Ophthalmologist, Ophthalmosurgery
Gevorkyan
Armine Seyranovna
15 years of experience
Ophthalmologist, highest qualification category, member of the Russian Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgeons (RSCRS) and the European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgeons ESCRS
Make an appointment
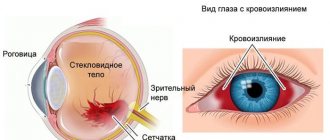
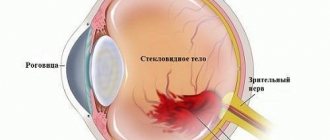
Hemophthalmos involves blood entering the vitreous body of the eye. The cause of the pathology is damage to the retina, its rupture, or newly formed vessels, which are characterized by increased fragility compared to normal vessels.
Hemophthalmos can be observed in a risk group in patients with diabetes, hypertension, or after a heart attack or stroke. The disease often occurs after 40 years of age with elevated cholesterol levels. Representatives of the fair sex are more likely to develop hemophthalmia of the eye than the stronger sex, and in most cases hemophthalmia contributes to a complete loss of sensitivity of the visual organ, resulting in a disability group.
What is hemophthalmia, basic information about the disease
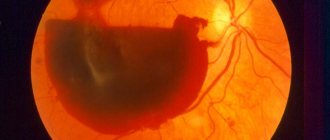
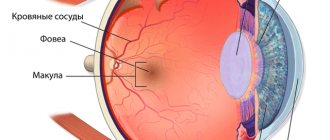
Hemophthalmos of the eye is a pathology in which blood clots enter the organ of vision; the essence of the process is the deep saturation of the organ with blood. On the third day, as a result of extensive hemorrhage, hemolysis of the blood occurs, hemoglobin leaves the red blood cells, and they become transparent. In this case, hemoglobin precipitates in the form of a granular sediment in the vitreous body of the eye.
Hemosiderin, which is formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin, acts as a toxin on the retina, resulting in the formation of clots of connective tissue that are fused to the retina. As a result, irreversible changes in the organ of vision are observed due to disruption of its normal structure and disruption of chemistry.
As clinical manifestations of the pathology, shadows with blackness or redness are observed in front of the eyes, the clarity of the picture decreases, and photopsia develops. In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, ophthalmoscopy, visometry, biomicroscopy, tonometry and ultrasound are prescribed. In the case of partial pathology, no medical measures are applied, and for total hemorrhage, hemophthalmos is treated with surgery based on the degree of the disorder - laser coagulation, vitrhemectomy.
Treatment of hemophthalmos with antivasoproliferative drugs
It is one of the modern and effective methods of combating hemophthalmia of the eye. Drugs such as bevacizumab or ranibizumab (Lucentis) are administered intravitreally to stop the processes of retinal neovascularization in the proliferative form of retinopathy that causes hemophthalmos. Treatment with antivasoproliferative drugs can be used either as monotherapy or in combination with laser treatment methods for hemophthalmos or surgery.
| Hemophthalmos. Treatment. Administration of anti-VEGF |
As an additional method, antivasoproliferative treatment is used before vitrectomy to reduce the risk of intra- and postoperative bleeding from areas of retinal neovascularization.
Main causes and categories of pathology
Among the causes of hemophthalmos it should be noted:
- penetrating type injury to the eyeball;
- contusions;
- severe eye injury;
- hemorrhagic glaucoma;
- arterial hypertension;
- inflammation of various origins of blood vessels or the retina;
- atherosclerosis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Hemophthalmos is divided into several types:
- partial – appears when blood enters from damaged vessels, blood fills the space by no more than 1/3;
- subtotal hemophthalmos – occurs after injury, the volume of hemorrhage exceeds half of the visual organ;
- total hemophthalmos - blood completely saturates the organ of vision.
If a disease occurs, it is important to promptly consult a doctor for medical help in order to avoid complete blindness, prevent total hemophthalmos, and save the eye.
Classification of hemophthalmos
Depending on the volume of hemorrhage, experts classify hemophthalmos as follows:
- total. Most often occurs against the background of trauma. Hemorrhage accounts for seventy-five percent of the total volume of the vitreous. Characterized by complete loss of objective vision. A person sees only at the level of light perception; he cannot independently navigate in space;
- subtotal. The volume of blood shed is 35–75 percent. Most often occurs against the background of retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. Massive dark spots appear that cover a significant part of the field of view. As the disease progresses, the patient can only see the outline and silhouettes of objects;
- partial hemophthalmos. Hemorrhage accounts for less than thirty percent of the total volume. Occurs against the background of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, retinal rupture or detachment. Partial hemophthalmos of the eye is mild and has a favorable prognosis. The disorder manifests itself as the appearance of black dots or stripes in the field of vision, as well as fogginess and general haze before the eyes. Patients complain of the appearance of shadows or cobwebs before the eyes.
With hemophthalmia of the left or right eye, a significant decrease in the fundus reflex is noted, in some cases its complete absence is diagnosed. During examination, the ophthalmologist may notice a red spot located at the bottom of the eye. Additional symptoms of the disease may include swelling of the upper and lower eyelids, as well as pain in the eye area.
With hemophthalmia, as a rule, one eye is affected. A symmetrical process is very rare
Recurrent hemophthalmos is a periodically recurring hemorrhage. In young people, pathology is often the result of injury, while in older people it is a physiological process in the body. Often, age-related hemophthalmos develops against the background of endocrine and cardiovascular diseases.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of hemophthalmia of the eye are determined by the volume of blood that enters the eye, as well as the stage of the pathology and its characteristics. Bleeding can last from a couple of seconds to a day, during which patients notice moving dots in front of the eyes, floating fog and other visual effects. The main feature that distinguishes hemophthalmos is sudden complete clouding, as well as black and red shades before the eyes. The level of clarity reduction is determined directly by blood filling. With extensive bleeding, patients cannot distinguish even bright lighting at all.
The most characteristic symptoms
Based on the severity of the disease, the patient feels the following symptoms:
- moving multi-colored dots and threads before the eyes;
- decreased vision, loss of sharpness, while vision improves in the morning only after waking up. This fact is explained by the fact that during a long stay in a horizontal position, blood collects in the lower compartment of the organ of vision;
- significant deterioration of vision, when the patient does not see objects, but distinguishes only between dark and light times of day.
In the case of small hemorrhages, the clarity of vision in patients decreases insignificantly, and ganglion cells against the background of retinal detachment provoke the development of photopsia. Noticeable pain occurs in the case of hemophthalmos of the eyes after significant trauma or iatrogenicity.
Symptoms
The main symptom of hemophthalmia is blurred vision. Patient complaints vary. Some patients note the appearance of many floaters, while others experience a significant decrease in visual acuity, including light perception. Clinical manifestations of hemophthalmos depend on the volume of blood poured into the vitreous body.
The peculiarity of the disease is that after sleep, in the morning, the severity of symptoms is less and the quality of vision is better. This happens because in a calm state (during sleep), blood settles in the lower parts of the eyeball, and during the day it “churns up” when moving.
Stages of pathology development
Let's consider the stages of development of the pathological process:
- fresh hematoma (up to 2-3 days) – signs of phagocytosis, when the patient notices shadows and fogs before the eyes due to the formation of blood clots;
- Days 3-10 – hemolysis of red blood cells, that is, hemoglobin and its derivatives pass into the eyeball, resulting in significantly reduced vision. When toxic substances are released, pain and general weakness are felt that accompany hemophthalmos;
- from day 10 – an irreversible process of degeneration of all elements of the visual organ. Within six months after the first symptoms, a person completely loses vision; eye problems cannot be restored even through eye surgery and performing the operation using modern equipment. The last stage is atrophy of the eyeball, after which the patient receives a visual disability group.
Causes of intraocular hemorrhage
Most often, the cause of hemophthalmos is a defect in the formation of blood vessels, in which they quickly rupture. This condition is typical for severe retinal damage in patients with diabetes mellitus. This problem occurs when blood flow in the retina is disrupted during postthrombotic retinopathy. The growth of defective vessels is also observed with dystrophy of the center of the retina and tumors of the choroid of the eyeball.
Causes of hemophthalmia:
- glaucoma;
- macular degeneration;
- damage to the eyeball;
- retinal or vitreous detachment;
- diabetic retinopathy;
- vascular thrombosis;
- hypertensive crisis (sudden increase in blood pressure);
- eye surgeries;
- neoplasm in the eyeball;
- autoimmune pathologies that cause vascular inflammation;
- abnormal development of eye vessels.
The cause of hemophthalmos can be injuries of a different nature: penetrating with destruction of membranes and blood vessels, as well as contusions and blunt trauma. Hemorrhages are often diagnosed when the retina is ruptured or detached when the retinal vessels are damaged. The most pronounced symptoms will be detachment of the posterior hyaloid membrane in those places where the vitreum is tightly attached to the vessels.
Hemophthalmos may indicate a disease of the circulatory system. Hemorrhages in the eye are often observed with hypertension, sickle cell anemia, vasculitis, vascular inflammation and oncological blood diseases.
Sometimes blood enters the vitreum from the subretinal space. This happens with the development of uveal melanoma or age-related macular degeneration. Hemophthalmos is possible with Treson syndrome, when subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs. In this case, the retinal vessels rupture due to a sharp jump in intracranial pressure.
In children, hemophthalmos develops as a result of shaken baby syndrome. Parents can cause hemorrhage even with a slight shake of the baby in an attempt to calm him down.
It is extremely rare that hemophthalmos is caused by uveitis, Eales' disease, sarcoidosis, chronic leukemia, Crohn's disease, and retinopathy in prematurity. Bleeding disorders and long-term anticoagulant therapy do not usually lead to hemophthalmos.
Diagnostics: how it works, procedures used
Diagnosis of hemophthalmos is based on the following methods:
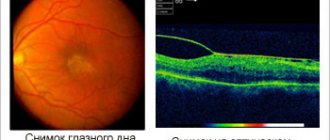
- indirect binocular ophthalmoscopy with punching – makes it possible to examine the peripheral zones of the retina, confirm retinal damage and hemophthalmos, as evidenced by visualization of mplanocytes;
- ophthalmoscopy – allows you to examine the retina in more detail and identify the size of the lesion;
- visometry - allows you to measure the clarity of visual perception; at different stages of pathology it varies from a slight decrease in sharpness to complete inability to distinguish light, which is characterized by total hemophthalmos;
- biomicroscopy - the method is used to identify melanocytes in the anterior zone, areas of bleeding;
- Ultrasound B-scan – an indication for this diagnostic method is a decrease in the transparency of the organ of vision, which is caused by darkening of the cornea or cataracts. The technique makes it possible to see damage or foreign bodies, blood clots, and identify adherence or detachment of the retina and vitreous body of the eye. The B-study mode allows you to identify melanoma and examine the back wall of the eye.
Also, when identifying hemophthalmos, it is necessary to prescribe tests for the patient: a general blood test, a coagulogram to detect coagulation, glucose levels, and the latter indicator is clearly increased in patients with diabetes in the last stage.
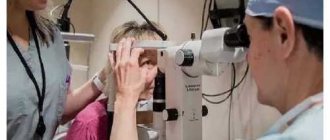
During the diagnostic process, the attending physician collects anamnesis, the patient’s complaints, performs an examination, and prescribes tests to confirm an accurate diagnosis. An ophthalmologist examines the entire condition of the eye, retina, and cornea. In the process of collecting anamnesis and choosing a treatment method, it is important to collect complete information about concomitant diseases and pathologies that could provoke the causes of this eye disease.
Consequences and complications of the disease
Due to delays in seeking medical help or the severe nature of hemophthalmia, a main list of negative consequences can be identified. Among them:
- scars and adhesions formed after hemophthalmos;
- retinal tear or separation;
- intraocular fibrosis;
- Vitreum cells are replaced by connective tissue;
- severe decrease in visual acuity;
- hemosiderosis of the organs of vision (extensive damage to the lens, retina and CT by residual products after the breakdown of red blood cells);
- glaucoma and complete loss of vision;
- the structure of the optic nerve is destroyed and atrophied.
Which doctor should I contact?
In case of eye problems, patients should promptly seek qualified help from an ophthalmologist. Treatment methods for hemophthalmia are determined after the initial appointment, examination and receipt of laboratory test results. For minor bleeding, the doctor prescribes preventive measures.
Conservative treatment consists of the use of plasminogen activators, and in the period from 3 to 28 days after the hemorrhage, it is recommended to take prourokinase. Subtotal and complete hemophthalmos require surgical intervention - vitrhemectomy is performed. When the retina is damaged, the coagulation technique using a laser device is most often prescribed.
Observing multi-colored flies, shadows, fog before your eyes against the background of the general sweetness of the body, you must immediately consult a doctor, since if prolonged, the pathology can cause complete loss of vision.
Doctors at the clinic JSC "Medicine" in Moscow have many years of practice and certificates confirming their qualifications, therefore they carry out qualified diagnosis and treatment of hemophthalmia using modern equipment. The cost of the initial appointment and consultation must be clarified with the clinic managers, who will make an appointment for you at a convenient time for a visit to the ophthalmologist. The decision on a specific method of surgical intervention and taking medications is made only by a qualified ophthalmologist after a thorough examination of the patient, obtaining blood test results, and carrying out diagnostic measures using high-precision equipment of the medical center.
Conservative treatment options
Conservative methods involve the use of the following measures:
- on the first day you need to apply cold to the eyes, which will reduce the manifestations and narrow the eye vessels;
- drops in the eyes and injection of drugs with calcium chloride, B vitamins to reduce the amount of bleeding;
- blood clot-absorbing medications for 1-2 days (potassium iodide, lidase, lecozyme, streptodecase), which reduces the visible signs of hemophthalmos;
- hirudotherapy.
Partial hemophthalmos implies a favorable prognosis; with total pathology in the eyes, the outcome depends on the timeliness of contacting a specialist and the speed of application of measures. That is, the sooner the patient applies and begins to treat hemophthalmos of the eye, the more favorable the doctors’ prognosis.
Conservative treatment of hemophthalmos
Small foci of hemophthalmos tend to resolve, but this is a very slow process. In some cases, complete resorption does not occur. Total and subtotal hemophthalmos is an indication for hospitalization of the patient. Treatment of partial hemophthalmia can be carried out on an outpatient basis. The course of treatment will depend on the cause of the vitreous hemorrhage, so it is important to make the correct diagnosis.
Therapy for hemophthalmos is always the same, but partial hemorrhage, as a rule, does not require great intensity and surgical intervention. You should prepare in advance for the fact that the treatment will be long, and it must be completed.
Principles of treatment
- If the hemorrhage has occurred recently, the patient is advised to rest in bed and wear a cold bandage.
- To avoid new hemorrhages, calcium supplements are prescribed (calcium gluconate 10% intramuscularly and calcium chloride drops 3% locally).
- Additionally, you can take vitamins B2, C and PP, as well as Dicinone and Vikasol.
- After 1-2 days from the start of treatment, enzyme preparations are prescribed to resolve clots. These are eye drops with potassium iodide, lidase or ronidase solution (0.1%).
- To prevent the formation of strands, hormonal therapy (eye drops or injections under the conjunctiva) is prescribed. For these purposes, use a solution of Dexamethasone (0.1%) or Prednisolone (0.3%). Parabulbar injections of collalysin, an enzyme preparation that dissolves collagen, are effective. You need to make 10 injections every other day. Additionally, injections of enzymes (Lecozim, Fibrinolysin) are prescribed.
- Anticoagulant therapy is recommended to prevent blood clotting. Solutions of heparin and streptodecase are injected under the conjunctiva.
- To enhance the resorption effect, sodium iodide solution (10%) is administered intravenously.
- It is possible to use autohematotherapy. 2, 4, 6, and then 8 ml of blood from a vein are injected intramuscularly.
- Sometimes medications with aloe extract are prescribed.
- We must not forget about physical therapy. For hemophthalmia, lidase electrophoresis is indicated (15 procedures, 15 minutes each). A month later, potassium iodide electrophoresis is performed with the same frequency.
- Additionally, phonophoresis of heparin and potassium iodide is prescribed.
- Laser treatment of hemophthalmos is possible.
- The effectiveness of hirudatherapy cannot be denied.
In cases where drug treatment is ineffective within 7-10 days, surgical treatment of hemophthalmos is required. Without treatment, strands begin to form in the eye, which provoke retinal detachment and atrophy the eyeball. Lack of therapy or its ineffectiveness is a sure path to complete blindness.
With complete and timely treatment of partial hemophthalmos, the prognosis is favorable in most cases. Conservative therapy promotes resorption of hemorrhage areas and restoration of vision. Subtotal and total hemophthalmos require urgent and powerful treatment, otherwise the risk of complications reaches one hundred percent.
Surgery
In the case when conservative methods of treating hemophthalmos do not bring success within 1-2 weeks, that is, the volume of hemorrhage does not decrease, the perception of visual images and the eyes are not restored, it is necessary to remove blood clots with a laser. Using laser technology, it is possible to remove tumors from the eye without affecting the eyeball and cornea, while selectively acting exclusively on hemoglobin.
If the doctor diagnoses total hemophthalmos, surgery is inevitable. Moreover, modern methods make it possible to treat hemophthalmos on an outpatient or inpatient basis; the rehabilitation period after surgery is minimal. Postoperative measures include bed rest and a sterile bandage is applied to the eyes after surgery. To increase the effectiveness of the operation and avoid relapses, calcium, vitamins C, B2, BB, dicinone and vikasol are prescribed.
To prescribe an operation, the doctor needs to establish the underlying causes of the pathology, because the success of treatment and the complete restoration of the eye and vision depend on the successful elimination of hemorrhage. If ruptures or damage to the retina are detected, laser coagulation or cryocoagulation is performed. As an alternative technique, injections into the eyes of medications that inhibit the formation of blood vessels (Avastin, Lucentis) are used. If hemophthalmos is accompanied by retinal detachment, immediate surgery is prescribed.
Vitrectomy is used as a treatment to remove intraocular bleeding and treat hemophthalmos. During this operation, the vitreous body of the eye is completely or partially removed; the reasons for surgical intervention are:
- retinal detachment;
- bleeding inside the visual organ, which occurs over 2-3 months;
- bilateral hemophthalmos, the doctor suspects extensive pathology. In children with diabetes, this helps avoid amblyopia;
- hemophthalmos in combination with concomitant eye pathologies.
By immediately contacting a doctor when the patient detects the first signs of the disease, the chances of a favorable treatment outcome, restoration of the eye and visual acuity increase.
Complications of hemophthalmos
A frequent complication of hemorrhage in the eye is severe destruction of the vitreous body. It happens that hemophthalmos becomes recurrent, provoking the formation of connective scar tissue in the vitreum. With prolonged intraocular hemorrhage, children often develop amblyopia and myopic shift.
Hemophthalmos can be complicated by hyphema. This is a hemorrhage in the anterior segment of the eyeball, which is localized between the iris and cornea. Even if prolonged hemophthalmos has not led to significant damage to the retina, and normal vision is preserved, the risk of developing secondary glaucoma increases.
Hemorrhage into the vitreous body can be prevented by timely treatment of pathologies that can cause hemophthalmos. It is very important to follow safety precautions and protect your eyes from damage.
Sources used:
- Changes in the fundus of the eye in internal diseases / M.G. Margolis, B.V. Pluzhnichenko. - Moscow
- Bloodstream of the ciliary body of the eye: monograph. / Alexey Pryakhin. - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2013.
- Clinical ophthalmology. Systematized approach / Jack Kansky. - M.: Logosphere, Elsevier Urban & Partner, 2009.
- International Council of Ophthalmology
Indications for the disease
After bleeding in the eyes, patients need to limit physical activity and stay in bed to avoid further aggravation of the pathology. Hemophthalmos suggests that for blood to accumulate in the lower part of the visual organ, it is necessary to lie horizontally, while the head should be elevated by 35-40°.
During prevention and treatment, it is necessary to avoid taking medications that thin the blood (aspirin, anticoagulants) and provoke further hemophthalmos. If the attending physician prescribed them earlier because hemophthalmia was accompanied by a concomitant disease, you need to weigh the risks of discontinuing the drug and the positive effect of taking it.
The prognosis of treatment is determined by the cause of the pathology, the timeliness of contacting a doctor, the correct selection of the surgical procedure, and whether the operation was performed correctly.
Symptoms of hemophthalmos
Hemophthalmos occurs with a number of characteristic symptoms, which make it easy to diagnose the disease:
- There is blurred vision.
- Black spots constantly flash before my eyes.
- Visual acuity deteriorates.
- If the hemorrhage is caused by an injury, then pain occurs, in other cases there is no pain.
- When examining the eye, you can see blood stains on the mucous membrane.
In the morning, vision is better than at other times of the day. This is due to the fact that during sleep, blood breakdown products settle.
Cost of initial appointment, research, treatment
Patients who have been diagnosed with hemophthalmos or are suspected of having this disease can have an initial appointment at the clinic of JSC "Medicine". Qualified ophthalmologists will examine the eye, diagnose it using modern devices, and prescribe appropriate medical or surgical treatment.
At the appointment, the ophthalmologist, by examining the vitreous body of the eye and cornea, draws conclusions about the volume of hemorrhage in the patient and how to treat hemophthalmos at a specific stage. The cost of appointments and treatment can also be clarified with specialists by phone or directly at the clinic.
Cost of some services for hemophthalmia:
| № | Service name | Price in rubles | Make an appointment |
| 2003004 | Repeated appointment with the leading surgeon | 1400 | Sign up |
| 2003006 | Repeated appointment with an ophthalmologist | 1500 | Sign up |
| 2003005 | Initial appointment with an ophthalmologist | 2500 | Sign up |
| 2011039 | Vitrectomy for uncomplicated hemophthalmos or vitreous opacities of the second category | 64500 | Sign up |
| 2011038 | Vitrectomy for uncomplicated hemophthalmia or vitreous opacities of the first category | 54000 | Sign up |
| 2011040 | Vitrectomy for uncomplicated hemophthalmia or vitreous opacities of the third category | 78600 | Sign up |
Making an appointment Today: 15 registered
Advantages of treatment at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
At JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg), patients with suspected hemophthalmos can undergo qualified treatment on an outpatient basis or in a comfortable hospital. The clinic employs ophthalmologists who have significant experience in treating various diseases of the vitreous body, cornea, and retina.
If a doctor prescribes surgery, the intervention is performed using modern laser equipment, which minimizes the rehabilitation period. During eye treatment, patients stay in the hospital, where comfortable conditions are provided, which makes it possible to completely cure hemophthalmos and prevent relapses in the future.
Vitrectomy
An operation is prescribed only if the patient cannot be helped in any other way.
Indications for surgery:
- a persistently severe form of rhinopathy, in which laser treatment of hemophthalmos was unsuccessful;
- subtotal and total stage of the disease with the risk of retinal detachment or rupture;
- bilateral hemophthalmos.
Vitrectomy is a microsurgical operation for partial or complete removal of the vitreous body and replacing it with an artificial analogue (silicone oil, saline solutions, etc.). This type of eye surgery is considered quite complex and can take from 2 to 3 hours. However, on the same day, if the prognosis is favorable, the patient can be discharged home.
Vitrectomy allows you to achieve positive results in severe eye pathologies, in cases of long-term extensive hemorrhages of various origins. However, everything is decided by the degree of advancedness of the disease; there are cases when surgical intervention remains powerless (retinal detachment by more than 50%).
Ophthalmic surgeons often practice combining types of therapy, for example, laser treatment of hemophthalmos and vitrectomy.