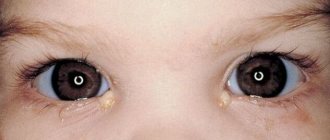
Often after childbirth, mothers discover strabismus in children, the causes and treatment of which E. Komarovsky recommends identifying and prescribing only after the first 4-6 months of life. Strabismus in newborns is a normal physiological phenomenon; in the first months of life it should not cause alarm. But if the child’s eyes continue to work inconsistently, the strabismus must be treated - and the sooner the better.
Why do newborns cross their eyes?
When a newborn's eyes wander in different directions, it can alarm even an experienced mother. Strabismus in infants can be of two types:
- Functional. This condition is not a pathology. During intrauterine development, the child had no need to focus his gaze, so his eyeball muscles are not trained. The centers of the brain that control eye movement reach a level of sufficient development by 3-4 months. Until this age, the pupils of infants act uncoordinated and can move horizontally, only mastering vertical movement. The skull of newborns has a peculiarity: its right and left halves form an angle, so from the outside it seems that it is squinting. Functional strabismus disappears by the first six months of life.
- Persistent strabismus - strabismus, heterotropia. The visual axes of both eyes are unable to connect to one point, and the eyes always look in different directions. If a baby has this pathology from birth, it is in vain to expect that strabismus will go away by 4-6 months of life. Persistent strabismus occurs in 2% of newborns; it is due to the following reasons:
- oxygen starvation of the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth leads to disruption of the visual centers of the brain;
- infectious diseases of the mother, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- complications after infections suffered by the newborn itself;
- congenital brain diseases (cerebral palsy, Down's disease, etc.);
- severe fear, other mental or physical trauma;
- hereditary factor.
Authoritative pediatrician E. Komarovsky warns: if after 6 months the child’s strabismus does not go away, he must be taken to an ophthalmologist.
Advanced strabismus complicates the process of developing binocular vision; the baby’s brain will form compensatory reflexes, the strengthening of which will complicate treatment. A decrease in visual acuity is inevitable.
Strabismus in children under one year of age can be recognized by the following signs:
- The baby's gaze cannot concentrate on one point.
- No synchronous eye movement.
- In bright light, one eye closes or moves to the side.
- The baby turns his head to see the object with one eye.
- The child bumps into surrounding objects, because... Poorly assesses spatial depth.
How does strabismus manifest in a newborn?
As soon as a child is born, he is not immediately adapted to external environmental conditions. This applies to all sense organs, which are not fully developed and gradually return to normal as the baby grows. Regarding vision, in some newborns you can notice that the eyes do not obey their owner and spontaneously move apart or are reduced to the bridge of the nose, and this process can occur discordantly, and not synchronously.
Strabismus (strabismus) accounts for 2 to 3.5% of the total number of pathologies of the visual organs (more than 10 million patients).
With strabismus, the eyes of a newborn from time to time move apart to the sides, then converge towards the bridge of the nose, and in turn
At the beginning of life, a child has a lot to learn, including how to fully control his body. Taking control of eye movements is as important as developing dexterity and precision in hand movements. However, to fully see is a paramount task, since he receives 90% of the information about the world around the child through vision. Controlling the movement of the eyeball, focusing your gaze on a specific object, observing the actions of others simultaneously with both eyes - not every newborn is able to immediately master such complex work.
How quickly can a child master the skill of eye movement control? The so-called functional strabismus disappears by 3–4 months of the baby’s life. It is believed that by this moment the baby should learn to focus his gaze and concentrate it on the object of interest. Before this period, strabismus is normal and does not require treatment.
A baby in the first months of life is still learning to fix his gaze - he tries to focus it on the rattle for a few seconds, and then his eyes get tired, and one of them moves to the side
If strabismus has not gone away by the age of six months, you should definitely show the child to an ophthalmologist, since this pathology can negatively affect the formation of vision for the rest of his life.
Video: Dr. Komarovsky’s opinion on strabismus
Causes and types of strabismus
True strabismus is not always a congenital pathology. During the first 3 years, when binocular (3D) vision is actively developing, the following reasons lead to the appearance of an asymmetrical gaze:
- congenital farsightedness or myopia - the difference in refraction between the right and left eyes;
- diseases of the central nervous system: cerebral palsy, brain tumor, etc.;
- severe stress: bruise, fright, vaccination, acute respiratory viral infection or other viral disease.
Normal operation of both eyes produces two images; the visual analyzer combines them into one and forms a three-dimensional image. With strabismus, the images fail to connect and the brain ignores what the squinting eye sees. His visual acuity gradually decreases, lazy eye syndrome may develop, he stops moving and perceiving objects. The child develops a flat image of the world. Established pathology is difficult to correct, so it is important to start treatment on time.
If there are cases of hereditary strabismus in the family, parents should regularly check the child's vision in the first three years.
Dr. Komarovsky emphasizes that in the period up to 3 years, any injury can provoke heterotropia, and at this time, hidden strabismus, invisible in a newborn, progresses. Therefore, visits to the ophthalmologist should be mandatory at 2, 6, 12
months, and then once a year until school age.
In total, there are about 25 types of strabismus, the formation mechanism of each of them is different, and, therefore, the treatment methods are different. Based on the displacement of the visual axes, 4 types of strabismus are distinguished.
- esotropia - convergent strabismus, when the eyes converge on the bridge of the nose, this deviation occurs with congenital farsightedness;
- exotropia - divergent position of the eyes, when the ocular axes are shifted towards the temples, this type is characteristic of myopia;
- vertical heterotropia - displacement of the visual axis up or down.
Development of the disease
There are two different mechanisms for the development of strabismus.
- A concomitant form of strabismus, when refraction (refraction of rays) is impaired in one or both eyes. It is hereditary and manifests itself in childhood. It is treated with glasses and lenses if accommodation – vision focusing – is impaired. If there is organic damage to the optical media, corneal surgery or lens replacement is necessary.
- Paralytic form. The work of the eye deviates from normal fixation due to paresis of one or more muscles. Eye movement is limited to one direction; a glance in this direction is accompanied by a characteristic turn of the head. Paralysis of the eye muscles is most often an acquired pathology (trauma, severe stress, brain damage). Restoring normal eye movement function occurs through physical therapy and subsequent surgery to correct the paralyzed muscle.
As you can see, different forms of strabismus require their own treatment methods.
Dr. Komarovsky warns that self-treatment of strabismus with folk remedies can be harmful if the mechanism of its occurrence is unknown. Only an ophthalmologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Modern methods of treating strabismus
The concomitant type of strabismus is treated for 2-3 years. The image on the retina is corrected using lenses and special glasses. Occlusion is used to correct low vision in the squinting eye (amblyopia). The healthy eye is switched off from the act of vision (atropine and special stickers on the eye - occluders are used for this). In this regard, Komarovsky advises sending a child with strabismus to specialized kindergartens, where all children are treated using this method, and there is no discomfort in communication. We list other treatment methods:
synaptophore exercises – training of the eye muscles and nerve centers responsible for binocular vision;- amblyopanorama – treatment with moving blinding fields, can be used from infancy;
- computer-based treatment using special game programs, used for children 3-4 years old and older;
- the Rucheek device trains the accommodative work of the eye muscles;
- virtual 3D glasses for the formation of three-dimensional vision;
- restorative procedures: acupressure, vitamin therapy.
The unfriendly (paralytic) type of strabismus is treated in 2 stages:
- Conservative treatment: gymnastics of the eye muscles; exercises to eliminate duality; physiotherapy (electrophoresis, reflexology, etc.).
- Surgery consists of shortening or weakening the eye muscle that deviates the eye from proper fixation. It is carried out using computer modeling using high-frequency radio wave technology.
A successful result in the treatment of strabismus is possible with timely seeking help from a specialist, with sufficient patience and persistence in following all the recommendations of the ophthalmologist.
Treatment of strabismus
As mentioned above, with functional strabismus the child does not need therapy. However, the true disease must be treated, and as soon as possible. A special sign that helps to identify pathology of the organ of vision at an early age is a decrease in the mobility of the squinting eye or its complete absence, and if the optic nerve is damaged, the occurrence of pupil dilation and drooping of the eyelid.
Even if the disease is congenital, if therapy is started in a timely manner, it can be successfully treated. Unfortunately, all effective medical methods are applicable to children from the age of two. Therefore, you can only work with kids at home. Doctors recommend playing with infants games with focusing vision (with a rattle or ball, which are located at the optimal distance from the eyes - 40 cm) and other exercises that promote the full range of movements of the organ of vision (provoke the pupils to draw circles and figure eights, lead the baby to engage in extreme upper and lower positions of the eye). You need to start doing the exercises gradually, with two reactions a day, and by six months reach ten reactions.
If a congenital disease is confirmed and a strabismus angle is greater than 15 0, surgical intervention is often required. However, such treatment is allowed only from the age of three, and the optimal age would be to reach the age of 4–5 years, when the child is able to perform the set of orthoptic exercises prescribed after the operation.
Surgery to eliminate strabismus is prescribed in cases where other therapeutic measures do not help and the duration of treatment is more than a year.
At an early age, other methods of therapy are applicable, for example, if amblyopia is detected in an infant, he is prescribed treatment using the occlusion method (artificial closure of the healthy eye to improve the performance of the other).
The so-called direct occlusion method implies that the child’s healthy eye is switched off from work for a certain time.
Occlusion is possible in one of several types as prescribed by the treating specialist:
- straight - with the healthy eye closed;
- reverse - with closing the squinting eye;
- alternating - in this case, alternating closing of the eyes occurs.
The duration of exclusion of the eye from visual work depends on the complexity of the problem. Occlusion can be either temporary or permanent. Treatment of amblyopia using modern hardware methods is prescribed to children at an older age, but this method is not indicated for infants.
For children with vision problems, massage of the collar area is recommended, which helps improve blood supply to the brain and has a positive effect on the functioning of the visual organs. Only a specialist with a medical education can perform such a massage on newborns. Typically, the child is prescribed a ten-day course of massage, followed by its repetition after 6 months.
Among other things, if a baby has strabismus, it is important in the first months of his life (especially up to six months) to pay attention to supporting full breastfeeding, without early supplementary feeding with formula and introducing complementary foods. Mother's milk contains all the necessary elements for the development of the baby's vision.
Strabismus in newborns
If strabismus is detected in newborns - when does it go away, how to treat it? Such questions are often asked by parents whose children were born with strabismus. As a rule, mothers begin to sound the alarm, but in fact, this defect is easy to correct after birth. Moreover, most often strabismus goes away on its own. But it is still necessary to show the baby to an ophthalmologist, as complications may arise in the form of other ophthalmological diseases.
The main causes of strabismus in newborns
When a person is inside the womb, his body adapts precisely to such conditions. But when a child is born, he needs a new adaptation, this time to our world. It is difficult for any organ to immediately adjust, and even more so for the eyes. The eye muscles are not yet fully formed and do not have the necessary strength. Therefore, in the first days of life, the eyes squint a little. However, there are other causes of strabismus in newborns:
- Complicated childbirth and pregnancy. The fact is that the entire system of the longitudinal brain fasciculus, located behind, is responsible for the synchronous functionality of the eyeballs. If during pregnancy there is hypoxia of the unborn child, weakened microcirculation or other pathological disorders, then microscopic hemorrhage occurs, which disrupts the synchronous functioning of the eyes. If the baby was born for this reason, then parents should prepare for surgery. Because this type of pathology does not respond to conservative treatment methods.
- Another reason is infection of the mother during pregnancy. These can be such simple diseases as acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, acute respiratory infections, measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria, etc.
- A stressful situation for an infant also leads to the development of strabismus. But the disease is most often temporary and manifests itself only during crying or hysteria.
- Presence of ophthalmological pathologies.
- Cerebral palsy, hydrocephalus.
- Infectious diseases - ARVI, influenza, measles, scarlet fever, rubella, diphtheria.
- Injury to the visual organ.
- Genetic predisposition.
Types of strabismus in an infant
IMPORTANT! When will strabismus in a newborn go away? This is probably the most important and worrying question for parents. In fact, strabismus is considered normal up to six months. If it does not go away during this period, then it is important to conduct a more thorough examination of the visual organs by an ophthalmologist.
The main types of strabismus in infants include the following:
- Depending on the time of development, the pathology can be congenital or acquired.
- Stability of manifestation: constant and periodic appearance.
- Degree of involvement: intermittent, unilateral and monolateral.
- Type of deviation: vertical and horizontal. The vertical type of strabismus is characterized by an upward or downward displacement. The horizontal type can be converging (the eyes are shifted towards the bridge of the nose), divergent (the eyes are turned towards the temples) and mixed.
- Development mechanism: accommodative, non-accommodative and partially accommodative.
What to do?
When parents discover strabismus in their newborns, they should immediately contact an ophthalmologist. Next, it is important to visit this specialist every two months. And only after reaching 6 months will the doctor be able to accurately diagnose and identify the type of disease. For six months, parents must independently stimulate the functioning of the eye muscle system. To do this, you need to give your baby only bright and large toys. It is very important to hang rattles above the generally accepted height so that visual concentration is correct. It is advisable to do gymnastics with your newborn every day. These can be simple but effective exercises. The child needs to be in a reclining position. Mom should pick up a bright toy and move it from one side to the other. At the same time, the baby will follow the movement of the object and exercise his eyes, which leads to strengthening of the eye muscles. Then the toy must be moved up and down. If the baby does not respond to the object, then take a toy with sound.
Strabismus in newborns: when does it go away?
Immediately after birth, the baby's eyes cannot fixate the gaze, but the first fixation is noted after a week of life. But it is also short-lived, so at this age it is almost impossible to make an accurate diagnosis. If only the slanting is very pronounced. The child begins to steadily fix his gaze with both eyes at the same time only after a month or a month and a half. But by six months he should be able to distinguish objects and fix his gaze on them synchronously. That is why this age is considered the maximum for making an accurate diagnosis.
When strabismus in newborns goes away - Komarovsky, as an experienced pediatrician, largely agrees with the opinion of his colleagues. Because this physiological feature is characteristic of infants due to the unformed muscular system of the eyes. The point is also that in the first month and a half, babies can only see in the horizontal direction. And only after that vertical vision develops. If this does not happen, then binocular vision is impaired. Therefore, Komarovsky believes that up to six months it is necessary to be especially attentive to the reactions of the child’s eyes.
Rules for the treatment of strabismus in newborns
There is no point in treating strabismus in newborns up to six months. But it is important to carry out certain manipulations during this period. Firstly, it is necessary to create conditions for the normal development of the visual apparatus. This involves good lighting in the room, placing toys at a certain distance and allowing the child to play with large toys. If the baby has other ophthalmological abnormalities, they must be treated in a timely manner. Since strabismus can occur against the background of a stressful situation, parents should avoid them. Namely, you cannot make sharp and excessively loud sounds, appear in front of the child suddenly, and so on. In a word, fear must not be allowed.
A few words about strabismus in children
Very often, newborn babies experience minor or severe strabismus, which is why many parents begin to sound the alarm. As for heterotropia in infants, Komarovsky calls this a completely natural phenomenon.
The fact is that in the first months of life there is an active development of eye motor skills and babies are not yet able to master it. Both symmetrical parts of the face are slightly shifted, so they cannot take the correct position. As a rule, after a few months the correct position of the eyes is restored and the strabismus disappears. Every day the child masters the skills of proper eye coordination, measuring distance, etc.
According to the pediatrician, strabismus up to 4-6 months is not a cause for concern, but if it does not go away after six months, you should seek ophthalmological help to eliminate the problem.
Dr. Komarovsky insists that parents should carefully monitor the behavior and vision of their beloved child in order to be able to detect the problem in a timely manner and prevent its progression. Speaking about existing visual impairments in a child, Komarovsky strongly recommends sending children with heterotropia to specialized preschool institutions.
You may be interested in: What is convergent strabismus in a child and how to cure it?
When will strabismus in newborns go away: temporarily or permanently?
Running eyes in the first weeks and sometimes months of a baby’s life are a normal phenomenon. Because of its occurrence, it is impossible to say that the baby has persistent strabismus, since this symptom is observed at this age in all children.
It appears due to imperfect functioning of some systems of their body. So, if a child is not even six months old, then his eyeball muscles are still in the development stage, as well as the brain system of the longitudinal fasciculus, which affects their movement. As soon as they are fully formed, strabismus will no longer be observed in the infant.
What can cause a child's vision to deteriorate?
The following reasons may influence the development of strabismus in an infant:
- injuries he received during childbirth;
- infectious diseases of the brain;
- close proximity of toys and rattles in front of the baby’s face;
- a complication that arose due to the lack of treatment for farsightedness, astigmatism and myopia;
- genetic predisposition;
- extreme mental or physical stress;
- congenital diseases such as Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, as well as brain tumors or microcephaly;
- inflammatory, tumor or vascular changes in the eye muscles;
- infectious diseases suffered by the mother while carrying the baby;
- injuries he received after childbirth.
Why do babies mow?
Dr. Komarovsky encourages parents to remain calm and prudent when assessing childhood strabismus. If we are talking about a baby who has just recently been born, then the reasons can be quite physiological: the muscles that hold the eyeball and allow you to focus your gaze on a certain point are very weak in newborns, because inside the mother’s womb this function is not required for the baby’s eyes. These muscles will become stronger by about 3-4 months, and before that the baby can “mow” as he pleases - to the right, to the left, in different directions.
There is such a thing as pseudosquint, which also applies to children. The skull of newborns has structural features; its two halves meet at a slight angle, and therefore visually an adult examining the baby may get the impression that the baby has strabismus.
If strabismus does not go away after six months, the reason may already lie in a disease called persistent strabismus; with this pathology, focusing the eyes is difficult, which is why the baby looks in different directions. Such strabismus, unlike physiological strabismus, does not disappear after six months or later as the eye muscles become stronger.
Persistent strabismus in a child can be a consequence of a previous pathology - often caused by hypoxic changes during the period of gestation and birth, if oxygen starvation caused damage to the visual centers of the brain, acute infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy, severe infections suffered by the baby himself, cerebral palsy , Down syndrome.
Komarovsky also emphasizes that there is a hereditary reason, and the baby could have inherited the unusual look from his parents.
In any case, after six months of “mowing” the baby, according to Evgeniy Olegovich, it is worth showing it to an ophthalmologist.
Features of vision in infants
All babies are born farsighted. In the first few months of their life, babies are able to distinguish only those objects that are located at a distance of 40–50 cm.
Vision in infants is approximately 2 times lower than in adults. In addition, the eyes take longer to develop than other organs – for three years.
In children, strabismus is often considered a temporary phenomenon. This is explained by the fact that newborns are not yet able to control the movement of their eyeballs. It is for this reason that the eyes periodically roll to the temples and look in different directions, after which they converge towards the nose. In addition, the eyeballs may roll back due to increased weakness of the eye muscles.
Often this physiological feature of newborns causes concern among parents, but in most cases this pathology goes away on its own. In fact, the eye muscles, like other organs, require some training. As the child grows up, he begins to look synchronously and control his vision, as the eye muscles become well strengthened.
Strabismus in infants is considered a normal physiological condition of the eyes, which disappears on its own 3–4 months after birth.
How to determine if a child has a disorder?
This pathology is quite simple to self-diagnose, and parents can easily notice the characteristic signs and symptoms of visual impairment:
- the child, despite the age of six months, cannot focus his gaze on one point (to check, you can use a small bright object that is interesting to the child);
- eye movement when tracking a moving object is not synchronous;
- if you shine a flashlight into a toddler’s eyes, one eye closes or generally “floats” to the side;
- to look at a toy that interests him, the child is forced to turn his head towards the object;
- the baby does not estimate the distance to objects, often bumps into it or cannot reach out and touch it because he is reaching for an object that is too far away.
Causes of pathology
True strabismus in children is not always congenital, and during the first three years of life, as binocular vision develops and develops, certain deviations may occur. Strabismus can accompany farsightedness or myopia, diseases of the central nervous system, and brain tumors. A child can develop strabismus after injuries, a blow to the head, or a traumatic brain injury.
The danger, as Evgeny Komarovsky says, lies in the fact that visual acuity gradually decreases in the squinting eye, and the child’s picture of the world is formed flat. If you hesitate and do nothing for treatment and correction, then over time the pathology will become less amenable to therapy.
If parents know that there were people in their family with strabismus or other problems with the organs of vision, it is important to show the child to an ophthalmologist regularly. Therefore, the Ministry of Health of Russia has established a certain sequence of medical examinations by an eye doctor: at 1, 3, 6 months, and then at a year, 2 years, 3 years, and so on until school age.
There are many types of childhood strabismus, and therefore the treatment of one type will differ from the treatment of another, and only a doctor of the appropriate profile can understand this.
Causes
Strabismus can be either a congenital or acquired pathology resulting from a complicated pregnancy or delivery. So, the cause of strabismus in infants can be:
- weak eye muscles are the main cause of physiological strabismus in newborns;
- difficult birth (including hypoxia or asphyxia of the child during delivery);
- infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy;
- fetal hypoxia while in the womb;
- the child has a neurological pathology (for example, increased intracranial pressure);
- congenital abnormalities of the motor muscles of the eye;
- genetic inheritance of strabismus from parents or close relatives;
- congenital pathologies of one eye against the background of a second healthy organ of vision:
- myopia;
- farsightedness;
- astigmatism (impaired shape of the eye lens);
- cataracts, corneal opacity;
- optic nerve diseases, etc.