Causes of pathology
Intrauterine disruption of the formation of the vascular system leads to the appearance of hemangiomas after birth.
Dilated blood vessels group together and form a defect on the skin of the baby's eyelid. Main causes of the disease:
- genetic predisposition;
- Rh conflict - incompatibility of the blood of the mother and the embryo;
- multiple pregnancy;
- hormonal imbalances in the child or mother;
- viral diseases in early pregnancy;
- endocrinological pathologies of acute or chronic course;
- severe toxicosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- early delivery;
- Prematurity or underweight baby.
Unfavorable factors contributing to the manifestation of hemangioma:
Late pregnancy can provoke the formation of pathology in the baby.
- pregnancy at an older age;
- exposure to medications;
- environmentally unfavorable location;
- non-compliance with healthy lifestyle standards;
- unstable emotional state, increased nervousness.
Complications and prognosis
Hemangioma without treatment threatens to block blood vessels and cause blood clotting problems. When an injury occurs in the area where the pathology is located, bleeding develops, which is very difficult to stop. The expanding tumor puts pressure on surrounding tissues and nerves. Located near the eyes and ears, it can cause vision and hearing loss. With timely treatment, these complications can be avoided. The prognosis for hemangioma is good, as in most cases it goes away by the age of seven. After treatment, relapses almost never occur.
Symptoms of the disease
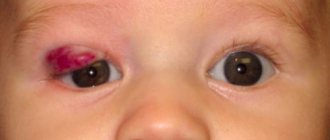
Hemangioma in a newborn is characterized by slight redness in the eyelid area. Subsequently, as the child grows, the tumor increases in size. The spot may be sharply defined or have no clear boundaries. The main manifestations of a neoplasm on the eyelids of an infant:
- the color of the tumor is from pale red to bright, possibly with a blue tint;
- swelling in the affected area, drooping of the upper eyelid;
- increased skin temperature at the site of formation;
- pain when pressed;
- enlargement of the tumor and increased coloring when stressed;
- blanching of the hemangioma upon exposure, followed by rapid restoration of the original color and size.
Indications for surgery
- violation of facial aesthetics;
- exposure keratopathy;
- compressed optic nerve;
- introduction of infection;
- amblyopia.
Treatment of eye hemangioma
The main methods of treating ocular hemangioma are subcutaneous steroid injections at an early stage of the disease, local resection of the tumor at later stages, and low-dose radiotherapy. A single dose of radiation for adult patients reaches 4 grays, sessions are done every other day. With the correct selection of the frequency of sessions, a good effect is achieved. It is also possible to use cryodestruction.
Prevention of eye hemangioma
Since eye hemangiomas begin in embryos, prevention includes monitoring and examination of women during pregnancy and preparation for conception. Before conception, it is necessary to treat chronic foci of infection, eyes, teeth, and ENT organs in advance. Avoid smoking and alcohol during pregnancy. Free the pregnant woman from hazardous work or transfer her to light work.
Blood pressure monitoring is necessary to exclude eclampsia.
If an eye hemangioma is detected in a newborn, immediately contact an ophthalmologist for examination and clarification of the diagnosis, following all instructions. Up
Diagnostics
If parents suspect such a formation, then they should show the baby to the doctor.
If a hemangioma is detected, it is necessary to show the newborn to a pediatrician or dermatologist. The doctor examines the affected area. To determine the extent and danger of a tumor, the following basic examinations are used:
- General blood analysis. Shows the state of the body and the hematopoietic system as a whole.
- Coagulogram is a study of blood clotting.
- Dermatoscopy is an examination of the tumor structure with a device that provides multiple magnification.
- Thermometry is the measurement of the temperature difference between healthy skin and the surface of the hemangioma.
- Thermography is the recording of thermal radiation from the skin, which determines the depth and boundaries of the tumor.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) is a study of the size, structure, size and depth of a neoplasm.
- Angiography - determination of blood circulation rate, size of hemangioma and spread to neighboring tissues using an injected contrast agent.
- Computed tomography (CT) is a cross-sectional scan of the affected area.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - detailed layer-by-layer visualization of the hemangioma and surrounding tissues.
- Biopsy is the removal of a sample of tumor tissue for microscopic examination.
- Histology - examination of the cells and structure of the tumor.
Why is it dangerous?
As the tumor grows, more and more capillaries and vessels are added to the tangle. In large hemangiomas, blood clots can form. This phenomenon leads to a decrease in the number of platelets in the bloodstream, which impairs blood clotting. Hemangiomas located near important organs, such as the ear, eye, nose, and respiratory tract, can lead to disruption of the functionality of these organs. Large tumors, growing, impair the baby’s vision and hearing, and disrupt his respiratory function.
When a cavernous hemangioma is injured, severe bleeding occurs that is difficult to stop. This is especially dangerous when the tumor is localized on internal organs. Their damage often leads to death due to bleeding into the liver, spleen, and brain. As you can see, hemangioma is not a completely safe neoplasm.
Despite the fact that most often the growth of a hemangioma ends by the age of one year, and by the age of seven it resolves, complications can arise at any time. That is why, if you find a spot of any size on your baby, you need to consult a doctor.
Treatment methods
Doctors recommend monitoring the growth dynamics of the formation.
In the first months after the birth of a child and the manifestation of hemangioma, observation of the tumor without medical intervention is recommended. During the first year of life, resorption and spontaneous disappearance of the defect may occur. If a neoplasm on the eyelid complicates visual functions, is susceptible to injury or grows, treatment or removal of the hemangioma is necessary.
Medicines
To eliminate hemangioma on the eyelid of a newborn, drugs of several groups are used in the form of local and internal effects. The form of use, duration of treatment and number of doses are determined by the attending physician to prevent complications and negative reactions. Fixed assets are described in the table:
| Drugs | Impact | Titles |
| Corticosteroids | Promotes resorption | "Diprospan" |
| Accelerate healing | "Prednisolone" | |
| Beta blockers | Reduces pressure in blood vessels | "Timolol" |
| Stop tumor growth | "Propranolol" | |
| Cytostatics | Stops excessive cell division and proliferation | "Vincristine" |
| Stimulate tumor regression | "Cyclophosphamide" | |
| Drops against glaucoma | Reduce the size of the defect | "Arutimol" |
| Prevention of growths | "Oftan Timolol" |
ethnoscience
After receiving permission from the doctor, you can try to get rid of the tumor with the help of mumiyo.
Home medicine recipes are used with great caution in infants with hemangioma in the eye area. There is a danger of developing allergic reactions, burns and tumor injury. Traditional methods are used after medical approval and in the proportions prescribed by the doctor. Basic treatments:
- Compresses: fresh cabbage leaf;
- green walnut juice;
- mumiyo;
- tea mushroom.
- celandine juice;
- linden tea;
Surgery
When a formation interferes with the baby’s vision, it should be removed.
Hemangioma on the eyelid of a newborn is dangerous due to complications. Removal of the tumor is indicated in the following cases:
- location that interferes with visual functions;
- bleeding and ulceration;
- accelerated growth;
- regular trauma to the eye area.
The main methods for eliminating a skin defect are described in the table:
| Method | Carrying out | Advantages | Flaws |
| Laser removal | Laser beam burning | Painless | High price |
| No scars | Multiple treatments required | ||
| Cryodestruction | Freezing at low temperatures | Painless | Scars |
| Sclerosis | Administration of drugs to seal the vessels feeding the tumor | Efficiency | Soreness |
| Healing time | |||
| Electrocoagulation | Exposure to electric shock | Low morbidity | Painful, only under anesthesia |
| No bleeding | Scarring | ||
| Radiation therapy | Radiation exposure | Efficiency | Duration of treatment |
| Negative effects on the body (not used until the 6th month of a baby’s life) | |||
| Surgical removal | Cutting with a scalpel | Use for large tumors | Effects of anesthesia |
| Bleeding | |||
| Scars |
Recovery
Antibiotics may be part of drug therapy in the postoperative period.
The duration of the rehabilitation period in a newborn after treatment of hemangioma depends on the method of exposure and the characteristics of the child’s body. After surgery, antibiotic therapy may be prescribed to prevent infectious complications, and local antiseptic drugs to disinfect surfaces.
Classification of hemangiomas
There are the following types of infantile hemangiomas:
- Capillary (simple) - occurs most often, is a network of capillaries intertwined. The vessels grow together, which gives the hemangioma a variety of colors: from all shades of red to brown and purple. Its dimensions are insignificant; in rare cases, hemangioma can reach large diameters. It is slightly raised above the surface of the epidermis, but does not grow into it. The more colorless the tumor, the more capillaries it contains that are not filled with blood. This indicates that the tumor is in the stage of reverse development and will soon disappear. Capillary hemangioma is a benign tumor that is a congenital cosmetic defect of the skin. Does not cause discomfort and does not degenerate into a malignant formation.
- Cavernous (cavernous) is a very rare tumor, characterized by the presence of cavities filled with blood. It receives nutrition from large arterial vessels and is located in the subcutaneous layer in the form of nodules and compactions. Its structure has a soft elastic consistency. The color of the skin above it does not change or acquires a bluish tint. When located cutaneously, the hemangioma does not spread deeply, so it can be treated with local techniques. When localized internally, cavernous tumors affect organs with an extensive vascular network (liver, spleen, lungs, kidneys and other organs), so there is a risk of bleeding due to blunt injuries to the abdomen or musculoskeletal system. Children's cavernous hemangioma of internal organs is asymptomatic and is often detected by ultrasound of neighboring organs.
- Combined - consists of a capillary and cavernous tumor located both in the subcutaneous layer and externally. Its clinical signs depend on the predominant form of the disease.
- Mixed - has a complex structure and contains not only vascular cells, but also connective, nervous and lymphoid tissues. The symptoms of manifestations depend on the predominance of certain tissues in the hemangioma.