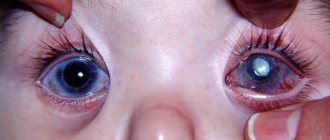
Surgery to correct strabismus is possible at any age. It is designed to correct an imbalance in the motor activity of the six eye muscles that control the position of the central axis of the eye. During treatment, the surgeon weakens or strengthens certain muscles, which leads to correction of the position of the pupil in a stationary position and when it moves, when the gaze is transferred from one object to another. The advisability of performing surgery for strabismus in childhood or later is determined by the results of an ophthalmological examination.
Surgery to correct strabismus in children
Surgical treatment of strabismus in children is most effective at the age of 4-5 years. In case of congenital strabismus, which is characterized by a significant angle of deviation of the eye from the normal position, the operation can be performed at an earlier age. However, the best results in restoring bipolar vision are obtained by treatment at an age when the child is able to understand and carry out regular eye exercises during the period of postoperative rehabilitation.
As a rule, surgical treatment for childhood strabismus is performed under general anesthesia. In certain cases, hospitalization is required.
Treatment of epiretinal membrane of the eye
For almost all nosological forms of retinal pathology in the area of the vitreomacular interface, which includes the epiretinal membrane, treatment is carried out mainly surgically. Removal of the retinal membrane is performed through microinvasive vitrectomy followed by removal of the retinal film, which eliminates the manifestations of the disease and restores visual functions.
For epiretinal membrane of the eye, surgery can be performed on any category of patients, however, surgical treatment is performed only in cases where the doctor is confident in the effectiveness and safety of the operation.
Clinical manifestations of the disease may slightly reduce the quality of vision; over time, patients get used to these minor changes, which do not in any way affect the quality of life. That is why each case of epiretinal membrane of the retina requires adequate examination, as well as an assessment of the risks and benefits of the upcoming treatment.
Surgical treatment of strabismus in adults
Most often, surgery for strabismus in adult patients is performed on an outpatient basis “in one day.” Local anesthesia is used. Hospitalization is not required, the patient goes home the same day.
Types of operations for the surgical treatment of strabismus
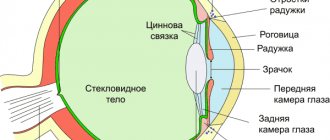
When surgically correcting strabismus, two types of surgical intervention are used: aimed at weakening or strengthening certain extraocular muscles.
If the cause of eyeball displacement is excessive muscle tension, the following surgical techniques may be used:
- recession (cutting off the muscle in the area of attachment and moving it to a point that gives less tension);
- partial myotomy (excision of part of the muscle fibers;
- plastic surgery of the oculomotor muscle aimed at lengthening it.
In situations where strabismus is a consequence of weakness of the extraocular muscles, intervention is carried out aimed at strengthening them:
- resection (shortening the muscle by excision and reconnection);
- tenorrhaphy (shortening of a muscle due to the formation of a fold in the area of the associated tendon);
- anteposition (cutting off a muscle and attaching it to a new place that provides its strengthening).
Most often, strabismus is caused by impaired tone of several extraocular muscles, some of which are weakened, while others are overstrained. Surgical care in this case is combined, including recession and resection. The results of an ophthalmological examination provide a complete picture of the nature of the disorders and allow the surgeon to develop an individual treatment plan for strabismus. The operation in most cases combines measures to weaken some muscles and strengthen others.
It is impossible to accurately predict the functioning of the extraocular muscles after surgery. Sometimes there is residual strabismus. If it cannot be corrected by exercise, repeat surgery is recommended. It is performed after 6-8 months, when the residual strabismus has stabilized.
For the most effective surgical treatment of strabismus, it is necessary to follow a number of rules:
- There is no need to insist on forced treatment of strabismus when gradual correction is recommended. If necessary, surgery on several oculomotor muscles is divided into two or more operations. The combination of multiple simultaneous excisions can lead to an unsatisfactory result.
- If several muscles are corrected simultaneously in one operation, an even combination of weakening and strengthening measures is desirable.
- Surgical intervention on the eye muscle should not completely disrupt its connection with the eyeball.
Procedural and surgical treatment of glaucoma. All the nuances
Here you will find answers to questions:
1. If the drops no longer help. What is surgery for glaucoma? 2. What tests need to be taken before glaucoma surgery and how long do they last? 3. Is it possible to operate on glaucoma in both eyes on the same day? 4. How long does the operation take? 5. How should you behave during glaucoma surgery? 6. How is the operation performed? Under general anesthesia or local anesthesia? 7. Is hospitalization necessary?
Answers your questions:
Bevza Victoria Yurievna
Specialization: Glaucoma, diseases of the optic nerve and central retina Work experience: 26 years
Procedures:
more than 27,000
If the drops no longer help. What is surgery for glaucoma?
At the middle stage of glaucoma, laser treatment is performed. It has many advantages:
- possibility of repeating the procedure (can be done many times on one eye)
- no need to take tests before the procedure
- You can return to work the next day after the procedure.
The 2 most popular laser treatment methods help improve the circulation of intraocular fluid - iridotomy (a through hole is created in the iris) and trabeculoplasty (the permeability of the trabecular network is improved). Laser procedures can reduce intraocular pressure by 3-5 mmHg. The effect lasts from 3 months to 1.5 years.
In later stages of glaucoma, it can be treated with surgery. The essence of the operation is to create a new channel to drain excess intraocular fluid. With the help of a micropuncture, excess fluid leaves the eyeball and is absorbed into the general bloodstream. Such operations are much more effective - they reduce intraocular pressure from any level by 16-18 mmHg, and also help to avoid surges and fluctuations in pressure during the day, the effect lasts for 5-8 years.
In some particularly difficult cases, glaucoma does not respond to the first two treatment options. This may happen due to:
- special anatomical structure of the eye
- concomitant diabetes mellitus, central retinal vein thrombosis
- post-traumatic scars on the eye.
Even in such cases, glaucoma can be stopped by installing a special biocompatible shunt (a tiny hollow tube, only 3 mm long) to drain excess fluid. Similar operations have been carried out since 1993; we can already talk about a large amount of clinical data on them and the extensive experience of specialists in preserving vision in patients with glaucoma.
All types of treatment, from drops to surgical installation of a shunt, have been successfully carried out by specialists from Intervzglyad MC for 21 years. With a diagnosis of glaucoma, our patients maintain good vision for years. The main thing is to contact specialists in time to select the appropriate treatment. The most valuable thing with glaucoma is time. The sooner you get to a competent ophthalmologist, the easier it will be to stop the development of glaucoma.
What tests need to be taken before glaucoma surgery and how long do they last?
- General blood test (14 days)
- Biochemical blood test (Albumin, ALAT, ASAT) (14 days)
- Clotting time, bleeding time (14 days)
- Blood sugar test (14 days)
- Prothrombin index (14 days)
- Blood microreaction to syphilis (3 months)
- Australian antigen HBs-Aq (6 months)
- Antibodies to viral hepatitis C (6 months)
- ELISA for the presence of antibodies to HIV (6 months)
- General urine test (14 days)
- Fluorography (1 year)
- ECG with description (1 month)
- Certificate of oral sanitation (1 month)
- ENT doctor's report (1 month)
- Therapist's report (1 month)
Is it possible to operate on glaucoma on both eyes on the same day?
No, surgical treatment of glaucoma is not performed on both eyes at once.
How long does the operation take?
The entire operation, including anesthesia with special drops, takes about 15 to 30 minutes.
How should you behave during glaucoma surgery?
If necessary, you will be given a mild sedative before surgery to help you relax and not worry. Try not to tense up, do not make sudden movements, do not turn your head, talk only if necessary. If something bothers you, be sure to tell the surgeon about it. The doctor will tell you which direction to look and what to do, and will comment on his actions during the operation.
How is the operation performed? Under general anesthesia or local anesthesia?
The operation is performed under local drip anesthesia. It completely removes all pain, is easily tolerated, and does not put stress on the patient’s organs and blood vessels.
Is hospitalization necessary?
No. Currently, glaucoma surgery is performed as an outpatient procedure. On the day of surgery, the patient spends about 2 hours in the clinic and then returns home.
Possible complications after surgery to correct strabismus
Modern ophthalmic surgery gives very high results in the surgical treatment of strabismus. Only in 10-15% of cases there is a residual slight strabismus. In this case, it is not entirely correct to say that there is a “complication”, since this mild violation does not affect the quality of life and professional activity. If, as a result of the operation, the strabismus remains significant, a repeat operation is possible. Treatment of strabismus affects only the extraocular muscles, so surgical procedures do not pose a risk to vision. Re-intervention is recommended if there is significant residual eyeball obliquity.
One of the possible complications after surgical treatment of strabismus may be infection of the surgical field. However, this problem is easily solved with drops containing antibiotics. These drugs can also be prescribed for prophylactic purposes in the first postoperative days.
In the first hours or days after surgery for strabismus, double vision (diplopia) may be observed. If vision does not return to normal within a few days, additional corrective measures may be required. Fortunately, this complication is extremely rare.
How is eye removal surgery performed?
The operation to remove the eyeball is divided into several stages:
- The decision regarding the inevitable removal of the eye is made by the attending physician based on the results of a comprehensive examination.
- This is followed by the stage of preparing the patient for surgery, which consists of simple actions - following a diet and correctly performing hygiene procedures on the eve of the operating day.
- Eye removal in children is performed under general anesthesia (in the absence of contraindications); adult patients are given local anesthesia.
- After the administration of anesthesia, the patient is placed on the operating table, the eye is opened using an eyelid dilator. Next, the conjunctiva of the eye is dissected and separated, this is done along the perimeter.
- After cutting off the conjunctiva, a special hook is inserted into the orbit and the rectus muscles are cut off. The severed rectus muscles are slightly brought out, after which the oblique muscles and the optic nerve are cut off.
- The eyeball is removed, the bleeding is stopped with a pressure swab soaked in a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
After the operation, an artificial implant made of modern, environmentally friendly and safe for health materials is inserted into the eye socket. It is attached to the remainder of the tendons and muscles, and is covered on top by the conjunctiva. Thanks to the latest materials and modern technologies implemented in our clinic, the artificial eye is almost indistinguishable from the real one, which allows you not to worry about the aesthetic consequences of enucleation.
Removing an eye is a serious procedure that requires an informed decision by the doctor and the consent of the patient. There are the following indications for enucleation:
- Severe pain (intractable) syndrome in the blind eye.
- An exceptional cosmetic necessity.
- Glaucoma at the terminal stage.
- High risk of developing sympathetic ophthalmia.
- Rapidly developing inflammation in complete blindness.
- Severe injuries or complete atrophy of the eyeball.
- Malignant tumors of the eye.
The operation is not performed if there is a high probability of infection or pus entering the brain, or if a general infection is detected.
Postoperative period and rehabilitation
Surgical treatment of strabismus gives an immediate visible result - the position of the eyeballs during the visual process becomes correct (symmetrical). However, eliminating a cosmetic problem does not mean complete normalization of visual functions. Since strabismus leads to significant disturbances in the brain processes of visual perception and image analysis, the patient, as a rule, after surgery will undergo a course of exercises and procedures that help restore binocular vision and three-dimensional perception of the surrounding picture of the world. The main task of postoperative rehabilitation after surgical treatment of strabismus is to “teach” the visual system to function correctly again. Most often in modern ophthalmology, hardware treatment is used for these purposes. An individual course of rehabilitation exercises allows you to expand the fusion reserve and re-include the eye in which the movements of the eyeball were impaired in the work of the visual system. The goal of such a course is to achieve an equivalent perception of the pictures formed on the retina of both eyes, and to merge them in the corresponding structures of the brain into a single image.
The ophthalmological clinic offers patients with strabismus a comprehensive examination and multi-stage treatment, including surgery and rehabilitation, individual programs of conservative care, hardware and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Indications for removal
If you experience complications during or after implant treatment, then you should not panic right away - in many cases, the implant can be saved, but it is important not to waste time. Symptoms, after which you should immediately consult a doctor, as a rule, make themselves known very clearly. Most often, these are swelling, pain in the implantation area and fever. In most cases, such symptoms are associated with peri-implantitis, an inflammatory disease that affects soft and hard tissues. If the inflammatory process has affected only periodontal tissue, then the situation can be corrected with the help of antibiotics and rinses. In extreme cases, an incision is made in the gum, after which the damaged part is treated. If the inflammatory process has reached the bone, then the situation is much more complicated: when there is still a chance to save the implant, the doctor tries to eliminate the inflammatory process and may perform additional osteoplastic operations. If an x-ray confirms severe destruction of bone tissue and mobility of the implant is observed, then there is only one way out - removing the titanium root from the jaw.