Retinal angiosclerosis is a pathology associated with impaired functioning of the visual analyzer. This is one of the most dangerous eye diseases, requiring a competent approach and timely drug treatment. If symptoms are ignored, the patient risks developing chronic vision problems or complete blindness. The causes of the disease lie in instability of blood pressure, but there can be many provoking factors. A number of experts consider angiosclerosis not as an independent disease, but as one of the stages of an even more severe pathology - hypertensive retinopathy.
Retinal angiosclerosis: what is it?
Atherosclerosis of the retina, what is it?
The sensitive tissue layer located on the inner back of the eye is the retina. Its function is to convert light signals into nerve signals, and they already serve as a signal for the brain.
This is the basis, consisting of nervous tissue, which provides vision. Its structure consists of ten layers, where there are cellular tissue, nerve cells, and many blood arteries, which ensure metabolic processes and normal functioning of the retina.
Numerous studies of the fundus have confirmed that atherosclerosis of this part of the eye in ophthalmology is the most common problem associated with vascular pathology and causing serious problems with visual impairment. This disease occurs against the background of atherosclerotic manifestations of cerebral vessels, but this can occur in any part of the human body.
Increased pressure in the arteries, metabolic disorders, disruptions in the functioning of the heart, all this can cause changes in the walls of blood vessels, their narrowing and, as a result, a decrease in blood flow.
One of the most serious and common pathologies is retinal detachment. This is caused by malnutrition. This complication requires immediate surgical intervention, as it can lead to loss of vision.
Indirect provoking factors
There are a number of factors that, in addition to hypertension, increase the risk of developing retinal pathologies. These include:
- diabetes;
- bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking);
- eye and head injuries;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- elderly age;
- blood clotting disorder;
- autoimmune diseases that are accompanied by inflammation of the inner lining of blood vessels.
If the professional activity of a hypertensive patient involves frequent contact with toxic substances, this can also become a trigger for the development of vision problems. Aggressive chemical compounds poison the entire body and worsen the course of hypertension, which, in turn, leads to the development of complications in other organs and systems. In addition, harmful working conditions negatively affect the functioning of the liver and brain, so it is better for weakened people to avoid such work and give preference to other specialties.
Without treatment, retinal angiosclerosis threatens vision loss and thrombosis
Progressive angiosclerosis without the necessary treatment often causes the development of retinopathy and swelling of the internal structures of the eye. Retinopathy is a complex of pathological changes in the retina, which can lead to retinal detachment, scarring and complete blindness. To prevent this, you must immediately contact an ophthalmologist if any questionable eye symptoms appear.
Causes of atherosclerosis of the ocular vessels
Among the most common causes of the disease, pathological changes are observed in the form of:
- Arterial hypertension;
- Generalized atherosclerosis.
With high blood pressure, the vascular walls throughout the body are first affected.
Ophthalmologists are among the first to detect hypertension by changes in the circulatory network of the eye, since one of the accessible places to recognize these changes is the fundus of the eye.
Having discovered vasospasm or atherosclerosis in the vessels of the nerve membrane of the eye, they firmly confirm hypertension.
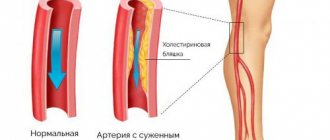
The cause of hypertension and other diseases associated with disorders of the vascular system is elevated plasma cholesterol over a long period. The causes of retinal atherosclerosis are fatty deposits in the vessels, which interferes with normal blood circulation.
This can happen for several reasons:
- Due to sleep disturbances, constant overwork or being under stress;
- Lack of physical activity and, as a rule, a decrease in metabolic processes in the body;
- The cause may be excess weight, fat accumulation and metabolic disorders;
- Smoking and alcohol, which are provocateurs of vascular spasms and their damage;
- Wrong foods that contribute to the development of vascular plaques due to “bad” cholesterol in large quantities.
With atherosclerotic lesions, plaques form that interfere with normal blood circulation, and oxygen ceases to flow sufficiently. And this is a direct path leading to the formation of blood clots, poor coagulation and serious pathology of the vascular system. As a result of these negative manifestations, the fundus of the eye, its stem branches and the central vein become easily vulnerable.
Limited blood supply atrophies retinal tissue, damages small capillaries, forms blood clots and reduces the elasticity of the arteries.
Sometimes the disease is not detected for years, since the signs of the disease are often concomitant. The clinical picture is often expressed by spasms in the circulatory system of the eye, blockage in thin arteries and their rupture. Therefore, often, the disease can only be identified during a crisis period, with a sharp drop in vision and the formation of edema.
Review of medications
It is impossible to prevent the development of retinal angiosclerosis without medications. Ophthalmologists warn that almost all medications will have to be taken for life. In order to avoid possible complications, you will need to take not only specialized medications for the eyes, but also medications that normalize blood pressure and stabilize the condition of blood vessels.
Table. List of necessary drugs.
| Group of drugs | List of the most effective drugs |
| Calcium antagonists to prevent ion loss | Amlodipine, Felodipine |
| Beta blockers for adrenaline receptor inhibition | Bisoprolol, Nebivolol |
| Medicines with a pronounced diuretic effect | Indapamide, Hypothiazide |
| Angiotensin receptor antagonists for rapid suppression of ACE activity | Losartan, Candesartan |
| Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors | Perindopril, Lisinopril |
Felodipin
Treatment is supplemented with blood thinning medications - statins. Rosuvastatin is considered one of the most effective.
Rosuvastatin
Symptoms of the disease
Bearing in mind that the causes of the disease are systemic in nature, atherosclerosis is usually observed in both eyes. At an early stage, symptoms are quite difficult to identify. If you identify the disease at an early stage, you can quickly and efficiently stop its development. To do this, you should understand and be able to distinguish its main features.
Its symptoms are very similar to the main symptoms associated with atherosclerotic lesions:
- Dizziness and frequent headaches;
- Pain and pain in the eye sockets;
- Deterioration of vision;
- General poor health and eye fatigue;
- At a later stage, double vision, fogginess, and loss of fields from the view appear.
Due to the slow blood flow in the capillary system of the eye, oxygen starvation occurs, the structure is disrupted and becomes tortuous, this can be seen when diagnosing the disease.
There are other reasons that contribute to the development of retinal atherosclerosis, these are concomitant ailments and various injuries, among them:
- Diseases of the vertebral thoracic and cervical regions;
- Surgeries on the brain and spinal cord;
- Extensive vascular lesion of a sclerotic nature;
- Endocrine system disorders;
- Various injuries and disruptions in blood flow;
- Heart pathologies.
Signs
Initially, the pathology does not manifest itself. The only thing that worries the patient is the periodic flashing of spots before the eyes and rapid overexertion, for example, when reading, watching TV or working at the computer. Most patients do not attach any importance to this and attribute everything to fatigue. As the problem develops, the unpleasant manifestations of the disease intensify. Common symptoms of retinal vascular angiosclerosis include disorientation in space, migraine, loss of image fields and a decrease in its clarity, tension in the eyes (it does not go away even during rest). Not so typical symptoms include tinnitus, sleep disturbances, memory problems, and regular nosebleeds.
Attention! In patients with angiosclerosis, the pupils react inadequately to light (possibly their excessive dilation or, conversely, narrowing).
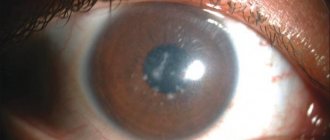
Already based on the patient’s complaints, angioscoerosis can be suspected. However, to confirm these assumptions and identify the nature of the problem, a number of diagnostic procedures are prescribed. First, the specialist examines the fundus of the eye. To eliminate pupil accommodation, a special drug is instilled into the eyes before this. During the procedure, the doctor evaluates the condition of the lens, eye chambers, retina and blood vessels.
In addition, fluorescein angiography is prescribed. It is needed to find out what condition the eye vessels are in and how passable they are. During the examination, a specialist can identify a violation of capillary tortuosity, swelling of nerve fibers, and disruption of the choroid plexuses. The essence of the procedure is the introduction into the body of a drug that has fluorescence (glow). As it moves along the capillary, the specialist can see the areas of narrowing and widening of the walls.
Diagnosis of the disease
First of all, the general picture of the disease and its symptoms are studied. An ophthalmologist deals with this problem. He conducts basic examinations and, through blood tests, determines the presence of cholesterol levels. Then it collects information about past complications, genetic predisposition and chronic manifestations.
To determine the stage of the disease, a specialist performs fundus ophthalmoscopy and fluorescein angiography of the vascular system. With the help of medications, such as tropicamine, atrophin, the pupils dilate, this allows for a high-quality examination, but vision may deteriorate for some time and the light sensitivity of the eyes will increase.
Ophthalmoscopy or fundoscopy is an examination that allows one to penetrate into the back of the eye and detect various pathologies of the retina, blood arteries, optic nerve head, and choroid.
In addition, the examination is carried out by:
- Visometry - determination of vision in the area affected by atherosclerosis, the condition of the entire fundus of the eye;
- Computer perimetry – examination of the periphery;
- Electrophysiological diagnostics - finding out how cells are able to survive;
- Tonometry - measuring eye pressure;
- MRI, CTM, ultrasound.
Using numerous diagnostic methods, through a serious examination, the following pathologies can be identified:
- The presence of narrowing of the lumen in the blood arteries, the thickness of their walls;
- Changes in arteriovenous junctions;
- Tortuosity of the structure of blood vessels;
- Hemorrhages, blood clots and swelling of the optic nerve;
- Location of changes.
Stages of development of hypertensive retinopathy
There are four main stages in the progression of the anomaly:
- Angiopathy. All changes that occur at this stage are reversible. There is an expansion of the veins and a narrowing of the lumen between them;
- Angiosclerosis. The vessels lose their elasticity, the walls of the arteries have different thicknesses along the entire length;
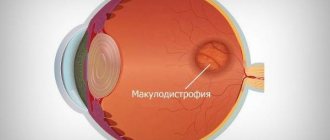
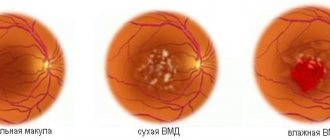
- Angioretinopathy. The retina swells, and opacities appear in places. A narrowing of the visual fields is diagnosed, and eye acuity decreases. Focal hemorrhages in the retina are observed, shaped like flames;
- Neuroretinopathy. At the last stage of progression of the disease, the optic nerve swells. A star or crescent-shaped image appears on the macula.
| The main danger of retinopathy is that it progresses at a rapid pace and can reach the final stage in just twelve months. Once neuroretinopathy develops, the disease cannot be stopped; in most cases, complete loss of vision occurs. |
Treatment
When treating atherosclerosis of the retina, the entire problem of the disease is solved, with the participation of an ophthalmologist and other specialists: a neurologist, a cardiologist and a therapist . The main focus of treatment should be thinning the blood flow, increasing the elasticity of capillary walls, with a mandatory reduction in cholesterol levels.
The nature of the pathology may be different, but the main thing in successful treatment is an integrated approach.
- Medications aimed at increasing blood supply to all structural parts of the eye. It provides treatment courses such as: mildronate, vasonite, solcoseryl, arbiflex. Due to the plasticity of red blood cells acquired under the influence of drugs, they quickly move through the narrowed capillaries. Medicines should be selected on a personal basis, taking into account the characteristics of each patient’s body, chronic and concomitant diseases. Often, medications are taken by instillation into the eyes. With conventional drug therapy, the following are prescribed: angioprotectors, vasodilators, antiplatelet agents and anti-sclerotic agents.
- Taking vitamin complexes necessary to maintain health.
- A diet based on the prohibition of eating foods high in calories and carbohydrates, and limiting salt. With strict adherence to the correct diet, the effectiveness of treatment increases several times.
- Physical activity that promotes the flow of energy into muscle tissue and accelerates metabolic processes, removing toxins and salts from the body.
- Quitting bad habits, such as alcohol and smoking.
- Physiotherapeutic methods such as laser, magnetic therapy or acupuncture.
- Reducing the load on the eye organs is also an important part of treatment. During the therapeutic period, it is worth stopping sitting in front of the TV, computer and limiting reading books.
- Folk remedies that help enhance the healing effect. There are many recipes and recommendations based on many years of experience and cases of successful and quick recovery from illness.
Prevention of the disease
The main prevention is aimed at achieving normal blood pressure levels. For this purpose, it is recommended to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, avoid severe stress, nervous strain, and give up alcohol and cigarettes. It is important to promptly identify and treat diseases that lead to the development of hypertension. Such pathologies include diseases affecting the nervous, cardiovascular, endocrine, and urinary systems. To prevent sudden surges in pressure, an effective course of physiotherapy is indicated, including galvanization, electrosleep, hydrokinesis, and radon baths.
Patients who experience initial manifestations of angiosclerosis should immediately seek help from an ophthalmologist. Only through timely receipt of medical care can dangerous complications and irreversible deterioration of vision be avoided.
Atherosclerosis is a common progressive disease of the vascular system, manifested by narrowing of blood vessels or complete blockage. The source of pathology can be localized anywhere, the organs of vision are no exception. The consequence of the pathology is ischemia, organ dysfunction, and disability. Atherosclerosis of the retina is dangerous due to the development of complications and complete loss of vision.
Treatment with folk remedies
Helpful inclusions in your diet include:
- Juices of fresh vegetables and fruits, especially parsley;
- Infusion of dill seeds;
- Tea using red rowan berries and black currant leaves.
Herbal mixtures from medicinal herbs and plants:
Recipe No. 1
- Chamomile-100g;
- St. John's wort-100g;
- Immortelle-100g.
Infuse with half a liter of hot water and drink throughout the day.
Recipe No. 2
- Valerian rhizome - 20 g;
- Melissa-20
A glass of hot boiling water. Drink for 20 days in small portions before meals.
It should be noted that consultation with a specialist regarding the use of any folk remedies is mandatory, as there may be contraindications and side effects.
To prevent the disease, such remedies as chokeberry fruits, red currant juice, and olive oil drunk on an empty stomach are successfully used. All these natural natural remedies contribute to excellent results.
What to watch out for
Patients suffering from high cholesterol levels should monitor their levels, reduce them in time, and do this for life.
You should constantly take medications that contribute to the normal maintenance of the ocular circulatory system, anti-sclerotic agents and vitamins, since an advanced stage of the disease can lead to dire consequences, such as:
- Glaucoma;
- Eye infarction;
- Nerve atrophy;
- Thrombosis;
- Recurrent hemophthalmosis;
- Loss of vision;
- Irreversible blindness.
Adjust your diet, do as much physical activity as possible, take homeopathic remedies and vitamins, monitor your cholesterol levels, quit bad habits once and for all, and check your eyes periodically. With timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment, your eyes will remain the mirror of your soul for a long time!