Eyelashes are hair that is located on the lower and upper eyelids. They are designed to protect the eyes from small foreign particles. The roots of the eyelashes end in a bulb, which is responsible for hair growth. It is located approximately 2 mm deep in the eyelid. The cilium shaft consists of three layers: the core or shaft, the cortex and the cuticle. The latter serves as a protective shell from external influences.
What is it and why can it hurt?
Eyelashes have the same structure as any hair on the human body:
- bulb or hair follicle;
- sheathed rod:
- hair shaft.
You can often hear complaints about pain at the roots of hairs. This problem can be caused by several factors, ranging from ordinary fatigue to more complex diseases of the eyelids or eyelashes.
If your eyes hurt from overwork, the main symptoms are a feeling of sand under the eyelids, redness of the whites, swelling of the eyelids and tearfulness. With such external manifestations, it is worth leaving the activity that causes such problems for a while and giving your eyes a rest using soothing measures. Compresses made from strongly brewed tea will help.
Other reasons why eyelashes hurt can be caused by diseases or parasitic lesions of the bulbs:
- Demodectic mange or eye mite often affects people with weak immune systems. The location of small arachnid creatures is the hair follicles of the eyelashes and eyebrows. The main symptom of the disease is irritation of the eyelids at the roots of the hair and itching. My eyes and eyebrows itch very much in the morning. Then redness of the skin at the base of the hairs and peeling become noticeable. Ticks threaten the complete loss of vegetation around the eyes as they destroy the roots.
- A stye on the eye is formed due to inflammation of one or more hair follicles. This pathological process in the skin of the eyelid is accompanied by the formation of an abscess, which, depending on the location, is divided into external and internal barley. In medicine, the disease is called hordeolum.
External purulent inflammation of the eyelid is a more common phenomenon than internal hordeolum and is characterized by pain, the sensation of a foreign body in the eye and a local increase in temperature.
Our readers recommend!
The cause of the disease in most cases is staphylococcus.
- Chalazion translated means “hailstone” or “knot”. This disease is marked by the appearance of a tumor on the lower or upper eyelid due to blockage of the sebaceous gland, which swells inside the skin.
- Blepharitis is an inflammatory process of the skin at the edge of the eyelashes, which is characterized as a chronic disease and is accompanied by redness of the eyelids, swelling, itching and flaking. Blepharitis can be caused by a fungus, infection, mites, or bacteria.
Treatment of eyelash diseases
Treatment of eyelash diseases
As you know, eyelashes are hairs located on the free edge of the eyelid and protect the eyes from foreign bodies. Eyelashes are structured in the same way as hair. Near the eyelashes are the openings of the pampiniform glands, and the Meibomian glands lie in a dense mass of connective tissue. In total, there are about thirty such glands in the upper eyelid, and twenty-five in the lower eyelid. The main purpose of the Meibomian glands is to secrete oily lubricant from the eyelids and protect the skin from external influences. Doctors quite often diagnose diseases of the eyelids and eyelashes. Let's talk about the most common diseases and methods of treating them.
Conjunctivitis
Over thirty percent of all eye diseases are diseases of the conjunctiva. The leader among them is infectious conjunctivitis.
1. Infectious conjunctivitis
The cause of this disease is viruses and bacteria that enter the mucous membrane of the eye and cause inflammation. The occurrence of conjunctivitis is caused by general hypothermia of the body, a flu-like state, sand or dust getting into the eyes, as well as ENT diseases.
Conjunctivitis can be acute or chronic. Conjunctivitis is most common in kindergartens, schools and other educational institutions. Perhaps everyone knows the signs of conjunctivitis, since sooner or later any person living in society encounters this disease. The patient complains of severe lacrimation, redness, pain and pain in the eyes. With conjunctivitis, mucus and pus come out of the eye. Usually, upon waking up in the morning, the patient realizes that his eyelashes and eyelids are stuck together with dried pus.
Treatment
To treat acute conjunctivitis and remove pus, frequent rinsing of the eyeball is performed. For these purposes, you can use a solution of furatsilin or a two percent solution of boric acid; it is also possible to wash your eyes with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (pale pink). Between rinsing, antibacterial drops are instilled into the eyes in the dosage recommended by the attending physician.
Since conjunctivitis has a coccal flora, it is advisable to use antibiotics: albucid, tetracycline and tetramycin. In acute forms of conjunctivitis, it is strictly forbidden to put a bandage on the eyes, because only thanks to the blinking movements of the eyelids is it possible to separate and evacuate pus from the conjunctival cavity. Treatment for this disease can last from several days to several weeks, depending on the severity of the disease.
It should be said that conjunctivitis is a fairly contagious disease, so everyone who is in contact with the patient is recommended to put Albucid drops into their eyes as a preventive measure. Until the purulent contents are separated from the eye cavity, you should change the towel and bed linen every day. The disease is transmitted through dirty hands, contact with common household items, and also through airborne droplets.
You should not take inflammation of the conjunctiva lightly, because in severe cases, the cornea of the eye is involved in the inflammatory process, which ultimately leads to a decrease in visual acuity and the formation of an eyesore.
2. Blepharitis
There are simple blepharitis, ulcerative, seborrheic, allergic and demodectic.
Simple blepharitis is an inflammatory disease of the free edge of the eyelids. With simple blepharitis, there is a slight thickening of the edge of the eyelid. This disease is characterized by tender scales or thin yellowish crusts on the skin at the base of the eyelashes, as well as hyperemia. The eyes become sensitive to external irritants - dust, smoke, wind and get tired very quickly under artificial lighting. Blepharitis most often affects young adults and children. The main cause of the disease is constant exposure to a stuffy, poorly ventilated room and severe eye strain.
Treatment
First of all, a sick person is provided with a healthy environment. Eyelid hygiene plays an important role. Crusts and scales should be carefully removed. The edges of the eyelids are lubricated with a special ointment or almond oil. Also, for therapeutic purposes, the edges of the eyelids are lubricated with hydrocortisone-POS eye ointment - 1%. Instillation of eye drops is performed: natural tears or oftagel. In case of conjunctivitis, dexamethasone eye drops 0.1% are indicated.
3. Ulcerative blepharitis is essentially eczema of the eyelid margin. In a mild form, the disease is expressed by redness and thickening in some places of the edge of the eyelids, while the eyelashes stick together and pustules form at the base. A severe form of ulcerative blepharitis involves damage to the entire eyelid margin. In this case, the eyelids swell, become red and thickened, and become covered with yellow crusts. Most eyelashes die in ulcerative blepharitis. In addition, the edges of the eyelids may turn outward due to scarring, thereby causing excessive tearing. The cause of ulcerative blepharitis is scrofula.
Treatment
The crusts should be removed and a 2-5% solution of lapis should be applied every other day to the ulcerated areas. The edges of the eyelids are treated with yellow sedimentary mercury and washed with a light solution of sublimate. In addition, the doctor prescribes general treatment for the body.
4. Demodectic blepharitis
It is worth noting that blepharitis can be parasitic in nature. So demodectic blepharitis is an infection of the eyelids by mites.
Treatment
Reduce the level of parasite damage. The eyelids should be wiped twice a day with a cotton pad soaked in saline solution diluted in a 70 percent solution of ethyl alcohol and ether. Eye ointment is applied to the eyelids: hydrocortisone-POS 2.5% or dex-gentamicin ointment. Before going to bed, it is necessary to generously lubricate the edges of the eyelids with greasy ointment, this will disrupt the life cycle of mites. It is advisable to massage the eyelids followed by treatment of the edges of the eyelids.
5. Allergic blepharitis
The disease occurs through direct contact with an allergen and is the body’s reaction to an irritant. Allergic blepharitis in most cases is combined with inflammation of the eye mucosa. The disease can also be caused by increased sensitivity to medications, perfumes and cosmetics, dust, pollen, wool, feathers, fluff, cockroaches, household chemicals, and chemical air pollution.
Acute allergic blepharitis can occur unexpectedly. The first signs are swelling of the eyelids, profuse lacrimation, pain in the eyes, mucous discharge, itching of the eyelids, sensitivity to light. Typically, both eyes are affected.
Chronic allergic blepharitis has severe, unbearable itching of the eyelids. Exacerbations occur seasonally, as the body’s reaction to pollen during the flowering period of cereals, grasses, and trees.
Drug-induced blepharitis can develop due to the abuse of eye ointments and drops, as well as when the medication is administered orally.
Treatment
Of course, the most effective method is to remove the “culprit” allergen. To treat the disease, antiallergic eye drops are used - alomide and lecrolin. The eyelids are lubricated with anti-inflammatory corticosteroid eye ointment. In case of infectious-allergic blepharitis, the edges of the eyelids are lubricated with Maxitrol or Dex-gentamicin eye ointment.
Seborrheic blepharitis is usually combined with seborrheic dermatitis. A clear sign of the disease is the formation of many small thin gray greasy scales along the edges of the eyelids. In some cases, eyelashes may fall out and turn gray.
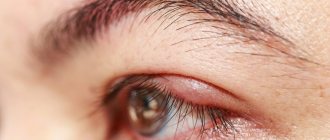
6. "Barley"
Acute purulent inflammation of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle of the eyelash, as well as the surrounding connective tissue, is popularly called “barley”. With the disease, there is pronounced inflammation in a limited area of the eyelid margin. The connective membrane of the eye and the edges of the eyelids swell greatly, sometimes it is impossible to open them. A yellow dot forms at the outer edge of the eyelid after two to three days. Barley occurs due to the entry of pyogenic microorganisms into the sebaceous gland.
Treatment
In the first days of the disease, warm lotions and poultices are applied. The edges of the eyelids are lubricated with ointment made from yellow sedimentary mercury.
7. Diseases of the tissue containing eyelashes
If there is a disorder in the tissue containing the eyelashes, it may happen that the roots of the eyelashes directed towards the eye will rub it and cause chronic inflammation of the cornea and connective membrane. The cause of this disease may be chronic blepharitis.
Treatment
Eyelashes that are in the wrong position are removed with tweezers. But the most effective remedy is electrolysis.
Double row of eyelashes
This is a congenital anomaly in which one row of eyelashes is in a normal position, and the second one touches the shell of the eye. The deficiency can be eliminated surgically in the clinic.
As you can see, there are a lot of diseases of the eyelids and eyelashes, but it’s not in vain that they say that prevention plays an important role in preventing the disease.
Therefore, follow basic hygiene rules, never use other people’s towels, eat right and strengthen your body. In most cases, eyelid diseases cause a decrease in the human body’s immunity, as a result of which it cannot resist diseases. But, if, nevertheless, you notice signs of the diseases described above, consult a doctor immediately. Unfortunately, the mentality of Russians is such that ordinary redness of the eyelids is not considered a serious illness. But an advanced case can not only cause the loss of eyelashes, but also lead to a decrease in visual acuity. In the section Eyelash diseases Tags: blepharitis, eye inflammation, eyelid diseases, conjunctivitis, barley
What can lead to purulent inflammation of the glands
Styes on the eye are the consequences of damage to the hair follicle by staphylococcal or streptococcal bacteria.
In 90% of cases, it is this infection that causes inflammation of the glands at the roots of the eyelashes. More often, children with weak immune systems are exposed to such neoplasms on the eyelids. Less commonly, adults succumb to pathological processes in the skin on the eye. Foci of infection in the body that have become chronic, and diseases that reduce immunity, can provoke the frequent appearance of inflamed tumors on the eyelids.
These factors include:
- untreated caries;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- chronic sinusitis;
- helminthic lesions;
- diabetes;
- HIV infection.
Blepharitis - what kind of disease?
Blepharitis is an inflammation of the eyelids that affects the outer edges of the eyelids. This concept combines a whole group of pathologies with similar symptoms. In most cases, blepharitis is chronic, but there is also an acute form of inflammation.
Depending on the location of the lesions, blepharitis is divided into anterior marginal, posterior marginal and angular. In the first case, the inflammatory process affects the edge of the eyelids along the eyelash growth line, in the second it spreads to the meibomian glands. With posterior marginal inflammation of the eyelids, the conjunctiva and cornea can often be affected. Experts note that most often these two types of blepharitis appear in parallel. In the angular form of blepharitis, the damage affects the corners of the eyes.
Most often, eyelid inflammation occurs in adults over 40 years of age, but sometimes children also suffer from it. Blepharitis must be treated, because its long course can lead to complications such as keratitis, conjunctivitis, decreased visual acuity, or chalazion.
It is worth noting that the disease is quite difficult to treat, and in rare cases, complete recovery can be achieved. But it is quite possible to reduce the risk of complications and the frequency of exacerbations with properly selected therapy.
Reasons why eyelashes become light at the roots
Premature graying of hair around the eyes is called poliosis. With this anomalous phenomenon, the hair around the eyes loses its natural color while the rest of the vegetation on the body has not changed color. Polyosis or white roots can be observed in young people whose age is not conducive to gray hair.
In medicine, it is generally accepted that the cause of this phenomenon is a shock, a long stay in depression, or severe stress experienced. Another source of premature whitening of eyelashes may be a surgical intervention with complications or the presence of an ailment such as trigeminal neuralgia.
Eyelashes are colored by the hair root. But due to the stress it has experienced, it ceases to perform this function and the hair around the eyes becomes white. The white hair no longer changes its color and retains its shade for the rest of its life.
Traditional recipes for relieving itching
Inflammation of the glands at the roots of the eyelashes can be caused by various reasons. In order to get rid of such a symptom, you need to know the exact diagnosis of eye disease.
At home, calendula tincture will help get rid of itching due to demodicosis. A small amount of liquid should be applied to a cotton pad or napkin and wipe the edges of the eyelids, being careful not to get the drug on the mucous membrane. In parallel with this procedure, you need to apply Demalon ointment to the roots twice a day, which will have a negative effect on the pathogens.
For eyelash lice, which is also accompanied by itching, a decoction of tansy helps well. To do this, you need to brew 1 tablespoon of crushed inflorescences in half a liter of hot water and leave for an hour. Then you need to strain the infusion and wash with warm liquid several times a day.
For blepharitis, chamomile and calendula flowers will help relieve itching. Half a teaspoon of each herb should be brewed like tea in a glass of boiling water. The infusion should be allowed to stand for 10-15 minutes and then strained. This tea is consumed orally, 1/3 cup three times a day. At the same time, you can apply fresh basil leaves to your eyes. The plant needs to be washed, slightly dried with a towel and crushed to release the juice. In this form, it should be applied to the eyelids for a few minutes for 3-5 days.
What to do if your eyes hurt
If you experience any unpleasant sensations after eyelash extensions, you need to contact an extension specialist to remove artificial hairs, and then see an ophthalmologist.
If your eyes hurt after eyelash extensions, you can treat them with pharmaceutical products prescribed by a doctor or with your own methods. In the latter case, you should be careful; not all methods are effective and will completely help if discomfort occurs. Improper use of drugs can worsen the situation or cause allergies.
Folk remedies
Procedures using folk remedies will help if your eyes hurt after eyelash extensions. They are effective for swelling, itching and redness, but are not very disturbing. The effect will occur within two to three days. To eliminate unpleasant sensations, remove the eyelashes, then use:
- Tea compresses in bags. They relieve redness and help if the eyeballs hurt. Take black or green tea and brew it. Make a compress using cotton pads or gauze and leave for 10-15 minutes.
- Compresses made from decoctions of chamomile, calendula or sage. Helps with inflammation of the eyeball. Boil the decoction, leave to infuse for an hour, and then moisten cotton pads, apply to the eyes, and leave for 30 minutes. Repeat several times a day.
- A mask of crushed aloe or Kalanchoe leaves. They are applied to the areas around the eye that have become red after eye extensions for 10-15 minutes.
- Oatmeal. Helps if your eyes hurt after eyelash extensions, with irritation and itching. Boil it, wait until it cools completely and, wrapped in gauze or bandage, apply it to the eyes and leave for 5 minutes.
- Cucumber juice. Eliminates swelling and redness. Recommended to use if your eyelids hurt. Using a sterile bandage, apply a compress for 15-20 minutes (the same can be done with grated raw potatoes). This helps tighten the skin around the eyes and give them freshness.
- A piece of cold wheat bread. It will help with redness, burning, if your eyes hurt after eyelash extensions. It is applied to the eyelids for 5-10 minutes.
- A decoction of dry dill. Leave for 30 minutes and wash your eyes with it 3-5 times a day. It helps against itching, redness and swelling.
To be effective, you can combine several procedures at once, applying them at intervals of 20-30 minutes. Each can be used 2-3 times a day.
Drug treatment
For more serious consequences after eyelash extensions, doctors prescribe medications:
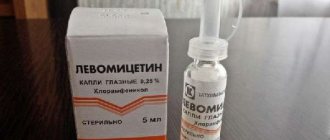
- Eye drops "Albucid" (sodium sulfacyl). They have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects for various purulent diseases (barley, conjunctivitis and others) or for itching and burning.
In severe cases, use 2-3 drops in each eye every 4 hours (more is possible). To treat diseases at the initial stage, drip 1-2 drops every 8 hours (more if necessary). The course should last 7 days.
- Visine. It is used if the eyes hurt, against redness and itching caused by exposure to chemical or physical factors, and during an allergic reaction. Use two or three times a day, one or two drops for 7 days.
- Vitabact. Effective against bacterial infections, to prevent complications. Use two to six times a day (depending on the progression of the disease), 1-2 drops in each eye. Extend the course to 10 days.
For allergic reactions, take antihistamines such as Suprastin, Zodak, Fenistil and others.
If your eye hurts after eyelash extensions, your ophthalmologist may prescribe other medications, so you should consult your doctor. If you refuse to visit a specialist, you should check the above medications for an allergic reaction and use them according to the instructions.
Rules to help maintain healthy eyelashes
The first and most important rule that will help prevent eyelash diseases is personal hygiene. It is also worth remembering that using someone else’s towel, mascara and other things can result in problems with the health of the eyelids and eyes.
Also, for the beauty and excellent appearance of eyelashes, you need to carry out strengthening procedures with natural oils, for example, castor oil. And soothing compresses made from green tea or sage, cornflower and chamomile flowers will relieve fatigue and moisturize the skin of the eyelids.
The article has been verified by the editors
General recommendations for treatment and prevention
Depending on the etiology of the disease, the ophthalmologist may refer the patient to doctors of other specialties - ENT, dentist, allergist, gastroenterologist. In the systemic treatment of various types of blepharitis, methods such as immunostimulation, vitamin therapy, and physiotherapy (darsonvalization, UHF, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy) are often used.
For preventive purposes and to increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is important to clear chronic foci of infection, increase immunity, normalize nutrition, and, if necessary, treat for helminths. For myopia, farsightedness, and astigmatism, it is important to choose the right means of vision correction together with an ophthalmologist.
In the treatment of any form of blepharitis, eyelid hygiene is very important. It involves cleansing of crusts and scales, tear replacement therapy, and in some cases, washing the conjunctival cavity. Eyelid massage and compresses on the eyes help improve the functioning of the meibomian glands and drain their ducts.
It is important to understand that blepharitis is a serious ophthalmological disease that is difficult to treat even by qualified specialists. If you self-medicate, this can lead to serious complications. Therefore, for any inflammatory processes in the eye area, consult a doctor.