Canaliculitis is inflammation of the tear duct. This is an ophthalmic pathology that involves the lacrimal canaliculi, a physiological structure that produces and drains tear fluid. Most often it develops against the background of other pathologies of infectious etiology and can occur in acute or chronic form. Middle-aged and elderly people are most susceptible to it. Patients with chronic eye infections caused by chlamydia (so-called trachoma) are susceptible to it: it is detected in 70% of cases. You can undergo diagnosis and treatment of inflammation of the lacrimal duct in Moscow at the ophthalmology department of Professor Eskina. We have a unique set of diagnostic and surgical equipment that allows our specialists to identify the problem in the early stages and successfully carry out treatment in advanced stages.
What is dacryocystitis
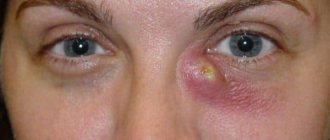
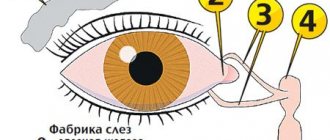
Dacryocystitis is a severe inflammation of the lacrimal sac, which is located between the nose and the inner corner of the eyes. Most often, this pathological phenomenon is observed when the duct is blocked . In this case, tear fluid is not removed from the eye through the nose and pathogenic bacteria begin to actively multiply in the lacrimal sac. The disease can be acute or chronic. This problem can be caused by obstruction of the duct, any eye diseases or infections.
The tear duct often becomes inflamed in newborn babies. Ophthalmologists identify this disease as a separate term – dacryocystitis of newborns. This is caused by underdevelopment of the ducts or a strong gelatinous film covering the channels, which must break at birth. This leads to the development of infection with all the ensuing consequences.
Inflammation of the tear duct can recur several times in a row. For many children, the problem resolves on its own when they grow up a little. But there are also children whose illness is extremely severe, and they cannot do without medical care.
Treatment for inflammation of the tear duct
What to do if the tear duct is blocked? The disease is treated with medications, massage and folk remedies. In severe cases, surgery is performed.
Medicines
For the treatment of dacryocystitis, drugs are prescribed for both oral and topical use.
Levomycetin - eye drops
| Group of drugs | Action | Examples |
| Antibiotics | Destroy pathogenic microflora in the body, fight bacteria | Ampicillin, Oxacillin |
| Eye drops | Suppress the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms | Sulfacyl sodium, Levomycetin, Gentamicin |
| Antiseptics | Disinfect, prevent suppuration and decomposition of tissues at the site of inflammation | Furacilin, Dioxidine, Chlorhexidine |
| Ointments | Have a local antibacterial effect, prevent the growth of bacteria | Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Floxal |
| Immunomodulators | Stimulate the immune system to actively protect the body | Tsitovir-3, Arbidol, Dibazol |
Important! If improvement does not occur within 3 days, the prescribed medications are not effective - inform your doctor.
Massage serves as a preventive procedure against eye diseases
Treatment of inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct only with pharmaceutical drugs has been found to be ineffective: along with taking medications, it is necessary to regularly massage in order to clear the lacrimal sac from accumulated pus as quickly as possible.
How to treat with folk remedies?
Treatment of obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct with folk recipes at home is permissible in combination with pharmaceutical drugs, provided there is no hypersensitivity to the components.
The most effective folk remedies:
- Aloe. Dilute fresh aloe juice with cold boiled water in a 1:1 ratio and drop it into your eyes 4-5 times a day.
- Kalanchoe. Squeeze out fresh Kalanchoe juice and place 2 drops in each nostril while lying down. To administer to a child, dilute the juice in equal proportions with boiled water. Kalanchoe causes sneezing, during which the tear duct is naturally cleared of pus. Do the procedure once a day.
- Chamomile. Brew 3 tbsp. l. dried chamomile flowers in 1 liter of boiling water, let it brew for 1 hour. Soak a cotton pad in the infusion and apply to the sore eye. The lotion should be warm, not hot. Keep the compress until it cools completely. It is recommended to apply chamomile lotions 2 times a day until recovery.
- Thyme. Brew 1 tsp. dry thyme in 200 ml of boiling water, strain after 30 minutes. Rinse your eyes with warm infusion of thyme 2 times a day.
- Tea. Make a very strong brew of black tea and use it to wash your eyes and remove pus from them at least 4 times a day.
- Propolis. Take 30 drops of propolis aqueous extract orally 3 times a day. Propolis is a natural antibiotic, strengthens the immune system and relieves inflammation from the inside.
Propolis extract serves as a natural antibiotic against inflammation
Make compresses and rinses not only for an eye clogged with pus, but also for a healthy one - this way you can protect the healthy eye from inflammation.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is carried out when the therapeutic effect from the use of medications and massage does not occur. In adults, the process takes place under local anesthesia, in children - with general anesthesia.
Types of operations for dacryocystitis:
- Probing – cleaning the canal using a thin rod. During the probing process, adhesions and films formed as a result of inflammation are removed.
- Bougienage is the expansion of a canal that was narrow from birth or spasmodic.
- Dacryocystorhinostomy is the creation of a passage for fluid from the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity. During the operation, the lacrimal sac is thoroughly washed and the pus that has accumulated in it is removed.
- Dacryocystectomy - removal of the lacrimal sac through an incision in the skin.
Expansion of the tear duct
Massage for tear duct obstruction
Massage is done to remove pus from the lacrimal sac. The procedure is an integral part of the treatment of dacryocystitis in children. Massage is effective in the initial stages of the disease.
Do not massage with long fingernails - they can injure the eyes and mucous membranes.
Technique:
- Wash your hands thoroughly and treat them with antiseptic.
- Using a clean cotton swab soaked in furatsilin, clean the eye from accumulated pus.
- Feel the lacrimal sac: it is located below the inner corner of the eye. Place your finger on the lacrimal sac and massage it with slight pressure for 10 seconds, first clockwise, then counterclockwise.
- Finger on the lacrimal sac. Make 5-7 jerky upward movements with slight pressure, squeezing the pus inside upward.
- Repeat the same movements in the downward direction.
- Place your finger on the bridge of your nose at the inner corner of your eye. Using massaging movements with pressure, move your finger from the bridge of the nose to the corner of the eye, repeat 5-7 times.
- During the massage, pus will be separated from the lacrimal canal - upon completion of the massage, remove it from the eye using a cotton swab soaked in furatsilin.
Perform the massage in strict order. Frequency of execution – 5 times a day. Children are recommended to massage the lacrimal sac before feedings.
Important! You cannot massage if dacryocystitis is advanced - this can lead to the development of inflammation of the orbit or eyeball.
Classification
Inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct can be acute or chronic. In the latter case, periods of exacerbation and remission of the disease alternate. In adults, this condition is often observed with swelling of the nasal mucosa. Because of this, fluid accumulates in the lacrimal sac and pathogenic bacteria begin to actively multiply. If the inflammation continues for too long, then pus begins to accumulate in the cavity.
If treatment is not carried out, the pathological process can affect healthy tissue. If pus enters the circulatory system, it can be life-threatening. Sometimes so much pus accumulates that it thins the skin and breaks out on its own. After severe inflammation, the mucous membrane of the lacrimal sac becomes covered with a number of adhesions, which increases the chances of a re-exacerbation of the disease.
Causes
There are many causes of dacryocystitis in children and adults. But in some cases, doctors cannot determine what caused this disease. The cause of inflammation may be:
- Congenital anomaly of the duct development - narrow or too tortuous tear ducts.
- Injuries of various types.
- Damage to the nasal cavity caused by syphilis.
- Sinusitis.
- Blepharitis and keratitis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Pneumonia.
- Children's infectious diseases - measles, rubella, mumps and chickenpox.
- Tumors of various types.
Frequent stressful situations can provoke inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct. It’s not for nothing that people say that all diseases are caused by nerves.
The cause of blockage and subsequent inflammation of the duct can be a foreign body that gets into the lacrimal duct.
Etiology of canaliculitis of the lacrimal duct
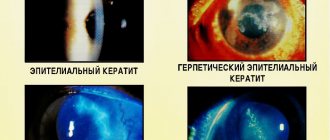
Depending on the pathogen, inflammation of the lacrimal canal of the eye can have a bacterial, fungal or viral etiology.
| Etiology | Pathogen | Diseases that provoke development |
| Bacterial | Streptococci |
|
| Staphylococcus |
| |
| Treponema pallidum | Syphilis | |
| Koch stick | Tuberculosis | |
| Escherichia coli |
| |
| Viral | Herpes viruses: simplex, varicella, cytomegalovirus |
|
| Adenovirus |
| |
| Mushrooms | Candida | Candidiasis |
| Actinomycetes | Actinomycosis | |
| Aspergellus | Aspergillosis |
Penetration of pathogens into the lacrimal canaliculi occurs through the conjunctival membrane, eyelids, lacrimal sac or nasolacrimal canal. Infection is possible if:
- the patient does not comply with the rules of personal hygiene,
- there are microdamages to the ocular structures;
- a foreign body has entered the eye.
Symptoms
Dacryocystitis occurs with a number of characteristic symptoms, regardless of the form of the disease.
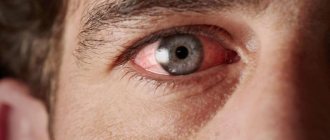
- there is swelling and severe redness in the inner corner of the eye;
- there is pain in the area of the inner corner, which intensifies when touched by hand;
- purulent discharge appears;
- one eye is swollen and wet. Upon examination, you can see that there is always a tear in it;
- Only one visual organ is affected. Bilateral dacryocystitis is extremely rare.
The disease may be accompanied by a number of other symptoms. In severe cases, general intoxication of the body is observed. There may be weakness, fever and loss of appetite.
Clinical manifestations of lacrimal duct inflammation in adults
Based on the clinical picture, acute and chronic canaliculitis are distinguished. Due to the variety of medications that can cure the first, the second is extremely rare.
| Form | Clinical manifestations |
| Acute |
|
| Chronic |
|
Diagnostics
Dacryocystitis is diagnosed based on examination of the patient and a series of examinations. An experienced doctor only needs one look at the patient to understand what exactly triggered the disease. Typically, the following research methods are used:
- test with neutral dyes;
- probing to clarify the patency of the lacrimal canals;
- bacterial culture of discharge from the eyes.
In addition, the patient is given a referral for a blood test. Based on the results of this analysis, the doctor can determine how severe the inflammation is in the body.
How to treat dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is treated mainly comprehensively. The treatment regimen is determined by the doctor, based on the results of studies and tests. Adults and children are prescribed antiseptic solutions for washing the canals and antibacterial drugs that prevent the spread of infection. Newborn babies are prescribed a course of special massage that normalizes the patency of the tear ducts.
Drugs
For dacryocystitis, eye drops and ointments with an antibacterial effect must be prescribed. The following medications are most often prescribed:
- Levomycetin drops. The active substance of this drug has a detrimental effect on a number of pathogenic microorganisms. Thanks to these inexpensive eye drops, it is possible to quickly eliminate conjunctivitis and other infections of the visual organs.
- Phloxal. This drug is often prescribed to newborns diagnosed with dacryocystitis and other eye infections. The medicinal solution is dripped into the eyes several times a day, after which the tear duct is gently massaged.
- Tobrex. A powerful antibiotic that is active against many pathogens. Tobrex can be prescribed to treat adults and children.
For dacryocystitis, various ointments can be prescribed. Such drugs have a viscous structure and remain on the eye mucosa longer. The doctor may prescribe Levomycetin or Tetracycline ointment. Floxal and Tobrex ointment helps a lot. Medicines are placed 1 cm behind the lower eyelid. 2-3 eye treatments are required per day. After the procedure, close the eyelids and actively move the eyeball so that the medicine spreads evenly.
Before using eye drops and ointments, the mucous membrane is washed. To do this, you can use a solution of Furacilin, Miramistin or a weak solution of boric acid. Eye rinsing is carried out several times a day. For each eye, take a separate cotton pad, pre-moistened in a warm solution.
The eyes should be wiped from the outer corner to the inner. This will help prevent the infection from spreading to surrounding tissue.
Massage
Newborn babies with dacryocystitis must be prescribed an eye massage. Thanks to such procedures, the gelatin film is broken and patency in the canal is restored.
Diagnosis of canaliculitis
Diagnostic studies involve palpation of the tubule, which makes it possible to identify its density, pain, and exudate. Carrying out a canalicular test to determine the patency of the duct gives ambiguous results: either negative or positive.
Bacterial culture helps to accurately determine the etiology. Thanks to it, the ophthalmologist is able to determine the type of pathogenic microorganisms that provoked the disease. Transillumination of the eye tissues with a transmitted light source (diaphanoscopy) reveals dark areas.
The pathology must be differentiated from papillomatosis. To do this, radiography is performed using contrast enhancement. If there is canaliculitis, the lacrimal canaliculus is unevenly dilated, and if papillomatosis is present, it is filled.
Possible consequences
If dacryocystitis is not treated, it can lead to serious consequences. The most commonly observed complications are:
- constant watery eyes;
- spread of infection to healthy tissue. This can lead to orbital cellulitis, sinus thrombosis, meningitis or general blood poisoning;
- chronic inflammation of the tear ducts;
- atony of the lacrimal ducts.
The infection can quickly spread to the ENT organs. The consequence of this may be sinusitis, otitis media and other infectious diseases.
Dacryocystitis is often observed in weak and premature babies. But such a disease can also occur in adults as a complication of various infectious diseases.