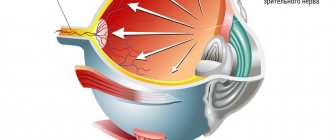
Glaucoma, like cataracts, is one of the most common ophthalmological diseases. There are at least 66 million patients with this diagnosis worldwide, and this number is growing. Glaucoma is extremely dangerous - it causes blindness, and irreversible, since the ganglion cells of the retina die.
Non-penetrating deep sclerectomy (NPDS) is an operation performed to treat glaucoma and normalize intraocular pressure. It ensures the achievement of a lasting clinical effect and normalization of fluid outflow for a long time. Non-penetrating deep sclerectomy can prevent the possible threat of vision loss - the operation saves patients from disability by eliminating visual field defects and pathology in the optic disc caused by glaucoma.
Advantages of non-penetrating deep sclerectomy:
- painlessness: non-penetrating deep sclerectomy does not cause serious discomfort and is well tolerated by patients even with a low pain threshold;
- targeted impact: the integrity of the eye organ is not violated - only pathological areas are affected;
- rapid restoration of vision: within a few days, the ability to work and the ability to take care of oneself at home are restored;
- absence of significant complications: hypotension and other dangerous conditions typical for microsurgical manipulations;
- performing non-penetrating deep sclerectomy under local anesthesia: this eliminates the need for complex and lengthy preoperative preparation;
- no hospitalization required in the Ophthalmic Surgery hospital - after the operation, the patient can leave the clinic, continuing observation on an outpatient basis.
- quick rehabilitation: usually it does not exceed 2 days.
The essence of the method
The essence of non-penetrating deep sclerectomy is to create a path for the outflow of intraocular fluid. That is, the goal is to normalize the natural process of fluid exchange, without stress for the organ itself and adjacent tissues. The balance is restored slowly, the intraocular pressure gradually stabilizes - normally it is 10-22 mmHg, and this norm is achieved within the first week.
The outflow of intraocular fluid is restored due to partial removal of the scleral flap. The area up to the circular ligament is affected, which eliminates penetrating effects and injury to the ocular apparatus.
Kinds
The most common technique for the surgical treatment of glaucoma was the technique of Svyatoslav Fedorov and his colleague S.I. Kozlova - non-penetrating deep sclerectomy .
Its essence is to restore the natural mechanisms of tissue filtration by creating an additional pathway for the outflow of intraocular fluid.
Since 1989, the method has been successfully used to treat patients with glaucoma. At first, microsurgical instruments were used for operations, and now a laser beam . Its use made this technique as safe and effective as possible.
Therefore, such surgical intervention has become quite popular among ophthalmologists.
Advantages of laser sclerectomy:
- preservation of natural mechanisms for regulating intraocular pressure;
- the intervention is painless, patients feel only mild discomfort;
- microinvasive technology (without traumatizing the tissues of the eyeball);
- simplicity of preoperative preparation (ophthalmoscopy, measurement of intraocular pressure, refractometry, general blood and urine tests, ECG, consultations with a therapist, cardiologist, anesthesiologist);
- smooth recovery of IOP, without a sharp decrease;
- The duration of the procedure is about 30-40 minutes, it can be easily combined with drainage and installation of bioimplants to improve tissue healing processes;
- patients do not require hospitalization or long-term bed rest (the operation is performed within one day);
- rapid recovery and rehabilitation of patients (1-2 days);
- minimum restrictions on maintaining a normal lifestyle;
- more persistent hypotensive effect compared to other surgical interventions;
- low risk of complications (hemorrhages, retinal detachment);
- a small list of contraindications (severe illnesses of the body).
The surgical technique is quite complex to perform, but in the hands of an experienced microsurgeon it is safe and effective. It is performed under local anesthesia. with a laser scalpel and a thin segment of the sclera is removed, which makes it possible to form a natural drainage system for the affected eye and normalize the outflow of fluid from it. Thus, IOP is restored.
In the postoperative period, patients may experience discomfort:
- increased lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- tingling sensations, sand in the eyes, burning and itching;
- moderate redness of the conjunctiva.
If symptoms do not disappear within the first few days, you must make an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
Preparing for surgery
The first step is for the patient to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist. The doctor will prescribe a comprehensive examination, taking into account the degree of progression of glaucoma and the general condition of the eye system. Before the operation, the following are required: ophthalmoscopy, refractometry, tonometry. Gonioscopy is prescribed to determine the location of glaucoma (main pathological areas). Other studies are indicated and at the discretion of the ophthalmologist.
Before non-penetrating deep sclerectomy, it is necessary to avoid alcohol intake for at least 3-6 days. If there are inflammatory, infectious, bacterial diseases, the first step is therapy with specific medications.
On the day of surgery, it is necessary to exclude physical and emotional stress. The patient should arrive at the clinic in a good mood.
How is non-penetrating deep sclerectomy performed?
Non-penetrating deep sclerectomy is performed for all forms of open-angle glaucoma. The technique of this operation does not involve opening the anterior chamber of the eye, so the surgical procedure is minimally invasive.
The outflow of intraocular fluid is restored through the trabecular apparatus. To restore the movement of the liquid substance, Descemet's membrane is exposed, and the outer walls adjacent to Schlemm's canal are removed.
Stages of the operation:
- use of local anesthesia;
- fixing the position of the eyelids;
- surgical incision of the conjunctival membrane of the eye;
- detachment of the conjunctival membrane in the upper segment;
- formation of two flaps;
- partial excision of Schlemm's canal and outer wall;
- suturing the surgical incision;
- applying an aseptic bandage to the eyes.
The duration of eye sclerectomy does not exceed 40 minutes. After surgical treatment, the ophthalmologist talks with the patient, gives recommendations and discharges him home. It is necessary to return for an appointment within a week after surgery. The doctor will measure intraocular pressure and evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment, and, if necessary, prescribe maintenance drug therapy to prevent the risk of relapse of glaucoma.
Technique
Non-penetrating deep sclerectomy allows you to gradually restore the physiological volume and balance of aqueous humor. In this case, the anterior chamber is not opened by the surgeon, and the fluid accumulated in it gradually flows out through the trabecular apparatus. Its filtration capacity is enhanced by resection of the outer part of Schlemm's canal and exposure of the surface of the descement membrane.
In order to normalize ophthalmotonus, the limbal edge of Descemet's membrane is released using instruments.
The superficial scleral and conjunctival flaps are then closed with nylon sutures. The doctor administers antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs under the conjunctiva.
The neovascular form of the disease is considered an absolute contraindication to non-penetrating sclerectomy, since in this case a fibrovascular membrane forms above the angle of the iris of the cornea, which makes filtering through the decementum membrane impossible.
Removal of the underlying scleral flap results in an empty scleral space known as a "decompression space" where fluid accumulates before it is drained.
NGSE lasts 30-40 minutes and is often combined with implantation of collagen drainages. It prevents tissue scarring and thereby increases the effectiveness of the intervention. This implant is a cross-linked, collagenous, biocompatible material made primarily from porcine scleral tissue.
NGSE is often carried out using various laser beams: excimer, YAG, argon. This method does not violate the integrity of the eyeball. By operating in fast, ultra-short pulse mode, damage to surrounding tissue can be avoided. Another advantage of the CO 2 laser is its hemostatic effect. Because the CO 2 laser energy is absorbed when exposed to an aqueous environment, controlled dissection of scleral tissue is achieved with less risk of perforation.
Goniopuncture is considered an additional procedure for antiglaucomatous surgery.
Rehabilitation
After non-penetrating deep sclerectomy, it is necessary to follow a postoperative anti-inflammatory therapy regimen. A regimen with limited physical activity and limited visual stress for a week is recommended in order to prevent possible overstrain and achieve a maximum reduction in intraocular pressure.
During the recovery period, you should take antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs - they are prescribed by the doctor individually (these can be non-steroidal or steroid drugs).
Typically, the rehabilitation period is easy, without complications and does not require significant effort from the patient.
Advantages
The intervention is carried out without violating the integrity of the organ, which minimizes the percentage of infectious contamination. This technique is low-traumatic, since its second stage is performed using laser energy.
The patient does not require preliminary hospitalization in a hospital. Microsurgical manipulation is performed in an outpatient setting, and after it is performed there is no need to remain in bed.
After the procedure, all patients receive corticosteroid drops (prednisolone acetate 1%) for at least 6 weeks. During observation, ophthalmotonus and visual acuity are measured. The presence of a filtration cushion and early complications, as well as the need for drug therapy, are determined.
Using this technology, it is possible to achieve a stable reduction in intraocular pressure even in situations where antiglaucomatous manipulations and drug administration do not provide the necessary hypotensive effect. The average rehabilitation period in most cases is one or two days. A person sometimes experiences slight discomfort and pain in the operated eye, and a sensation of a small foreign body. But the unpleasant symptoms pass quickly enough.
After this, the doctor does not place restrictions on the patient’s usual lifestyle. The value lies in the fact that after a few days the operated person is able to take care of himself in everyday life and even start working.
| During sclerectomy, the patient does not feel pain; slight discomfort is possible. |
To increase efficiency, a collagen implant saturated with cytokines is used (for example, the drug “Superlymph”).
After the procedure, regular examinations and examinations by an ophthalmologist are necessary (on average, once every three months). Standard automated perimetry is performed every 6 months.
An important feature of the technology is that it eliminates the severe hypotension that occurs after trabeculectomy by improving the process of outflow from the anterior chamber into the subconjunctival space without perforating the organ.
Non-penetrating deep sclerectomy at the Ophthalmic Surgery Center ON CLINIC
The Ophthalmic Surgery Center ON CLINIC successfully uses the method of non-penetrating deep sclerectomy to treat glaucoma and normalize intraocular pressure. Surgical operations are performed by experienced ophthalmologist-surgeons, doctors of the highest category, candidates and doctors of science. The excellent equipment of the Ophthalmic Surgery Center allows doctors to conduct a wide range of preoperative examinations, obtain reliable diagnostic data and monitor the clinical situation using high-precision research methods.
Operating equipment with expert class ophthalmological multisystems. This allows treatment of any complexity, ensuring the achievement of the desired clinical result.
If you or your loved ones have glaucoma or there are signs of its development, make an appointment with the specialists of the Ophthalmic Surgery Center! Doctors pay special attention to your health, taking all measures to relieve dangerous syndromes, reduce the risk of glaucomocyctic crisis and preserve vision!
Trust your vision to professionals - contact experienced doctors at ON CLINIC!
Glaucoma surgery prices
The cost of non-penetrating deep sclerectomy in our ophthalmology center starts from 30,00 rubles (for one eye) and depends on the surgical technique, as well as the use of drainage. You can find the entire list of prices for the treatment of glaucoma and other eye diseases in the PRICES section.
Microsurgical technique, the name of which is included in the title, refers to methods of treating glaucoma, and to understand the essence of this operation it is necessary to remember what we know about the disease itself.
The most common and, in principle, correct answer that can be heard to the question “What is glaucoma?” sounds something like this: “It’s pressure in the eye.” Indeed, glaucoma is a condition of chronically increased pressure of intraocular fluids, caused by their excessive secretion, violations of the natural drainage system of the eye, or a combination of these main reasons. In fact, this is not one disease, but a whole group of pathological conditions that differ in origin (congenital or acquired, i.e. primary or secondary glaucoma), anatomical features (open-angle or more rare closed-angle), course, prognosis, etc. Among the clinical variants of glaucoma, there is even such a seemingly paradoxical form as normotensive glaucoma, in which specific glaucomatous symptoms develop with relatively normal intraocular pressure (IOP).
One way or another, over time, disturbances in the natural hydrodynamics of the eye lead to degenerative changes in various intraocular tissues; The most dangerous is degeneration of the retina and optic nerve head, since this process leads to a progressive and irreversible decrease in visual function. According to statistics, today glaucoma is the second, after cataract, cause of acquired blindness in the world. As for the total number of people suffering from this disease, various sources provide estimates from 60 to 100 million people (at the same time, in developing countries the epidemiological situation with glaucoma is much worse than in developed countries). Most patients are mature and elderly people, although congenital and early, in particular, juvenile (adolescent) forms are also not unique. It should be noted, finally, that almost all serious medical and statistical studies reveal a significant trend towards an increase in the incidence of glaucoma.