11/06/2019 Obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct is one of the common pathologies of early childhood. The disease occurs in 5% of newborns. It is based on obstruction of the lacrimal duct with a plug from natural mucous secretions. In children, the nasolacrimal duct is quite narrow. When amniotic fluid, dust particles and mucus enter, a blockage occurs.
How to understand that a child has a blocked tear duct
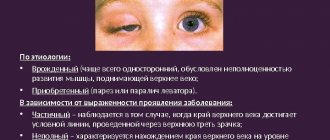
The first symptoms of tear duct blockage appear in newborns. Usually in this case, experts will formulate a congenital form of the disease. Parents notice their baby's tendency to tear up.
| If the disease is caused by the ingress of amniotic fluid with the formation of a mucus plug, the problem can be easily solved with a light eye massage. This method does not provide relief in the congenital form of the disease and the presence of certain anatomical defects. |
Symptoms of a blocked tear duct worsen when the baby cries. Children are sensitive to bright light, cold temperatures and windy conditions. Constant stagnation of tear fluid leads to blurred vision, which is accompanied by the appearance of a characteristic “veil” before the eyes. Constant flow of tears down the cheeks causes skin irritation and increases the risk of secondary infection. In this case, yellow-green crusts appear on the child's eyelids, and the eyelashes usually stick together. The disease can be complicated by dacryocystitis, obstruction of the lacrimal ducts with the formation of stones.
Manifestations of dacryocystitis in newborns
Symptoms of dacryocystitis in an infant develop in the first week of life. If the child is premature, then a little later - after 1-3 months. Most often the process is one-sided.
The following manifestations are distinguished:
- the child’s eyes are constantly wet due to stagnation of tears,
- the inner corner of the eye and part of the sclera are red,
- the lower eyelid has increased in size,
- Mucus constantly flows from the eye, which is why the skin on the cheeks begins to turn red and peel,
- discharge of pus from lacrimal openings,
- eyelashes stick together after sleep.
Symptoms most often subside within a few weeks. The gelatin plug comes off on its own, the outflow in the canal is restored and the disease regresses. If this does not happen, therapy is required.
Causes of blocked tear duct in a child
The lacrimal gland produces tears that bathe the eyeball and are then directed into the common duct, which opens in the area of the inferior turbinate. The obstruction causes a disruption in the regular outflow of tears, as a result of which the tear fluid begins to stagnate, which leads to the formation of stones consisting of sodium chloride and other inorganic substances.
The main causes of lacrimal duct obstruction in children are associated with obstruction of the lacrimal ducts by a mucus plug. Some newborns experience underdevelopment of the nasolacrimal duct, which leads to a narrowing of its lumen and contributes to stagnation.
Other possible causes of the disease:
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the skull and eyelids;
- the presence of concomitant diseases, including cleft palate and Down syndrome;
- chronic infectious diseases of the organ of vision;
- development of conjunctivitis, rhinitis, creating favorable conditions for the formation of adhesions in the area of the nasolacrimal duct;
- injuries to the bones of the nose and orbit that occur during probing or lavage;
- tumors of the bone walls, lacrimal sac and other bones of the face;
- entry of dust particles and cosmetics into the tear duct.
A pediatric otolaryngologist must determine the exact causes of the disease. It is important to conduct a high-quality examination and prescribe a comprehensive diagnosis, which will identify all etiological factors and select the most effective treatment.
Children's clinic No. 17
Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac. During intrauterine development, the nasolacrimal canal is closed with a film. This is necessary to protect it from amniotic fluid. At the moment of birth, during the first breath and cry, this film breaks through and the nasolacrimal canal becomes passable and tears flow out through it (into the nose). But if for some reason this does not happen, then the tear, instead of ending up outside, stagnates inside, in the lacrimal sac, and this stagnation is often accompanied by an infection. This is how acute dacryocystitis begins to develop.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis in newborns: The eye is red and inflamed. By the 8-10th day of life, purulent discharge appears. When pressing on the area of the lacrimal sac, pus is released from the lacrimal opening. Possible lacrimation. The process is often one-sided, i.e. one eye is inflamed. This is another sign indicating that the disease is not banal conjunctivitis. With conjunctivitis, both eyes are often inflamed. In some children, by the 14th day of life, the gelatin plug dissolves on its own, and the inflammation subsides. And the disease itself ends without any consequences. But in some cases this does not happen, and then the help of an ophthalmologist is required.
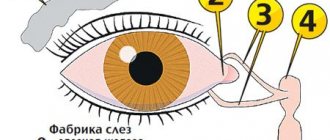
Once the diagnosis of dacryocystitis has been established, treatment must begin. The disease in a newborn child should be treated according to the following scheme: 1. We start the day by toileting the eyes : rinse the eyes with a sterile solution of furatsilin in a dilution of 1:5000, purchased at a pharmacy or prepared independently - dissolving 1 tablet. in a glass of warm boiled water (if they are sour), and then, using a damp cotton swab or cloth-bandage swab, clean the eye itself from pus, that is, remove all crusts from the eyelids and eyelashes, in the direction from the temple to the nose 2. Perform a massage the area of the eye where the lacrimal sac (I) is located by pressing it with your index finger towards the back of the head (don’t be afraid to push your finger towards the eye, you will rest against the muscle without harming the eye, producing a high-quality massage) and from top to bottom. This is necessary in order to squeeze out the gelatin plug (III) from the nasolacrimal duct (II).
Additionally, you can use a rubber bulb to pull mucus from the nasolacrimal duct through the nose after the massage. Perform 2-3 times a day; pulling with a pear in one application - 3 times
3. Apply disinfectant drops , for example: sodium sulfacyl (albucid); Vitabact ; okomistin; It is worth carrying out these manipulations 4–5 times a day if your baby is under 2 months old. It is useful to do this before feeding, since during meals the child himself continues the effectiveness of the massage due to the difference in pressure in the nose and mouth. Course 2 weeks. In case of severe infection of the eyes, antibacterial agents are prescribed: floxal 0.3% (4-6 times a day); tobrex 0.3% (4-6 times a day); Fucithalmic 1% thick suspension (2 times a day); their course is from 5 to 7 days, further treatment with disinfectant drops. It is not recommended to use eye ointments, as they are petroleum jelly based, which creates additional unnecessary viscosity in the tear duct. Before carrying out these manipulations, you need to thoroughly wash your hands and trim your nails.
Dear parents, please be patient while following this pattern. A good result largely depends on your persistence. YES, children “cry” because they still cannot communicate in any other way, they don’t like having their faces touched, but delicious food from their mother is the best reward for certain inconveniences.
Why is massage in the lacrimal sac area so important? The child's body develops gradually. The lacrimal sac is surrounded by muscles that compress it, pushing tears into the nose when blinking in children from 4 months. Since they already sleep less and use their eyes more often. Children under 2 months have a different rhythm of life. They sleep more and blink less, so massage should replace muscle work. If you don’t do a massage, but wait until the body itself begins to try to push tears into the nose, then you miss the opportunity to heal at home. After all, not only the muscle becomes stronger, but the gelatin plug also thickens due to the accumulation of calcium in it. As a result, the muscle is not able to push through this valve, so probing of the nasolacrimal duct is prescribed. This is why proper massage is so important in the early stages of a child’s life.
From the age of 2 months, the lacrimal gland begins to function in children, and full-fledged tears appear. They can massage you 2-3 times a day for a course of 2 weeks. From 3 months, massage is carried out in a course of 1 week with a recommendation to sign up for “probing”. The most favorable time frame for probing the nasolacrimal duct is from 3 to 6 months.
If your child has been diagnosed with dacryocystitis, now you know how to competently help your baby at home in the early stages of development. When a mother is afraid to give a massage, another adult (father, grandmother, grandfather, aunt, uncle...) should come to the rescue. Let's work together to help the child without surgery. However, do not despair, those parents whose children were prescribed “probing”. Once prescribed, it means it won’t go away on its own, and this issue needs to be resolved within 6 months. Parents, do not be afraid of the diagnosis, because the unknown creates fear. When you know what to deal with and how, it will give you strength and confidence in helping your baby.
Ophthalmologist Ivanova N.V.
Principles of treatment
Treatment depends on the form of the disease and the severity of clinical manifestations. Newborn babies are most often prescribed massage of the lacrimal sac, with the help of which it is possible to get rid of the mucus plug and restore the normal outflow of tears. If the expected effect does not occur after a month, it is recommended to carry out probing. This technique is used mainly in the first six months of life, before teething.
If the child has an acquired form of the pathology, treatment begins immediately with rinsing the nasolacrimal duct.
If there is no therapeutic effect from probing, dacryocystorhinostomy is performed. During the operation, specialists create an artificial passage between the nasal cavity and the lacrimal sac. With the help of intubation stands it is possible to prevent relapse of the pathology in the future. Making an appointment Today: 14 registered
Complications of dacryocystitis
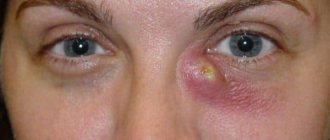
A dangerous complication of the disease is an abscess or phlegmon of the lacrimal sac. A red bulge appears under the baby's eye. Its palpation causes concern. The temperature also rises and the baby's sleep is disturbed. He becomes restless, cries, and may refuse to eat. Sometimes the baby does not want to take the breast from a certain side, because... Sucking causes pain. This complication is very dangerous and requires immediate hospitalization of the baby.
Very often the disease is confused with conjunctivitis. This is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. These pathologies have a similar clinical picture. Distinguishing them is quite simple: gently press on the area where the lacrimal sac is located. With dacryocystitis, mucopurulent discharge will appear from the lacrimal openings. You should not do this yourself; it is better to entrust the diagnosis to a professional.
Bougienage
If the massage does not lead to the expected result, you will have to bougie the sealed canal. The manipulation is quite simple: the doctor inserts a special probe into the lumen of the canal, destroying the plug of embryonic tissue located there. Purely psychologically, this may be unpleasant for both the baby and the parent, but there is nothing to fear, since the child will not experience any pain or discomfort during the manipulation.
Surgery
After this, a course of the already familiar massage and instillation of a solution against the formation of adhesions is prescribed. It is better to avoid the latter, as they lead to relapse of the disease.
Bougienage of the tear duct
Usually one session is enough for the child and his parents to completely forget about the problem. If after two months the symptoms return again, the probe is inserted again.
Postoperative care
Establishing diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by an ophthalmologist and an otolaryngologist based on the West test and external examination. The test consists of instilling a three percent solution of collargol into both eyes of the patient, which is then placed on a cotton wick. inserted into the subject's nose. Next they look at the reaction. If the channel is not blocked, then after about a quarter of an hour the cotton fibers will become colored. This means that collargol easily penetrated into the nose along the nasolacrimal duct and did not encounter any obstacles (positive result). But if the color of the cotton wool has not changed, it means that the plug is preventing the coloring composition from flowing into the nose.
Features of disease diagnosis
The West test reliably makes it clear whether the nasolacrimal duct is free or not, but cannot give an idea of the degree of blockage and the nature of the obstacles. That is why the West test alone is not enough; consultation with an otolaryngologist is required. A specialist will help to accurately determine whether this obstruction is associated with swelling of the mucous membrane or other pathologies.
Test Vesta
Prevention and prognosis
The prognosis for this disease is favorable. Most often, only a massage is enough for recovery. Dacryocystitis in newborns, which is fully treated, never recurs.
It is impossible to predict the development of dacryocystitis, because The anatomical features of babies lead to the disease. Prevention of complications lies in early diagnosis of the disease and proper treatment. The process cannot be left to chance. Be sure to consult an ophthalmologist!
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of dacryocystitis is based on the patient’s characteristic complaints, the typical picture of the disease and data from a number of specific studies:
- Biomicroscopy of the eye.
- Determination of the state of the lacrimal ducts and lacrimal punctum (Vest test).
- Determination of patency of the nasolacrimal duct (diagnostic probing).
- Rinsing the lacrimal sac (the procedure is both diagnostic and therapeutic).
- Carrying out bacteriological analysis to determine the type of pathogen and the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics.
- If a tumor process is suspected, CT and MRI are indicated.
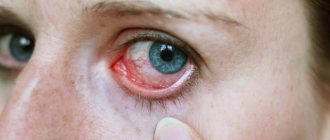
Rice. 6 and 7. Acute dacryocystitis in adults.