injuries;
- glaucoma;
- myopia;
- metabolic disease;
- avitaminosis;
- drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking.
As a rule, the most common causes of secondary cataracts are:
- proliferation of epithelial cells on the posterior capsule of the lens. It occurs mainly after surgery to remove cataracts;
- old age. This disease is more likely to occur in people over 70 years of age. With age, the organs of vision weaken because they do not receive the required amount of vitamins;
- diabetes. With this disease, the metabolism in the body is disrupted.
Postoperative rehabilitation
The recovery period after cataract surgery is divided into three stages:
1. The first 7 days after lens replacement. Immediately after the operation, the patient notes a significant improvement in vision, but this period may be accompanied by swelling of the eye, pain and general discomfort. To relieve disturbing symptoms, topical medications (eye drops) are prescribed.
2. The first month after surgery. In the three weeks following the first stage, vision may be unstable. The visual system gradually adapts to the action of various external and internal factors. The final result of the entire treatment depends on strict adherence to the instructions and restrictions during this period. Avoid visual fatigue, physical exertion, stress, any contact with dangerous toxic substances (including, of course, alcohol and nicotine), as well as vibration and ultraviolet exposure, i.e. At this stage, it is necessary to especially carefully protect your eyes from direct sunlight.
3. Next 3-6 months. Visual acuity reaches the maximum that was possible in this particular case, and the functioning of the visual system becomes naturally stable. If concomitant refractive errors are detected, a method for their correction (contact lenses, glasses) is selected. For six months, you should still avoid heavy lifting, sudden bending of the body, and visual fatigue.
Symptoms
Symptoms of secondary cataracts may begin to appear several months after surgery.
To recognize this disease, you need to know its causes:
- decreased visual acuity. A person may have difficulty seeing at very close or far distances;
- the appearance of glare in the eyes, especially in night lighting;
- blurred and blurred vision;
- the occurrence of problems with the perception of contrasts;
- difficulty reading books and recognizing illustrations.
Useful video
Secondary cataract after lens replacement:
Types of artificial lenses (IOLs)
In the surgical treatment of cataracts, two types of artificial intraocular lenses are used: “hard” and “soft”.
Rigid IOLs have a permanent, unchangeable shape. Their installation requires a fairly large surgical incision. At the final stage of the operation, in this case, sutures are placed on the wound, which carries some risks and lengthens the rehabilitation period.
More preferable in most cases (however, not always) are “soft” lenses, which are a mechanically elastic implant, which, when folded, is inserted into the eye cavity through a self-sealing micro-incision, and then fixed in the lens capsule, taking on its final shape. As shown above, such a flexible polymer lens can be placed in place of the natural lens through an incision, or rather a puncture, as small as 1.6 mm, requiring no stitches. Healing and regeneration after such an operation proceeds faster, with fewer restrictions and a minimal likelihood of complications.
In addition, lenses differ in their refractive (refractive) characteristics. Depending on lifestyle, the dominant visual load regime and the presence of concomitant diseases, the following types of IOLs may be recommended:
- Monofocal (provide correct vision at a certain average distance, implying the additional use of glasses in a number of situations);
- Multifocal (allows you to see well both at long and near distances);
- Toric (simultaneously with cataracts, existing astigmatism is eliminated).
We offer our patients lenses from leading manufacturers that have proven their effectiveness, have been certified and are widely used throughout the world. This is, first of all, an IOL from Alcon Inc. (Alkon, USA), Baush&Lomb (Bausch & Lomb, USA), Zeiss (Zeiss, Germany). In addition, budget models of intraocular lenses Rumex (Rumex, UK) and Silco (Silco, USA) are also available.
Diagnostics
If you suspect this disease, it is necessary to conduct a diagnosis. Her procedures include:
- examination by a specialist who will determine the sharpness and clarity of visual functions, visual angle and intraocular pressure;
- ultrasound examination of the eye;
- diagnostics using a slit lamp;
- examination of the fundus to determine retinal detachment.
After carrying out all the above procedures, the doctor will determine the degree of pathology and prescribe treatment.
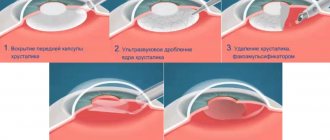
Stages of surgical treatment of cataracts
1. Diagnostics and selection of an intraocular lens. 2. Drip anesthesia. 3. Providing surgical access using a micro-incision. 4. Emulsification of the clouded lens using ultrasound, aspiration of the resulting mass and small residual fragments. 5. Implantation of a folded intraocular lens. 6. Straightening the artificial lens and fixing it. 7. Antibacterial/antiseptic eye treatment. 8. Self-sealing of the surgical incision.
The ultrasound phacoemulsification method in combination with soft compact lenses allows lens replacement even for those patients, including very elderly patients, for whom many other types of surgical treatment are not recommended. Local anesthesia also removes a number of contraindications. This technique is characterized by predictability and controllability of results, easy and rapid restoration of visual functions and a minimum of restrictions at the rehabilitation stage. Many patients return to their normal lifestyle as soon as the next day after surgery, following individual instructions.
Therapy
To treat secondary cataracts, lens replacement surgery is not necessary. Another technique is used - removal of the overgrown epithelium. There are two treatment methods - surgery and conservative procedures.
Expert opinion
Slonimsky Mikhail Germanovich
Ophthalmologist of the highest qualification category. Has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating eye diseases in adults and children. More than 20 years of experience.
Surgery refers to surgery using a laser. This method is good because it does not use surgical instruments. The second method is used if the operation is contraindicated for some reason. In this case, therapy is prescribed with medications and therapeutic devices.
This is necessary to saturate the organs with oxygen and ensure intensive work. Treatment with color therapy and pneumomassage is prescribed. This is the observation of a flashing precise or moving light stick.
Lens replacement using phacoemulsification
Cataract surgery is performed on an outpatient basis in a one-day procedure. Local drops are used as an anesthetic, which allows you to reliably eliminate any pain and at the same time avoid all the adverse effects of general anesthesia. The incidence of cataracts in modern medical statistics, unfortunately, occupies a stable leading position. Lens replacement is carried out daily by specialists in ophthalmological clinics around the world, today being, in the best sense of the word, a routine operation. Unpredictable development of the situation here is excluded due to advanced technologies, enormous accumulated experience and the use of modern biocompatible materials, which, in their optical and mechanical properties, with each technological innovation are increasingly closer to the natural lens. In our clinic, lens replacement is performed using advanced technology from Alcon (USA).
At the initial stage of the operation, through a micro-incision no more than 2.6 mm long, the clouded lens is destroyed by exposure to ultrasonic waves. The resulting lens emulsion is aspirated, freeing up space for implant placement. An artificial intraocular lens is selected in advance, taking into account the diagnostic results, concomitant diseases and the patient’s usual visual load. Modern artificial lenses are flexible, thin lenses that do not require a larger incision than the minimum required for phacoemulsification. The artificial lens is inserted into the lens capsule in a folded state, straightened out and naturally fixed there.
Sutures are also not required for a micro-incision, since such a minor surgical wound easily self-seals without leaving scars. The entire operation lasts no more than half an hour in total. Upon completion of surgical procedures, an antiseptic solution is instilled into the eye. After receiving individual recommendations, the patient can return home.
Is a relapse of the disease possible?
After the first cleaning of a secondary cataract, recurrence of the disease is impossible. Epithelial tissue stops growing after the first time. But to control the subsequent appearance of the film, doctors recommend visiting an ophthalmologist. This must be done once a month.
Preventive measures
The most important thing is to maintain the correct work and rest schedule. It is not recommended to strain your eyesight, or to stay in front of a TV or computer monitor for a long time. Be sure to visit an ophthalmologist in a timely manner. And also do not forget the general rules of prevention:
- After surgery, it is recommended to wear sunglasses;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, avoid getting dust in the eyes;
- Eat healthy, eating foods enriched with vitamins and antioxidants.