If you've recently watched a crying baby or the latest sentimental Hollywood movie, you're well aware that tears run down your face.
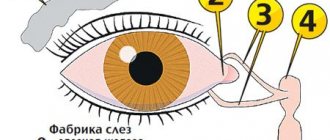
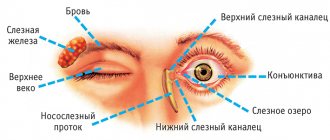
However, we also have a tear duct (also called the "nasolacrimal duct" and "tear duct"). through which tears pass through the nose. These drainage tubes cause a runny nose when crying or an allergic reaction in the eyes.
When the tear duct becomes blocked, problems arise. Let's look at the causes of blocked tear ducts, how it happens and how to get rid of it.
What it is?
Dacryocystitis is an infectious and inflammatory disease characterized by damage to the lacrimal sac of the eye. Typically, this disease is most often observed in people aged 30-60 years. In women, this disease occurs more often due to the narrower anatomical structure of the nasolacrimal ducts.
As a rule, in adults, the lesion with dacryocystitis is always one-sided.
The disease occurs due to blockage of the nasolacrimal canal. As a result, tear fluid accumulates in the lacrimal sac and cannot penetrate outside. Due to the disruption of the outflow of tear fluid, active proliferation of microorganisms occurs, which leads to inflammation and the formation of mucopurulent discharge.
Manifestation of dacryocystitis in adults
Causes
In adults, dacryocystitis occurs due to narrowing and closure of the nasolacrimal duct. Due to the narrowing of the channels, fluid circulation is disrupted. As a result of this, stagnation of the tear secretion occurs, in which microorganisms begin to actively develop.
Swelling of the tissues surrounding the nasolacrimal duct occurs as a result of inflammatory diseases of viral or bacterial origin (respiratory infections, chronic rhinitis, sinusitis).
The disease can also be caused by:
- fractures of the bones of the nose and orbit;
- damage and disruption of the integrity of the lacrimal canaliculi;
- nasal polyps;
- penetration of debris, dust and other foreign bodies into the eye.
Also, the following factors may contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- metabolic disease;
- diabetes;
- weakening of the immune system;
- allergic reactions;
- interaction with chemicals hazardous to the organs of vision;
- sudden temperature fluctuations.
Symptoms
The following clinical manifestations occur with dacryocystitis:
Swelling of the lacrimal caruncle
- constant lacrimation;
- mucopurulent discharge from the eyes (mucopurulent conjunctivitis);
- hyperemia and swelling of the lacrimal caruncle, conjunctiva and semilunar fold;
- swelling of the lacrimal sac;
- sore eyes;
- narrowing of the palpebral fissure;
- increased body temperature;
- general intoxication of the body.
Dacryocystitis can have an acute or chronic form of the disease. Clinical manifestations of the forms of the disease vary.
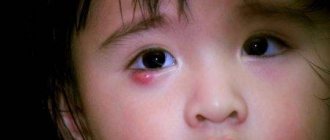
In the acute form of the disease, clinical symptoms manifest themselves most clearly. In the area of inflammation of the lacrimal sacs, sharp redness of the skin and painful swelling occur. Due to swelling of the eyelid, the palpebral fissures become very narrow or completely closed . The patient may experience pain in the eye area, chills, fever, and headache.
Advanced stage of dacryocystitis
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by constant lacrimation and swelling in the area of the lacrimal sac. When pressing on this area, mucopurulent exudate is released from the lacrimal canals. A swollen neoplasm forms in the area of the lacrimal sac, visually resembling a bean . As it develops, it becomes densely elastic.
Inside the cavity of this neoplasm, pus accumulates, which, when pressed, is released out. With further development of the infection, phlegmon of the orbit or fistulas may occur.
Read more about the symptoms of conjunctivitis here.
How does rinsing happen?
The manipulations are carried out in a specially equipped ophthalmologist's office. Diagnostic, preventive and therapeutic procedures are the same, only the administered drug changes.
- The patient takes a sitting position with a slight bend forward.
- The doctor uses a syringe, but instead of a needle, a cannula with a blunt end is attached to the syringe.
- The doctor pulls back the eyelid and inserts the cannula into the lacrimal opening as deeply as possible, until it stops, and then moves it back 2-3 mm so as not to damage the walls of the lacrimal canaliculus.
- By slowly pressing on the syringe plunger, the ophthalmologist evaluates the speed, ease and volume of fluid passage.
Diagnostics
In order to identify the disease, the patient must be examined by an ophthalmologist. As a rule, dacryocystitis is quite easily diagnosed due to its characteristic clinical symptoms. During the examination, the doctor conducts an external examination and palpation of the area of the lacrimal sac, performs the West lacrimal-nasal test, instillation fluorescein test, and radiography of the lacrimal ducts.
First of all, the ophthalmologist listens to the patient’s complaints and carries out an external examination of the lacrimal sac area. When palpating this area, purulent secretion should be released from the lacrimal canaliculi.
The most commonly performed test is the West nasolacrimal test. It is one of the most common diagnostic techniques. During this procedure, a solution of collargol or protargol is instilled into the conjunctival sac. These staining substances are used to determine the patency of the lacrimal canal. A cotton wool or turundum swab is inserted into the sinus. Traces of the coloring substance should appear on the tampon no later than after 5 minutes. A delay in the entry of the substance into the nasal cavity or its absence indicates a violation of the patency of the nasolacrimal duct.
Read more about perimetry in the article.
The degree of patency of the entire lacrimal drainage system, as well as the level and localization of areas of obliteration, are determined using contrast radiography. During this diagnostic method, iodolipol solution is used.
If it is necessary to identify microbial pathogens of dacryocystitis, bacteriological culture is performed.
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient must additionally undergo examination by an otolaryngologist . As a rule, an otolaryngologist performs rhinoscopy for dacryocystitis. The patient may also need to consult a dentist, traumatologist, neurologist or neurosurgeon.
Forecasts
In most cases, bougienage of the tear duct is a highly effective procedure. 80% of treatment results are positive. But here it is necessary to build on how timely the patient went to the doctor and how he complies with the doctor’s recommendations. Of course, negative aspects cannot be ruled out. But they arise only for two reasons: the doctor’s inexperience and an incorrect diagnosis. To prevent the development of relapse and dangerous complications, it is necessary to stop using contact lenses. Well, most importantly, never self-medicate. If the patient does not follow all the doctor’s instructions, his health condition will worsen, which will lead to loss of vision.
Treatment
As a rule, if dacryocystitis is without complications, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Treatment of dacryocystitis, first of all, depends on the form of the disease and the causes of its occurrence.
The treatment process for dacryocystitis is generally divided into two parts:
- restoration of patency of the nasolacrimal canal;
- anti-inflammatory therapy.
When treating dacryocystitis in adults, bougienage and rinsing of the nasolacrimal duct with disinfectant solutions and the use of antibacterial eye drops and ointments are performed.
Bougienage is the most common, gentle method of restoring the patency of the nasolacrimal canal. During this procedure, the blockage of the nasolacrimal canal is physically removed using a special rigid probe (bougie).
Initially, patients suffering from dacryocystitis are prescribed enhanced antibacterial treatment to avoid infectious complications. This is necessary because with dacryocystitis there is a possibility of a purulent form of encephalitis or a brain abscess.
Dacryocystitis in old age
The acute form of the disease is treated in a hospital setting. As a rule, in this case, intramuscular injections of benzylpenicillin sodium salt (3-4 times a day) or oral administration of tetracycline (4 times a day), sulfadimezine (4 times a day) are prescribed.
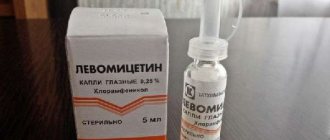
If an abscess of the lacrimal sac has formed, it is opened through the skin. Before opening the abscess, systemic vitamin therapy and UHF therapy are performed. After opening, the wound is drained and washed with antiseptic solutions of furatsilin, dioxidin, and hydrogen peroxide. To prevent further development of infection, antibacterial drops (chloramphenicol, miramistin, sodium sulfacyl, gentamicin drops) and antibacterial ointments (erythromycin, tetracycline eye ointment, floxal) are instilled into the conjunctival cavity.
In addition to local treatment, systemic antibacterial therapy with broad-spectrum drugs is carried out. For this purpose, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, and penicillins are used.
In advanced forms of dacryocystitis, when standard drug treatment is ineffective, dacryocystoplasty or endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy is performed.
Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy
Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy is a surgical procedure used to treat dacryocystitis in adults. Special modern minimally invasive equipment is used to perform the operation. Dacryocystorhinostomy can only be performed on patients who do not have an allergic reaction to anesthetic drugs. During the operation, a special flexible tube is inserted into the tear duct - an endoscope with a microscopic camera.
An endoscope is used to make an incision in the blocked tear duct. The rehabilitation period after surgery is 6-8 days. To avoid inflammation of the cornea, he prescribes a course of antibiotics. The advantage of this operation is that it does not leave visible skin scars on the face or damage to the tear ducts.
Possible risks
Bougienage of the lacrimal canal in children is a safe manipulation. To perform it, special instruments are used, and the patient is given local anesthesia. To prevent infection, care must be taken to ensure that pus does not enter the ears or second eye. As soon as the bougienage has been completed, rinse the eyes with a disinfectant solution.
The sooner you were able to see a doctor, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome. Bougienage should be carried out in the first year of a child’s life. It is best to do this before 5 months. The fact is that in babies at 8 months of life the gelatin plug becomes hard, so it will be difficult to get rid of it.
Doctors advise parents to protect their child from colds and runny nose during the first months. Otherwise, it is fraught with repeated suppuration. If we talk about complications, the most common is the formation of adhesions in the lacrimal canal. But the development of relapse when bougienage is performed correctly is minimized. So parents should pay due attention to choosing a specialist so that he can do everything correctly, and the baby will forever forget about such an unpleasant illness as dacryocystitis.
conclusions
Dacryocystitis is a dangerous eye disease in adults that can lead to serious complications. A similar disease is temporal arteritis, which is fraught with great consequences if misdiagnosed and untimely treatment at the clinic. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out correct, timely treatment and, of course, preventive measures to avoid the occurrence of this disease. There are various techniques to prevent the disease, such as massage, eye exercises to improve vision, yoga.
Symptoms of tear duct obstruction in children
One obvious manifestation is excessive tears, which may begin to flow with a vengeance after a cold or sinus infection. Additionally, symptoms may be more noticeable after exposure to cold, wind, or sunlight.
When the tear ducts are blocked, bacteria growing in the nasopharyngeal sac can lead to an infection called dacryocystitis .
Symptoms of dacryocystitis include:
- inflammation (swelling), tenderness, and redness of the inner corner of the eye or around the eye and nose;
- recurrent eye infections;
- secretion of eye mucus;
- brittle eyelashes;
- blurred vision;
- bloody tears.