When blood cells enter the vitreous cavity, the passage of light to the retina is disrupted. Depending on the volume of hemorrhage, the degree of decrease in visual acuity varies. This manifestation is called hemophthalmos. The disease is relatively rare, although it can occur in people of different age categories and gender. Hemophthalmos may indicate the presence of general diseases of the body. In addition, this disease becomes quite dangerous, leading to tissue defects in the visual organs.
Eye contusion - what is it?
An eye contusion is an injury to the visual organ as a result of exposure to heavy blunt objects or intense mechanical force.
ICD-10 code
Eye contusion according to ICD-10 (international classification of diseases) is designated by code S05 and is one of the most dangerous injuries to the eyeball.
S05 Trauma to the eye and orbit Classification:
- S05.0 Conjunctival trauma and corneal abrasion without mention of a foreign body.
- S05.1 Contusion of the eyeball and orbital tissues.
- S05.2 Laceration of the eye with prolapse or loss of intraocular tissue.
- S05.3 Laceration of the eye without prolapse or loss of intraocular tissue.
- S05.4 Penetrating wound of the orbit with or without the presence of a foreign body.
- S05.5 Penetrating wound of the eyeball with a foreign body.
- S05.6 Penetrating wound of the eyeball without a foreign body.
- S05.7 Eyeball avulsion.
- S05.8 Other injuries of the eye and orbit.
- S05.9 Injury to unspecified part of the eye and orbit.
Features and treatment of eye injuries in children
Most eye injuries in children are of a domestic nature and relate to blunt injuries and microtraumas. Burns and penetrating wounds account for no more than 8 and 2% , respectively. The main reasons are insufficient childcare and poor organization of games. Boys susceptible to eye injuries than girls ( 85% vs. 15% ).
Symptoms of damage to the visual organs in children do not differ from those in adults. Treatment has its own nuances, which should always be accompanied by good pain relief , especially with penetrating trauma.
in childhood . If surgical intervention was performed and no races were applied?
Possible complications
Trauma to the visual system can provoke a number of dangerous consequences:
- Purulent inflammation followed by removal of the eye. Usually occurs when the treatment of wounds is delayed.
- Penetration of staphylococcus threatens blindness and even death.
- Inflammation of the cornea. Negatively affects visual acuity.
- Development of ophthalmia. Diagnosed some time after the contusion.
- Displacement of the optic nerve.
- Infection with further blood poisoning.
- Drooping of the upper eyelid.
- Brain abscess.
To avoid serious complications, it is extremely important to start treatment in a timely manner. Moreover, only a doctor should select the course of therapy! Return to contents
Causes of eyeball contusion
Violations of the integrity of the visual apparatus can be provoked by various factors:
- Ignoring safety during work.
- Irresponsible attitude towards your health.
- An accident, such as a blow, a fall or an attack.
- Antisocial behavior, alcoholism and drugs.
- Sports injuries due to insufficient protection.
- Presence in the combat area.
- Powerful changes in the atmosphere, gusty winds.
- A stream of water or gas.
Depending on the cause of its appearance, pathology is usually divided into two types:
- Direct . The occurrence is caused by the influence of an external force directly on the eye (for example, due to a bruise).
- Indirect . Appears when force is applied to the area adjacent to the eye, to the tissues surrounding it (bones of the skull, face, orbit) or to more distant areas of the body (compressed by the chest). As a rule, the consequences are observed in changes in the ocular structure.
Types of damage to the eyelid
Injuries to the eyelid can be through or superficial, punctured, cut, or torn.
Erosion
There are abrasions or scratches on the skin of the eyelid , bleeding and pain are present. This type of injury most often does not require medical attention.
You can treat the wound yourself with an antiseptic , apply a cold compress to relieve swelling and redness, and then wear a bandage with antimicrobial ointment until the skin is completely healed.
Contusion
This type of eyelid injury is caused by a bruise on a blunt object and is always accompanied by significant soft tissue swelling and pain. A little later, an extensive hematoma or small bruise appears, depending on the force of the blow. The pain intensifies when you move the eye. In severe cases, the conjunctiva or tear ducts may rupture and the eyeball may be damaged. In the first minutes, it is important to apply ice and use an anesthetic .
Wound
In most cases, eyelid injuries occur due to damage from a sharp object and can be:
- superficial - only the skin and muscles of the face are affected;
- through , that is, passing through the entire thickness of the century.
The tissues often swell, and if the tear ducts are damaged, excessive lacrimation occurs, or, conversely, a violation of the outflow of fluid. For lacerated wounds , surgical intervention for minor superficial injuries antiseptic treatment , application of cold and further treatment with antimicrobial and healing drugs ( Levosin, Levomekol, sodium sulfacyl , etc.) are sufficient. If the lacrimal canal , a Polak probe .
Photo 5. Perforating wound of the eyelid with a fishing hook. The eyeball was also damaged.
Mechanism of injury
At the moment of contusion, the eyeball is displaced and the structures that make it up are compressed.
At the same time, intraocular pressure increases and the pupil sharply dilates. Fluid rushing into the anterior chamber can cause tears in the iris along the pupillary edge or in the corners of the chamber.
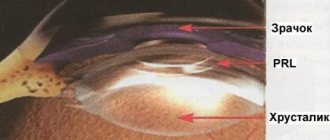
The lens shifts, the ligament supporting it may not withstand the load and may break. Subluxation or dislocation of the lens occurs, and it falls out into the vitreous or anterior chamber. Ruptures of the lens capsule cannot be ruled out.
From vessels damaged by trauma, blood flows under the mucous membrane, chorionic membrane, retina, or into the chambers of the eye. The degree of hemorrhage that occurs varies.
Due to the tension of the structures at the time of injury, separation, ruptures or detachment of the retina is possible.
With severe injuries, rupture of the fibrous capsule of the eyeball may occur. More often this happens at the border of the limbus or at the attachment points of the extraocular muscles.
Ruptures or compression of the optic nerve are possible when the bone structures of the orbit are damaged.
Diagnostic methods
The examination begins with an external examination , during which the ophthalmologist can detect a foreign body, wound, hematoma, bleeding, or swelling. In this case, the doctor always everts the upper eyelid to exclude or detect foreign bodies.
Visual acuity must , since in many injuries it decreases due to impaired transparency of the optical media of the eye (opacity of the vitreous body or lens). Intraocular pressure is measured, which can be either high or low.
Instrumental and hardware methods used in the diagnosis of eye injuries:
- Gonioscopy - examination of the iris and anterior chamber angle.
Photo 1. The process of performing gonioscopy. The iris and anterior chamber angle are examined for damage.
- X-ray of the skull in the orbital area in 2 projections to identify fractures and intraorbital foreign bodies.
- Ultrasound and CT of the eye allows you to assess the condition of the tissues.
- Perimetry is an assessment of the sensitivity of the cornea, which decreases with burns and some injuries.
- Ophthalmoscopy (direct, indirect and with a Goldmann lens) - detects retinal detachment or contusion, foreign bodies.
- Biomicroscopy - examination of the cornea with fluorescein drops.
The patient also takes a blood test (general, biochemistry, for syphilis and HIV) and urine (for leukocytes, sugar, etc.).
Development order
As a result of contusion of the visual apparatus, disturbances occur leading to deformation of the ocular structures. Therefore, it is necessary to understand what processes occur in a short period of time of its formation.
The algorithm characteristic for the development of eye contusion is as follows:
- After mechanical impact, contusion of the eyeballs occurs.
- There is a short-term sharp jump in intraocular pressure.
- Then the visual apparatus returns to its original position.
- Due to processes that temporarily take place inside the eyes, blood circulation changes.
- Vessels and eye tissues are torn.
- Biochemical changes occur in the intraocular fluid.
- The development of a stress reaction is observed.
Why does hemophthalmos occur?
The reasons for this may vary. In accordance with this, the mechanisms of its formation also differ. Here are the main factors influencing the formation of hemorrhage:
- Diseases of the retinal vessels, as a result of which it is exposed to ischemia. Due to the lack of oxygen, new formations of fragile vessels are revealed, bursting at the slightest impact on them. This deviation may occur as a result of diabetes mellitus, thrombosis or retinopathy.
- Vascular diseases of the retina, which are not related to ischemia. The causes of the disease in this case are arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis and congenital anomalies of vascular development.
- Rupture of retinal vessels that are in good condition. Hemorrhage occurs due to injuries and detachments of the retina or vitreous.
- Rupture of healthy retinal vessels as a result of anemia, surges in intracranial and intrathoracic pressure, and blood clotting disorders.
- Age-related changes leading to hemorrhages without retinal detachment.
Here is a possible scheme for the occurrence of hemophthalmos:
Most often, hemophthalmos occurs due to diseases of the cardiovascular and hematopoietic systems. Sometimes vitreous hemorrhage is noticed in newborns after attempts to soothe them while crying.
Diagnostics
The examination of the patient begins with collecting an anamnesis. It is extremely important for the doctor to obtain information about how the injury was caused. The ophthalmologist examines the cornea and retina, the lens, and the eyelid. Primary measures are taken to treat the damaged area, and if necessary, the foreign object is removed.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a number of procedures are required:
- Ultrasound of the visual apparatus.
- Visometry.
- Perimetry (analysis of optical fields).
- Radiography.
- Ophthalmochromoscopy.
- Measuring intraocular pressure.
- Rheography.
Diagnosis of hemophthalmos
First of all, the ophthalmologist examines the eye, setting out to detect damage. What happens in the fundus of the eye can be seen using an alkaline lamp. When making a diagnosis, the doctor may use the following methods:
- Ultrasound of the visual organs.
- Biomicroscopy.
- Tests to help determine visual acuity.
- Ophthalmoscopic examination.
- Measurement of arterial and intraocular pressure.
- Collection of analyses.
Comprehensive studies help determine the stage of the disease and identify its cause. The localization of the consequences of hemorrhage significantly influences the treatment regimen.
Severity
There are four degrees of severity of eye contusion:
- 1st degree – transient traumatic failure of the eyeball. The organ is fully capable after therapeutic assistance. Varieties include corneal edema and retinal clouding.
- 2nd degree – persistent and more serious impairment of eye function, slightly reducing visual acuity. Varieties: corneal erosion, retinal tears, hemorrhages.
- 3rd degree - a strong blow to the eye, capable of causing more than half damage to vision. Varieties include: eyelid tears, retinal tears, lens pathologies.
- Grade 4 is the most severe form, which can cause 100% loss of visual function in the damaged eye.
Consequences for the eyeball
The consequences of an eye contusion can be very serious, including complete loss of vision, without the possibility of recovery.
Corneas
Damage to the cornea is the most common consequence of eyeball contusion. Signs of such defects are erosion of varying depths and areas. They have the ability to change their size upward within a week.
The first indicators of corneal injury include:
- decreased visual acuity;
- unpleasant sensitivity to light;
- uncontrolled production of tears;
- feeling that something is in the eye;
- blepharospasms.
Blurred vision occurs if the central zones of the cornea are eroded. When the stroma is damaged, visual acuity noticeably decreases. Destruction of the endothelium leads to edema in the depths of the stroma, and opacification of the cornea in the form of stripes and latticework leads to the penetration of purulent composition into other areas of the stroma.
Important! In particularly severe cases of corneal defect, 3rd degree eye contusion may develop. At this stage, the eye becomes cloudy and takes on a gray tint.
Lens
Eye contusion is often a consequence of traumatic cataract. The reason is caused by clouding of the lens due to a change in its location (luxation). Due to the fact that moisture enters through microcracks in the capsule of the anterior chamber of the eye, the volume of fluid may increase with visible bruising.
Fibers in the form of a swollen mass fill the entire volume of the capsule if its cracks are significant. Sometimes the fibers block part of the anterior chamber, increasing pressure inside the eye and causing glaucoma. Lens luxation is characterized by deformation of the anterior chamber and displacement of the iris. The lens itself takes the form of a drop filled with fat.
Retina
Retinal injury is one of the most severe types of damage and the most difficult to treat. The cause is caused by retinal shock. Damage may be accompanied by clouding of the eye, which in turn provokes inflammation of the internal structure of the retina; concentric narrowing of the field of view. The color of such clouding ranges from light gray to milky, this is due to inflammation of the internal cells of the retinal structure. With a minor injury, the structure of the eye and vision quickly and independently resume their functions. If it comes to severe cases (for example, 2nd degree contusion of the eyeball), then visual acuity is significantly reduced, and bleeding may develop:
- preretinal;
- retinal;
- subretinal.
Read more about the symptoms of various types of contusions in this article.
Forecast
The outcome of an eye injury resulting in contusion can be predicted taking into account the nature of the damage.
- In the case when the skin of the eyelids remains intact, there are no bruises or tears, a mild degree of contusion is diagnosed. At the same time, a person easily opens his eyes and sees any images in a clear picture. The chances of a complete cure are equal to 100%.
- If the retina is damaged, 1-2 hours after the injury occurs, a cloudy color forms in the eye, and swelling of the cornea becomes noticeable. At the same time, the person sees poorly and practically cannot raise the upper eyelid. Symptoms indicate a severe injury. The victim must go to the clinic within a short period of time to receive medical care. In such a situation, the risks of hemorrhages of various types increase. To localize the problem, drug therapy and sometimes surgery are required.
Reference! For more serious injuries, the victim needs complex treatment and correction of visual function. It is difficult to predict a positive result due to the high risk of complications.
With second-degree injuries, morphological changes are noted that reduce visual acuity. Reconstructive surgery is required to restore it. The third degree is characterized by irreversible morphological changes. Such lesions lead to cosmetic defects and loss of eye functionality.
Clinical picture
When bleeding in the eye, the following symptoms appear:
- acute pain in the eye area, which intensifies when the head is tilted and light enters the eye;
- dizziness (with such damage is often accompanied by double vision);
- damage to the second eye (as the hematoma develops, it becomes bilateral, which in medicine is called glasses syndrome);
- throbbing headache (typical of hematomas resulting from traumatic brain injury);
- progressive or temporary visual impairment;
- nausea and vomiting.
First aid and treatment
Before the ambulance arrives, you need to be able to properly assist the victim:
- Be sure to apply a bandage or gauze to the damaged area; if you don’t have anything at hand, any clean piece of fabric will do.
- The injured area must be cooled by placing a damp cloth on top.
- If the victim has nausea, it is necessary to sit him down with a cushion under his head and give him a sedative.
Attention! It is necessary to provide first aid to the victim and take him to the hospital. Doctors often allow bruise treatment at home.
Subsequent inpatient treatment includes:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are usually prescribed by injection or infusion. The following medications are most often prescribed: Dexamethasone, Flosteron, Diprospan, Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Nimesulide.
- Antidepressants and tranquilizers, for example Tazepam, Elenium, Phenazepam.
- Antihistamines - HI receptor blockers: Loratadine, Tavegil, Suprastin.
- Enzyme preparations: Lidaza, Gemaza, Fibronolysin.
- Hemostatic agents: Dicynon, Vikasol.
- Diuretics such as Diacarb.
- Be sure to administer instillations into the conjunctival sac of the eye using: antibacterial drugs: Floxal or Vigamox, Antiseptics, Glucocorticoids.
- Non-steroidal drugs: Indocollir or Uniclofen.
Combination medications are often used, combining several active substances at once. In some cases, surgery is used. This type of treatment is used in the presence of various tears, ruptures, and anatomical defects. A prerequisite for the treatment of eye contusion is that the treatment must be prescribed by a medical specialist.
Treatment of hemophthalmos
Treatment of hemorrhage in the vitreous body is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Normalizing the pH balance in the vitreous body.
- Acceleration of the process of resorption of formed blood clots.
- Removal of toxic formations.
- Reducing the level of cholesterol that enters the eye along with the blood.
Hemostatic drugs, glucose, sodium chloride, and diuretics help achieve these goals. Drug treatment is prescribed if it is impossible to resolve the spilled blood on its own. An approximate list of prescribed medications for hemophthalmia is reflected in this commentary:
If medications do not help within 10 days, the doctor prefers surgery.
Laser treatment
This method will be used to influence the ischemic area of the retina. Thanks to this, hemorrhage is prevented in almost 85% of cases for up to 5 years. If we talk about the treatment of already existing hemophthalmos, then the newly formed vessels die off. This reduces the risk of recurrence of the disease.
Antivasoproliferative treatment
Used as an independent treatment method or in addition to laser procedures. Involves the injection of bevacizumab or ranibizumab into the vitreous cavity. Limits the spread of pathological vessels.
Vitrectomy
It is an intervention into the structure of the eye through three micro-incisions. The vitreous body, filled with blood, is removed. It is replaced by an implant, which is filled with a gaseous substance while natural functions are restored, which then dissolves. Surgical intervention helps restore the function of the visual organs in a short time, regardless of the location of the disease.
Doctors describe the treatment method for hemophthalmia in this way:
Diagnostic measures
The most important factor at the first stage of the examination is the severity of intraocular pressure: increasing ophthalmotonus against the background of lens displacement and cessation of fluid exchange between chambers can quickly worsen the severity in the post-traumatic period. In addition to tonometry, the doctor will perform the following studies:
- ophthalmoscopy;
- biomicroscopy;
- ultrasound scanning;
- X-ray in different projections or computed tomography of the orbit.
It is important to accurately assess the condition of intraocular structures and the severity of traumatic injury in order to select optimal treatment methods.