Treatment of pterygium.
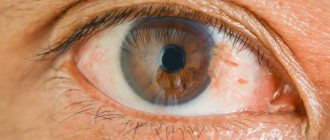
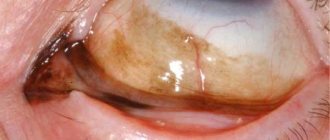
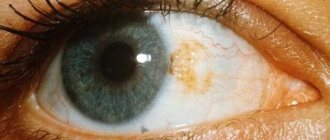
Pterygium is a dystrophic disease of the conjunctiva of the eyeball. As a rule, the process of growth of the conjunctiva on the cornea begins on the nasal side of the eye, as a result of which the pupil is partially or completely blocked. As a result, a person’s visual acuity decreases and he feels a kind of “interference” in front of the eye. The pterygium itself has the appearance of an opaque consistency. It is most often noted in those whose eye apparatus is constantly in contact with dust, sand, and chemical reagents.
At the initial stage, the patient does not experience discomfort, then dryness, irritation of the eye, foreign body sensation, increased lacrimation, decreased vision and astigmatism appear. To prevent the disease from reaching an advanced stage, it is necessary to undergo timely diagnosis and remove the pterygium.
Causes of the disease
Today there is no consensus on the causes of pterygium, but it can be provoked by:
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- prolonged eye strain;
- genetic factors;
- dry air;
- long work at the computer;
- ultra-violet rays;
- infections and injuries.
Pathology worsens the characteristics of the tear film, which leads to chronic irritation that turns into inflammatory processes. Timely seeking medical help allows you to avoid infection and prevent the development of pathology in time.
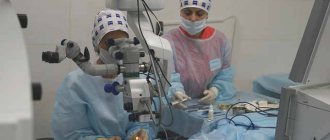
Operation technique
During the operation, intervention is carried out only on the surface of the eye; penetration into the eye is not required. The pterygium tissue is removed, and the area where it was located is covered with healthy conjunctiva, which is removed from under the upper eyelid. This is necessary to prevent relapse and to achieve an optimal aesthetic effect. The conjunctival tissue is secured with several sutures or with bio-adhesive (with less postoperative discomfort). After surgery, a special drug is used to prevent recurrence (mitomycin).
MORE ABOUT: Contact lenses for astigmatism Lenses to correct astigmatism Vision correction
The operation to remove pterygium is performed under local anesthesia (drops with anesthetic are instilled). After surgery, a bandage is applied to the eye. In case of pain, the doctor will prescribe painkillers. Postoperative requirements include preventing water from entering the eye and using eye drops prescribed by your ophthalmologist. For several days after the intervention, vision may be blurred, but this passes without consequences.
Possible complications of surgery are bleeding, infectious complications, postoperative granuloma (tissue scarring), relapse.
Surgical treatment of eye pterygium and the postoperative period are individual for each person, however, you can read reviews of patients who have undergone such treatment, or describe your own impressions.
To ensure that the rehabilitation process goes without complications and risks, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- Wearing an aseptic bandage on the operated eye for 24 hours. Changes as it gets dirty
- One day after surgery, the use of medications begins. The average duration of therapy is a month, unless the doctor decides otherwise.
- For severe pain, analgesics are used in tablet form.
- For the first two weeks, you need to wear glasses that have ultraviolet filters.
- You can’t get your eyes wet for a week after surgery, which means swimming pools, sea swimming, and other factors that carry risks are excluded.
- Two weeks after the operation should pass without physical activity.
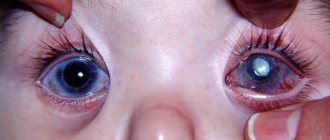
The first time after removal of the pterygium, vision may be impaired. If the operation was successful, visual acuity returns. This may happen in 5 days, or maybe in a month. Any eye irritation can trigger new growth of pterygium, and at a faster rate. The sooner you go to the clinic, the smaller the area of intervention will be, and, therefore, the risk of complications.
Symptoms of pterygium
An opaque triangular formation can be seen on the eye, similar to a yellowish film with a sharp end directed towards the pupil. Blood vessels are clearly visible. At the initial stage, the pathology does not cause any problems, but later the symptoms become clear:
- tearfulness;
- the cornea darkens;
- vision decreases;
- itching and burning;
- discomfort and dry eyes.
Already at the first manifestation of the disease, you should urgently seek medical help from an ophthalmologist.
Classification of pathology
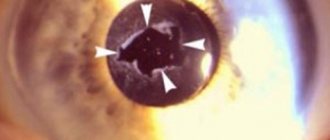
Pterygium can be progressive or stationary. The diagnosis is made based on the condition of the patient’s blood vessels:
- first degree – the formation is transparent and atrophic, progression is minimal;
- second degree – partial viewing of vessels with a protruding formation;
- third degree - the formation is opaque and highly active, the network of vessels is clearly visible.
Prevention methods
The most effective method of preventing the development of pathology is to protect the eyes from harmful influences. In summer, it is recommended to wear glasses that protect against ultraviolet radiation, which is considered the main cause of pterygium.
When the first symptoms appear, you should consult an ophthalmologist. After the examination, he will give recommendations for prevention. Sometimes surgical intervention is not required due to the absence of increased pathology.
Patients with pterygium should undergo regular medical examination to monitor the neoplasm, if growth is detected
the doctor will be able to send you
for surgery
, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
After the operation
It is important to visit your doctor on time to monitor for possible changes and seek help if any changes or symptoms that have not been observed before appear.
Treatment
Any therapy begins with diagnosis. Since pterygium manifests itself visually in the form of an increase in the conjunctiva, making a diagnosis even for an inexperienced specialist does not cause difficulties. To confirm the diagnosis, an examination is performed using a slit lamp.
Drug treatment for this type of ophthalmological disease is not provided due to its ineffectiveness. If the pathology does not progress and affects only the edge of the cornea, then the doctor may decide not to perform any intervention in this area. But with the development of the disease, it is assumed that the pterygium is removed by excision of its body.
If the pathology progresses, then it is better to perform surgery in the early stages, when visual manifestations have just begun to make themselves felt. Excision of the pterygium is performed with wrapping of the body. When a defect is removed, areas of cloudiness often appear on the cornea. Therefore, the pathology is disposed of before it reaches the center of the optical zone.
The pterygium is removed on an outpatient basis using local anesthesia. To do this, the appropriate drug is dripped into the conjunctival sac. Next, the growth is excised using one of three methods:
- By connecting the healthy edges of the conjunctiva;
- By replacing the pterygium with an amniotic membrane. An autograft can be used, which is a section of the membrane taken from under the upper eyelid.
- By suturing the conjunctiva in the form of folds to the sclera, retreating approximately a few millimeters from the cornea.
The last two techniques are considered more effective than conventional excision. With such methods, relapses rarely develop, and the risk of developing complications in the form of visual impairment is reduced. This factor is relevant when the pterygium grows strongly.
To hold the tissue together, a special suture material is used, which dissolves on its own in about 7-10 days. Sometimes biological glue may be used. Upon completion of the manipulations, the eye is covered with an aseptic bandage. All manipulations take about half an hour, and after a couple of hours the patient is sent home.
Laser excision
Removal of pterygium with a laser requires the availability of equipment in the clinic. This procedure is less traumatic for the organ of vision. It is carried out in the same way as during surgical intervention, but the use of a modern method eliminates the influence of the human factor on the area of influence. This eliminates the possibility of infection and the development of complications after surgery.
The cost of such a procedure averages about 15 thousand rubles. Clinics can also offer autoplasty, in which a piece of cornea is sutured onto the remaining area of the pterygium. This procedure is also called excimer corneal resurfacing. This procedure allows the eye to return to its previous appearance. Accordingly, the price of this procedure is added to the cost of laser excision, which amounts to a total of about 21 thousand rubles for all manipulations performed with the pterygium.
This type of treatment without excision does not produce positive results. In general, medications are used only after surgery. Often, after surgery, complications and even relapses of the pathology develop. Therefore, appropriate treatment with drug prophylaxis is used.
To suppress the growth of the conjunctiva, the site of surgical intervention is treated with the pterygium of the eye after surgery with either liquid nitrogen or Miramistin. After removal, an appointment is scheduled:
- Antibiotics that will prevent infection of the operating area with various pathogens. Drops like Tobrex or Albucid are mainly used.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs of the drop type or in the form of an ointment, for example, Dexamethasone, Indocollir.
- Be sure to use moisturizing drops such as Clean Tear or Visine.
MORE ABOUT: Headache after eye cataract surgery
It is necessary to understand that drug therapy is preventive measures against re-growth, and not a complete treatment of an eye defect. They will not replace surgery to remove the body of the pterygium.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are also used as a prophylactic against pterygium. Any mention that the pathology went away on its own and the defect decreased under the influence of any prescription is a lie. Folk remedies are not an alternative to surgical treatment. But to strengthen the cornea, prevent conjunctival growth and improve the functioning of the organ of vision, the following techniques can be used:
- Eating berries and blueberry juice. It has been proven quite a long time ago that this product is a panacea for tired and sore eyes. With regular use of berries, visual acuity is not only preserved, but also improved.
- Carrots and juice from them. This root vegetable also enjoys constant success among traditional healers. Carotene is very important for visual acuity. If you mix blueberry and carrot juice, you can get a cocktail that is not only tasty, but also very healthy for your eyesight.
- Make chamomile decoction according to the classical scheme - 2 tbsp. add the herbs to a glass of water, then boil in a water bath for half an hour. Cool until warm, then strain and bring the liquid to its original volume. Please note that you need to strain carefully, since you need to wash your eyes with the decoction three times a day. It is a natural anti-inflammatory agent.
- Black tea is also used as an eye wash. Brew one bag of black tea in a cup by pouring boiling water over it. Let it infuse and cool. Rinse your eyes with the solution. This recipe, if used twice a day, can relieve fatigue and redness of the eyes. At the same time, the look is significantly refreshed.
- If you feel dry eyes, fatigue and irritation, you can brew two tea bags, then cool them and apply them to your eyelids as compresses until they cool completely. The product also helps when work requires you to read a lot and work with your eyes and not get enough sleep.
- Juice from raw beets. Daily consumption of just 100g of the juice of this root vegetable helps prevent the development of neoplasms in the body, not only pterygium, but also oncological pathologies. Take it daily on an empty stomach.
If the pterygium does not show a tendency to grow and does not affect vision, it is not removed. For redness and discomfort, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory and steroid-based drops. When the formation grows, it is removed surgically. There are no other ways to cure pterygium; folk remedies and medications will not help. They will only allow the disease to progress.
Since the nature of pterygium is unknown, there are no medications to eliminate its cause. To alleviate the patient's condition, soothing and moisturizing drops are prescribed. Among them:
- Nevanak.
- Broxinac.
- Tsiprolet.
- Diclofenac.
The same drugs are prescribed to prevent inflammation after surgery.
Surgical removal of pterygium has several types. The practice is simple excision of the formation followed by sutures, plastic surgery with local tissues, the use of autoconjunctival grafts (applying them to fibrin glue and cauterization), transplantation of a donor membrane and laser removal. When choosing a method, the statistical frequency of relapses when using it, the cosmetic effect on the appearance and general condition of the patient are taken into account.
A large removed hymen leaves a wound that is covered with the tissue of the patient or donor. The operation itself takes 35–40 minutes, and the patient is provided with local anesthesia. During the intervention, the affected part of the conjunctiva is cut out, and a “patch” is applied in its place. This is usually a piece of conjunctiva taken from the bottom of the eyeball.
After the operation, the doctor will tell you what regimen to follow and what is unacceptable. In the first few days, you should refrain from watching TV and working on the computer, reading, going to the shower, bathhouse or swimming pool. When washing your hair and washing your face, it is important that water does not get into your eyes. The operated eye should be monitored by an ophthalmologist for a year, as relapse may occur.