Cysts on the retina are often the cause of stratification of the substance of this membrane. In the presence of peripheral cystic degeneration, in some cases, fusion of retinal microcysts occurs, which leads to the formation of slit-like spaces. These spaces can delaminate the entire retina. In the delamination zone, ruptures quite often form, which can be single or multiple. If retinal detachment occurs due to cystic degeneration, even if the membrane is ruptured, visual function can remain at a high level for a long time. Some scientists believe that cysts in the retinal substance arise as a result of impaired blood flow in the area of the macula and the peripheral region of the retina. This process is accompanied by swelling of the retina and its subsequent delamination. As a result of these changes, degeneration and death of retinal structures occurs.
What is a conjunctival dermoid cyst?
A cyst is a formation on the conjunctiva. It is not filled with anything and can disappear on its own. Often noticeable only in the morning. In general, cysts are usually called dermoid (benign). In appearance it resembles a bubble.
Types: retention, dermoid
Types of conjunctival cyst:
- teratoma (hard, retention, can degenerate into malignant);
- exudative (traumatic);
- pigment (medicinal);
- congenital (developmental anomaly, has a greater predisposition to growth).
The typology of the cyst can only be determined by a specialist.
If you detect any strange formation on the conjunctiva, you should consult an ophthalmologist. You should not touch your eyes with your hands, rub or try to remove a possible cyst yourself.
A product for moisturizing and protecting the sclera - instructions for Iridina eye drops.
Cysts can often go away on their own without medical intervention.
What kind of disease is iridocyclitis read in the article.
Causes and symptoms of optic cysts
The main reasons for the development of such education are:
- congenital pathologies and genetic disorders of the visual organs;
- parasitic, inflammatory and degenerative processes occurring in the organs of vision;
- infections of the organs of vision (scleritis, conjunctivitis, etc.);
- as a result of long-term use of medications;
- penetrating wounds of the eyeball, resulting in the entry of epithelial particles into the wound.
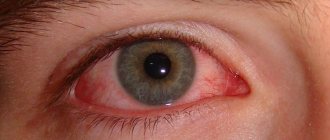
Symptoms of a cyst on the eye manifest themselves in the form of changes in visual acuity. This includes blurred vision, blurred contours of objects, limited horizons, and the appearance of floating spots before the eyes. Pain also occurs, especially at the site of damage to the cornea, a feeling of constant discomfort, and redness of the eye. More obvious manifestations include the appearance of a formation, and in the case of a dermoid cyst, displacement of the eyeball. If intraocular pressure increases, then all these symptoms become more acute and brighter.
Delayed complications
The main surgical risks include infection, side effects from general anesthesia, bleeding, etc.
Careful hemostasis and possible antibiotic therapy will help prevent the progression of complications.
Men who have undergone varicocele repair through surgery should understand that the following undesirable consequences may occur:
- periodic pain in the groin;
- testicular size discrepancy;
- insufficient motility of sperm and their total number.
Sometimes, long after varicocele surgery, certain problems may arise:
- Hydrocele of the testicle after varicocele (hydrocele) surgery. It occurs only if the lymphatic vessels in the testicle were crossed during the operation. The appearance of dropsy after surgery was recorded in 9-10% of operations performed. Almost all cases are patients who underwent open surgery.
- Pain after varicocele surgery (3-5% of cases). Discomfort can last for quite a long time (its occurrence is associated with stretching of the testicular appendages by venous blood).
- Very rarely - testicular atrophy or hypertrophy, problems with sperm production.
- Isolated cases of damage to the genital-femoral nerve in the inguinal canal (manifested by loss of sensation on the inner side of the thigh).
- Sometimes after surgery the veins still remain dilated. In this case, a repeat operation or correction may be prescribed.
- Rarely, surgery can negatively affect the amount of testosterone produced.
- Recurrence of the disease is also possible (25-40% - relapse after open surgery, 10-15% chance of disease return after the endovascular method, endoscopic method - 10% chance of relapse, microsurgical treatment - 2%). Children are more likely to have the blood flow problem return.
Pain after varicocele surgery, slight swelling and hyperemia of the skin in the first hours are considered normal and gradually disappear on their own. For severe pain discomfort, patients are prescribed analgesics.
Warning symptoms should include:
- fever,
- severe swelling of the scrotum on the operated side,
- purulent discharge from postoperative sutures,
- severe nagging pain in the groin.
READ MORE: How much does the stitch hurt after varicocele?
The most dangerous early complication is considered to be swelling after surgery of varicocele on the operated side.
The rehabilitation period has ended successfully, the stitches have been removed, but even in this case there is no need to relax. Late postoperative complications may also develop:
- Dropsy. The testicle on the operated side increases significantly in size, and upon palpation in the scrotum, watery contents will be detected. This only occurs during intervention using the Ivanissevich method, when there is a high risk of damage to the lymphatic vessels.
- Prolonged one-sided pain in the groin, aggravated by erection, appears if nerve fibers are affected.
- Testicular atrophy is a dangerous consequence in which the organ atrophies and sperm production completely stops. Difficult to restore.
- Development of relapse. After resection of the altered vessel, another section of the vein may swell, re-provoking stagnation of blood and lymph in the testicle.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=62KmqCqVzeU
Medical statistics show that most postoperative complications arise not through the fault of surgeons, but because the patient did not follow medical recommendations.
Complications
The situation may worsen: up to a malignant tumor. A small conjunctival cyst does not cause discomfort and does not reduce vision. As it increases, it causes a feeling of squeezing, pain, and the person begins to see worse.
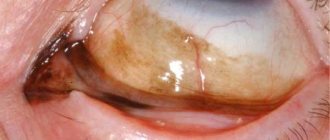
The dermoid type of the disease is often diagnosed in children: parents notice a round, pale yellow formation localized in the upper lateral regions. The minimum size is 5 mm, but in the absence of medical assistance, the affected area grows, sometimes spreading to the temple.
| When blinking, the cyst is damaged by the eyelashes. The result is microtrauma, overflow of blood vessels, and the addition of secondary conjunctivitis to the clinical picture. |
When blinking, the cyst is damaged by the eyelashes. The result is microtrauma, overflow of blood vessels, and the addition of secondary conjunctivitis to the clinical picture.
Treatment, even under the supervision of experienced doctors, does not guarantee protection against relapse. After surgery, allergies, subconjunctival hemorrhage, infection, corneal erosion, and suture dehiscence are possible.
Causes
A conjunctival cyst can occur due to:
- fibrosis after conjunctivitis;
- eye injuries;
- surgical intervention;
- scleritis;
- genetic factors.
The tumor may appear for no apparent reason or from simple rubbing of the eye.
Determining the cause of the cyst is important to determine its type and prescribe further therapy.
Smart correction - which glasses lenses are best to choose.
Tonometry
Find out when the prescription of Catarax eye drops is indicated here.
Causes
Let us emphasize the factors that provoke the disease:
- other pathologies - scleritis, blepharitis, canaliculitis, fibrosis after viral, bacterial, fungal conjunctivitis;
- trauma, friction of eyelashes, eversion of eyelids;
- hereditary predisposition;
- degenerative processes;
- parasites;
- ophthalmic drugs (phosphacol, physostigmine, pyrofos);
- operations, poor-quality sutures, unqualified therapy;
- ignoring hygiene.
What happens after surgery?
It is believed that complications after varicocele surgery are quite rare.
Basically, they are caused by the careless work of the doctor or unexpected difficulties that arise during the operation. However, you should not ignore all possible risks.
Sometimes after varicocele surgery the following consequences are possible:
- small hematomas;
- skin redness;
- swelling of the tissue around the incisions;
- There may be pinkish or clear discharge from the wound.
Such symptoms are considered normal and do not require medical intervention.
It's easier to prevent than to treat. Find out the causes of varicocele so you don't have to resort to surgery. A drug that improves blood circulation, Troxerutin, reviews of which you can read in our material, helps with many venous diseases.
But sometimes the following symptoms may occur:
- prolonged fever after surgery;
- severe pain in the testicles, swelling, descending redness;
- yellowish, brown discharge from the wound, smells unpleasant;
- enlargement of the scrotum on the side where surgery was performed (lymph stagnation occurs).
Symptoms and diagnosis
You can suspect the presence of a cyst based on the following signs:
- visual presence of yellow or brown spots on the white of the eye;
- tearfulness;
- pain in the eyes;
- discomfort;
- redness of the white;
- movement of the eyeball may occur;
- sometimes there is a cloudy spot in visual perception.
Sometimes the cyst does not manifest itself in any way other than being visible on the sclera. Even if other symptoms are not felt, you should consult a specialist.
When an invisible enemy creates noticeable problems - eye demodicosis symptoms and treatment.
Tearfulness is one of the first signs of cyst development
Diagnosing education is not difficult. This is done by using:
- visual inspection;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- visometry;
- tonometry;
- biomicroscopy;
- histology and biopsy of the material (after removal).
Tissue examination after separation of the cyst is necessary to determine the atypicality of the formation.
How to treat retinal dystrophy is described in detail in the article.
Retention view
Before starting treatment, carefully read the instructions - instructions for using Katachrom eye drops.
Symptoms and types
All types of the disease are characterized by the presence of a rounded bag on the surface of the eye. Most often this manifests itself on the cornea and is localized in its extreme regions.
In rare cases, cysts may develop in the inner areas (located between the eyelid and cornea) of the lower and upper eyelids.
The contents and appearance of such bags may vary and depend on the type of cyst. The following varieties are distinguished:
| Type of cyst | Manifestation |
| Pearl | It is a bluish-white formation that is distinguished by dense walls and opacity |
| Serous | Transparent and filled with liquid. It is this type of cyst that most often appears in people. Tends to increase in size, which can lead to swelling of the eye |
| Epithelial | Small flat translucent formations are brown in color. They consist of epithelial tissues: skin, hair, nails. These tissues enter the eye chamber during the embryonic period |
| Stromal | The rarest type of disease. It differs from epithelial formations in the greater transparency and unpredictability of its development: both the complete disappearance of the cyst and its rapid increase in size are possible. Its location in the eye chamber is unstable, and over time it can move to different areas. Occurs in the first year of life |
Health effects
The impact of a cyst on a person's well-being can range from being completely painless to causing significant vision problems.
As a rule, an epithelial cyst is painless for humans: it does not increase in size, does not reduce visual acuity, and does not cover its corners.
Serous and stromal cysts, increasing in size, can increase intraocular pressure and provoke the development of glaucoma, reduce visual angles, and seriously worsen a person’s appearance.
They also correspond to an unpleasant sensation of squeezing in the eyes, which intensifies when they close (especially when blinking); blackheads and other foreign objects may appear before the gaze.
In the long term, such manifestations lead to deformation of the eyeball and decreased visual acuity due to displacement of the lens.
Treatment methods for dermoid on the eye
The choice of dermoid treatment method depends on:
- localization of education;
- quantities;
- extent of distribution;
- reasons for occurrence.
Medication
Conservative treatment includes:
- eye drops;
- antibiotics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- trichloroacetylic acid injections.
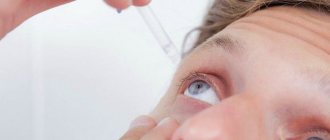
The following are prescribed as eye drops:
- moisturizing (Defislez, Alkon Systane, Slezin);
- anti-inflammatory (Dexamethasone, Inndocollir, Tobradex).
During treatment of a conjunctival cyst, it is forbidden to use contact lenses to avoid additional infection.
To prevent dry eye syndrome from interfering with your life and work, use Cationorm eye drops.
Differential diagnosis
Operations
If there is no effect from conservative methods, the patient may be indicated for surgery:
- surgical;
- laser
Surgical intervention:
- carried out in the presence of a voluminous education;
- Before surgery, local anesthesia and contrast agent are administered;
- the painted area is removed and a self-absorbing suture is applied;
- In some cases, plastic surgery is performed.
Laser Application:
- necessary for small-sized formations;
- the affected area is cauterized with a special beam.
Artificial tears will help relieve discomfort
Advantages of laser surgery:
- short rehabilitation period;
- absence of cosmetic defect;
- bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect;
- there is no chance of infection;
- passes almost always without complications.
This method is not used for large lesions due to the risk of burning the conjunctiva. The contents heat up and the cyst may rupture.
After any intervention, the patient is prescribed a gentle regime and anti-inflammatory therapy. Forbidden:
- lift weights;
- visit the pool and sauna;
- use cosmetics;
- wear contact lenses.
In some cases, treatment of the cyst is not indicated for the patient. Regular outpatient monitoring and specialist supervision are carried out. Even after removal, the risk of pathology returning remains.
The tumor may fester. Inspections should be performed as often as possible.
Read what the diagnostic method of keratometry is here.
Non-steroidal pain reliever
Conjunctival cyst of the eye: causes, types, symptoms and treatment
A disease accompanied by the formation of a hollow formation on the outer mucous membrane of the eyeball is defined in medicine as a conjunctival cyst.
The vesicular cavity is benign and does not pose a threat to human life.
The neoplasm requires mandatory treatment under the supervision of a specialist, but in some cases the cystic sinus can resolve on its own.
Cyst - what is it?
A round liquid formation that is located on the skin of the eyelid or on the membranes of the eye is called an ocular cyst. It is a liquid enclosed in a capsule. It occurs in both men and women in all age categories.
The cyst is benign, that is, it is not prone to degeneration into cancer. But it still requires treatment to prevent vision deterioration.
Classification
Depending on their location, cysts can be on the conjunctiva, cornea, retina, skin of the eyelids, and in the corners of the eyes. The most common is a conjunctival cyst.
There are several types of cysts. The tactics of treating the disease depend on this.
- Congenital. It is formed when the separation of the pigment layer of the iris is disrupted in the prenatal period. A congenital cyst on the eye is detected in a child in the first days after birth.
- Traumatic. Appears after mechanical damage to the visual organ due to penetration of the integumentary epithelium into the eye chamber.
- Exudative. It is a consequence of glaucoma or long-term use of anticholinesterase drugs.
- Conjunctival. It can be implantation (postoperative) and retention (stagnation of lymph and tear fluid due to the inflammatory process).
- Stromal. Prone to changing location, rapid growth, and disappearing on its own.
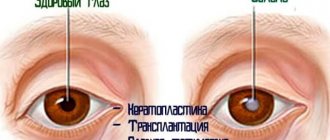
- Dermoid cyst (teratoma). It occurs due to disruption of developmental processes and is detected immediately after birth. Teratoma contains fragments of epithelial tissue (hair, nails, teeth).
- Spontaneous. It develops for no reason. It can be pearly (white contents with a pearlescent sheen) or serous (transparent contents).
brief information
The lacrimal glands are responsible for producing fluid and draining it into the nasal cavity. These are paired organs that perform tear secretion and tear drainage functions.
The lacrimal ducts are presented in the form of: lacrimal stream, lake, puncta, canaliculi, sac and nasolacrimal duct. The functioning of the glands is regulated by the fibers of the facial and branches of the trigeminal nerves.
The lacrimal apparatus is supplied with blood through a special artery, and return flow occurs through the vein adjacent to the gland.
The tear fluid contains water, urea, mineral salts, protein, mucus and lysozyme. The latter is an antibacterial enzyme, thanks to its properties it cleanses and protects the eyeball from harmful microbes. The secreted liquid washes away grains of sand and foreign small objects from the eyes.
Symptoms
Small eye cysts may not manifest themselves for a long time. A person may not notice the appearance of a tumor or not attach any importance to it. As the size increases, clinical symptoms appear:
- Feeling of discomfort, compression.
- The appearance of floating flies before the eyes.
- Redness of the eyeball, swelling.
- Limitation of visual fields, decreased visual acuity.
- Deformation in the area of the neoplasm.
- Pain in the eyeball.
- Displacement of the eyeball with large cystic formations.
The larger the diameter of the cystic formation, the more pronounced the symptoms. In addition, a person is concerned about a cosmetic defect when a cyst occurs on the white of the eye or eyelid.
Conservative therapy against cysts on the eyeball
Treatment for an eye cyst should be tailored depending on where the growth is located. If the location is the eyeball or the eyelid area, the specialist must first determine the size of the cyst and determine whether it has caused an inflammatory reaction in the eye.
In the absence of infectious processes, the patient is prescribed conservative therapy, which involves the use of:
- medicinal ointments based on dexamethasone and hydrocortisone;
- eye drops with antiseptic (Albucid).
Eye drops can help get rid of conjunctival infections. In addition, they are an excellent preventative against scarring after cyst removal.
Important! If there are no signs of inflammation, it is simultaneously recommended to resort to physiotherapeutic procedures (eyelid massage, UHF, electrophoresis, warm compresses).
Diagnostics
If a cyst is detected on the eyeball, you must contact an ophthalmologist at the clinic. To establish a diagnosis, the following examination methods are used:
- External inspection.
- Tonometry to determine IOP.
- Perimetry allows you to evaluate the boundaries of the visual fields.
- Visometry characterizes visual acuity.
- Biomicroscopy to determine the condition of the optic nerve head and retinal vessels.
- To determine the exact location of the pathological formation, ultrasound of the eyeballs, CT, and MRI may sometimes be needed.
- Puncture followed by examination of the cellular composition.
Folk remedies
There are very few traditional methods and methods for treating cysts, and the most effective of them are the following:
- Using guava leaves as a compress. To do this, you need to prepare a decoction (50 grams of leaves per 200 grams of boiling water), cool it, take a clean cloth (tampon, sterile bandage), moisten it and apply it to the cyst area for 7-12 minutes. This compress relieves redness and reduces pain.
- Boil a few acacia leaves and place a cloth in the resulting broth. Then place the cloth on your eyelids for 10-13 minutes. It is believed that the cyst disappears naturally using this method.
- Used tea bag. This is the most popular and effective folk remedy for the treatment of cysts of the eyelids and eyeball.
Most folk methods involve the use of decoctions based on medicinal herbs. It is important to remember that such treatment can only be used after examination in a hospital. It provides support and can provoke resorption of the cyst, but will not cure if the tumor occupies a large area.
The most commonly used means:
- Algae tincture - dry seaweed called Fucus is used.
The collection is purchased at the pharmacy. Three tablespoons of the dry mixture are poured with boiling water into a thermos and allowed to brew overnight. Then pour into an ice tray and freeze. Use the resulting cubes to wipe the eye area and eyelids. Fucus is poured with boiling water, after which it is frozen into cubes and ground at the site of the tumor. - Herbal infusion - you should take cornflower petals, plantain leaves and cumin. All herbs are well crushed and then poured with boiling water. The cooled solution is filtered. You should drop 3 drops into the eyeball at least five times a day.
- Guava decoction - only leaves are used. The affected eye is washed three times a day.
The following decoctions are used as compresses and for rinsing: acacia leaf based, chamomile tea, rose water with honey.
Treatment of a cyst in the eye with folk remedies can aggravate the course of the disease, so it is recommended to consult a doctor. The main thing to remember is that traditional methods are only an auxiliary means of treatment.
Treatment of cystic neoplasms
Treatment tactics for eye cysts in adults and children depend on the cause and type of cystic formation. In some cases, drug therapy is effective, but a more radical method is surgical removal. Folk remedies are auxiliary in nature and help reduce clinical manifestations.
Drug therapy
Treatment with drops and ointments is justified for inflammatory or allergic processes. For the treatment of infectious eye diseases, Floxal and Tobrex drops are prescribed; eye ointments "Tetracycline", "Erythromycin". To relieve allergy symptoms, Opatanol, Cromohexal, and Allergodil drops are prescribed.
Treatment of the underlying cause in some cases leads to a decrease in size, sometimes to the complete disappearance of the cyst. But the most effective method is surgical removal of the cystic formation.
Surgical removal
Surgical treatment consists of removing the formation along with the cystic capsule. The removal process is carried out using a scalpel or laser. Small superficial formations such as retinal cysts are suitable for laser treatment. For larger sizes, the classic surgical method is usually used.
Source: https://PrimaMed-kzn.ru/bolezni/kista-konyunktivy-glaza.html
Treatment of the disease
Eye drops are necessary for the patient if the formation is infectious. If the cyst is small, does not grow and does not cause danger, therapy is not prescribed. The patient needs to monitor its condition; there is a high probability that the formation is spontaneous and will disappear on its own. Treatment is necessary if the disease has an infectious etiology. In this case, anti-inflammatory drops are prescribed. The goal of the treatment course is to stop the process, and the cyst disappears over time.
If the formations are large, they should be removed. A safe method is laser surgery. With its help, the doctor performs a non-contact opening of small retention cysts of the eyelids and conjunctiva. The entire body of the formation is removed with a beam and the area is sanitized. It is very important to cleanse the membrane of pathological components, otherwise there is a risk of relapse. The operation is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. The risk of complications is practically reduced to zero. The excised material is sent for histology to exclude the development of cancer.
Symptoms
In the early stages of development, the cyst in the eye does not manifest itself in any way and is practically asymptomatic. When massaging the eye, you may feel a small painless nodule on the upper or lower eyelid. In some cases, a couple of weeks after detection, the neoplasm resolves on its own, and in other cases it increases in size up to the size of a pea, and then a whole complex of symptoms appears:
- narrowing and blurring of visual fields;
- translucent dots before the eyes;
- dull bursting pain;
- deformation of the eyelid;
- redness and swelling of the sclera;
- A yellowish area forms in the center of the cyst.
The location of the cyst in the eye area: the formation can occur on the eyelids, on the surface of the eye (often this is its outermost part).
What is the danger of the disease
The appearance of a conjunctival cyst in itself is not dangerous. Neglected forms may result in:
- tumor growth;
- visual impairment;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- degeneration of pathology into a malignant form.
Any non-standard formation on the sclera of the eye must be shown to a specialist.
If there is a need or a bad family history, it is better to remove the cyst immediately to avoid consequences.
An examination will help you quickly and correctly establish a diagnosis.
A dangerous disease that cannot be left untreated is keratopathy.
Diagnostics
In the case of secondary retinal cysts, visual acuity in patients is reduced to 15-20%. In the case of primary changes, visual acuity often reaches one hundred percent (subject to correction).
When studying the visual fields, loss of certain areas that correspond to the zone of the dissected retina can be identified.
An informative examination method that allows you to establish a diagnosis is optical coherence tomography. In this case, the doctor can establish the nature, features and height of the dissection using absolute values.
Varieties
There are several types of the disease in question. Each person has a specific treatment program.
- Exudative. It is a consequence of glaucoma.
- Congenital. Appears due to the separation of part of the iris, which protrudes beyond the mucous membrane.
- Traumatic. Damage leads to it. For example, during impacts or as a result of surgical work.
- Post-inflammatory. It originates from illiterate treatment of concomitant diseases.
- Spontaneous. The reasons for the appearance cannot be determined. Such a cyst is usually transparent, and its relative inconspicuousness makes it difficult to detect.
- Dermoid. Solid in consistency. Characterized by disturbances in the development and order of movement of epithelial cells. As a result, vision deteriorates and the eyeball becomes displaced. Often occurs against the background of Goldenhar syndrome (for example, certain abnormalities of the ears).
- Pigmentary. It is provoked by potent anticholinesterase drugs designed to reduce intraocular pressure. As a rule, for recovery it is enough for the drug to stop entering the body.
- Retentional. The most harmless form. This is a thin-walled bubble filled with colorless contents. In most cases it disappears on its own. It only causes discomfort when it is located in the center of the organ.
| Single and multiple cysts are also distinguished. The former affect the upper or lower part of the eyeball, the latter, the proximal fornix of the conjunctiva. |
Single and multiple cysts are also distinguished. The former affect the upper or lower part of the eyeball, the latter, the proximal fornix of the conjunctiva.
Classification
Cysts in the retina can be primary, secondary, or hereditary. Primary cysts are usually detected at a young age in patients with myopia. Sometimes they can appear at the age of 50-60 years as a result of senile degenerative processes. Secondary cysts always occur against the background of some pathological process in the eyeball.
Another type of classification of retinal cysts distinguishes the following varieties:
- Degenerative cysts (acquired, senile) can be typical or reticular (dome-shaped retinoschisis, giant retinal cyst).
- Hereditary cysts.
- Secondary retinal cysts occur against the background of many diseases:
- vascular pathologies (retinopathy of prematurity, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, central retinal vein occlusion, sickle cell retinopathy),
- inflammation (chronic iridocyclitis, peripheral and chronic uveitis),
- congenital pathologies (optic disc fossa, Coats disease),
- trauma (forced shaken infant syndrome, blunt head trauma, retinal hemorrhages of newborns),
- oncological diseases (choroidal hemangioma, malignant melanoma, combined hamartoma with damage to the pigment epithelium and retina),
- other diseases (rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with long-term existence, aplastic anemia);
- teratogenic pathology that occurs when using diphenyl dihydropyrimidine.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for detecting a conjunctival cyst is favorable. If you consult an ophthalmologist in time, you can avoid any consequences. Preventive measures include:
- compliance with hygiene standards and rules (removing makeup, prohibiting rubbing eyes with hands, etc.);
- timely examinations by a specialist;
- regular replacement of contact lenses when using this method of vision correction;
- self-massage.
We also recommend that you read our article which will tell you how to put on lenses for the first time.
If the disease is manifested in relatives, the patient must consult an ophthalmologist at least 2 times a year.
After surgery it is not recommended to swim in the pool
Recovery after surgery
Varicocele is a common disease that often occurs in men of all ages. Its diagnosis is possible as early as 10 years of age, if appropriate symptoms are present. Thus, timely detection of vascular dilation in the area of the spermatic cord increases the possibility of a positive outcome of the chosen method of eliminating pathology and preventing infertility in a man.
Proper recovery after varicocele surgery increases the chances of a successful treatment prognosis.
The first and most important factor influencing the duration of rehabilitation after surgery is the man’s age. The features of the chosen treatment method are taken into account.
If a Palomo or Ivanissevich operation is performed, which involves excision of a vein, the recovery period can last up to 3 weeks or more.
Endovascular treatment involves blocking dilated vessels using special devices (balloons, spirals). Full or partial recovery occurs within a few days after the procedure.
Microsurgery is convenient because the patient’s well-being noticeably improves within 2–5 days. It all depends on the exact fulfillment of all the doctor’s instructions during the rehabilitation period.
The overall positive dynamics of recovery depends on the absence of swelling and pain, and the appearance of dropsy in the problem area. Improving sperm count is very important.
Even if the patient tolerated the operation well and feels satisfactory on the first day, he should spend as much time as possible in a lying position.
At the slightest fatigue, complete rest and maximum inactivity are indicated. Prolonged sleep contributes to a speedy recovery.
As for the diet, it may include foods familiar to a man. If you have an upset stomach, it is recommended to eat soft foods that contain a small amount of fat. These are fermented milk products, chicken meat, boiled rice, fresh vegetables and fruits.
During the recovery period after varicocele, patients complain of irregular bowel movements. It is important to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract as soon as possible, since strain during bowel movements can cause pain and discomfort. In some cases, your doctor will prescribe a mild laxative.
A cold compress or ice that is applied for 10 to 15 minutes, no more, is good for reducing pain after surgery in the groin area. Be sure to have a soft cloth between the skin and the compress.
Regular examination and compliance with all instructions from your doctor will be a key part of a speedy recovery from varicocele. At the slightest deterioration in health, a trip to a medical facility is inevitable.
First, we propose to define what a varicocele is?
This is an exclusively male disease associated with impaired blood flow in the testicles.
The vessels in this organ have a characteristic feature - they form a pampiniform plexus, which receives blood from the testicle and vas deferens. This plexus forms the testicular vein, from which blood enters the abdominal cavity.
However, for certain reasons (weak vessel walls, pressure), blood flow in the testicle worsens and blood stagnation occurs, the temperature in the genital organ rises, sperm die, and testicular necrosis occurs.
According to statistics, 15-17% of men develop varicocele. 35% of cases of varicocele are diagnosed using ultrasound in men who have reached puberty. The largest number of onset of the disease was recorded in adolescents (14-15 years old) – 19.3%.
If detected in time, the disease can be treated. In the initial stages, it is enough to eliminate the accompanying cause (for example, varicose veins).
At stages 3-4 of the disease, treatment is exclusively surgical.
Surgical intervention for varicocele is not very difficult and recovery after varicocele surgery occurs quickly and without any problems.
The patient can be discharged to home rest in a day or two (usually it is recommended to stay at home for 7-10 days). However, each case is individual, sometimes it is necessary to keep the patient in the clinic longer.
On an outpatient basis, the patient visits the doctor after a month, six months, a year and a half. An examination and spermogram are carried out. The doctor gives general recommendations regarding physical. loads and preventive measures.
The recovery period depends on the type of operation performed (for example, surgery using the Ivanissevich method requires 7-14 rehabilitation days, endovascular surgery - 1-2 days, microsurgical varicelectomy - 2-3 days).
Also, the period will depend on the age of the patient (the higher the age group, the longer the recovery takes).
Rehabilitation after varicocele surgery includes:
- selection of a suitable mode of sexual and physical activity;
- therapy to prevent inflammation;
- further methods will depend on the success of healing and recovery of the testicle.
The duration of the recovery period depends on the technique of the intervention:
- according to Ivanissevich – 1–2 weeks,
- microsurgery – 2–3 days,
- laparoscopy – 1–2 days,
- endovascularization – no more than a day.
But this does not mean that after the specified period a man can completely return to his usual lifestyle. For 30 days, you must limit the following:
- Lifting weights. You are allowed to lift no more than 4 kg. If the work involves physical labor, then for this period the sick are given a recommendation to the employer about providing easier conditions or are issued a sick leave.
- Sports activities. Running, cycling or strength training can cause late complications.
- Sexual activity. Having sex or masturbation after varicocele surgery is prohibited for at least 3 weeks. This is not due to erectile dysfunction, but to the fact that in case of premature sexual contact, the vein of the spermatic cord will cause painful discomfort when a large amount of blood flows.
- Overheat. It is forbidden to visit baths and saunas, and a bath can only be taken on the 5th day after varicocelectomy.
READ MORE: What not to do after cataract eye surgery Do's and don'ts Studies have shown that the spermogram, regardless of the type of intervention, improves after about a month. The same amount of time is required to restore full blood flow in the testicle.
Even if a man does not experience discomfort after surgery, this is not a reason to assume that a complete cure has occurred. Neglect of medical recommendations often provokes the development of late postoperative complications.
Vitrectomy
During vitrectomy, the altered substance of the vitreous body is removed, after which the surface of the retina is cleaned of fibrils. Next, the fluid that has gotten under the retina is removed. The resulting cavity in the eyeball is filled with silicone oil, a gas-air mixture, sterile air or perfluoroorganic compounds. Laser coagulation is carried out directly during surgery using a special intraocular tip. Local anesthesia is usually sufficient for vitrectomy. If the resulting cavity is filled with air (gas-air mixture), then this gas is gradually replaced by intraocular fluid, that is, there is no need to perform a second operation. If the cavity is filled with silicone oil, the latter must be removed from the eye after a certain time, which is determined taking into account individual indicators. Usually the second operation is performed after a month or more. In some cases, in addition to vitrectomy, the surgeon also performs extrascleral filling.
If during the operation it was not possible to achieve a tight fit of the retina, then most likely we are talking about a long-term detachment due to diabetes mellitus or other systemic diseases. Most often, in this case, scar tissue forms, which prevents the fusion of the retina. In this case, visual function will continue to decline until the eye goes blind. In addition, subatrophy of the eyeball may develop, which will require removal of the eye.
In this regard, it is very important to seek qualified help in a timely manner and perform surgical treatment of retinal detachment.
Feedback on treatment results
Reviews from patients indicate that the choice of treatment method for conjunctival cysts is purely individual. Surgical intervention or drug treatment is based on determining the size of the formation and the degree of spread.
- Marina, 34 years old, Olenegorsk: “I treated a conjunctival cyst twice. The first time - with the help of drops. It resolved quite quickly. It’s just not clear: spontaneously or due to the effects of the drug. Now I had to have surgery because the pathology had returned. It went by very quickly. There’s nothing left anymore.”
- Vladimir, 40 years old, Nizhny Novgorod: “The cyst appeared not so long ago. It grew very quickly. It became difficult and painful to watch. The doctor decided to perform surgery. After it, the eye began to look terrible. I had to resort to plastic surgery. Everything is fine now, I hope there will be no relapse.”
- Svetlana, 58 years old, Saransk: “My grandson has a small lesion on the white of his eye. They showed him to the ophthalmologist. It turned out that it was a cyst. The doctor recommended not to use anything for now. And he turned out to be right. The cyst resolved on its own in just a couple of weeks.”
See the world with healthy eyes
Conjunctival cyst of the eye: retention, dermoid, treatment and drops
A conjunctival cyst is a small, hollow neoplasm formed on the thin, transparent tissue that envelops the eye from the outside, which is commonly called the conjunctiva.
Such a pathological formation does not pose a danger to the functioning of the visual apparatus, but it causes a lot of inconvenience, accompanied by such unpleasant symptoms as tearing, discomfort, and the sensation of a foreign body in the eye. Treatment of the problem must be comprehensive.
What it is?
The conjunctiva is a transparent thin film covering the external organs of vision. The main task of this part of the visual apparatus is to produce the secretion of tear fluid, which moisturizes the surface of the eye.
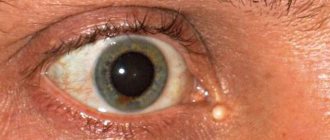
A conjunctival cyst is a small cavity neoplasm filled with transudate (mucus, liquid) . The epithelial formation looks like a pink or yellow bubble, which can be easily seen upon visual inspection.
Most often, the pathology is noticeable only in the morning.
Such a tumor is benign in nature, but if not treated in a timely manner, it can turn into a cancerous form. Depending on the nature of origin, dermoid (benign) conjunctival cysts can be:
- Congenital. It is an anomaly of embryonic development that occurs as a result of dissection of the iris, extending beyond the mucous membrane. Has a tendency to grow rapidly.
- Spontaneous. They appear for unknown reasons on any part of the eyeball and are transparent and inconspicuous.
- Traumatic. They are a consequence of mechanical action. Most often they occur as a result of a blow or surgical intervention on the organs of vision.
- Pigmented. They are formed against the background of long-term use of certain medications. After stopping the drugs, the tumor goes away quickly.
- Degenerative. Occurs due to glaucoma.
Treatment of conjunctival cysts with medications
Drug therapy is prescribed for conjunctival cysts caused by infectious agents. To eliminate this pathology, the following medications are prescribed:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Nimid, Xefocan.
- Glucocorticosteroids: Dexamethasone, Prednisone.
- Ophthalmic drops: Tobradex, Defislez, Albucid.
- Sclerosing agents: trichloroacetylic acid solution.
Such drops will help relieve unpleasant symptoms.
These medications do not contribute to the resorption of the retention cyst, but they eliminate symptomatic manifestations, prevent scarring of the mucous membrane and eliminate the root cause, due to which the formation disappears.
Phytotherapy
In the simplest clinical cases, the use of herbal medicine (herbal therapy) may be recommended for the treatment of conjunctival cysts. Most often, the following drugs are used for this diagnosis:
- Herbal decoctions and infusions based on the leaves of cornflower, plantain and other plants that have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Morning dew collected from the grass.
- Pharmaceutical algae. The herbs should be poured with a glass of boiling water, left overnight, and in the morning, rinse your eyes with the resulting infusion.
- Cornflower. A tablespoon of blue cornflower leaves should be poured into a glass of boiling water, let it brew for 1 hour, then drop 3 drops into the eyes 5 times a day.
Some people use urine therapy to treat conjunctival retention cysts. Folk remedies and herbal medicine will help get rid of the tumor only at the initial stage of development of the pathology and with adequate use.
Surgical intervention
In advanced situations, when dermoid cystic formation cannot be eliminated with the help of medications and folk remedies, surgical intervention is performed. The operation is not complicated and can be performed under either general or local anesthesia (special drops). Its essence lies in excision of the contents and walls of the cyst.
At the end of the procedure, which lasts no more than 30 minutes, the eye is treated with antibacterial ointment and bandaged, after which the patient can go home. This operation is rarely accompanied by complications, and the patient does not need long-term rehabilitation.
Laser surgery
For small tumors that are not amenable to conservative treatment, laser surgery is used.
Excision of a cyst with laser radiation is a more gentle surgical technique, with which you can quickly, painlessly and safely get rid of the problem, eliminating the risk of the formation of cosmetic defects. Compared to surgery, laser surgery has the following advantages:
- anti-inflammatory effect;
- bactericidal effect;
- fast recovery;
- no risk of infection;
- minimal likelihood of relapse.
Specifics of treatment in children
Preschoolers and newborns are more susceptible to developing dermoid cysts than adults. The reason is a violation of the development of the embryo. Drops and ointments will not help here. The patient’s readiness to “go under the scalpel” is determined by the ophthalmologist to whom the parents register the baby.
During a fifteen-minute operation performed on a child under seven years of age, general anesthesia is used. Local anesthesia is used for older children. In a boy or girl, conjunctival cystosis requires regular monitoring in the hospital. There is a risk of developing astigmatism, strabismus, and amblyopia.