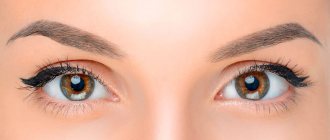
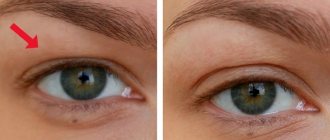
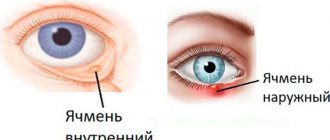
Eyelid ptosis is a drooping of more than 2 mm relative to the edge of the iris. Normally, the fold covers the iris by 1.5 mm or less; if the figure is greater or one eyelid is significantly lower than the second, we speak of pathology. The disease can occur in people of any age.
The asymmetry of the eye sizes is visually noticeable. The defect often causes vision loss. Treatment is aimed at increasing muscle tone.
Ptosis of the lower eyelid is much less common. In the early stages of development of the pathology, swelling and “bags” under the eyes are noticeable. With advanced disease, the edges of the fold are separated from the eyeball, which leads to eversion.
Causes
Correct diagnosis of the causes of ptosis of the upper eyelid allows the doctor to choose an adequate strategy to combat the pathology using therapeutic or surgical methods.
Among the reasons:
- oculomotor nerve palsy;
- weakening of muscles;
- pathology of the autonomic nervous system;
- consequences of operations;
- incorrect therapy with Botox injections;
- diabetes;
- endocrine diseases;
- ophthalmological diseases.
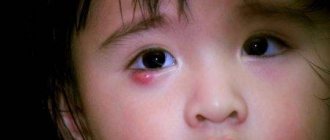
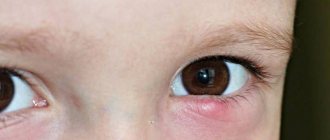
Ptosis in children
In infancy, it is very difficult to notice pathology, since newborn children spend most of their time with their eyes closed. To identify the disease, you need to constantly monitor the baby's facial expression - if he constantly blinks when feeding or the edges of the eyelids are at different levels, parents need to consult an ophthalmologist.
Ptosis of the upper eyelid in a child
In older children, the pathological process can be detected by the following manifestations: when reading or other activities that require visual strain, the child constantly throws back his head, which is associated with a narrowing of the visual field. Sometimes uncontrollable muscle twitching is observed on the affected side, which resembles a nervous tic, and patients with a similar pathology often complain of eye fatigue, headaches and other similar manifestations.
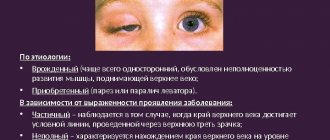
Types of drooping eyelid
Depending on the cause of its appearance, there is the following classification of eyelid ptosis according to its form:
- Aponeurotic – stretching and weakening of muscles, loss of tone. It can occur as a complication after plastic surgery for a facelift, when botulinum toxin is administered by a non-professional specialist and with a violation of technology, or with too frequent and prolonged use of Botox.
- Mechanical – muscle damage after injury, scarring, tumor growth, which, due to its severity, does not allow the eyelid to remain in its normal position.
- Neurogenic is a pathology of the passage of the nerve impulse that controls the muscle. It is necessary to examine the brain to exclude diseases of the central nervous system (meningitis, neuritis, sclerosis).
- Age-related ptosis of the upper eyelid - aging of the body provokes stretching of muscles and ligaments, their weakening.
- False – with anatomical features (large volume of the fold), strabismus, hypotonicity of the eyeball.
There are acquired and congenital ptosis of the upper eyelid.
Classification
Based on the nature of occurrence, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- congenital ptosis.
- acquired ptosis.
Based on the nature of the lesion, the following are distinguished:
- unilateral ptosis;
- bilateral.
Based on the etiology of the pathological process, the following forms are distinguished:
- neurogenic ptosis.
- aponeurotic.
- myogenic.
- mechanical.
- pseudoptosis (false).
Based on the severity of the pathological process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- ptosis of the first degree or partial - the edge of the eyelid covers only the upper part of the pupil;
- ptosis of the second degree (semiptosis of the upper eyelid) - the segment descends to half the pupil;
- ptosis of the third degree or complete - in this case, the upper eyelid covers the entire pupil.
Clinicians note that in most cases the unilateral nature of the development of the pathological process is diagnosed ( in approximately 69% of cases ).
Features of congenital pathology
- In the presence of Horner's syndrome, prolapse is combined with a narrowing of the pupil, decreased sweating on the face, and a deeper location of the eyeball.
- Ptosis occurs in Marcus-Gunn syndrome, when the prolapse disappears when opening the mouth, yawning, and chewing food.
- The defect occurs in Duane syndrome (a form of strabismus), in which the functioning of the nerves responsible for eye movement is impaired.
Isolated ptosis is often inherited. The disease is characterized by abnormalities in the development of the levator tendon. The cause may be congenital myasthenia gravis, cranial nerve palsy.
Symptoms
It should be noted that the congenital form of this disease is quite often combined with other ophthalmological diseases, which is due to the peculiarities of the physiological structure of the organ of vision.
In this case, the clinic of congenital or acquired ptosis is characterized as follows:
- the patient is forced to throw his head back in order to ensure normal vision.
- blinking movements are difficult.
- increased eye fatigue.
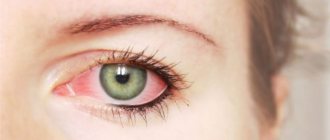
- frequent inflammatory processes.
- irritability of the visual organs.
- decreased visual acuity.
- infection of the organs of vision, which significantly worsens the course of the clinical picture.
Due to the fact that one eye is constantly closed, over time the patient develops amblyopia (deterioration of vision in one eye). The development of other ophthalmological diseases is also not excluded. Since the clinical picture is quite specific, there are no problems with making a diagnosis.
At the first symptoms, you should seek medical help, and not ignore the signs of the pathological process.
Characteristics of acquired ptosis
The problem occurs as a result of trauma, tumors, age-related changes, and stroke, which causes levator (facial nerve) palsy.
A possible complication due to excessive use of botulinum toxin preparations or violation of technology. The muscles paralyzed by Botox do not provide lymph outflow, fluid accumulates, pulls the tissue down - the eyelid droops. This problem can arise due to individual intolerance to the drug and the unprofessionalism of the cosmetologist.
There are several stages of pathology:
- partial ptosis of the upper eyelid (1st degree) – 1/3 of the pupil is closed;
- incomplete ptosis of the upper eyelid (2nd degree) – half to 2/3 of the pupil is closed;
- full (3rd degree) – the pupil is completely closed.
One eyelid or both may be drooping. With the first degree of eyelid ptosis, a person does not feel discomfort. With incomplete and complete prolapse, the following symptoms may be observed:
- difficulty blinking;
- the eye does not close completely - the mucous membrane dries out, irritation appears;
- a burning sensation, as if sand had been poured into the eyes;
- appearance of everted mucosa;
- frequent conjunctivitis;
- headache, eyes.
With advanced pathology, vision is impaired, double vision occurs, and strabismus occurs. With neurological ptosis of the upper eyelid, the eyeball sometimes sinks, and the size of the pupil may change.
Manifestations of the disease
The drooping of one eyelid below the other can be 1- or 2-sided and of varying degrees of severity. People with pathology have to raise their eyebrows, straining the forehead muscle, and tilt their head back. This helps them see the object better with the eye with blepharoptosis. Blinking becomes difficult, which can lead to increased fatigue and irritation of the organ of vision. Pathology creates favorable conditions for infection of the affected eye.
With congenital drooping of one eyelid below the other, amblyopia and strabismus occur, and visual acuity decreases. The acquired disorder occurs with double vision, exo- or enophthalmos, and sensitivity disorder of the cornea.
Diagnostics
To prescribe treatment, it is necessary to determine the root cause of the disease. In the early stages, the prolapse is almost invisible. The doctor determines whether ptosis is congenital or acquired in order to rule out brain diseases. If the patient cannot remember when the problem began, the specialist will prescribe additional tests.
Diagnostic stages:
- inspection, determination of the degree of prolapse;
- checking visual acuity and fields, pressure inside the eye, examining the fundus;
- conducting eye biomicroscopy;
- checking muscle tone and blinking function;
- ultrasound examination, electromyography;
- radiography;
- MRI of the brain;
- testing for binocular vision;
- consultation with a neurosurgeon, endocrinologist, neurologist.
Massage for eyelid ptosis
Acquired or congenital defect requires almost the same treatment. In this case, gymnastics and massage will be the most effective, since there is a direct effect on the muscle layer.
Massage treatment will be effective for both children and older people. The procedure can be carried out not only by a massage therapist, anyone can do it, the main thing is to follow the basic principles. This is the regularity, duration and localization of manual influence.
It is deciphered as follows: massage is carried out daily, the procedure lasts at least 10 minutes, movements are concentrated around both eyes. Stages of massage to eliminate ptosis:
- Preparation - you need to thoroughly wash your hands with soap and check the skin around the eyes for abscesses, irritations, redness or ulcers. If this is not detected, you need to wash and dry your eyes. After this, take a moisturizer and apply a small layer to the eyebrow and a little to the eyelid.
- The beginning of the massage is stroking, moving your index fingers around the eyes. The fingers do not touch the eyelid itself, but pass along the eyebrow. You need to do 5 circles, then blink a little.
- The main part is rubbing, place your index fingers at the point where the eyebrows meet, and move along the eyebrows with symmetrical movements. Movements are made only in one direction, fingers are placed back. Repeat up to 15 times.
- After rubbing, you need to finish the procedure again by stroking.
Advice! Massage can be used for better penetration of the medicine. Therefore, instead of moisturizing cream, you can apply ointments and mixtures prepared at home.
Features of treatment
After finding out the reasons, the doctor selects adequate treatment. When congenital pathology is detected in the early stages, if vision is not impaired, comprehensive prevention is sufficient. To treat ptosis of the upper eyelid, they resort to conservative methods - without surgery - or perform surgical interventions. If the problem occurs after injury or nerve damage, it is recommended to wait 1 year. During this time, proper treatment can restore nerve function without surgery.
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to remove ptosis of the upper eyelid with threads. Non-surgical methods of blepharoplasty with threads give good results for drooping eyelids. Rehabilitation lasts 2 weeks, the results last a long time. The thinnest biocompatible threads create a strong frame and provide support to weakened tissues.
Massage and self-massage
Massage to lift the upper eyelid will also be effective only if performed regularly.
There is no need to devote special time to it; it is enough to carry out the procedure while applying the cream to the area around the eyes.
The idea is to lightly tap the fingers over the upper and lower eyelids. At the top, movements should be from the outer corner to the inner, and at the bottom - vice versa.
What you should know about self-massage of the eyes:
- It is not recommended to rub your eyelids too hard. This will stretch the skin even more, but the procedure will have the opposite effect.
- You can use absolutely any cream , for example, with hyaluronic acid.
- It is necessary to ensure that the cosmetic product does not get into the eyes.
The effect of the massage does not appear immediately. But if you don’t give up, doing it twice a day every day, the result will be a complete opening of the eye, skin rejuvenation and even a slight tightening.
Effective methods for treating facial swelling in the morning, depending on the cause of its appearance. In this publication you can see photos after upper eyelid blepharoplasty by day.
Here https://cosmetolog-expert.ru/plastika-litsa/veki/rekomendatsii-reabilitatsii-posle-blefaro.html you will find out how long rehabilitation lasts after lower blepharoplasty.
Treatment of prolapse after Botox
The drug, which is obtained from botulinum bacteria, is used to disrupt the passage of nerve impulses to the muscles and completely relax them. Inaccurate or incorrect insertion can lead to problems.
Experts recommend waiting until the effect of botulinum toxin wears off. This can take from 2 weeks to six months. To improve the situation and not wait long, therapy is carried out. Elimination of blepharoptosis is performed using physiotherapy: massage, electrophoresis, UHF, microcurrents. The administration of Proserin, vitamin B, and neuroprotectors are also prescribed. This treatment of ptosis of the upper eyelid after Botox promotes rapid resorption of the drug.
Prevention
There are no specific prevention methods for the congenital form of pathology. As for the acquired type of disease, it is advisable to use the following recommendations from clinicians:
- prevention of eye injuries;
- timely and correct treatment of ophthalmological diseases;
- prevention of neurological diseases, as they are one of the causes of this pathological process.
Persons who have a family history of chronic ophthalmological diseases should regularly undergo a preventive examination by a doctor. Self-medication is excluded, as this is fraught with the development of extremely negative consequences.
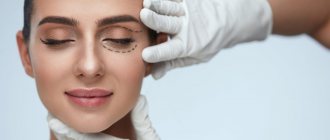
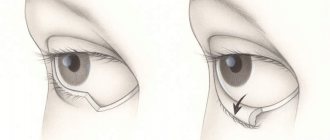
Surgical intervention
Surgery to eliminate prolapse is prescribed at an advanced stage, when the quality of vision is impaired. The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia in an outpatient setting. The procedure involves shortening the relaxed muscle by cutting or removing part of it. The muscle is also folded and stitched. The suture is hidden in a natural fold of the skin; after a while it dissolves, or the suture is removed after 3-5 days. Rehabilitation lasts 1 month, the patient is observed by a surgeon. Surgical treatment has a favorable prognosis - the patient gets rid of the defect for life, the risk of complications is minimal.