Main symptoms:
- Incorrect eyelash growth
- Involuntary closure of eyelids
- Sensation of a foreign body in the eye
- Photophobia
- Tearing
Trichiasis is a specific eye disease that is characterized by abnormal eyelash growth. It is equally common among men and women; there is no exact data on the prevalence among the population, since in uncomplicated situations patients rarely seek help. It can often be detected in older people. ICD-10 code – N 02.0.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
The clinical picture of such a disease is quite well expressed and has specific signs, so, as a rule, there are no problems with diagnosis.
Treatment is selected by the doctor individually, since everything depends on the severity and form of the pathological process. The prognosis is favorable in most cases.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Medical center on Pionerskaya Polikarpov Alley 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Medical center South-West Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Medical center in Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
Etiology
Clinicians identify the following etiological factors for the development of this disease:
- eye injury;
- inflammatory and infectious diseases of the organ of vision;
- burns of various etiologies;
- history of eye surgery;
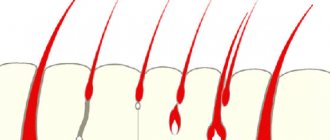
- due to previous reasons, a scar appears on the eyelid, which leads to abnormal eyelash growth directed towards the cornea;
- after inflammatory diseases, follicles die, and new ones grow in their place, but they grow in the wrong direction.
At the first symptoms you should consult a doctor.
Treatment of trichiasis
Abnormal eyelash growth can be corrected through surgery. The following methods are used for this:
- Epilation is the easiest way to remove eyelashes. The procedure is carried out using tweezers. After removing eyelashes, there is no lasting effect, but only a temporary effect, so the procedure should be repeated every 4-6 weeks. However, frequent hair removal causes eyelashes to become thinner and more difficult to respond to other treatment methods.
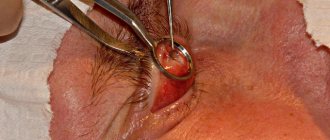
- Electrolysis is the extraction of eyelashes using electric current. The procedure is performed with a special needle, which is placed in the hair follicle and processed until bubbles of curled tissue begin to appear on the surface. The method gives a good result, but it is achieved only with repeated repetitions, which lead to the appearance of scars at the site of exposure. Electrolysis is used only to remove single abnormally growing eyelashes.
- Cryotherapy is the removal of eyelashes by cold (first the eyelashes are frozen at a temperature of -20 degrees, then they thaw). Today this method is the most effective when removing a large number of eyelashes. Disadvantages: possible scarring of tissue along the edge of the eyelids, skin necrosis.
- Argon laser coagulation – removal of individual incorrectly growing eyelashes. The procedure is performed from the point where the hair exits the skin or mucous membrane and is carried out in the direction of its growth. To correct incorrectly growing eyelashes, 1-2 sessions are enough. After the procedure, antiseptic drugs are prescribed.
If signs of trichiasis are detected, you should consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will examine the patient, conduct visometry and biomicroscopy, and prescribe appropriate treatment. Timely diagnosis will allow you to avoid structural changes in eye tissue and prevent surgical intervention.
Trichiasis
Treatment tactics for trichiasis depend on the form of the disease. For local damage, the method of choice is diathermocoagulation using a special needle-shaped electrode. The procedure is carried out along the growth of the eyelash up to its bulb. Also, for single changes, argon laser coagulation can be used as a minimally invasive technique on the skin of the eyelid at the site where the eyelash with abnormal growth emerges. After coagulation for 3 days, it is recommended to use antiseptic drops or ointments before bedtime. A widely used method of treating trichiasis - eyelash epilation (removal with tweezers) is ineffective. Due to the rapid growth of eyelashes, the procedure must be repeated every 30 days.
Eyelashes with trichiasis can be removed using the electrolysis technique. In this case, the electrocautery electrode is applied to the hair follicle and the tissue is coagulated. A side effect of the procedure is the formation of small scars in the area of effect of the electrocautery. For common forms of trichiasis, surgical intervention is necessary. The essence of surgical treatment of trichiasis comes down to the implementation of end-to-end resection of the area with abnormal eyelash growth, followed by bringing the edges of the wound closer together and layer-by-layer suturing.
For generalized trichiasis, the most effective treatment method is reconstruction of the posterior pole of the affected eyelid using a flap transplant from the patient's lip mucosa. Also, autocartilage and preserved aponeurosis can be used as a material for plastic surgery. An alternative is to rotate the diamond-shaped segments of cartilage or hair follicles. A minimally invasive technique for the generalized form of trichiasis is cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen. If the procedure protocol is not followed, the cells of the epithelial layer may die. After removal of eyelashes with the wrong direction of growth, patients with pinpoint keratopathy are recommended to use antibacterial ointment for 3 days to eliminate clinical symptoms.
Forecast and prevention of trichiasis
There is no specific prevention of trichiasis. Non-specific preventive measures boil down to compliance with industrial safety regulations when working with acids and alkalis. For preventive purposes, all patients with a history of blepharitis are recommended to be monitored and promptly treated by an ophthalmologist. After traumatic injuries or burns to the eyes, the costal edge of the eyelid should be carefully sutured or an ankyloblepharon should be formed. To prevent the development of frequent relapses of trichiasis, specific therapy should be carried out only by a specialist.
The prognosis for life and ability to work with trichiasis is favorable. In the absence of timely treatment, a slight decrease in visual acuity or secondary complications may occur.
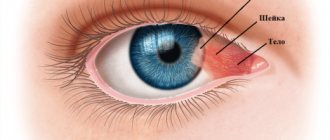
What is trichiasis?
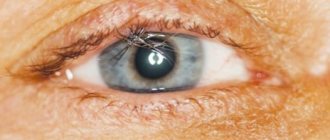
With trichiasis, the eyelashes curl inward, toward the eyeball. This disease causes discomfort and can also cause mechanical damage to the conjunctiva or cornea. Trichiasis is subject to mandatory treatment, as it is fraught with complications in the form of ulcerations of the cornea.
What are the causes of this disease? Most often it occurs after chronic blepharitis (inflammation of the edges of the eyelids). It can also be triggered by trauma, the consequences of surgery, or trachoma, an inflammatory eye disease caused by chlamydia. In some cases, the cause of trichiasis remains unidentified even by experienced ophthalmologists.
The main symptom of trichiasis, as mentioned above, is the curling of the eyelashes inward. This position of the eyelashes causes discomfort because they come into contact with the eyeball, causing irritation of the cornea. Additionally, the patient may be bothered by photophobia and blepharospasm - intense and uncontrolled closing of the eyelids. It is important not to confuse this disease with others, for example, madarosis or distichiasis. With madarosis, eyelashes are completely absent from birth or begin to fall out as a result of an infection such as leprosy. If the patient has distichiasis, then an additional row of eyelashes begins to grow. However, they are quite thin, so they can even be difficult to notice during a slit lamp examination. Therefore, at the first disturbing symptoms, it is necessary to contact a qualified specialist to establish an accurate diagnosis.
If trichiasis is confirmed, the ophthalmologist may suggest one of the following treatment methods:
1. Epilation. This method is quite common, but, unfortunately, not very effective. The fact is that long-term hair removal thins the eyelashes, they lose pigment and are more difficult to respond to other treatment methods in the future. 2. Diathermocoagulation. It is advisable to use it to remove individual eyelashes. The removal procedure is carried out using a needle electrode. 3. Argon laser coagulation is also suitable for local removal of multiple eyelashes. The procedure is carried out using special equipment, after which the patient must use antiseptic drops and ointments. 4. Surgical treatment. It is prescribed in the most severe cases and is considered the most effective method.
After treatment with any of these methods, you must carefully monitor your eye health. If inflammatory processes occur on the eyelids, you must immediately contact a specialist and carry out treatment. You should not delay contacting a doctor, as this is fraught with complications and relapses of the disease.
MagazinLinz.ru team
What is trichiasis and symptoms
The eyes are bordered by cilia, which protect against sand, dust, dirt, small insects, and help focus the image. Updated every 90 days. Incorrect eyelash growth causes a lot of inconvenience: an unaesthetic appearance, injury to the eye.
Symptoms of the disease:
- redness of the cornea;
- sunlight causes pain;
- tears flow uncontrollably;
- I want to squint;
- frequent involuntary blinking;
- burning sensation in the eyes.
This all happens because the hairs bent inwards irritate the eyeball. If symptoms are left untreated for a long time, the mucous membrane of the eye is damaged. This can lead to clouding of the cornea and decreased visual acuity.
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) provides code H00-H06 - diseases of the eyelids, lacrimal ducts, orbits.
Why do eyelashes grow in different directions?
The result of external influence or birth pathology is the movement of hair follicles located at the edges of the eyelids to the inner edge. Due to this, the direction of eyelash growth changes. The shape of the skin fold remains unchanged. Reasons why trichiasis occurs:
- Changes in follicles in certain diseases: trachoma, entropion, chronic blepharitis.
- Trauma or damage to the eyelid.
- Inflammation and conjunctiva.
- The presence of an extra fold of skin (epiblepharon). Hairs grow directly into the eye or form an additional row (distichiasis). This causes discomfort.
Trichiasis can be unilateral or bilateral. The disease occurs in men and women of any age. Sometimes it is impossible to find out the cause of the disease. The most common factor causing illness in children is trauma.
Diagnostics
You should consult an ophthalmologist . To begin with, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the patient and finds out the following:
- how long ago the first manifestations began;
- is there a history of burns, injuries to the organs of vision, chronic ophthalmological diseases;
- whether you have had surgery on the affected eye;
- personal and family history is clarified, since a genetic predisposition to such a pathological process cannot be ruled out.
It is not possible to make an accurate diagnosis based on an initial examination alone, so several diagnostic techniques are used, namely:
- visometry.
- biomicroscopy using a slit lamp.
- biomicroscopy with contrast agent.
- analysis of tear fluid.
Due to the fact that the clinical picture may be somewhat ambiguous, differential diagnosis may be necessary regarding the following pathological processes:
- distichiasis (quite common in humans);
- entoprion;
- epiblepharon;
- turning of the eyelids.
Based on the results of the study, the doctor can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. Self-medication, especially through traditional medicine, is excluded.
In this case, this is impractical, since folk remedies do not provide the desired therapeutic effect.