Author Peter Deryabin
03/26/2008 09:28 (Updated: 05/04/2020 13:48)
Health » Vision » Prevention
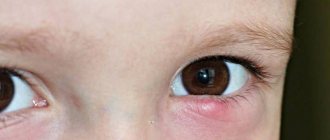
At first it can be confused with nascent barley. A lump appears on the eyelid, which gradually grows and hurts. But this attack is called differently - chalazion. Olga Tsareva, an ophthalmologist of the highest category, told Pravda.Ru what it is and how to deal with it.
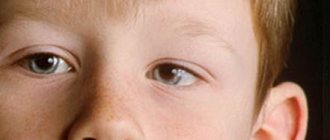
Chalazion removal on the upper eyelid
Signs of pathology
Chalazion of the lower and upper eyelids in people of the adult age group has a number of minor differences. In general, the disease manifests itself with a typical clinical picture, disrupting the functioning of the organ of vision and causing a cosmetic defect.
The development of chalazion is expressed in the following symptoms:
- a small seal forms on the affected eyelid, which looks like a pea;
- as the disease progresses and glandular secretions accumulate in the blocked canal, the volume of benign neoplasm increases;
- the patient feels severe itching in the area of chalazion formation, which sharply changes to acute pain if you try to scratch the affected area of the eyelid;
- there are pronounced signs of an inflammatory process, which manifests itself more acutely in the evening and at night, and in the morning and during the day there is a decrease in the level of pain;
- when a chalazion forms on the surface of the upper eyelid, a benign neoplasm hangs over the general contour of the outer part of the eyeball;
- the chalazion of the lower eyelid has a larger volume on its inner side, which causes compression on the organ of vision;
- the patient has signs of involuntary lacrimation, which is accompanied by stinging and pain;
- the affected eyelid becomes swollen, the epithelial layer turns red, and the mucous membrane of the eyeball acquires signs of inflammation;
- in the case of a decrease in local immunity and the addition of a bacterial infection, an increase in body temperature to subfebrile values is possible - 37°.
In the early stages of development, a chalazion of the upper or lower eyelid appears only externally. As the glandular secretion accumulates in the cavity of the blocked canal, the inflammatory process increases, tears appear, and a sharp pain appears, which is felt especially clearly at the moment of pressing on the benign neoplasm.
The acute form of chalazion may be accompanied by spontaneous opening of the capsule and the release of purulent contents from the side of the conjunctiva of the eye.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of this disease include:
- The appearance of swelling of the eyelid;
- Soon, upon palpation, you can detect a small compaction, as a rule, not particularly painful and sensitive only to the touch;
- The child may complain of burning or itching, which may make him want to rub his eyes;
- The skin over the resulting “pea” is mobile and unchanged, sometimes it can turn red and peel;
- On the inverted eyelid, you can see a limited reddened area of the mucous membrane on the side of inflammation, grayish in the center;
- The formation does not disappear after a few days; on the contrary, it slowly increases in size, forming a noticeable bulge on the eyelid;
- If a bacterial infection occurs, purulent inflammation occurs, the skin over the capsule turns red, the eyelid swells, and pain appears, often throbbing.
Chalazion is often confused with a condition known as stye (folliculitis) due to similar symptoms. In fact, stye is a bacterial (staphylococcal) infection of the hair follicle of the eyelash, therefore, as a rule, it is located at the edge of the eyelids. A chalazion is formed in the thickness of the cartilaginous plate of the eyelid; in some cases it can be seen by turning the eyelid out. Stye is an acute disease, characterized by redness and swelling of the eyelid, sometimes quite severe, as well as pain. The duration of folliculitis is several days, and it can go away on its own, even without treatment.
Causes of chalazion in adults
Chalazion of the upper eyelid in adults develops as a consequence of blockage of the meibomian gland canal.
Such a pathology of the visual organ can occur under the influence of the following factors or concomitant diseases:
- prolonged hypothermia of the body, exposure to drafts, gusty winds;
- decrease in general or local immunity caused by poor nutrition, bad habits, lack of sufficient amounts of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients in the patient’s diet that are necessary for the normal functioning of the organ of vision;
- diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2;
- infection of the conjunctiva of the eye with bacterial microorganisms;
- violation of the rules for using contact lenses, or wearing them too often and for a long time;
- diseases of the endocrine system, the course of which leads to an excess or deficiency of hormones that affect the functioning of the meibomian gland;
- a person’s individual tendency to frequent formations of barley, which ultimately led to blockage of the secretory canal;
- diseases of the digestive system that disrupt metabolism and absorption of food eaten.
In addition to the pathological causes of the development of the disease, there are other factors that relate exclusively to insufficient hygiene. This is untimely removal of makeup from the surface of the eyelids and eyelashes, and the entry of dirt particles into the cavity of the secretory canal.
Types and stages of the disease
Chalazion of the lower and upper eyelid in adults is characterized by sluggish chronic development.
In this regard, doctors distinguish the following stages of the disease:
| Chalazion stage | Characteristics of current symptoms |
| 1st stage | On the surface of the skin of the contour of the upper or lower eyelid, a slight redness forms with the formation of a pea. When palpating the tumor, the patient does not feel pain or any other pathological signs. At the 1st stage of the disease, chalazion is often confused with barley, using anti-inflammatory ointments and dry heat, which do not bring a positive result. |
| 2nd stage | The patient exhibits symptoms of increasing inflammation. The lower or upper eyelid, on which a foreign tumor has formed, turns red and takes on a swollen appearance. During palpation of the chalazion, the patient feels acute pain, which is also accompanied by severe itching. Inflammation of the mucous membrane leads to involuntary release of tears. |
| 3rd stage | A benign neoplasm reaches critical development sizes. The blocked canal becomes filled with excess meibomian gland secretions. The central part of the chalazion acquires a yellowish tint, which is due to the accumulation of purulent contents inside the capsule. The tumor may rupture with the release of serous exudate. |
Timely initiation of treatment allows you to prevent further progress of the disease, preventing it from moving to stage 2 or 3 of development. The severity of a chalazion is determined by the attending physician during a diagnostic examination of the patient.
Features of the upper and lower chalazion
Chalazion of the upper eyelid in adults differs from damage to the lower part of the organ of vision by the specificity of the formation of a benign neoplasm. In the first case, the accumulation of glandular secretions leads to a more uniform filling of the meibomian gland canal.
This is due to the larger area of the upper eyelid. In this case, the tumor hangs over the eyeball, practically not affecting the inner side of the affected eyelid. It is possible that swelling may spread to the entire surface of the upper part of the eye: from its edges to the corners.
The formation of a chalazion of the lower eyelid is distinguished by the fact that the main part of the benign formation is localized on the inner side of its surface.
In this regard, the capsule with glandular secretion seems less voluminous, but its main part is directed towards the eyeball, irritating its mucous membrane, provoking severe pain, increased lacrimation and the development of the inflammatory process. The remaining manifestations of the disease are almost identical and have no distinctive features.
Pathogenesis
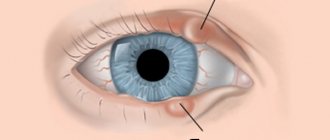
Meibomian glands are located along the edge of the eyelid (from 50 to 70 pieces on one). They provide hydration to the cornea by secreting a special sebaceous secretion. When the duct is blocked, the secretion continues to form, but it is not able to come out and begins to accumulate under the skin. If the blockage of the duct does not resolve on its own, a chalazion will form over time. The size of a chalazion is from millet to a pea.
Immune cells perceive the formation as foreign. The eyelid begins to turn red and swell. There may be redness of the eye and skin of the eyelid. Ophthalmologists distinguish several stages in the development of the disease:
- slight swelling, slight itching, slight swelling;
- the appearance of a dense subcutaneous lump, painful when touched;
- gradual growth of the lump, increasing pain;
- the large size of the chalazion threatens the integrity of the eyeball; surgical intervention is necessary.
Diagnostics
Chalazion of the lower eyelid in adults, like damage to its upper part, is a disease with a chronic course. Therefore, it is very important to perform high-quality diagnostics, establishing not only the presence of blockage of the meibomian gland canal, but also the reasons that caused its pathology.
A patient who comes to the clinic with signs of chalazion undergoes the following stages of examination:
- external examination and palpation of a benign neoplasm, which is performed by an ophthalmologist (the doctor asks questions about the symptoms that bother the patient, the approximate timing of the development of the disease, after what events the formation of the capsule began);
- donation of capillary blood from the ring finger for clinical analysis of glucose concentration, level of vital cells (donated in the morning on an empty stomach);
- venous blood sampling to determine hormonal levels;
- biochemical urine analysis, the results of which reflect the general health of the patient;
- a smear from the mucous membrane of the eyelid, if there is a suspicion of a bacterial or fungal infection;
- biochemical analysis of purulent exudate, which is released from the burst capsule of the secretory canal (carrying out this study is a prerequisite to exclude the presence of pathogenic microflora, as well as the degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a cancerous tumor).
Based on the results of the examination, a diagnostic report is drawn up, which displays the data of laboratory tests. Taking this information into account, the attending physician forms a tactic for further therapy.
Symptoms
The main sign of the development of this disease is the formation of swelling in the area of the edge of the eyelid, closer to the eyelash growth line. Subsequently, an elastic seal with smooth edges, shaped like a pea, appears in its place. There is redness on the inner surface of the eyelid.
Chalazion rarely causes pain in the eyelid area. If an infection joins such a pathological process, then all the signs of an acute inflammatory process will additionally appear: pain, swelling, redness, and spontaneous opening of purulent exudate from the inner edge of the eyelid is also possible. In such cases, treatment includes antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy, as well as the use of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Upon initial examination, a chalazion resembles a stye in many ways. They differ in that barley usually resolves after the pus “breaks through” and all symptoms gradually disappear. The chalazion, in turn, rarely breaks through, gradually gains in size and becomes quite dense.
Meibomian gland blockage can occur in one or both eyelids.
If a child with a chalazion is not given the necessary treatment for a long time, the seal can grow to the point where, putting pressure on neighboring tissues, it can provoke the development of other diseases of the visual system. Therefore, you should not delay visiting an ophthalmologist, even if a painless lump on the eyelid does not cause your child any discomfort. Remember that conservative treatment of chalazion is only appropriate in the initial stages of the disease or after it has broken through.
Cases of recurrent multiple chalazions are not often reported in children. Usually, a chalazion can reappear in the same place where it was previously removed. This is due to the fact that during the operation the tumor was not completely removed.
There is a theory that suggests that the presence of hypermetropia () in a child contributes to the development of chalazion. In any case, this type of refractive error requires glasses or contact correction, as well as other treatment methods (hardware therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, etc.).
The appearance of chalazion can occur against the background of decreased immunity. This can also be explained by hereditary or acquired instability of the immune system to gram-positive microflora. In this case, the treatment plan should be drawn up with the participation of an immunologist. A chalazion can appear as a result of an anatomical defect, which is manifested by a too narrow lumen of the meibomian glands, as a result of which the normal outflow of fatty secretion is disrupted.
Another reason for periodic blockage of the meibomian gland ducts is the weak functional activity of the muscular system, which affects the movement of secretions in a certain direction, as well as the low content of the protective protein secretory immunoglobulin of tears. In such cases, the child usually periodically develops multiple chalazions.
Treatment
Therapy for chalazion of the upper or lower eyelid involves the use of external medications in the form of ointments and gels, or surgical opening of the formed seal. Traditional medicine recipes and physiotherapeutic techniques can also be used.
Medicines, gels, ointments, eye drops
At all stages of chalazion treatment, the following medications have proven themselves to be the best for restoring the normal functioning of the organ of vision:
- Balsamic liniment. This product contains castor oil, xeroform and tar; a small amount of ointment is applied to a sterile gauze bandage, and then attached to the diseased surface of the eye using an adhesive plaster. The procedure is performed in the morning and evening, wearing an antiseptic bandage for 2 hours. The duration of the therapeutic course is 7 days. The cost of the medicine is 45 rubles. per tube of 40 g.
- Hydrocortisone ointment is an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agent that needs to be used to treat a benign neoplasm 2-3 times a day for 6-14 days, depending on the dynamics of recovery. The cost of the drug is 110 rubles. per tube 10 g.
- Ichthyol ointment 10% concentration is an effective anti-inflammatory agent that eliminates signs of edema and can be used to prevent the addition of a bacterial infection and the formation of a purulent abscess. The affected area of the eyelid is lubricated with a thin layer of ointment 2-3 times a day until the symptoms of chalazion completely disappear. The average cost of a medicine is 90 rubles. per tube 30 g.
- Oftalmodek - eye drops that relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane of the diseased eye (especially if the chalazion has affected the lower eyelid), 1-3 drops are applied 4 to 6 times a day for 5 days, can be used in the postoperative period, if the doctor has decided about surgical removal of a capsule filled with secretions. The cost of the drug is 120 rubles.
When using the above ointments, you must follow safety rules. The active components of the drugs should not be allowed to come into contact with the mucous membrane of the eyeball. The only exception is Ophthalmodec drops. Prescription of medications should be carried out exclusively by the attending physician.
Intracavitary drug injections
The use of the method of injection treatment of eyelid chalazion with the introduction of a drug directly into the neoplasm is not widely used.
This is due to the low effectiveness of intracavitary injections, as well as the risk of complications in the eyeball area (inflammation, mechanical injury, blurred vision, allergic reaction and side effects).
In the cold season, steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be used, namely:
- Flunisolide;
- Dexamethasone;
- Prednisolone;
- Beclomethasone.
These are potent drugs based on synthetic hormones. Their purpose, dosage selection, frequency of intracavitary injections and course of therapy are determined exclusively by the ophthalmologist.
If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner, then in most cases, injection of steroid medications is not required.
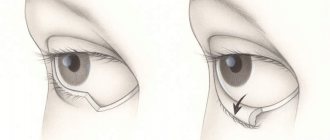
Operative measures to treat the disease
Surgical intervention is a radical method of therapy, which is used for long-term and chronic chalazion, when the use of local anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agents has not brought a positive result, or the tumor continues to increase in size.
The surgical operation is carried out in compliance with the following therapeutic protocol:
- The patient is in the operating room. Takes a sitting position or lies down on the couch.
- The doctor administers a local anesthetic.
- Using a special clamp, the area of accumulation of meibomian gland secretion is fixed.
- Using a scalpel, the surgeon makes a small incision in the eyelid, through which the entire contents of the capsule are completely removed.
- An antiseptic bandage is applied to the surgical area.
The operation is not complicated or dangerous to the life and health of the patient. The total duration of surgical procedures is no more than 15 minutes. Over the next 5 days, the patient must visit the dressing room, where he will undergo antiseptic treatment of the eyelid and change the bandages.
The main disadvantage of the surgical treatment method is that there remains a high probability of relapse of the disease. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the cause of chalazion. In general, the prognosis for recovery is favorable.
Treatment with folk remedies
There are alternative methods of treating chalazion of the upper or lower eyelid, which involve the use of traditional medicine recipes.
Water tincture of calendula
You need to take 10 g of dried flowers of this medicinal plant, pour a glass of boiling water over them, and then leave to infuse for 1 hour.
After the specified time, the tincture is used to wash the diseased eye, the procedure is done 3 times a day for 10 days.
Dry heat method
You will need to soft-boil 1 chicken egg, wait until it cools down to a comfortable temperature, then tie it in a handkerchief or any other fabric, and warm the sore eyelid so that the accumulated secretion matures and comes out of the meibomian gland canal on its own. Therapeutic manipulations are performed 2 times a day for 15 minutes. until the benign tumor completely disappears.
Chamomile decoction
To prepare this folk remedy for chalazion, you will need to take 2 tbsp. l. dried leaves, flowers and stems of a medicinal plant, pour them into a metal container, add cold water and boil for 10 minutes.
After the decoction has cooled, it is necessary to moisten a piece of sterile cotton wool in the medicinal liquid and make lotions by wiping the sore eyelid.
Ointment based on aloe and flower honey
Homemade medicine is prepared by mixing 1 tsp. bee product collected in the spring season, as well as 1 tsp. juicy aloe pulp. All ingredients are thoroughly mixed until a homogeneous mass is formed, and then the product is used as an ointment, which is used to lubricate the surface of the chalazion 3 times a day until it completely disappears.
The effectiveness of traditional medicine has not been established by laboratory studies. Therefore, before using them, you must first consult with an ophthalmologist. In case of deterioration of health, exacerbation of the inflammatory process, the appearance of an abscess or an increase in the volume of the capsule, you should immediately seek help from a doctor.
Physiotherapeutic treatments
This direction in the treatment of the consequences of blockage of the meibomian gland canal can be used in combination with other therapeutic techniques.
The greatest effect is observed in the case of simultaneous use of medications and physiotherapeutic methods, namely:
- heating with electrophoresis, which is carried out under the supervision of a nurse, the temperature of the dry heat supply is controlled (on average, 3 to 7 procedures may be required, which are performed free of charge in public hospitals);
- massage, which can be performed independently, while at home (the principle and technique of massage movements is to massage the sore eyelid in a clockwise direction to stimulate the natural outflow of meibomian gland secretions and prevent stagnation).
The above physiotherapeutic techniques are not recommended for use as independent methods of treating chalazion, since the likelihood of achieving a positive effect is minimal.
What to do if the chalazion ruptures?
A rupture of a chalazion of the upper or lower eyelid requires taking immediate measures to sanitize the damaged part of the eye.
In such a situation, it is recommended to do the following:
- Take a piece of sterile cotton wool and then soak it in 3% hydrogen peroxide.
- Close the eye tightly, then carefully, avoiding contact of the antiseptic solution with the mucous membrane of the eye, treat the wound surface.
- Using leisurely movements, remove any remaining purulent contents from the rupture site.
- Place a piece of sterile bandage on the surface of the eye, securing it with a medical adhesive plaster.
- Go to the hospital to see an ophthalmologist or surgeon.
If your home medicine cabinet does not contain all of the above first aid supplies, or if a person does not have special skills in treating wounds on the surface of the eyelid, then it is better to immediately seek help from a specialist.
To minimize the likelihood of a bacterial infection entering the wound, you should cover your eye with a sterile bandage on the way to the doctor.
Prevention of chronicity of the process
It is very important to take timely measures to prevent the transition of a benign neoplasm to a chronic form.
To do this, it is recommended to follow the following prevention rules:
- timely treat inflammatory diseases of the organ of vision (especially those caused by infectious microorganisms);
- observe sanitary and hygienic standards for caring for the skin surface of the eyelids, wash at least 2 times a day with warm water using hypoallergenic soap;
- use only high-quality and certified cosmetics, do not allow mascara, shadows and other products to remain on the eyelids and eyelashes for a long time;
- begin treatment of barley from the first days of its appearance, while acute inflammation of epithelial tissues does not yet increase;
- monitor your diet so that it contains a sufficient amount of fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs, lean meat and ocean fish;
- people who have increased hyperactivity of the sebaceous glands should eat less fatty foods, clean the skin surface of the eyelids with ethyl alcohol, preventing the solution from coming into contact with the mucous membrane of the eye.
If a chalazion of the upper or lower eyelid has already developed in an adult, there are pronounced signs of swelling, inflammation or just a space-occupying formation, then you need to seek help from an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
This is a guarantee that treatment will begin on time and the disease will not become chronic. Chalazion is not a dangerous disease, but it significantly reduces the patient’s quality of life, causes an aesthetic defect, and low-grade inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyeball.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Postoperative period
After removing a chalazion on the eye:
- for 5–7 days, eye drops are prescribed that suppress the activity of microbes and relieve inflammation;
- if during the operation the conjunctival mucosa was dissected, then for 5 days you should wear a soft contact lens, which will prevent friction of the wound surface on the eyeball, preventing pain;
- local swelling of the eyelid and postoperative bruises disappear after a few days;
- the excised tissues are sent for histological examination to exclude cancerous cell degeneration (malignancy).
After classical surgery, as well as after laser chalazion removal, you should avoid for a week:
- water getting on the injured eyelid;
- physical activity, head shaking, prolonged eye strain (reading, computer, TV).
- use of cosmetics;
- visiting a sauna, bathhouse, swimming pool, swimming in reservoirs.
A chalazion on the eye is a tumor-like formation that occurs as a result of blockage and swelling of the sebaceous gland in the eyelid, called the meibomian gland. Based on this, the localization of characteristic formations, which, by the way, develop very slowly, is obvious.
The disease is quite common; people of absolutely all age groups can suffer from it, although the proportion of adults is several times higher than the number of children. The main age period during which chalazion may appear is 30-50 years.
Very often the disease is confused with barley, which also manifests itself in the form of a certain swelling on the eyelid. However, stye is an infectious disease and causes swelling and redness.
As a rule, with barley formations occur somewhat closer to the surface of the eyelid. In some cases, stye that was poorly treated or not treated at all can develop into chalazion eye disease.
The disease in question is characterized by certain causes, symptoms and treatment options. However, we should start studying with the fact that there are two types of chalazion: on the upper and lower eyelids.