Myopia in adults
A decrease in visual acuity is caused by various refractive errors, but myopia occupies one of the leading positions in the list of eye pathologies faced by modern ophthalmologists.
In this article
- Myopia in adults
- General characteristics of the disease
- Main symptoms of myopia
- Types of myopia
- True and false myopia - what is the difference?
- Why does myopia develop?
- Modern methods of treating myopia in adults
- Physiotherapeutic method for treating myopia
- Surgical treatment of adult myopia
- Methods for correcting myopia
- What happens if myopia is not treated and corrected?
This disease of the visual system is diagnosed in children and adults. It can be either congenital or acquired. Myopic people experience great discomfort because with this disease the ability to see what is at a far distance is weakened: the image appears blurry and indistinct. Modern methods of treating myopia make it possible to stop the disease or stop its progression, even without resorting to surgery. There are effective methods of correction and treatment, alternatives to surgery, that allow you to restore one hundred percent vision. Let’s take a closer look at what modern techniques help get rid of visual discomfort with myopia, and also figure out how effective they are.
Why did farsightedness turn into nearsightedness and is it the other way around?
Users often wonder whether it is possible for a farsighted person to become nearsighted? Yes, such a phenomenon is possible. In the early stages of hypermetropia, only near visual acuity is impaired, but clear vision at long distances is maintained. However, there are also more severe forms of farsightedness, in which it is difficult to see both close objects and objects that are too far away. In such situations, you often have to readjust when looking at different distances and strain yourself excessively. Such constant adjustment of eye focusing can lead to low degree of farsightedness turning into nearsightedness.
Does it happen that myopia is replaced by farsightedness? No, this can't happen. But the onset of presbyopia (age-related farsightedness) cannot be avoided by anyone, even nearsighted people. At the same time, for those who had low degrees of myopia, this will not particularly harm; there may even be some compensation for the minus diopters. But patients with moderate and severe degrees sometimes have to use two pairs of glasses - for viewing objects near and far. The doctor may also prescribe bifocal glasses, which simultaneously have two zones for long and short distances. However, in this case, many people experience inconvenience. But, since changes in accommodation are irreversible, there are only two ways to treat presbyopia: using spectacles or contact optics, or, in the absence of contraindications, using a microsurgical operation - lensectomy, in which the lens is replaced with an intraocular lens.
Thus, myopia and farsightedness are visual impairments that can be successfully corrected with glasses or contact lenses, as well as through modern microsurgery. It is important to be attentive to your eye health and, if you experience any unpleasant sensations, visit an ophthalmologist to find out the cause. Successful treatment of farsightedness and myopia depends on timely diagnosis.
General characteristics of the disease
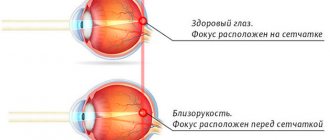
Myopia is usually called an anomaly of human visual functions that occurs due to deformation of the eyeball or disruption of the optical system of the eye. With myopia, a person cannot clearly see distant objects, but often does not experience discomfort when working with objects at close range. This is due to the fact that the image is incorrectly focused, or rather, the light rays, which, instead of being refracted in the center of the retina, as is normal, are projected in front of it. In other words, myopia is a defect in which refraction, that is, the refractive ability of the eye, is impaired. According to medical statistics, more and more cases of the corresponding disease are diagnosed around the world every year. Ophthalmologists explain that this is due to the lifestyle of a modern person, which exposes the eyes to excessive stress.
How to choose the right glasses for myopia
The method for selecting glasses is quite complex; it requires deep specialized knowledge, extensive clinical experience and mandatory analysis of diagnostic data. You cannot trust the selection of glasses to anyone other than an ophthalmologist - this would be unreasonable and unsafe. In particular, glasses with interchangeable lenses are used to determine the required degree of correction. It sometimes happens that a patient subjectively feels satisfactory clarity of vision when using several different types of lenses: “this way and that way.” In such a situation, of all the options that are comfortable for the patient, glasses of the lowest optical power are prescribed; excessively strong glasses can cause excessive accommodation and provoke the development of the reverse pathology - hypermetropia (farsightedness).
Thus, the degree of myopia is determined by the lens of the lowest power that provides sufficient visual acuity. Visual acuity is diagnosed in both eyes simultaneously, and in each one separately, since in some situations (for example, with an uneven spasm of accommodation) the right and left glasses must differ in optical power.
The maximum range of clear vision is also important. In particular, the technique of measuring the degree of myopia using font No. 5 or No. 6 from the Golovin-Sivtsev table is practiced. In a position in which this font is clearly distinguishable and confidently recognized by the patient, measure the distance from the eyes to the table.
The degree of myopia in this technique is calculated by the formula:
M=100/X, where X is the distance in centimeters.
For example, if the font is readable at a distance of 33 cm, the degree of myopia is 100/33 = -3.0 D.
This technique, however, is not entirely accurate; it is used only for a general, indicative assessment of the degree of myopia. Due to eye strain while reading letters, the accommodation spasm may intensify, which, in turn, can lead to overdiagnosis (a higher degree of myopia is established than is actually the case).
The method for determining the degree of myopia using interchangeable lenses is also not completely accurate. The measurement error is due to the fact that the lens at the time of diagnosis is located at a certain distance from the eyes, which may vary depending on the frame and the individual characteristics of the facial structures.
Therefore, real ophthalmological diagnosis and vision correction for myopia is a much more complex and responsible clinical task. Special equipment is used, and a number of factors are taken into account (age and development dynamics, lifestyle and main activity of the patient, risk of progression, etc.). In addition, moderate and high myopia is often accompanied by pathology of the fundus structures, i.e. refers not to functional disorders, but to diseases with organic changes in the tissues and environments of the eye. In this case, correction is necessarily combined with complex treatment and, being consistent with other methods, becomes one of the components of therapy.
Wearing glasses for moderate and high myopia is important not only as a method of compensation, but also as a prevention of further deterioration of vision, since myopia tends to progress over time. Sometimes it causes complications or, on the contrary, is itself a consequence of a more severe pathological process, as a result of which, if measures are not taken, vision rapidly deteriorates to the point of complete blindness.
Main symptoms of myopia
It is not difficult for an experienced ophthalmologist to unambiguously diagnose the condition of myopia. However, with a moderate or severe degree of the disease, the patient himself may suspect a problem.
The main signs and symptoms include:
- Decreased clarity of distant vision;
- Blurry contours and unclearness of distant objects;
- Rapid eye fatigue;
- Frequent headaches, etc.
It happens that myopia occurs against the background of astigmatism. In such situations, patients not only see objects blurred, but may also experience a feeling of double vision. With myopia and astigmatism, straight lines often appear curved and the image is distorted. With a high degree of myopia, people sometimes cannot clearly distinguish what is in front of them at arm's length. In most cases, myopia is corrected by optics, however, if for some reason a person cannot use glasses or contact lenses at a particular moment, he will be disoriented in space. That is why modern medicine pays special attention to the study of myopia, and leading scientists strive to develop new effective ways to treat this disease.
What is farsightedness?
In this vision disorder, light rays are focused not on the retina, but on the area behind it. The difference between farsightedness and nearsightedness is that in this case a person, on the contrary, sees everything blurry up close, but clearly and clearly distinguishes distant objects. The reason for farsightedness is that the axis of the eye is too short or its weak refractive power. The pathology most often manifests itself after the age of 40-45, and therefore its second name is age-related farsightedness. It occurs because the accommodative properties of the eye are disrupted: the lens loses its elasticity, and the muscles lose their ability to contract fully. But sometimes hypermetropia also occurs in childhood. Parents need to be especially careful. The child does not see the text in front of him well, and quickly gets tired of trying to see the letters, moving the textbook further away from him. If your child complains of eye fatigue, you should definitely visit an ophthalmologist.
Farsightedness, if not corrected, can lead to negative consequences:
- frequent inflammation of the organs of vision (conjunctivitis, barley, blepharitis and others);
- rapid eye fatigue when reading or writing;
- headaches;
- the appearance of amblyopia in children;
- development of glaucoma.
With severe degrees of farsightedness, there is a risk of developing glaucoma. Too short an axis and forward displacement of the iris of the lens can lead to the fact that the iris partially or completely blocks the drainage pathways through which intraocular fluid is drained, and this provokes an increase in pressure inside the eyeball and, accordingly, the risk of glaucoma.
Types of myopia
There are stationary, progressive and complicated myopia. In the first case, the disease is characterized by a sluggish course and absence of complications. With a progressive form, a stable decline in vision occurs. Complicated myopia can lead to serious adverse effects on the fundus and optical media. Each person suffering from myopia can be diagnosed with a different degree and severity of this pathology. According to the nature of development, the disease is divided into three types:
- progressive;
- transient (occurs against the background of concomitant diseases);
- complicated (complications arise from the fundus, etc.);
- stationary.
The progressive form is dangerous because each year the patient’s vision drops by more than 1 diopter. When impairments become permanent, it can lead to visual impairment in the future. A milder form of myopia is considered to be transient, which bothers a person for a short time, usually during an exacerbation of any concomitant diseases or taking medications. Stationary myopia is easily corrected and does not progress. With weak myopia, the index of refractive error does not exceed 3 diopters (with a minus), with an average degree of myopia, deviations of up to 6 diopters are diagnosed. Values exceeding this threshold are characterized as high degree.
Postoperative period
Sick leave after laser correction of myopia is not required, performance is maintained. However, during the first time after laser vision correction, the patient experiences:
- pain;
- photophobia;
- feeling of a speck in the eye;
- my eyes are watering.
In this regard, as well as to avoid complications from the disturbed cornea, the operated patient is given special recommendations on the regimen for the first few days:
- Avoid bright light, both natural and artificial: wear dark glasses, use dim lighting indoors;
- do not touch the operated eyes with your hands, do not rub them;
- Avoid contact with eyes with detergents and tap water;
- use prescribed eye drops to prevent the development of infections and relieve discomfort;
- avoid increased physical activity;
- do not drink alcohol, if possible refrain from smoking, especially indoors;
- Avoid eye strain while reading, working at the computer, or watching TV;
- Girls are advised to avoid eye cosmetics for the entire postoperative period.
Unpleasant sensations after getting rid of myopia using LASIK disappear already on the second or third day after the intervention; in the case of PRK, the postoperative period lasts about a week. After finishing it, it is useful to do special exercises for the eyes. For example, this simple complex helps a lot:
- Blink frequently for 15 seconds.
- Eye movements from bottom to top and top to bottom, from right to left and vice versa.
- Circular movements of the eyes.
- Alternate refocusing from a near object to a distant one.
In this video, experts talk about the features of the postoperative period:
True and false myopia - what is the difference?
With true myopia, a person’s eyes increase in size or disturbances occur in the functioning of their optical system (without changing shape), while false myopia is provoked by a spasm of accommodation. Typically, this condition does not require constant glasses correction and goes away as a result of drug treatment or after undergoing a course of physiotherapy.
Regardless of the nature of the disease and the characteristics of its course, it should not be ignored. Even if a patient is diagnosed with false myopia, the lack of proper treatment can lead to complications (myopia will turn into a true form). Treatment of myopia should occur at any stage.
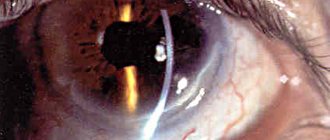
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK)
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) is a laser correction of myopia based on evaporation of the surface layer of the optical center of the cornea using high-intensity ultraviolet radiation from an excimer laser. PRK surgery, depending on the radiation dose, changes the shape of the cornea, which leads to a decrease or increase in the refractive power of the cornea.
The advantage of this method
Correction of myopia using photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) allows you to very quickly, accurately, without the use of conventional surgical instruments, change the curvature of the cornea to the required size, which is necessary to improve visual acuity. The advantages of PRK are the simplicity of calculation, precisely observed dosage of radiation exposure, short operation time, and a more accurate prognosis than, for example, with keratotomy. The operation is not technically difficult. Millions of surgeries around the world have shown that PRK surgery is safe, effective and has no serious side effects.
Progress of photorefractive keratectomy surgery
The treatment of myopia itself using PRK is painless, does not require general anesthesia and includes the following steps. Before the operation, anesthetic drops are instilled. Myopia correction using PRK does not require any general anesthesia. The patient is placed on the operating table, the skin around the eyes is treated with a special germ-cleaning solution and covered with a sterile delimiting bandage. Painkiller drops are instilled once again. Correction of myopia using the PRK method is carried out as follows:
| The laser is centered and focused on the cornea of the operated eye. The excimer laser, acting in the form of a wide beam according to a program pre-calculated based on the data entered by the doctor, evaporates the epithelium and part of the corneal tissue and thus models its new surface. After the operation is completed, anti-inflammatory drops and antibiotic drops are instilled. The eye is covered with a bandage. The PRK operation is completed. |
Myopia treatment is carried out on an inpatient or outpatient basis. During inpatient treatment, correction of myopia using the PRK method is carried out on both eyes at once, after which a hospital stay of 3–4 days is required. During outpatient treatment, myopia correction is carried out first on one eye, then, after about 5 days, on the other.
Postoperative period
- During PRK, the corneal epithelium is evaporated, so that during the recovery period, which takes 2-3 days, the patient is left with an open surgical surface and may experience pain (to reduce which medications are used). The operated eye will be covered with a bandage for 3 - 4 days. From 3 to 4 days, visual acuity begins to increase.
- After removing the bandage on days 3-4 after PRK, you can freely wash your face and use cosmetics; after 1 - 2 weeks - watch TV; after 2 weeks with high visual acuity - drive a car.
- After laser treatment, you will need to regularly instill anti-inflammatory drops into the operated eye (up to 2 months).
- The healing process after PRK occurs differently in patients, but all patients are recommended to exclude factors that contribute to an increase in intraocular pressure and maintenance of corneal edema: visual stress at close range for 2 - 3 weeks, heavy physical labor, especially with the torso tilted, and visiting a bathhouse for 2 - 3 months, take large volumes of liquid orally, avoid drinking alcohol.
Why does myopia develop?
Scientists predict that by 2050, 4.8 billion people (more than half of our planet's population) will suffer from myopia. Therefore, researchers are constantly striving to find new effective treatments. Most often, the list of reasons for the development of this eye pathology includes:
- Abnormal structure of the eyeball. The length of its front axle exceeds the norm. As a result, when focusing, light rays do not reach the desired point on the retina.
- Increased refractive indices (malfunction of the cornea or lens). The dimensions of the eye fully correspond to normal values, but strong refraction of the rays prevents correct focusing.
In addition to the main causes, ophthalmologists identify some factors that contribute to the appearance of myopia symptoms. Among them:
- Heredity. In this case, we are not talking about the direct transmission of a “bad” gene from parent to child. Implies a predisposition to the disease.
- Weakening of the tissue of the sclera of the eye. This process leads to an increase in the size of the eyeball.
- Violations of the focusing (accommodative) ability of the eye.
- Disorders of the musculoskeletal system (scoliosis, flat feet).
- Infectious hepatitis.
- Allergic reactions.
- Infectious diseases.
- Diabetes.
- Decreased protective functions of the body.
- Dental diseases, etc.
In addition to the above reasons, a special role in the development of myopia is assigned to increased visual stress, lack of a balanced diet, poor environment, etc.
Modern methods of treating myopia in adults
There are no universal ways to combat myopia today. The choice of treatment method is always based on the individual characteristics of the disease. Doctors note that acquired myopia in adults is easier to deal with than the hereditary form. First of all, before prescribing treatment, the doctor tries to establish why the pathology occurred, as well as determine its type and degree. Treatment of acquired myopia begins with eliminating the cause that influenced its development. In parallel, the patient undergoes medication and physiotherapeutic courses of treatment. In addition, vision correction products are used. Spectacle optics, like contact lenses, should be used constantly for moderate and high myopia to prevent eye fatigue, which can cause complications of the disease. However, correction agents, although they help eliminate visual discomfort, do not have a therapeutic effect.
The following techniques are considered the most useful in the fight against myopia:
- laser microsurgical operations (LASIK, Super-LASIK);
- surgical intervention (scleroplasty, keratophakia, etc.);
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapeutic influence.
In parallel with the main therapy, gymnastics is often indicated, which helps improve accommodation. Exercises are always aimed at correcting gaze focusing, training distant vision, strengthening intraocular muscles, and relaxing the eyes after prolonged exercise.
Correction methods for farsightedness
In the treatment of myopia and farsightedness, generally the same methods are used - glasses, contact lenses, microsurgical operations on the eyes, but with some nuances. For farsightedness in children, it can be treated using hardware methods, which include a whole range of procedures:
- laser therapy;
- Ultrasound and magnetic therapy;
- electrical stimulation;
- vacuum massage;
- computer audio training and others.
This complex has a beneficial effect on the eyeball, helps improve metabolic processes in the eye structures and stop the progression of farsightedness. Another operation for hypermetropia is the implantation of phakic lenses. It is performed in cases where the accommodative ability of the lens has not been lost and its removal is not required. Essentially, these are contact lenses, only installed inside the eye. They help focus light rays directly onto the retina, enabling the ability to see clearly both far and near. As for correction with glasses and contact lenses, the principle of their operation and indications for use are identical, only for farsightedness optics with a “plus” sign are required.
Physiotherapeutic method for treating myopia
Physiotherapy is widely used in modern medicine to treat myopia in adults. These methods include: electrophoresis, phonophoresis, electrical stimulation, as well as special glasses that massage the eye area. During physiotherapy, the duration of exposure lasts about 7-15 minutes. The full course of treatment is usually 10 procedures. To achieve the desired effect, it is important to undergo treatment systematically. The course is selected individually, in accordance with the characteristics of the patient’s visual system.
Surgical treatment of adult myopia
Surgical intervention for myopia is indicated for severe cases of the disease and its tendency to progress. In addition, this method is used by patients who, for some reason, do not want or cannot constantly use correction means. In most cases, modern surgical methods for treating progressive myopia guarantee a successful result: preventing further decline in visual function and returning clear vision without the need for correction. There are two types of eye surgeries: refractive and sclero-strengthening. In the first case, the purpose of the intervention is to correct the optical functions of the eye, in the second - the introduction of a substance into the back of the eyeball (it blocks the process of its further expansion).
Often in surgery, lens extraction, keratophakia, keratotomy, keratomileusis, etc. are practiced. In some modern clinics, innovative technologies are used that make it possible to successfully treat even a high degree of myopia.
Recovery after surgery and possible complications
It is important to understand that after any type of operation a rehabilitation period is required, which lasts about one month and involves compliance with a number of rules.
Experts recommend in the postoperative period:
- Do not rub your eyes with your hands or expose them to other mechanical influences;
- Avoid drinking alcohol;
- Refuse to visit the swimming pool, sauna and bathhouse;
- Wear sunglasses, especially if it is sunny outside;
- Avoid staying in very dusty rooms;
- Minimize the load on the visual system - do not use gadgets for a long time, work at the computer, read, etc.;
- Wash only with warm boiled water;
- Avoid physical activity;
- Women should not wear eye makeup.
If the doctor’s instructions are not followed, the patient runs the risk of causing complications in the form of inflammation, scarring, irritation, dryness, and relapse of pathology. If complications and pain occur after surgery, you should immediately contact the specialist who performs the surgery.
Treatment of myopia with laser
This is the most common way to combat myopia, which is not prescribed for children, but is suitable for adults. This correction involves exposure of the cornea area to a laser beam in order to partially change its shape. This allows you to normalize focusing and restore clarity of vision without glasses or lenses. The technique has a number of advantages, such as speed and painlessness, the absence of preparatory measures, a quick rehabilitation period, etc. Treatment of progressive myopia with laser is quite effective. The most popular methods are LASIK, Super-LASIK and Femto-LASIK. They have proven their effectiveness and are actively used today.
What is myopia?
A vision pathology in which a person has difficulty distinguishing objects at long distances and well near them is called myopia. With it, the eye focuses light rays from distant objects in front of the retina. Myopia can be axial, when the eyeball is elongated, or refractive - when the refractive power of the eyes is too high. Often these two types are combined.
Myopia usually develops in childhood due to a genetic predisposition or due to too much visual stress. Most often, this disease appears in younger schoolchildren from the age of six to seven, when the child begins to experience increased stress on the eyes during the learning process. It is progressive in nature. At this time, the entire child’s body is actively growing, including the organs of vision. Sometimes it is growth that causes the development of the anteroposterior axis of the eyeball to be accompanied by disturbances, for example, stretching of the retina, which leads to its rupture or detachment. In childhood, if a child has myopia, it is very important to correct it correctly and choose the appropriate method for this.
Refractive surgeries
Such radical treatment methods involve correction of the optical functions of the visual organs. These include:
- Keratotomy (small knife cuts are made on the cornea that do not reach the optical zone). The method is used for mild and moderate myopia.
- Keratomileusis (a layer of corneal tissue is removed). The operation is indicated for persons with a high degree of myopia.
- Extraction of a transparent lens (the native lens is removed and an artificial one is installed in its place). Intervention is advisable for dioptre readings from -12.
Phakic intraocular lenses are another modern treatment method. Unlike conventional contact optics, such products are installed inside the eye rather than outside. The method of correcting refractive errors in the area of the posterior wall of the cornea relieves a person from visual discomfort and the need to use additional correction means, however, the method is relevant provided that the disease does not progress (otherwise the operation will have to be repeated to enhance the optical properties).
Sclera-strengthening injections for myopia
This is another modern solution. The method does not involve direct surgical intervention. A foaming polymer material is introduced into the posterior outer part of the eye, which takes the form of an elastic gel on the scleral surface and subsequently serves as a kind of frame for the formation of new connective tissue, as well as an element that stimulates collagen formation. Foam material tends to dissolve over time. Myopia, when such treatment is applied, stabilizes. A sclera-strengthening injection is given to people with progressive myopia. This method is most often indicated for adults, but in case of urgent need, manipulation is carried out in childhood and adolescence.
Methods for correcting myopia
Effective methods for correcting myopia are contact lenses and spectacle optics. With their help, you can restore clarity of vision and get rid of discomfort. If the symptoms of the pathology are mild (with a weak degree of myopia), special optics are worn as needed. Permanent correction is required for refractive errors of more than 3 diopters (moderate). Modern soft contact lenses are safe and have a number of advantages. Unlike glasses, they do not restrict the user’s movements, since they form a single optical system with the eye. These optical products do not narrow your horizons or peripheral vision. Their regular use helps stop the progression of myopia.
Another method of treating myopia is orthokeratology, which involves wearing rigid gas-permeable lenses that change the shape of the cornea. They are used during sleep, and upon awakening, after 6-8 hours, the products are removed. After application, the cornea takes the correct shape and retains it for some time, which significantly improves a person’s vision without the need to use other corrective agents. Night lenses are effective in correcting high myopia.
Classification of myopia
In ophthalmology, progressive myopia is divided into several types depending on its inherent characteristics. For example, in terms of the degree of visual impairment, it can be:
- weak, with reduction rates ranging from 1 to 3 diopters;
- medium – visual acuity decreases by 3-6 diopters;
- high, with a decrease in visual acuity by more than 6 diopters.
Depending on the causes of the development of pathology, myopia is divided into the following types:
- axial - the disease is characterized by deformation of the eyeball with preservation of the anatomy and physiology of the eye structures responsible for refraction, that is, the cornea, vitreous body and lens;
- refractive - pathology can develop against the background of the normal shape of the eyeball, and a violation of the refractive abilities of the visual organs occurs due to pathologies of the optics of the eye, that is, the cornea, vitreous body or lens, and sometimes all of these elements;
- mixed, when the cause of myopia is refractive and axial changes.
Subtypes of progressive myopia are divided into separate groups
, the appearance of which is caused by specific or nonspecific, systemic or localized diseases:
- congenital, arising from a genetic tendency to loss of visual acuity;
- false, in which refraction is disrupted by overly tense muscles of accommodation;
- transient, which develops due to insufficient blood supply to the eye due to diabetes or the use of medications;
- nocturnal, developing with an acute lack of lighting;
- complicated, accompanied by other eye pathologies.
Good to know! Myopia can progress quite quickly. In medicine, there have been cases where a decrease in vision by 10-20 diopters could occur in less than a month. This form is practically impossible to correct.
What happens if myopia is not treated and corrected?
Myopia should be treated as early as possible, since as it progresses, visual acuity will decrease. If glasses or contacts are not used for myopia, its gradual development can lead to other ophthalmological pathologies and serious impairment of vision. Modern methods of treating myopia make it possible to stop even difficult cases of progressive myopia. However, success always depends on how timely the person sought help and received proper treatment. The recovery process (even with new treatment methods) is significantly complicated if the patient develops complications from the retina and other intraocular structures.
Indications and contraindications for surgery to correct myopia
Eye surgery is usually prescribed for people whose vision decreases by 1 diopter per year. Ophthalmologists warn that this phenomenon is dangerous due to the complete loss of visual ability. If, after a comprehensive eye examination and correction of myopia with glasses or lenses, vision stops falling, the patient has the right to decide independently whether he needs surgery. Age may be a determining factor here. Many young people with an active lifestyle play sports, travel, etc., so they want nothing to interfere with them. That is why they decide to undergo surgery to correct myopia, despite the lack of indications.
The key factor that will influence the possibility of carrying out the procedure for correcting acquired myopia is the absence of contraindications.
Doctors include the following as the main reasons for refusal to perform surgery (contraindications):
- Cataract;
- Strabismus;
- Amblyopia;
- Endocrine pathologies;
- Retinal detachment;
- Autoimmune diseases.
In addition, surgery to correct myopia is not performed on pregnant and lactating women, as they experience hormonal changes in their bodies. The procedure is also undesirable for children under 18 years of age. At the same time, ophthalmologists note that some contraindications can be considered relative. For example, after treatment of an endocrine disease, eye surgery can be performed.