Myopia is considered progressive if there is a decrease in visual acuity by 1 diopter over the course of a year. It has been noted that the rate of development of pathology is significantly influenced by the intensity of visual loads. For this reason, progressive myopia is most often characteristic of school-age children. An additional factor causing this pathological process is active growth. In particular, eye development can become pathologically intensive and lead to elongation of the eyeball. At the same time, the nutrition of the eye deteriorates, and there is a risk of stretching, rupture and detachment of the retina, and clouding of the vitreous body.
Progressive myopia is not only a functional pathology, but over time can lead to irreversible changes in the central parts of the retina.
Taking this into account, detected myopia imposes certain restrictions on lifestyle. In order to prevent the intensification of the pathological process, the following should be avoided:
- lifting weights;
- working in a bent position (with your head tilted down);
- practicing sports associated with concussions and sudden shocks of the body (boxing, wrestling, jumping).
- Such loads carry the risk of not only progressive myopia, but also retinal detachment and even complete blindness.
Symptoms
There are several common symptoms that can help identify progressive myopia:
- Decreased visual acuity when viewing distant objects.
- Squinting of the eyes when looking at a picture.
- Clenching of teeth, tension in the muscles of the eyes and face, holding your breath when examining an object.
- Increased anxiety. These symptoms are especially pronounced in children. They begin to put their fingers and pencil in their mouth while looking at objects.
- The habit of keeping the head in a slightly bent position.
- Asthenic body type.
- Wide palpebral fissure, which can increase as a result of the growing eyeball.
- Stretching of the retina and choroid of the visual organ.
- An increase in the number of blepharitis and conjunctivitis due to chronic damage to the eye muscles during squinting.
- Narrowing of the field of view.
Causes
There are a sufficient number of reasons leading to the development of progressive myopia. Among everything, only basic factors can be identified that significantly influence the pathogenesis of the disease:
- Heredity. Myopia can be inherited from parents in two types: autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant. If inheritance occurs according to the first type, then the risk of consequences and rapid progression of myopia will increase. When inherited according to a dominant type, the disease begins to make itself felt at a later age and does not reach a high degree.
- Visual work in combination with weakness of accommodation. When a patient writes, reads a lot, spends time at the computer and overloads his vision at close range in every possible way, this weakens accommodation. The body changes the optics of the eyes in all sorts of ways, adjusting it to external conditions. It does this as a result of lengthening the axis of the eye, which is extremely dangerous during its formation and active growth. This contributes to the development of progressive myopia in childhood.
- Weak ability to accommodate. This occurs due to the fact that from birth the ciliary muscle is morphologically defective or it is negatively affected by general diseases.
- Weakening of the ocular sclera under the influence of intraocular pressure. Very often, the development of progressive myopia in young patients is influenced by dynamic pressure. It is formed with any rotation of the head and body. As the pressure increases, the intraocular fluid begins to actively put pressure on the back wall of the organ of vision, causing its deformation and creating a prerequisite for the development of myopia.
There is another type of pathology - adaptive myopia, which manifests itself and intensifies only with the intensive growth of the child.
ABOUT VISION
The ability to ignore research-based knowledge in medical practice for decades is astonishing. This position, as a rule, accompanies blind faith in authorities and the absence of the need to justify, at least to oneself, how the prescription of treatment is related to the cause of the disease. Otto von Bismarck
Accommodative theory of the emergence and growth of myopia
In 1611, Johannes Kepler, a German mathematician, astronomer, and physiologist, proposed a theory according to which myopia develops due to prolonged eye strain at close range. The essence of eye strain for the next 200 years was represented as tension of the ciliary muscle, and the movement of the eyes towards the nose as convergence. Convergence is the movement of the eyes towards the nose when looking at a close distance. Divergence is the opposite movement of the eyes - outward when looking into the distance. This was obvious at the time, since myopia is more common in people who spend a lot of time with eyestrain. The image of a reading and intelligent person wearing glasses led to the creation of an idea of a possible cause-and-effect relationship. Since people spend more time on near-exertion, myopia is associated with near-exertion. Myopia has become established as a sign of a reading person who spends time reading books, writing texts, and studying music. What is different about people who spend time reading books? That's right - they strain your eyes. Based on this, it can be assumed that reading leads to tension in the ciliary muscle, and this, in turn, causes the growth of the eyeball. This is exactly what they thought for a long time.
In 1824, the chemical drug atropine was first synthesized, which later became one of the main drugs in ophthalmology. It is used to paralyze the ciliary muscle and dilate the pupil to examine the fundus. Now it is rarely used for this purpose: paralysis of the ciliary muscle and wide pupils can persist for a long time, and this is inconvenient. Atropine is literally experiencing a rebirth - it has gained unprecedented popularity as a means of stabilizing progressive myopia. Atropine began to be widely used for this purpose in the early 2000s; before that this happened extremely rarely.
Dutch ophthalmologist Francis Donders described the use of atropine in the treatment of myopia in his book Anomalies of Refraction and Accommodation in 1864. In 1916, Inglis Polak, an ophthalmologist from Glasgow, first described the long-term use of atropine in the treatment of progressive myopia in Scottish schoolchildren, linking its effect to the fact that children began to read and write less. In 1971, Dr. Bedrossian (USA) and colleagues published the first large study on the use of atropine in the treatment of progressive myopia. They injected 1% atropine into one eye, noting differences in the rate of increase in myopia between eyes. After Bedrossian, many other studies were conducted on the effects of atropine, which showed its effectiveness. 1% atropine dilates the pupils and blocks accommodation for a long time. There was no doubt that this was the mechanism of its action (which confirms the theory of Johannes Kepler). If tension in the ciliary muscle leads to an increase in myopia, which seemed to be confirmed by atropine, which slows down the growth of myopia, it was quite logical to look for other ways to influence accommodation. This led to the creation of various ciliary muscle simulators and methods for assessing the volume of eye accommodation. Physiotherapy methods have appeared that affect the ciliary muscle, which is mainly involved in accommodation, in various ways. They began to use drops in the hope that their action would slow the progression of myopia. Since Kepler's assumptions, several more theories have emerged about how exactly the work of the ciliary muscle and/or convergence is related to the progression of myopia. Any scientific theory is good when it is confirmed not only by observations, but also by practice. In practice, neither exercises for the ciliary muscle, nor numerous simulators that develop accommodation, nor even various ciliary muscle irradiators have shown effectiveness. Moreover, it turned out that atropine slows the growth of myopia in some birds and does not affect their ciliary muscle at all, since they simply do not have receptors for atropine. Myopia can be caused in some species of squirrels that do not have active accommodation. These data began to suggest that not everything was as previously thought. You may ask: how can this be, since there are eye simulators that our children use in clinics? My answer is: these simulators are difficult to find in modern clinics in Europe and the USA. I think that as soon as they stop bringing them profit, they will sink into oblivion here too. Ophthalmology, oddly enough, is very different and differs depending on the region. In Russia, Kazakhstan and Ukraine it is one, in Europe and the USA it is completely different. And if you see the use of accommodation training methods, you can be sure that this is a purely local development. The fact that accommodation is not associated with an increase in myopia became clear from experiments on animals. Thus, in experiments with induced myopia in chickens, atropine shows good results. However, chickens do not have muscarinic receptors on the ciliary muscle, which atropine should block, that is, it does not act on the ciliary muscle of chickens and does not affect the process of accommodation. At the same time, the effect of atropine is similar to that in humans. This calls into question the assumption that atropine inhibits the progression of myopia because it blocks accommodation and its tension as an important factor in the growth of myopia. Previously, the effectiveness of atropine was explained precisely by its effect on accommodation, but not by its effect on the ciliary muscle in chickens and its effectiveness in doses that do not cause paralysis of the ciliary muscle in humans. This is also confirmed by experiments in which atropine was applied by cannula to the posterior pole of the eye and did not affect accommodation at all. Destruction of the nucleus involved in accommodation (Edinger-Westphal nucleus) in primates does not prevent the development of myopia. Myopia can also be caused in some squirrels without a functioning accommodation system. That is, bypassing accommodation in the experiment does not in any way affect the ability to induce myopia, nor the ability of atropine to stop it. Research has now shown that very low concentrations of atropine (0.05% and 0.01%) can be used to slow myopia. This diluted atropine has no effect on accommodation, but the effect on the growth of myopia in atropine at this concentration is only slightly lower than at a concentration of 1%, which paralyzes the eye's ability to accommodate for several days and has other side effects.
Visual load
Visual stress consists of tension in the ciliary muscle. It is clear that with excessive visual loads, the ciliary muscle is in constant tension. If tension is constant and it is the cause of myopia progression, it should be recommended to limit visual loads, then the growth of myopia should slow down or even stop. For centuries, near vision stress has been blamed for causing and increasing myopia. However, recent studies conflict with previous studies. Apparently, limiting visual load has no effect and does not reduce the rate of growth of myopia.
What could be simpler than canceling all loads? Myopia must stop. (I must say that I know parents who did exactly this, and myopia continued to grow, although I personally did not systematize these observations.) But not everything is so simple. Research shows that removing exercise does not prevent the increase in myopia. How can this be if it was the load that was blamed for the cause of the increase in myopia? It was the observation that the abolition of visual stress at close range does not reduce the rate of growth of progressive myopia that prompted researchers to search for other causes of progressive myopia. But let’s return to accommodation, which, oddly enough, is not so easy to leave and forget - its participation in the growth of myopia rests on the faith of many doctors and ordinary people. It finds expression in the idea of visual gymnastics.
The idea of visual gymnastics
The idea is that if the action of the ciliary muscle is somehow related to myopia, its participation in any additional movements will not contribute to the development of myopia, or at least to a lesser extent. Since the time of Kepler, it has been believed that it is the tension of the ciliary muscle that leads to myopia. It is logical to assume that by influencing this process, we will change our work. Many gymnastics techniques have been invented and developed. To this day, marketers of eye drops make advertising postcards with a gymnastics diagram for doctors to hand out at appointments. The gymnastics scheme gives apparent seriousness to the whole action, as if it is important in what sequence the ritual movements of the eyes are performed. Someone might think that this particular sequence of eye movements has some kind of physiological meaning that is understandable to dedicated people. However, it is not. Studies show that in the treatment of progressive myopia, various types of gymnastics and physiotherapeutic effects on the eye are useless. Gymnastics has enormous placebo potential. Many patients note improved vision after exercise. But when studies determined objective indicators such as visual acuity, refraction and others, no progress was noted after gymnastics courses. Human eyes are in constant motion, even during sleep. In such a situation, it is very naive to imagine that additional ritual eye movements will make some contribution to the overall picture. It’s the same as believing that it matters how many times a homeopath shakes a medicine so that it is the number of shakes that leads to it obtaining some properties (homeopaths argue that sometimes a medicine needs to be potentiated in order for it to become effective). It’s the same as recommending walks to the postman; he already walks. There is no point in recommending a walk to the postman if he complains of pain in his legs. However, faith in eye gymnastics is endless. I say many times a day that there is no point in tormenting children with it. The ciliary muscle has nothing to do with fitness. It is basically impossible to train her. The word "training" comes from sports, so let's define it for correct use in relation to the eye and bring it back to sports. In sports, the term “training” refers to physical activity aimed at developing physical abilities and improving the quality of performing some action. For example, a swimmer, honing his skill, raises his arm so that each stroke becomes minimally energy-consuming and maximally effective. A boxer practices a punch, a basketball player teaches his brain to contract the muscles of his legs and arms so as to jump the ball into the basket. That is, not only muscles are involved in training, but also the brain, which hones skills at the management level. In relation to the ciliary muscle, such a word as “training” is not entirely correct; we can simply cause its contraction and relaxation when moving our gaze from near to far. The mechanics of this process itself do not change; we cannot “learn” to contract the ciliary muscle. Consequently, the skills are not honed, only additional work of the ciliary muscle occurs. Such actions in sports can be compared to working on weight machines, when a person wants to increase the strength of a muscle, pump it up. Although even on strength training equipment a person learns to perform movements more skillfully. There is a significant difference between the muscles that we train in the gym and the ciliary muscle. The ciliary muscle is smooth and cannot be pumped up in the same way as skeletal muscle. There is no improvement. We cannot pump up smooth ciliary muscles like skeletal muscles, and even more so we cannot teach them to contract in a more correct manner, as we try to force muscles to act in sports training. Even if we could do this, nature is not obliged to slow down myopia for this reason. Which she doesn't do. Tension of the ciliary muscle does not lead to an increase in myopia.
I discuss in detail visual gymnastics, the Bates method and other methods that exist but should not be used (as well as modern ideas about myopia) in the pages of my book "The History of Vision"
Rethinking
For a long time, visual stress was considered the main factor influencing the growth of myopia. It would be too simple: remove visual stress, if any, and... myopia will stop. Not so. It turns out that if you cancel all the loads, myopia still progresses and it seems that the rate is not slowing down. How is it possible: if visual stress leads to myopia, it cannot be that removing visual stress will stop myopia. But that's exactly what happens. In such a situation, another person is needed to blame for the increase in myopia.
Genetics of myopia
The taste of the pie depends on each of its components. L. N. Tolstoy
Is there a genetic tendency to myopia? Do we acquire any properties from our parents that can increase or decrease the risks of myopia? Why do different children, under seemingly identical conditions, develop different degrees of myopia, while some do not develop it at all? Yes, of course, the tendency to myopia is inherited. A very large number of genes are responsible for the structure and growth of the eye. It is impossible to say how much yet, but it is a lot. Sometimes, for some reason, the eye lengthens more easily (which is the essence of progressive myopia). Unfortunately, we are very limited in knowing exactly what reasons lead to this, as well as in methods of influencing this process. Imagine that you need to build a wall. For what reasons might this wall not be strong enough? There may be several reasons: a bad brick, a worthless mortar, not enough mortar, a brick of the wrong shape... Or maybe there are even more of them: the brick or mortar is a little weaker, the builder lays the masonry a little worse, there is more sand in the mortar than necessary, the brick is not burned as expected. Imagine that there are hundreds of reasons, each of which is uncritical, but in the end everything leads to the fact that the wall is not as stable as we would like. Each trait is a gene that can be inherited. When one gene is altered, for example in Marfan syndrome, we can list it as the main one. When there is polygenic inheritance, this situation is too difficult to assess and predict. In conclusion, we can say that myopia has a hereditary predisposition. Parents or siblings with myopia are a risk factor. However, we cannot accurately assess these risks. We cannot influence heredity. All we can do is change our lifestyle. Let's discuss this.
Walks
Two hundred years after Johannes Kepler's hypothesis, scientists again began to look for the cause of myopia. Visual stress, which has long been considered its main cause, has become unsatisfactory for many due to the large number of inconsistencies in the facts. The research was conducted in this way. A group of children (several thousand in some studies) were studied over several years. When children with myopia appeared in this group, attempts were made to determine how other health and lifestyle parameters differed from those children who were not myopic. As a result, an interesting connection was established: the more time the children spent walking, the less often progressive myopia occurred. It is clear that everyone has different inclinations. It was later discovered that natural sunlight causes the retina to produce dopamine, which blocks eye growth and prevents the development of myopia. There is a lot of research with walking. One of them used a classroom where children continued to strain their eyes and their myopia stopped increasing.
What happens?
The connection between walking, dopamine and increased myopia turned out to be a serious argument against the accommodative theory. Various influences on the ciliary muscle (trainers, gymnastics, medications, load limitation, destruction of the Edinger-Westphal nucleus) and experiments on animals with direct and indirect effects on it show that myopia does not develop due to simple tension of the ciliary muscle, as previously thought. Experiments on animals show that it is not the tension of the ciliary muscle, but the effect on the retina that affects myopia. Light, dopamine, defocus, and atropine affect the refraction of humans and other vertebrates through their effects on the retina.
How to deal with visual stress and gadgets?
As a parent, I am a big supporter of the fact that a child should develop in communication with real people, in active games and involvement in sports. Sure, I'm not a perfect parent, and I don't do everything well. All my children love electronics, and sometimes I don't have the strength to influence it. I hope they won't nag me when they're adults that I'm not that advanced and can't set up my Apple ID. (My mom doesn’t remember any passwords for any account, and I understand that I will be the same, but I can’t bring myself not to grumble.)
To console myself and other parents like him, I want to say that there is no convincing evidence that visual stress, displays and video games lead to myopia (this does not exclude the possibility that they may have harm that is not related to visual stress at all). However, recent epidemiological studies contradict previous ones. Most likely, the active increase in myopia in children involved in various types of activity is due to the fact that children stop walking outside a lot or walk less. If loads are related to myopia, then they are definitely not in first or even second place. Heredity and time spent outdoors are more important factors.
Does myopia suddenly start to increase?
Parents often note that myopia began to increase suddenly. It didn’t grow, didn’t grow, and suddenly it starts. Is it so? Changes in refraction at a young age are called refractogenesis. This name suggests that refraction is created in order to then remain in some meaning for life. Refraction is actually created throughout childhood and young adulthood and then, once fully formed, changes little until the end of life (age-related problems with working at close range are not associated with changes in refraction, but with the ability to accommodate). Most children are born farsighted. First, to some extent (and for everyone at different rates), farsightedness decreases, then for some, after farsightedness falls, myopia increases. This is a direct reflection of the growth of the eye in length. The eye grows - farsightedness decreases, myopia increases. The eye is growing all the time. Imagine that you have a certain amount on your bank card that you spend on all sorts of needs, and the balance goes into minus. You move towards debt by spending your positive balance, and not only when it is already in the red. This is an analogy. Myopia is noticed when it first begins, but when the eye approaches it during growth, the person does not feel anything. However, myopia does not suddenly begin to increase - it was growing before you felt it, it was just that then it was a decrease in farsightedness. I mention this because patients incorrectly associate myopia with some point in their life that coincided with the onset of myopia. It matched, but no more. If your child has myopia, it appeared suddenly, it grew even before that, until you felt it.
Growth curve
We often tell patients that the rate of increase in myopia is subject to sinusoidal fluctuations. Myopia increases faster in winter - this is due to the fact that the length of the day is shorter and the time the eye is exposed to natural light is reduced. In summer, growth is slower, which is reflected in more time for walking and longer days. Perhaps, based on this, it is in winter that it is worth walking as much as possible.
How much light do you need?
Please watch this video.
YOU CAN DISCUSS THE ARTICLE AND EXPRESS YOUR OPINION HERE
Types of myopia
Progressive myopia can be of the following types:
- Night - formed when there is a lack of lighting.
- False - occurs during a spasm of accommodation.
- Axial - develops with an increase in the axis of the organ of vision.
- Combination – mild degree of myopia with refractive error.
- Transient - its development is influenced by various diseases and the use of certain medications.
- Complicated – there is an anatomical pathology of the development of the organ of vision.
- Refractive – optical myopia.
Classification
Depending on the degree of myopia, there are:
- weak (from 1 to 3 diopters);
- medium (3 – 6 diopters);
- high (over 6 diopters).
Depending on the reasons, myopia occurs:
- axial, when the refractive power of the cornea, lens, and vitreous body remains within normal limits;
- refractive, when with a normal size of the anterior-posterior axis, the refractive power of the optical system of the eye is greater;
- mixed.
It is also customary to divide myopia into types:
- congenital (rare);
- true;
- false, arising from increased tension in the ciliary muscle;
- transient (occurs against the background of diabetes or the use of certain medications);
- night (develops with a lack of light);
- complicated (accompanied by changes in the eyes leading to loss of vision);
- malignant.
Exercise therapy for myopia
How to stop progressive myopia? Physical activity is perfect for this. They must be normalized, especially with a high degree of myopia. Then you will have to forget about sports such as track and field and weightlifting, boxing and other sports that involve sudden jumps, movements and impacts.
Any kind of sudden movements can lead to retinal detachment and blindness. Exercise therapy for myopia can normalize the condition of the eye muscles and improve visual function. Therapeutic exercise improves blood circulation in the organ of vision and makes the eye muscles stronger.
Exercise therapy is ineffective for congenital myopia. And physical activity is contraindicated if there is a risk of retinal detachment. The exercise therapy program includes:
- strengthening ligaments and muscles,
- improving blood supply to body tissues,
- strengthening the heart and blood vessels,
- strengthening the muscles of the organ of vision,
- strengthening the sclera,
- improving blood supply to the eye.
General strengthening gymnastics includes the following exercises:
- walking;
- breathing exercises;
- exercises for the muscles of the torso, shoulder girdle, neck and legs.
Eye exercises for progressive myopia consist of several groups: for the external eye muscles, the internal ciliary muscle and self-massage of the eyes.
Treatment of myopia in children
There are many methods for restoring vision for myopia, and a specific choice can only be made by a doctor, taking into account all individual nuances. However, the primary task is a thorough diagnosis, establishing the causes, stopping the progression of myopia - if it shows a tendency to worsen - and preventing the development of possible (quite severe) complications.
It is considered more or less favorable in prognosis if vision deteriorates at a rate not exceeding 0.5 diopters/year. In such cases, the absolute advantage in the therapeutic scheme is given to training, stimulating, and developmental correction methods. It is extremely important to comply with all the ophthalmologist’s instructions and strictly follow his recommendations, normalize sleep, nutrition, study and rest. In no case should you neglect the prescribed eye gymnastics - often the simplest exercises turn out to be more effective than a scalpel if you perform them patiently and for a long time (the treatment and preventive course can last several years, and parents need to be psychologically prepared for this).
The ophthalmology center strictly adheres to the principles of an individual approach to each patient, and especially if our patient is a child. The therapeutic strategy is developed taking into account many factors and features of the specific clinical picture. In any case, the maximum possible goals are set - namely, the complete restoration of the sharpness and clarity of children's vision. The dynamics of the condition during treatment are constantly monitored by the doctor, and if necessary, adjustments are made to the treatment course; parents are provided with all the necessary recommendations regarding visual gymnastics and diagnostics at home, and all sets of exercises are built in a playful way.
The Moscow Ophthalmology Center has the most modern high-tech equipment, which allows it to carry out diagnostic and treatment activities at the level of WHO world standards. Training and physiotherapeutic techniques are used with constant success, including laser, ultrasound, magnetic, infrared, electrical stimulation therapy, vacuum massage and many others.
Infrared laser therapy
The procedure is aimed at activating metabolic processes and nutrition of eye tissue, as well as eliminating accommodation spasm as one of the significant factors in the development of myopia. Infrared laser exposure at close range has the properties of a kind of massage for the accommodating system (ciliary muscle).
Vacuum massage
As the name suggests, the active component in this procedure is pressure changes from normal to very low. The method is aimed at stimulating blood circulation and nutrition of the ocular structures (in particular, the ciliary muscle), normalizing the tone of intraocular fluids and media.
Laser therapy
Therapeutic laser in ophthalmology is widely used to develop binocular three-dimensional vision, strengthen accommodative functions, and activate photosensitive receptor neurons of the retina and optic nerve.
Electrical stimulation
Ultra-weak electrical currents effectively improve the conduction functions of the optic nerve. The procedure is absolutely painless.
Lenses
In order for people suffering from progressive myopia to be able to use lenses, it is necessary to become familiar with some important points that guide ophthalmologists when prescribing optical correction. Lenses are not prescribed for high levels of myopia. The reason is that there is a risk of damage to the retina while constantly removing and putting on lenses. In myopia, the power of contact lenses is indicated by a negative number.
The main advantage of contact lenses over glasses remains that the focal length is reduced from 12 ml to almost 0. When wearing lenses, the size of the picture remains the same, but when using glasses, the focal length is longer, therefore, the refraction of rays occurs earlier than on the macula, from - this makes the picture seem smaller.
When using lenses, there is no focal length, and the image does not lose its size. Myopia makes everything look blurry, and when you wear glasses, they can become foggy or scratched, resulting in less clear pictures. In addition, when using a lens, it is possible to avoid such an unpleasant fact when the side frame becomes a barrier to the field of view.
Lenses can be freely used where it is necessary to achieve different values of optical power separately for the right and left eyes. With the help of lenses, you can stop the progress of myopia, since there is no distance between the lens of the eye and the refractive lens. This stabilizes the level of optical power of the eye, then progressive myopia becomes stationary. After wearing the lenses, you can undergo laser correction and continue to live your normal life without wearing lenses or glasses.
Lenses require special care. If you do not follow it, then there is a high probability of developing conjunctivitis. Eyes need to be moisturized, and lenses need to be changed and ordered additionally. Girls should be especially careful with their lenses when applying makeup. If any particle gets under the lens, it will irritate the eye.
Lenses are soft, transparent and with special filters. Due to the latter, it is possible to minimize the impact on the eyes from the computer and TV. Also, lenses can be calibrated, then the color of the iris will be new. With the help of lenses, it is possible to evaporate a lack of visual function of up to 2 diopters, and this can be severe impairments.
Progressive myopia and glasses
Progressive myopia can be treated with glasses. This is a classic doctor’s recommendation for correcting the defect that has arisen. He may recommend glasses that have a double-convex lens. It is concave on both sides and resembles the outline of an apple core. This lens focuses the rays and directs them directly to the macula on the retina.
Lenses can also be additionally tinted, for aesthetic reasons and to transmit a specific light spectrum. They come with a UV filter or against sun glare. People called them “chameleon”. The fact is that the surface of glasses that are coated shimmers. It can be crimson, green, blue. Lenses can be made of glass or plastic. The first option often breaks, and the service life is 2-5 years. But plastic frames need to be changed every 1-2 years.
Glasses to correct myopia are prescribed during work. For special cases, glasses with a plus optical power sign may be prescribed for work. But with a minus, it is advisable to assign it to look at signs, distances and everything that is on the street. In this way, the eye muscles will be able to restructure as much as possible and the value of vision will gradually return. But in combination with glasses it is necessary to use special exercises and vitamins. Wearing glasses alone will not lead to a positive result.
Congenital myopia (myopia) in children
Myopia can be either acquired during life or congenital, formed at the stage of intrauterine development. There are many known possible causes and risk factors (prematurity, family history, concomitant congenital pathology in other body systems, destructive habits of parents, etc.). Typically, congenital myopia is not limited to just a refractive problem and is accompanied by serious abnormalities of ocular tissues and structures (for example, the fundus).
In most cases, congenital myopia is stable, but sometimes it tends to further worsen. A child with congenital myopia should be registered at a dispensary under the constant supervision of a district ophthalmologist. In such cases, the prognosis is directly dependent on how promptly treatment begins and, in particular, the prevention of the development of amblyopia (“lazy vision syndrome”, which consists of a gradual decrease in the activity of the visual system with a particular pathology).
Laser correction
How to stop progressive myopia? For this, experts were able to develop such an effective and modern method as laser correction. It is completely safe and allows you to avoid contact lenses and glasses. The essence of the therapy is that with the help of laser beams it is possible to change the shape of the cornea. It becomes flatter, its optical power decreases. In other words, the laser beam creates a minus glass into the cornea, the effect of which is similar to that of glasses. Because of this, the image penetrates directly onto the retina, and the patient clearly sees objects located in the distance.
Today the following methods of laser correction of progressive myopia are used:
- Super LASIK. This method is in great demand for the correction of myopia all over the world. Using the individual parameters of the patient’s cornea, the laser beam creates optics of the visual organ that are close to ideal. Visual acuity can exceed 100%.
- PRK. Used for thin corneas or low degrees of myopia, when there are contraindications for use. This method is carried out according to individual parameters of the cornea, which were obtained during the diagnostic process using a topographer.
What is progressive myopia
Progressive myopia is defined as myopia in which vision deteriorates by 1 diopter or more over the course of a year. This is a dangerous disease: the elongation of the eyeball takes on a pathological character, causing the nutrition of the eye tissue to deteriorate, and there is a serious risk of rupture and detachment of the retina.
We recommend reading: Diopters for myopia
Progressive myopia leaves a serious imprint on the quality of life of patients. They are prohibited from any work that involves lifting heavy objects or bending their heads. They cannot engage in boxing, wrestling, or jumping, because these sports are fraught with damage to the organ of vision and even the development of blindness.
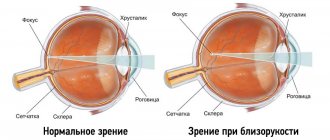
Rays entering a myopic eye are highly refracted. As a result, the focus does not reach the retina, but is concentrated in front of it. Objects located in the distance appear blurry. Patients note a rapid deterioration in visual acuity. With a malignant disease, the degree of refraction reaches -30 diopters.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies can only be used in the treatment of progressive myopia in combination with other methods of therapy. First of all, you need to adjust your diet. Consume only those foods that have a positive effect on the structure of the eye membrane:
- Carrots and blueberries are very good for the retina. They contain essential vitamins and antioxidants. The retina undergoes maximum changes in myopia.
- Sea fish and vegetables, the composition of which contains polyunsaturated fatty acids. These products are extremely important for the functioning of the retina.
- Dairy products rich in calcium. They are able to strengthen the connective tissue membrane of the organ of vision - the sclera. This inhibits the growth of the eye in length.
Ophthalmologists at the Excimer Clinic
All doctors
Pershin Kirill Borisovich
Leading ophthalmic surgeon and medical director of the Excimer clinics, doctor of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, professor, academician of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences
Pashinova Nadezhda Fedorovna
Chief physician of the Moscow ophthalmological clinic "Excimer", ophthalmic surgeon of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences
Plyukhova Olga Alexandrovna
Head of the laser therapy department, ophthalmic surgeon, doctor of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences
Surgical correction
This method of therapy is prescribed for a high degree of pathology, when conservative methods do not give the desired effect. Surgical correction is performed in two options:
- Removal of the transparent lens and its further installation in place of an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). This method is considered the most effective today. An artificial lens can completely eliminate varying degrees of myopia. Premium IOL models can perfectly cope with astigmatism, and can also see at any distance without the use of glasses.
- Actual lenses. This is the second method of surgical correction, which is not as popular as the previous one. These are contact lenses for the lens. They are installed inside the organ of vision or in front of the lenses, or even directly on it. Moreover, the natural lens still remains. This method is still young and does not have long follow-up periods. Although we can say for sure that it is absolutely safe.
Prevention
Progressive myopia is dangerous because it can lead to severe complications and progresses quickly. To prevent this, it is necessary to reconsider your lifestyle. Prevention necessarily includes a general strengthening regimen, walks in the fresh air, calcium and phosphorus supplements, and nutrition including vitamins. These are the basic rules for preventing vision deterioration. It is important to alternate work and rest correctly.
The general working regime is based on the rational distribution of workload and rest. In this case, you need to avoid excessive physical activity, sudden movements and head tilts. For visual work it is necessary to create special conditions. For this it is important to achieve good lighting. Every hour of work should be accompanied by a 15-minute rest.
If progressive myopia is detected, you must carefully monitor your health. Since most often this disease is diagnosed in childhood, parents are obliged to protect the child from spending long periods in front of the computer and TV. If the child is not yet 3 years old, then you should not allow them to do such things at all. Before entering school, a child can be at the computer for no more than 15 minutes a day. Further, the time can be increased with age, while taking a break after every hour of work.
Sources used:
- Kvasova M. D. Vision and heredity. - Moscow / St. Petersburg: Dilya, 2002.
- Primary glaucoma in patients with myopia and hypertension: monograph. / Elena Baudova. - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2011.
- D. Hubel. Eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- “Eye Microsurgery” named after Academician S.N. Fedorov" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation