A lump on the eyelid is not so much an unaesthetic phenomenon as it is painful, unpleasant and often even dangerous.
The seal can hurt, fester, and bother you . What does the body signal in such cases, what disorders and primary source diseases are “hidden” under a small bump on the eyelid?
Causes
Any lump or neoplasm on the eyelid, according to the ophthalmologist at the Excellent Vision clinic, A.V. Petrushina. — the body’s reaction to a virus, disease, inflammatory processes. All seals on the eyelid have their own nature and etiology. But there are common reasons, the so-called “risk zone” for the appearance of a lump on the eyelid:
- people over 50 - 55 years old;
- any previous eye disease;
- hormonal imbalance, dysfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- improper care and use of contact lenses can provoke pathology;
- stomach diseases, intestinal dysfunction, cholecystitis, any viral infection and even severe stress;
- poor hygiene (a woman does not wash off her makeup before going to bed or uses low-quality, expired cosmetics, uses false eyelashes, etc.);
- poor body resistance and weakened immunity are the root cause of any disease, including ophthalmological pathologies.
There are also reasons specific to a certain type of seal.:
- barley is a consequence of bacterial viruses and infections;
papilloma has “its own” virus and can appear anywhere on the body, including on the eyelid;- chalazion occurs from constant hypothermia and frequently transmitted acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections;
- The cause of the appearance of a boil is only staphylococcus aureus;
- The appearance of millet on the eyelid is explained by poor nutrition, genetic predisposition or metabolic disorders.
Types of seals
All seals that appear on the lower or upper eyelid are conventionally divided into subtypes:
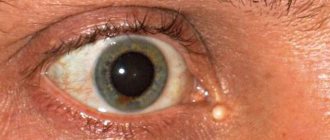
Papilloma
A benign lump, similar in appearance to a mole or wart, is small in size and can form on the eyelid. The surface is rough and can be located on a stalk.
Important. Papilloma is a cosmetic problem; it only brings psychological discomfort.
Melanoma (nevus)
Attention. It has the shape and size of a small mole, similar to a papilloma, but there is a risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Furuncle
Appears most often on the upper eyelid, next to the eyebrow. A dangerous and painful lump caused by inflammation of the hair follicle. Externally, the boil looks like a large eel and has dead tissue.
Important. It often has consequences (a scar remains) and complications may arise.
Xanthelasma
The formation looks like a small flat plaque. It has a yellowish color and is located on the eyelid and on the skin around the eyes. Over time, the compaction does not grow.
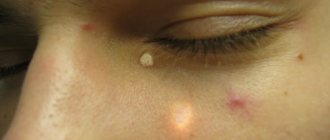
Milium
A white internal acne, called a prosyanka, is located on the upper or lower eyelid. It can be the size of a poppy seed, the compaction does not exceed 3 - 5 mm.
Important. It creates only an aesthetic problem, possibly rashes in groups located throughout the eyelid.
Chalazion
The literal translation is hailstone - a hard round-shaped compaction caused by chronic inflammation of the sebaceous glands, formed in the tissues of the cartilage, and does not come into contact with the skin. The formation is called cold barley, it can rot, and grows up to 5–7 mm.
Important. The formation can degenerate into a cyst; treatment is necessary.
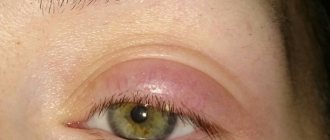
Barley
The most common pathology. The lump is painful and can be internal or external, depending on the type of inflamed gland.
What to do if a lump appears on the eyelid?
Lump on the eye
So, a lump appeared on the eyelid. It may be painful or cause no discomfort at all.
In this case, it will be located on the eyelash growth line or may swell on the inner side, on the conjunctiva, look almost invisible or create severe discomfort with its size.
What to do and what to do first so as not to cause harm?
In order to decide on the tactics of struggle, you will first have to find out what caused its appearance.
Barley
Improper treatment can only worsen the problem, and in some cases, threaten health and even life. Therefore, let's talk about diseases that cause bumps on the eyelids and how to treat these diseases.
It is difficult to confuse barley with something - a characteristic small abscess filled with a yellowish secretion, the size and shape of which resembles a barley grain.
When the sebaceous gland at the root of the eyelash becomes inflamed, an external barley is formed if one of the meibomian glands located on the inside of the eyelid, which secretes lubricant for the eyeball - the internal one - is affected.
The disease is provoked by problems with the immune system, hypothermia, and stress. Its first symptoms are itching, lacrimation, swelling of the eyelid and redness of the conjunctiva, a feeling of speck in the eye and pain.
After a few days, the abscess formed at the site of the affected gland is opened. Moreover, the entry of pus onto the mucous membrane of the conjunctiva and cornea during a breakthrough of the internal barley can lead to complications in the form of various inflammatory diseases.
When treating barley, eye ointments are used, for example, Levomekol, and drops with antibiotics, such as Gentamicin and Albucid, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs. Chamomile decoction and tansy flowers are widely known among folk remedies.
Timely initiation of treatment will help avoid the development of an abscess or speed up the process of its breakthrough and healing of the resulting wound as much as possible.
Under no circumstances should compresses or heat be used for barley - a warm, humid environment is favorable for the development of Staphylococcus aureus, which causes the disease.
If the stye has not opened within two weeks, you should consult a doctor to have it surgically removed.
Chalazion
Like barley, chalazion has a telling name: translated from ancient Greek it means “hailstone”. In Russian it is often called cold barley.
This is a slowly growing, painless, dense lump, formed due to a blockage of the meibomian gland duct, most often appearing in people suffering from chronic blepharitis or conjunctivitis, and also as a complication of stye.
The fatty secretion cannot come out naturally, which leads to the formation of a cyst. In the early stages of development, it causes virtually no inconvenience other than cosmetic ones.
But over time, it leads to the development of many complications: drying out of the eye due to non-closure of the eyelids, astigmatism resulting from constant pressure on the cornea, purulent inflammation and fistulas. Occasionally, a chalazion resolves on its own, but most often it cannot be treated without treatment.
If the cyst is small, it is treated with heat, drops and ointments containing antibacterial agents, anti-inflammatory agents; for larger lumps, corticosteroid injections are used directly into the cyst cavity.
An old chalazion is treated surgically; its removal is a simple operation that is performed under local anesthesia.
Externally, some oncological diseases, such as adenocarcinoma of the sebaceous gland, are very similar to chalazion.
Therefore, in some cases, especially in patients over forty years of age, a biopsy of tumor tissue may be necessary.
Xanthelasma
A flattened yellowish plaque, motionlessly soldered to the underlying tissues and not causing pain or discomfort is xanthelasma. Such a swelling can appear not only on the eyelid and is usually surrounded by several more of the same kind.
Most often, xanthelasma affects middle-aged women with metabolic disorders. Diabetes mellitus, obesity, hypercholesterolemia lead to their appearance.
There are no specific methods for getting rid of xanthelasma. Surgical removal is possible, but does not prevent the formation of new plaques.
In order for them to resolve naturally and not arise again, it is necessary to treat existing problems with lipid metabolism.
Prosyanka
Another disease along with barley, the characteristics of which are contained in its name. Millet, also known as millium, is a dense white ball under the skin, usually no larger than a grain of millet, but sometimes reaching the size of a grain of wheat.
In its origin, it is close to a chalazion, representing a sebaceous gland cyst, and can appear not only on the eyelid; its favorite localization is the skin of the cheeks.
Millions are usually completely harmless. They are treated not by an ophthalmologist, but by a dermatologist. Removing existing grasses in the doctor's office does not require anesthesia and takes no more than a couple of minutes.
Proper nutrition, which excludes too fatty foods, careful personal hygiene and the use of cosmetics to exfoliate dead skin cells will help get rid of old millia and prevent the appearance of new ones.
Furuncle
Of all the common eyelid diseases that manifest as lumps, this is the most dangerous. The purulent-necrotic process in the hair follicles and sebaceous glands, spreading to adjacent tissues, is not necessarily localized in the eyelid area, but sometimes appears there.
Most often, boils affect the upper eyelid closer to the eyebrow, where there are visible hairs on the skin, and much less often - the eyelash line.
Most often, the appearance of a boil is provoked by stress, colds and hypothermia - all those factors that negatively affect the immune system. Its development begins with the appearance of painful swelling, pain in the eye, and redness of the eyelid.
The first signs of inflammation are quickly accompanied by severe swelling of the periorbital tissues or the entire half of the face, as well as a general deterioration in physical condition: fever, headaches, weakness.
A few days later, the abscess opens, purulent-necrotic masses emerge from it. In its place remains a crater-like wound filled with the remains of dead tissue. After it heals, a depressed scar remains.
If you suspect a boil, you should not try to treat it yourself, but consult a doctor immediately. Under no circumstances should you squeeze it out - if pus comes out into the eye socket, this can lead to damage to the eyeball and brain.
To treat a boil, broad-spectrum antibiotics, dry heat, anti-inflammatory drugs, and, if necessary, painkillers and antipyretics are used.
Papilloma
Caused by HPV (human papillomavirus), small benign tumors most often form in areas with thin, delicate skin, which includes the eyelids.
Fleshy growths with an uneven surface on a thin stalk usually form in the corners of the eyes and at the eyelash line. They are painless, but due to their unpleasant appearance they often become a serious aesthetic problem.
A dermatologist removes papillomas. You can also remove them at home: pharmacies offer a large number of cauterizing and cytotoxic agents that are applied directly to the lump and after several applications lead to its necrosis and falling off.
However, some strains of HPV cause easily malignant papillomas, so even if they are quite small and few in number, before starting treatment you should be tested to identify the type of virus and determine further actions.
Some malignant tumors manifest themselves in a similar way to simple papillomas, therefore, if the surface of the suspected papilloma is not rough, but smooth, it ulcerates and bleeds, you may need to consult an oncologist.
Results
So, let’s briefly describe the most common reasons for the appearance of bumps on the eyelids:
A painful small abscess in the area of eyelash growth or on the conjunctiva - barley. A painless, round cyst on the inside of the eyelid is a chalazion. A yellowish flat plaque adherent to the surrounding tissues is xanthelasma. A small white subcutaneous formation is a millet. A painful abscess at the roots of the eyelashes or closer to the eyebrow growth line, accompanied by swelling and a general deterioration of the condition - a boil. A soft tumor on a stalk is a papilloma.
With proper treatment, all of them go away without consequences. The main thing is not to be overzealous in self-medication and not to start the problem due to fear of the hospital or a careless attitude towards your health.
Symptoms
Attention. Each seal has its own manifestations, signs and symptoms, according to which only a doctor makes a diagnosis.
Features of seals on the eyelid:
- Papilloma is a pathology without pronounced symptoms; only in some cases (mechanical damage) the mucous membrane or skin around the formation itself may turn red.
- Furuncle - the disease has several stages. First, the eyelid turns red, within 1-2 days pain and swelling appears at the site of the lump, and the lump becomes covered with a yellow crust. The pus almost always comes out on its own. Accompanying symptoms are severe swelling of the eyelid, fever, weakness.
- Xanthelasma - there is no pain or other unpleasant symptoms, such a thickening is evidence of non-eye diseases (diabetes mellitus, fat metabolism disorders, etc.).
- Milium is also an asymptomatic formation; no swelling or pain is observed. Inflammation is possible when an infection occurs if the patient tries to open the millet himself.
- Chalazion - hailstones do not cause pain when touched. When enlarged, the lump becomes noticeable, the skin becomes tense, redness and painful itching appear. Possible swelling and fever, tearing.
- A cyst is an advanced stage of a chalazion. The structure has a mucous content, the walls are dense, the cavities are filled with pus and liquid. The symptoms are pronounced - vision becomes “foggy”, dots appear before the eyes, lacrimation and pain increase.
- Barley is an acute inflammation of the follicles or sebaceous glands, always accompanied by redness of the eyelid and suppuration. Despite the rather large size of the lump, there is no great danger or complications. In most cases, self-opening occurs. The main thing is to prevent infection from getting to the eyeball itself.
Chalazion
Cones of this type are quite common. They develop from a sebaceous gland whose duct is blocked. This formation is also called a “grading lump” or “cold barley.” The continued production of sebaceous gland secretion leads to the accumulation of a viscous mass in the capsule, which stretches and thickens, taking the form of a dense lump. On palpation, the contents under the skin feel like a moving ball.
Cold barley develops at a slow pace, so it does not cause pain. Only a formed hard capsule can cause pain when squeezed. If a chalazion is not treated, it can develop into a cyst. As the lump develops, the risk of complications increases: inflammation, formation of a purulent fistula, granulation.
There are cases where chalazion spontaneously resolved without medical intervention. However, most often this formation does not develop back and requires prompt and conservative help. Treatment for such a lump on the eyelid is prescribed by an ophthalmologist. If the chalazion is small and not old, you can limit yourself to UHF therapy, ointments and eye drops. More severe cases are treated by injecting corticosteroids into the capsule cavity. Local drugs (ofloxacin, dexamethasone, sodium sulfacyl, hadrocortisone, levofloxacin, tetracycline ointment) can also be used as an addition to the injection.
If drug therapy is ineffective, the doctor decides on surgical treatment. The operation to remove a chalazion is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no longer than 15 minutes.
Diagnostics
A lump on the eyelid can be of different sizes and origins, it can be a benign lump, or it can become a huge problem and degenerate into a malignant formation.
As soon as the first symptoms appear, you should immediately seek help from a special clinic for examination.
An ophthalmologist performs a step-by-step diagnosis:
- the eyelid is examined from the inside and outside, depending on the location of the formation of the seal;
- the necessary blood tests are prescribed;
- If necessary, a biopsy and x-ray are performed.
Important. Based on the examination, the specialist makes an accurate diagnosis, gives appropriate recommendations and prescribes treatment.
Treatment
At the initial stage, local treatment is used - massage and heat therapy (warming compresses - 2 - 3 times a day or heating with ultraviolet rays).
Special eye drops are used - the purpose and dose are determined by the attending physician. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics (if the sebaceous glands are inflamed) in tablets or injections.
In modern clinics, a helium-neon laser is often used to resolve seals .
Attention. Breakthrough of the seal indicates positive dynamics of the disease.
In acute and chronic forms, drugs are injected directly into the lump itself. Throughout the entire treatment period - up to 2 weeks, the patient must be regularly monitored by a specialist .
Operations are carried out in exceptional cases, often using innovative laser technologies, which allow the seal to be removed without leaving a trace and without pain.
Features of treatment of different types of neoplasms:
Papilloma
It can be successfully removed with a laser if it enlarges or grows. It is also easily cauterized with iodine or celandine.
Important. Antiviral treatment is necessary to eliminate the harmful papilloma virus.
Furuncle
Important. You cannot open the abscess yourself; blood poisoning is possible.
Antimicrobials and antiseptic medications are usually prescribed. For healing, it is recommended to use lotions with aloe juice. In severe cases, the boil is opened in the hospital, the wound is drained, and then bandages with an antiseptic are prescribed.
Xanthelasma
It is removed only when the seal has grown to an impressive size. In this case, the primary disease is treated.
Milium
Millet is removed using all kinds of manual techniques (only by a specialist!) or laser; electrocoagulation is also used. In folk medicine, cucumber and viburnum juice are used. For inflammation of such formations, antimicrobial drugs are prescribed.
Chalazion
Local treatment is tetracycline, chloramphenicol ointment, compresses based on any antibacterial agents are used.
Treatment and rinsing of the eyes with Miramistin or any antiseptic is prescribed, and hydrocortisone drops are used. The medicine is also injected directly into the lump itself (kenalog or diprospan). The last resort is surgery under local anesthesia or laser dissection and removal of the capsule. Additionally, warm compresses and Kalanchoe lotions are used.
Cyst
When an infection occurs, drops are prescribed (dexamethasone, sofradex, etc.). Usually, the cyst is removed with medication in 10–14 days. Otherwise, surgical removal is necessary.
Barley
External stye is treated with antibacterial ointments (erythromycin, etc.). Internal - Tobrex or Albucid drops. For rinsing, use a solution of chlorgrexidine. The help of a surgeon is resorted to in very rare cases. Natural antiseptics are also used for treatment - a decoction of chamomile and sage soothe the skin, relieve swelling and redness.
Complications and preventive measures
If there is a lump in the eyelid area, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. For this, the patient is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist. The patient may be prescribed additional diagnostics, laboratory and instrumental testing.
It is forbidden to squeeze out, pierce or open the seal yourself. Otherwise, secondary infection of the cone will occur. Self-squeezing causes partial removal of pus, which can lead to complications.
The lump itself poses a danger to the patient. The larger it is, the stronger the pressure on the eyeball. The outflow of fluid and blood is disrupted. This can cause astigmatism and vision loss. Complications of a lump that appears on the eyelid include suppuration. If the infection penetrates into the formation, an inflammatory process develops. The patient complains of pain, severe swelling and redness of the skin. The possibility of developing an abscess and phlegmon is possible. Rarely, a chalazion is malignant. Prevention of the appearance of a growth in the eyelid area consists of proper nutrition and adherence to the rules of daily hygiene.
Originally posted 2018-05-26 17:46:10.
Prevention
The first and basic rule is clean hands, personal hygiene (linen, cosmetics, towels).- Strengthening the body through proper nutrition, hardening and sports.
- Passing a regular medical examination, visiting an ophthalmologist at the first signs of pathology.
In conclusion, it is necessary to recall: any seal on the eyelid cannot be ignored, much less treated independently. Only a doctor can determine how dangerous the tumor is, whether complications are possible, and how to get rid of it without harm to health.
The article was written by A.V. Petrushina, an ophthalmologist at the “Excellent Vision” clinic.