About 7-10% of newborns have congenital obstruction of the nasolacrimal ducts. Impaired drainage of tears from the corner of the eye into the nasal cavity leads to the child’s eyes becoming inflamed and purulent. In some cases, eye rinsing and drops are prescribed, as well as massage of the nasolacrimal duct to eliminate congestion and membranes that prevent the outflow of secretions. But often, in order to radically and quickly eliminate the problem, children are shown probing of the lacrimal ducts in order to restore the patency of the canal.
Why do tear ducts get clogged?
- 4.1 Eye hygiene
- 5.1 Third stage - after probing
- 6.1 Video - Probing of the nasolacrimal duct
Probing of the eye canal
When a child goes through the stages of intrauterine development, his tear ducts are protected at this time by special films consisting of thin connective tissue. This is necessary to protect the eyes from amniotic fluid. At the moment when the child is born, the films should be removed, but sometimes this does not happen, and the channels, both or one, remain closed. Because of this, inflammation develops in them.
By the way. As soon as the baby takes its first breath and cry after birth, air pressure builds up in the nose, which causes the protective duct film to burst. Usually this happens easily and goes unnoticed by either the child or the parents.
Dacryocystitis and conjunctivitis
But sometimes the film does not burst because its structure is too dense, or the first breath was shallow, or the cry was weak. The pressure in the nose is not enough to remove the film plug, and it remains, continuing to block the tear opening.
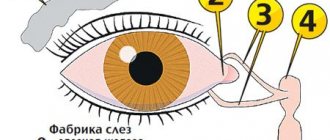
Since tears are normally produced constantly, they must flow down the canal and away from the eye. When the channel remains closed, this cannot happen. The tear fluid forms stagnation in the “sac” formed by it and gives rise to serious inflammation, which cannot be eliminated otherwise than by clearing the tear duct, giving the stagnant fluid an outlet.
Dacryocystitis
Important! In a blockage condition, tears lose their ability to flow into and move through the tear duct. As they accumulate, they aggravate inflammation.
Before and after probing the lacrimal canal
For what reasons does dacryocystitis develop in newborns?
The main reasons for the occurrence of this pathological situation include several anomalies that occur with a normally developed system of tear formation and tear secretion. Their character can be either congenital or independent of developmental defects.
Dacryocystitis in newborns - treatment
Table. Causes of dacryocystitis.
| Cause of occurrence | Description |
| Developmental anomalies | Even in the womb, the child’s eyes or eyelids, nose, and some skull bones begin to develop incorrectly. |
| Genetic pathologies | Those that violate the structure of the face in some way. |
| Congenital pathology of the lacrimal duct | The child's nasolacrimal duct is too short or narrow. |
| Acquired obstruction | Most often it occurs due to the fact that the canal is blocked mechanically with a so-called plug. The most common cause of dacryocystitis. |
| Eye infection | It can begin both in the womb and after birth, the second most popular cause of duct closure and tear obstruction. |
| Tumor | A tumor-like formation blocking the nasolacrimal duct is rare, but such cases have still been recorded in medicine. |
Important! Blockage of the tear ducts by plugs is the most common reason why a child may undergo probing surgery.
How to recognize dacryocystitis and distinguish it from conjunctivitis
Dacryocystitis in adults
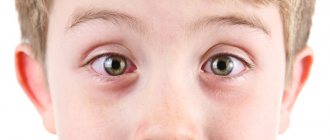
The very first sign of obstruction is tear stagnation, but it is not noticed immediately, although even in a newly born baby who is not crying at the moment, with dacryocystitis you can see an accumulation of tears in the lower part of the inner corner of the eye.
More obvious signs follow.
- Chronic lacrimation.
- Enlarged eyelids due to swelling.
- Sticky eyelashes.
- “Souring” of the eye, accompanied by discharge from it, especially abundant after a night’s sleep.
- Discharge from white-yellow to greenish (color indicates the stage of the inflammatory process).
Inflammation of the tear duct in a baby
If you don't try to fix the problem, the symptoms will get worse after a while.
- Pain appears in the eye, causing the baby to cry even with a light touch to the area of the inner corner.
- First the corner turns red, then the change in skin color spreads to both eyelids and the nose.
- The discharge becomes purulent, accumulates and dries out.
- A purulent “bag” swells near the inner corner.
- The temperature rises and stays.
By the way. At this stage, if not at the initial stage, any parent should be alarmed and take the child to the doctor. But it happens that, following the advice of grandmothers, mothers try to cope with the problem with folk remedies, washing their eyes with decoctions and applying various kinds of compresses to them.
Dacryocystitis in a child
If, when worsened symptoms appear and their constant presence, you ignore the problem and postpone a medical consultation, at which the doctor will suggest probing the canal, terrible things can happen.
Important! In a child, with prolonged blockage and inflammation of the lacrimal canal, pus spreads through the tissue, forming phlegmon. Then it breaks into the sinuses, reaches the brain, and meningitis begins.
Blocked tear ducts in young children
But just as often as the unnoticed first stage of canal blockage, the following thing happens - parents notice that something is wrong with the child’s eyes, and, after observing the baby for some time, they themselves make a diagnosis - conjunctivitis. Moreover, there will always be an older relative or neighbor who will tell you that everyone’s eyes fester in babies, and this is normal, this is childhood conjunctivitis. You just need to rinse with chamomile, bay leaf, and other available means, up to and including instilling breast milk.
Advice. The symptoms of these two ailments are similar, and not always even a pediatric eye doctor can distinguish them at first glance. But there is a way to clarify the diagnosis - the baby is first prescribed drops for conjunctivitis, and if they do not improve the situation, then there is reason to assume that the tear duct is blocked.
Blocked tear duct in newborns
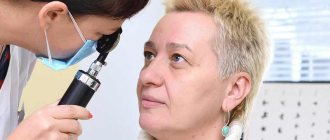
If the ophthalmologist suspects dacryocystitis, then a set of diagnostic procedures is prescribed, which allows not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also to identify the cause of the formation of stagnation and its exact location. The following diagnostic actions are carried out.
- Visual examination to determine the condition of the eyes.
- A smear of discharge to rule out an infectious nature.
- Channel test to determine condition. Collargol (a dye the color of iodine tincture) is instilled into the eye. The amount of it that the doctor places into the eye for testing should disappear within five minutes if there is normal tear flow. If the eye remains stained for five to ten minutes, a tear drainage obstruction is diagnosed.
Collargol
By the way. If the color lasts more than ten minutes, testing continues to prove or disprove complete loss of tear drainage function and to obtain definitive confirmation of obstruction.
Complete confirmation of obstruction is provided by the Vesta test. It can be called similar to canal, but its second name is nasal, since the main result will be obtained in the patient’s nose. A loose tourniquet of cotton wool is placed in the nostril and collargol is instilled into the eye. Coloring of the cotton cord should occur within three to five minutes. If it starts later, or the cotton wool is not colored at all, an obstruction is established.
Test Vesta
By the way. At this stage, before prescribing a probing procedure, the doctor must rule out structural pathologies in the patient's nose or skull.
How to prepare for sounding
Before probing, the doctor performs the Vesta test. A safe dye is dropped into the affected eye and a cotton swab is inserted into the nostril. If the channel is open, the fleece will become colored in a few minutes. If there is no staining on either side, or the canal is closed in one eye, probing is indicated. Before the operation, the child is examined by:
- pediatrician – excludes any contraindications;
- neurologist - determines whether local anesthesia is permissible, assesses whether the intervention can be performed;
- ENT doctor – excludes structural anomalies of the nasopharynx.
It is important to undergo general blood and urine tests to rule out possible complications.
Probing purpose
In fact, many parents are in vain afraid that as soon as the baby’s eye festers, they will immediately begin to pierce the tear duct with a probe. The treatment strategy for dacryocystitis is always two-stage. And at the first stage, if there are no direct indications for urgent probing, treatment is applied.
Important! A two-stage scheme is used if the baby has not reached six months of age. In cases where the child is not yet a year old, but has already turned six months old, most often, canal cleaning will be prescribed first, and then subsequent treatment, restoration and hygienic care.
Treatment of dacryocystitis in a newborn
Treatment is used in the same way as the first remedy, in cases where the anatomical characteristics of the child and his physiology allow him to wait until the film opens. In a number of such cases, probing can be avoided - the eye goes away.
What is included in the first stage of treatment
Hygienic eye treatment
Twice a day, with cleanly washed hands and short nails, parents wash the child’s eyes with furatsilin in solution or with ordinary boiled, but not hot, water. Discs or gauze for washing are taken separately for each eye and thrown away after use. Washing is carried out by moving inward along the eyelids, from the temple.
Washing a child's eyes
Eye massage
In fact, it is not the eye that needs to be massaged, but the lacrimal sac. This can be done by parents or other relatives. You cannot massage with nail polish or if your nails are not cut short. Hands are washed with soap and dried with a sterile towel.
Massage of the tear duct
The technique of the massage procedure is as follows.
- Lubricate the area from the nose to the eye with a neutral cream.
- In the direction from the wing of the nose up to the corner of the eye, draw 10 straight lines with your index finger.
- If liquid is released, collect it on a cotton pad.
- In the same direction, make 10 circular movements with your index finger, as if “drawing” a spiral.
- Cleanse the skin of secretions again.
- Draw 10 straight lines in the opposite direction from the corner to the wing of the nose.
- Near the corner of the eye, alternately tap with your index and ring fingers, creating vibration, for 10 seconds.
- Cleanse the skin of secretions and cream.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor.
Massage for dacryocystitis: technique
If the first stage of treatment does not bring results for two months or more, or if the child is approaching eight months of age, probing will be prescribed.
Before the appointment, the child is carefully examined by a pediatric ophthalmologist together with a pediatrician. Cough, runny nose, the presence of a general disease, malaise, and other eye diseases are excluded. Blood tests are performed to determine the effects of drug allergens and preparations used during the insertion of the probe.
Newborn tear duct massage
How to Avoid Probing
Piercing the lacrimal canal is performed when drug treatment for dacryocystitis and conservative therapy are ineffective. First, during the initial treatment, specialists prescribe eye drops, eye rinsing and a special massage. In some cases, following these recommendations gives good results and allows you to avoid probing.
For dacryocystitis, therapeutic massage is performed by a professional or mother after training. Duration, frequency and technique are determined individually. Massage movements are performed in light circular movements with the little finger.
Before performing a massage, you should cut your nails short, wash your hands thoroughly, and wipe dry. This reduces the risk of eye injury to the baby and undesirable consequences.
A special massage technique can improve the patency of the lacrimal ducts, remove purulent fluid and break through the gelatinous film. At the beginning of the procedure, the eyes are cleaned with a cotton swab with furatsilin. Then press up to 10 times on the area above the lacrimal sac and move it to the base of the nose.
After the procedure, it is necessary to remove the released exudate with an aqueous solution of chamomile or furacilin, or tea leaves. For this, only freshly prepared liquid at room temperature is used.
After cleansing the eyes, antibacterial drops - Tobrex, Tobriss, Vitabakt, Vigamox or others approved for age. It is extremely important to observe the dosage, frequency of use and duration.
Massage for newborns is carried out immediately before feeding or during up to 5-6 times a day for 14 days. If there is no improvement, you should not self-medicate or resort to traditional methods. Timely consultation with a doctor will help avoid complications and advanced forms of disease.
The second stage is the probing procedure
It is carried out in a clinic setting, on an outpatient basis. A pediatric ophthalmologist carries out probing with the help of a nurse or the child’s parents.
By the way. Half an hour to an hour after the manipulation, the patient can go home, if the obstruction of the canal is not complicated by a severe form of infection. If there is an infection, probing will be done in a hospital and the child will be left under observation for several days.
It is necessary to swaddle the baby in order to immobilize as much as possible and eliminate the possibility of flapping the arms.
The baby needs to be swaddled
The nurse or parents hold the child and fix the position of his head necessary for the procedure. The doctor instills an anesthetic substance, the so-called local freezing, into the eye that will undergo manipulation.
By the way. Since the procedure is performed under local anesthesia, the child does not feel pain. But almost all small children cry loudly and hysterically during probing. This is due to fear and uncomfortable sensations from manipulation.
How is probing carried out?
The doctor will need double probing - the lower and upper lacrimal canal.
- First, the upper one is probed. To do this, the eyelid is lifted up at the angular inner point, and the first probe is inserted into the lacrimal punctum. It is called a Sichel probe and is used to widen the opening of the lacrimal opening. After it, first horizontally, a Bowman probe is immersed into the hole. When it is turned and placed in a vertical position, the protective film breaks through.
- To clean and uncork the lower lacrimal canal, the lower eyelid is lowered down and to the side at the inner corner point. Further manipulations are carried out in the same order as for the top point.
- After the manipulations, the nasolacrimal ducts, cleared of mechanical blockage, are washed with a special treatment solution.
Probing the tear duct
By the way. If the child is less than two months old, due to the peculiarities of his physiology, endonasal sounding is possible. Anesthesia is not used in this case. The probe is inserted into the nasal passage and guided to the canal, then the passage freed from films is washed with antibiotics.
The third stage - after probing
It is necessary to carefully care for the manipulation area for two weeks after it is performed. To do this, a daily massage is performed using the technique described above in the first stage of treatment. The doctor will definitely prescribe eye drops containing an antibiotic to relieve inflammation and prevent the formation of new ones.
By the way. Most often (in 90% of cases), the procedure is sufficient and relapse does not occur. But it may happen that 100% cleaning did not occur, or the infection was introduced by parents during post-operative care. In this case, repeated cleaning with a probe is prescribed.
There is always a risk of relapse
Many parents ask the question why cleaning should be done at the earliest possible age, without waiting until the child grows up. After all, perhaps a child older than one year will undergo surgery more easily than a baby. But according to statistics, 90% of successful soundings, which do not require repeated manipulations, are carried out on babies under one year old, and even up to eight months of age. After a year, the child endures everything much more difficult, the possibility of relapses and the need for repeated probing doubles. In addition, the operation for children over 12 months is most often performed under general anesthesia.
Complications
Dacryocystitis in newborns or obstruction of the lacrimal duct
Probing is the most effective and least traumatic (albeit invasive) way to eliminate the inflammatory process in the lacrimal canal if the pathology cannot be treated conservatively. But it is used not only to remove film and free up tear ducts. A probe may also be inserted for diagnostic purposes to check the condition of the lacrimal canal or inject an antiseptic into it.
The injection procedure may be accompanied by complications of the following nature:
- rupture of the channel if the probe is selected incorrectly in size;
- rupture of a purulent sac with spillage of pus in the maxillary cavity;
- perforation of the bone wall, in which the probe penetrates into the nasal cavity;
- breakage of the probe in the canal, in which it will have to be urgently removed surgically.
Conical probe for lacrimal canal
Important! The appearance of blood after manipulation is not considered a complication; on the contrary, it indicates that the films blocking the tear flow have been successfully removed.
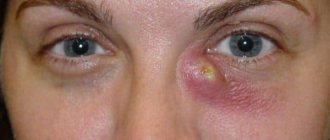
What happens if you don’t probe on time and don’t clean the tear ducts? Inflammatory stenosis will develop. Cellulitis of the lacrimal sac will occur. Periorbital cellulite is formed. Sinusitis or entmoiditis may begin. The state of purulent inflammation can lead to meningeal sepsis. In rare cases, visual impairment develops. Thus, this operation is a relatively safe and, by far, the most effective means of relieving a child of obstruction of the lacrimal ducts and preventing the development of serious diseases that pose a threat to the baby’s health.
This child has periorbital cellulitis, an eye disease
Symptoms of inflammation of the lacrimal duct in newborns
The development of dacryocystitis (inflammation of the lacrimal sac) most often develops gradually. The clinical picture may be supplemented by symptoms for two months.
Typically the disease develops as follows:
The child becomes restless and capricious, tear separation gradually increases.- In the corner of the eyeball, closer to the bridge of the nose, swelling appears , which increases in size every day.
- As the severity of the process develops, the discharge from the eye becomes purulent in nature.
- In the morning hours, the eyelids stick together, making it difficult for the child to open his eyes.
- The inflammatory process complicates the increase in temperature , with the development of symptoms of general intoxication of the body.
If parents do not pay attention to such manifestations and do not contact an ophthalmologist, the pathological process is aggravated by the appearance of an abscess or purulent melting of subcutaneous fat (phlegmon). Such complications tend to self-open and pose a real threat to the visual organ of a small patient.