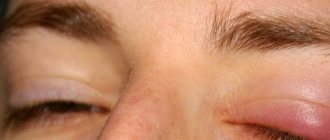
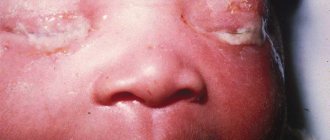
The occurrence of inflammation of the lower eyelid of the eye is a rather dangerous phenomenon, which can be the result of a serious pathology. That is why every person needs to be aware of all the main reasons that contribute to the occurrence of this problem. In addition, it is important to know the main symptoms of diseases that are accompanied by inflammation of the lower eyelid. What can cause this problem, what disease does it indicate and what to do about it?
The essence and symptoms of the problem
The cause of inflammation of the lower eyelid can be blepharitis. This is an inflammatory disease that occurs on the eyelids. The problem is that this pathology can last a very long time and then recur.
There are two types of blepharitis. In the first case, this is inflammation that occurs in the tissues of the ciliary area. In the second case, it is posterior marginal blepharitis, which affects the glands located inside the eyelid. This type of blepharitis can spread to the conjunctiva or cornea.
Main symptoms:
- a feeling of burning and itching in the area of the diseased eyelid;
- swelling of the eyelid;
- when pressing on the inflamed area, an oily liquid is released;
- the skin on the affected area may peel off;
- the skin on the sore eyelid acquires a reddish tint;
- visual heaviness of the century;
- excessive tearing;
- slow eyelash growth.
Sometimes, along with the above symptoms, blepharitis may cause blurred vision, as well as pain in the eyelid area. In some cases, eyelashes may fall out and cause severe swelling. General health may deteriorate, fatigue and lethargy may occur due to the fact that pain in the eyes interferes with even the usual daily activities.
Due to swelling of the eyelids, many people have difficulty putting on and wearing contact lenses. If the disease does not respond to treatment for a long time, complications may arise, such as eye styes, conjunctivitis and chalazion.
The clinical picture of blepharitis occurs suddenly and develops very quickly, so it is impossible not to notice the development of the disease. By the way, pathology can develop against the background of other ophthalmological diseases.
Treatment methods
Treatment largely depends on the underlying causes. An eye doctor or ophthalmologist may provide prescriptions or recommend some of the treatments. Factors to consider are age, medical history, location of the ulcers, and severity of the condition. Common treatments include:
Antihistamines and steroids
If the wounds, swellings, or ulcers are associated with an allergic reaction, then antihistamine eye drops or oral allergy medications should be used to help relieve the situation. Artificial tears drops can also be used to moisturize. For severe cases of allergies, steroid therapy may be recommended.
Antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral drugs
For bacterial, fungal, and viral infections of the eyelids, antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral medications can be used for treatment. They can be administered orally, topically, or by injection. Many of them are available by prescription.
Surgery
In severe cases of chalazion and xanthelasma, surgical procedures are recommended. Antibiotic eye drops should then be used after surgery to treat or prevent any potential infections.
Home Remedies
Minor eyelid problems can be easily treated using home remedies. A warm compress on the affected area helps increase blood circulation and, therefore, improve the condition and relieve itching. Other homemade products such as aloe vera, apple cider vinegar, avocado, tea bags and more can also speed up healing. These products are very effective for dry skin or swelling. Other home treatments include:
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Hygiene to reduce the risk of infection
- Rinse or wash your eyelids once a day
- Consultation with a nutritionist about proper nutrition that will help lower cholesterol levels
- Avoid substandard eyelash extension procedures
- Carefully monitor what your eyelids come into contact with to avoid allergic reactions.
- Moisturize your skin regularly.
It must be remembered that some causes may not respond to home remedies, so you should seek medical help if you suspect that home treatments are not working.
Infection
The occurrence of blepharitis is largely facilitated by various infectious diseases. Moreover, here it is worth talking not only about the entry of harmful microorganisms specifically through the eyes, but also about concomitant diseases. Treatment for inflammation of the lower eyelid may involve eliminating a fungal, viral or bacterial infection. Against this background, a weakening of the immune system may occur.
Pain in the upper eyelid and its characteristic causes
If the eyelid above the eye hurts, most often the cause is stye . To reduce pain before it matures, you can lubricate the swelling with alcohol solutions of brilliant green or iodine, or use antibiotics in the form of eye drops.
Know! Another common phenomenon that causes this symptom is inflammation of the frontal sinuses. When pressing on the eyebrows and above, pain occurs and there is a risk of infection spreading to the eyes.
Inflammation of the upper eyelid is also a sign of orbital cellulitis.
Very often this symptom accompanies purulent conjunctivitis. In this case, a number of other signs appear:
- swelling , accumulation of pus ;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- itching and burning, feeling of sand getting into the eyes;
- dilatation of blood vessels in the eyes, pain in bright light (photophobia);
- general weakness , headaches, fever, lacrimation.
Parasitism
One of the factors provoking the occurrence of the disease is damage to demodex mites. These parasites are very common, but the result of their vital activity does not often lead to the development of blepharitis. The activation of these parasitic organisms begins, as a rule, with a weakening of the immune system, with a general weakening of the body, or with other concomitant diseases. As soon as Demodex begins to actively multiply, it enters the eyelid tissue, where it interferes with normal blood flow and clogs the sebaceous glands. In this case, you need to aim not at treating inflammation of the lower eyelid, but at eliminating the subcutaneous mite.
Rare forms
Let's consider other inflammatory processes of the eyelids, which are not so common. First, let's talk about meibomeitis. The most common cause of the disease is coccal microbes. The development of meibomeitis is based on damage to the cartilage inside the eyelid. Most often, purulent secretion cannot come out, so the problem is solved surgically.
Impetigo is another inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of small pustules at the roots of the eyelashes. The causative agent of the disease is a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection. Impetigo is transmitted by contact and mainly occurs in childhood. The pustules disappear after a few days even without treatment.
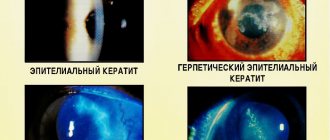
Molluscum contagiosum occurs more often in children. The viral infection is transmitted by contact and develops in a weakened body. Dense nodules appear on the skin of the eyelids, which do not cause discomfort. Lack of proper treatment can lead to chronic blepharitis, keratitis and conjunctivitis.
An eyelid abscess is a purulent inflammation of the eyelid. The formation is pink or dark red in color. When pressing on the abscess, severe pain occurs. The most common cause of an abscess is infection. The cavity is filled with bacteria and purulent secretion.
An abscess of the eyelid is a purulent inflammation that is treated surgically
Experts distinguish two forms of the disease:
- a skin abscess that develops on the outside of the eyelid;
- an internal abscess that can even affect the eyeball.
Attention! Antibiotics are unable to treat an abscess. To completely eliminate the pathological process, it is necessary to perform an autopsy followed by removal of pus.
Herpes eye infection is caused by the herpes virus type 1. The infection causes inflammation and scarring of the cornea. Even after successful treatment, the disease can return again. The exact causes of an outbreak of herpes infection are unknown, but doctors say that stressful situations, sunburn, and injuries may be associated with infection.
Mechanical damage
Trauma to the eye can also lead to the development of inflammation of the lower eyelid in a child and an adult. If the visual organ has really been damaged, hemorrhage may occur, for this reason the skin under the eyelashes acquires a bluish tint. Otherwise, the disease may develop as a result of a poisonous insect bite.
Treatment
To get rid of an unpleasant disease, you cannot do without the help of an ophthalmologist. First, a consultation is necessary to make a competent and accurate diagnosis. An experienced doctor must identify the nature of the pathology and determine the reasons that provoked the development of inflammation of the eye gland in the lower eyelid. The course of treatment will depend on the results of diagnostic measures.
Only a specialist can determine how to treat inflammation of the lower eyelid in an individual case. Treatment is based on drug therapy. The main objective of the course is to eliminate the causes that provoked the development of the disease and eliminate unpleasant symptoms. Depending on the nature of the pathology, special solutions and eye drops are prescribed.
If demodicosis has been detected, medications are prescribed that are designed to eliminate mites. Basically, such drugs are prescribed in the form of ointments, which are applied to the affected eyelid before going to bed at night. The components that make up such ointments have a negative effect on the vital activity of ticks, disrupting their natural life cycle. For this reason, their harmful effect on tissue is significantly reduced.
If the inflammation is allergic in nature, the task of therapy is first of all to eliminate the irritating factor - the allergen that caused the disease. If this is not possible, treatment consists of corticosteroid-type ointments, as well as antiallergic medications.
During treatment, it is especially important to adhere to good eye hygiene. For this purpose, special cosmetics are used, which are also recommended by an ophthalmologist. If you follow all hygiene recommendations, you can get rid of the disease much faster and prevent its recurrence.
Some doctors recommend following a special diet for acute forms of the disease. In this case, the diet should mostly consist of products of plant and dairy origin. It is advisable to consume meat only in boiled form. Excessively fatty and smoked foods, as well as alcoholic drinks, can aggravate the situation and intensify the inflammatory process.
Blepharitis
Inflammation of the eyelid margin can be caused by a variety of reasons, including:
- Meibomian gland dysfunction;
- bacterial infection. Bacteria live along the edges of the eyelids and at the base of the eyelashes, the excessive growth of which can cause activation of the pathological process;
- allergic reaction in response to exposure to a drug, microbes, cosmetics, dust, pollen, wool, food;
- autoimmune processes;
- fungal infection;
- long stay in dusty rooms;
- farsightedness and myopia;
- digestive problems;
- parasites. Blepharitis can be caused by Demodex mites. Usually, not only the organs of vision are involved in the process, but also the skin of the face. Acne, redness appears, and the oiliness of the skin increases;
- dry eye syndrome.
The disease causes itching and pain, swelling, redness, a feeling of heaviness in the eyelids, and lacrimation. Active loss of eyelashes, the appearance of scales, and pathological discharge may also be observed.
Symptoms of the disease may differ depending on the type of inflammatory process. Thus, with the demodectic form, intense itching is observed, which intensifies in warmth. There is a foamy discharge at the edges of the eyelids. The eyes quickly get tired and red. With the seborrheic type, scales appear on the eyelid that look like dandruff. There is a burning sensation, itching, and a feeling of the presence of sand. The ulcerative type is characterized by the appearance of purulent secretion on the edges of the eyelids. In the morning, the eyes stick together due to pathological secretions, so they are difficult to open.
Experts distinguish inflammation of the upper and lower eyelids. In the first case, swelling, redness, burning, severe itching, and narrowing of the palpebral fissure appear. Scales and ulcers appear on the side of the eyelash edge. In some cases, the process may affect general well-being, causing weakness and fever.
Folk remedies
Remember that with any disease, self-medication can lead to harmful consequences. Treatment of inflammation of the lower eyelid with folk remedies can be carried out only after the approval of your doctor. And do not forget to make sure before unconventional treatment that there is no allergic reaction or hypersensitivity to individual components.
However, it is recommended to use a special ointment to treat inflammation of the lower eyelid. For example, Erythromycin. Before doing this, you need to consult a doctor!
Oak bark
A decoction obtained from oak bark has pronounced anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, so it will be a very effective remedy for combating inflammation of the lower eyelid, a photo of which is in this article. To prepare the infusion, mix three tablespoons of ground oak bark with a glass of water. Heat the mixture in a water bath and keep it on the fire for about 25 minutes, then squeeze it out and add enough water to get 300 ml of the finished decoction. Rinse your eyelids frequently, but be careful not to get the liquid into your eyes.
Preventive measures against inflammation
The first thing you need to do to prevent the development of inflammatory diseases on the eyelid is to maintain the general condition of the body so that it can fight infections. A person suffers every day from harmful viruses and bacteria entering the body. In particular, this applies to the eyes, since the habit of rubbing the eyes with dirty hands provokes the development of pathogenic microflora. It is almost impossible to exclude this factor, so a healthy immune system is the key to healthy eyes and eyelids.
The main preventive measures for the inflammatory process of the lower eyelid include:
- proper and balanced nutrition, enriched with vitamin complexes; if this is not enough, it is recommended to use vitamins in tablets;
- In the morning after sleep, it is best to wash your face with cool water;
- Before you rub or scratch your eye, remember that there are a huge number of harmful bacteria on your hands, so wash your hands first, and only then can you touch your eyes;
- do not strain your eyes too much, limit your visual load, give your eyes a rest;
- Visit your ophthalmologist periodically as a preventative measure.
Remember that the eyes are a very vulnerable organ that is susceptible to inflammation and infections, which can later develop into a serious disease. All this, in turn, can threaten deterioration or even loss of vision. So, at the first symptoms of redness and pain in the eyelid area, immediately visit an ophthalmologist to understand the cause of the discomfort and receive competent recommendations for eliminating the symptoms. Do not self-medicate; only a complete diagnosis can help in making an accurate diagnosis and drawing up an effective course of treatment.
Barley
Barley is an acute purulent inflammation of the eyelids. The disease is accompanied by pain, redness, and swelling. The pathology tends to worsen in the autumn-winter period. Experts distinguish two main forms of the disease:
- external – damage to the hair follicle;
- internal – inflammation of the meibomian gland.
Often, the pathological process develops in response to a staphylococcal infection entering the hair follicle of the eyelash. Infectious agents can enter the body along with dirt and dust.
The disease occurs in four main stages. At the infiltration stage, itching, swelling, pain, and redness appear. After a few days, the inflammatory process ends with self-healing or the formation of a capsule within which pus forms.
Important! A stye may appear on the inside or outside of the eyelid.
It looks like a whitish formation on the edge of the eyelids. The cyst breaks out either independently or is done by a qualified specialist. After the pus drains, the capsule decreases in size, but a purulent secretion may still come out of it for several days. And at the last stage, a crust forms, under which healing processes occur.