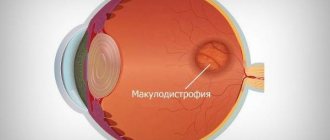
The inner layer of the eye is called the retina. It regulates the interaction between the central nervous system and the organs of vision. It is she who is responsible for translating light signals perceived by the organs of vision into corresponding nerve impulses sent to the brain.
A number of visual impairments, which are characterized by changes in the retina and are irreversibly destructive, are called dystrophy. Pathological changes in retinal tissue always lead to a stable deterioration of vision. To prevent its loss and progression of the disease, it is necessary to treat retinal dystrophy.
Causes of the disease
The impetus for the development of retinal dystrophy (acquired), a dangerous disease for eye health, can be many reasons of a different nature:
- any type of eye injury;
- toxic effects on the body of any origin;
- other diseases of the visual organs, for example, myopia, inflammation, etc.;
- complication after surgery;
- infectious diseases;
- systemic health problems (high blood pressure, kidney disease, diabetes, etc.).
All of these listed reasons can contribute to the development of the disease, but they are just risk factors. With a hereditary predisposition, the risk of the disease can be considered extremely high. For your information! Even stress, pregnancy, excess weight, and direct solar radiation can play a role as a trigger for the onset of the disease.
Causes of retinal degeneration
Medicine has never found the exact causes of the degenerative process. Some experts believe that the disease is hereditary. Often it begins to manifest itself only in old age. This phenomenon is associated with the accumulation of metabolic substances in nerve tissues. The main factors are considered to be the following.
- Impaired blood flow in the body. The cause may be increased blood pressure, diseases of the vascular system, elevated cholesterol and blood sugar.
- Poisoning or infection of the body.
- Myopia.
- Diabetes.
- Excess weight.
- Bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Exposure of the visual organ to direct ultraviolet rays.
- Unhealthy diet, where fatty foods predominate.
- Lack of vitamins in the body.
- Constant stressful situations.
Retinal degeneration can also develop at a young age as a result of:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases associated with the endocrine system;
- pregnancy;
- injury to the visual organ.
Diagnostics
Effective treatment of the disease requires competent, timely diagnosis and examination by an ophthalmologist. Among the studies that can be recommended are:
- retina;
- light sensations;
- Ultrasound;
- fundus;
- eye structures;
- determination of the boundaries of peripheral vision;
- visual acuity test;
- electrophysiological examination, which gives a picture of the state of the retina itself and nerve cells;
- fluorescein angiography to study the vessels of the eye.
Prices for diagnosis and treatment for retinal dystrophy
| Consultation with a laser surgeon (with standard diagnostics) | 2,500 rubles |
| Fundus examination (ophthalmoscopy) | 1,500 rubles |
| Comprehensive eye examination for retinal diseases (8 examinations) | from 8,600 rubles |
| Laser treatment of peripheral dystrophies and retinal tears | from 13,000 rubles |
| Intravitreal administration of drugs | from 22,000 rubles |
ATTENTION! The exact cost of treatment can only be determined after a face-to-face consultation, when the condition of the patient’s eyes is determined and a treatment plan is drawn up.
You can find out the cost of basic procedures and operations in the PRICES section.
Types of retinal dystrophy
The disease is divided into types, which is associated with its origin and the location of the inconsistent pathological process of the retina. There are hereditary and acquired forms of the disease.
Hereditary. This is an inherited dystrophy; it includes several types. But the most common are: dotted white and pigmented.
- Spot white. This pathology is congenital. Development occurs from early childhood, which leads to a deterioration in visual perception even before school.
- Pigmented. This is a genetic eye disease. Dystrophy of this type is characterized by disruption of the functioning of photoreceptors, which are important for human twilight vision.
The disease has a slow course with stable deterioration, despite alternating periods of remission after exacerbations. Most often the disease manifests itself while studying at school. By the age of 20, the disease clearly manifests itself and a diagnosis is made. With age, the condition worsens so much that it can lead to complete loss of vision.
Treatment of macular degeneration
The choice of treatment regimen for age-related macular degeneration depends primarily on the form (wet or dry) and stage of the disease. Treatment should be comprehensive and selected individually, taking into account the changes in eye tissue diagnosed in a particular patient.
All patients with AMD are advised to use drugs containing natural antioxidants - vitamins A, C and E, lutein and zeaxanthin, copper and zinc, omega-3. The same drugs can be taken to prevent age-related macular degeneration and prevent the progression of pathological changes in the retina in patients over 50 years of age, especially if they have the previously mentioned risk factors. In patients with the wet form of age-related macular degeneration, special treatment methods are used, the purpose of which is to suppress the formation of pathological vessels (drug treatment, photodynamic therapy, laser coagulation, etc.).
The most effective method of treating wet forms of AMD, recognized by the world's leading experts, today is the use of drugs that selectively suppress the proliferation of pathological choroidal vessels.
Their use allows not only to avoid rapidly progressing vision loss in patients with wet AMD and to achieve stabilization of its acuity, but also in some cases leads to improved vision.
The drugs are administered in the form of intravitreal injections (directly into the vitreous cavity), in an operating room, in compliance with all the rules of asepsis and antiseptics.
Thanks to targeted administration, it is possible to achieve a targeted effect on the pathological vessels of the eye and avoid the occurrence of systemic side effects. The frequency of use and duration of treatment are determined individually by the attending physician.
By contacting the Moscow Eye Clinic, you receive attentive attention from recognized Russian specialists, examination using the latest equipment and treatment using the most effective methods that guarantee effective results and allow you to preserve your vision.
Acquired dystrophy
This type of disease is typical for older people. It may occur in combination with other diseases of the visual organs associated with age-related changes. It is impossible to completely cure it conservatively. Depending on the affected area, there are:
- Generalized (with this type of dystrophy, damage to the retina affects all its areas).
- Central (macular).
- Peripheral.
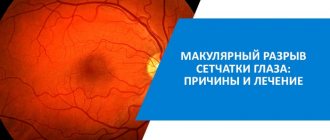
Central dystrophy. Macular degeneration of the retina is named for its location in the area of the retina (macula) that is responsible for the area of clearest vision. Types of macular degeneration:
Depending on the pathology and damage to the retina, the following types are distinguished:
- serous choriopathy;
- age (wet or dry);
- colloidal;
- cone (congenital);
- Best's disease;
- Franceschetti's disease;
- Stargardt's disease.
Important! In the central form of dystrophy without damage to peripheral areas, the development of the disease does not lead to blindness.
Patients experience discomfort and complain to the ophthalmologist of the following manifestations:
- doubling of objects;
- the image of objects is distorted.
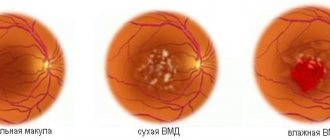
Age-related dystrophy. Treatment for macular degeneration of the retina depends on the clinical form (dry or wet) and the degree of pathology. Both forms of the disease are characteristic of the age group over 60 years. The central part of the retina is damaged due to age-related changes. It is the macula that is responsible for the eye's ability to distinguish small objects. But even in cases of severe disease, the peripheral parts of the retina continue to perform their functions and blindness occurs in very rare cases.
The peculiarity of the wet form is the penetration of fluid and blood into the retina. The loss of vision occurs extremely quickly, up to several days. Treatment of this condition is complex and surgical.
The most common is the dry form, in which the deterioration occurs gradually. The disease is characterized by the accumulation of cellular breakdown products between the retina and the lining of blood vessels.
Patients with age-related macular degeneration are recommended to undergo inpatient treatment once every six months, give up bad habits, and be required to wear sunglasses.
Peripheral. This type of retinal lesion is characterized by damage only to the peripheral area without affecting the macular area. Of the manifestations of the disease, a person can only note the appearance of “flies” before the eyes.
A feature of peripheral dystrophy is its difficult diagnosis. When an ophthalmologist examines the patient's fundus, the peripheral areas are practically invisible. Pathology can only be diagnosed using special equipment. Classification of peripheral dystrophy:
- pigmented;
- fine-grained;
- frost-like;
- lattice.
Often, against the background of myopia, retinal detachment may occur. In this case, the patient complains of a feeling of a veil before the eyes, but without surgery, vision can no longer be restored.
Causes
The most common cause of peripheral retinal degeneration, ophthalmologists call myopic refractive error, that is, banal myopia. With this disease, the eyeball becomes elongated along the anterior-posterior axis. With this shape of the eye, its periphery is constantly under tension, which causes the blood supply to tissues, including the retina, to deteriorate. On the latter, tractions are formed - areas with excessive tension, where a gap forms over time. The liquid fraction of the vitreous body “leaks” into it, which leads to peeling of the retina from the vascular substrate. Thus, this part of the visual apparatus finally loses its power sources and dies.
According to statistics, peripheral retinal dystrophy in 30-40% of cases is caused by myopia.
Farsightedness accounts for no more than 8% of all diagnoses. In people with normal vision and no refractive problems, such retinal damage is diagnosed in 3% of cases.
In addition to congenital or acquired myopia (myopia), dystrophy can be caused by:
- acute and chronic inflammation of the eyes and intraocular structures, provoked by viral and bacterial infections or autoimmune processes;
- cataract;
- eye damage, including trauma and surgery;
- chronic systemic diseases - diabetes mellitus, hypertension, vascular atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease and others;
- chronic poisoning, including alcohol metabolites and tobacco smoking products;
- chronic deficiency of nutrients, vitamins and minerals;
- age-related changes.
Good to know! According to statistics, those most susceptible to peripheral retinal dystrophy are those with fair skin and blue irises. In them, the main cause of pathology, in addition to those listed, is the traumatic effect of ultraviolet radiation on the eyes.
As for the age distribution of the disease, in young patients its causes are more often refractive errors, trauma and infection, while in older patients dystrophy occurs against the background of vascular anomalies and age-related changes.
Treatment methods
Dystrophy is a serious disease that can lead to complete blindness. Already lost vision at the onset of the disease and exacerbations cannot be restored. For the most part, treatment is supposed to be symptomatic, since, except for secondary ones, any types of degeneration have a hereditary predisposition. Treatment is mainly aimed at the following actions:
- stabilization of the condition;
- prolongation of periods of remission;
- strengthening the muscles of the eyes and blood vessels;
- improvement of metabolic processes in the organs of vision.
Methods of treating the disease:
- medicinal;
- physiotherapy;
- surgery;
- laser coagulation.
In some cases, eyes are treated with folk remedies, which can be used in combination with other treatment methods, but always under the supervision of the attending physician.
Laser coagulation
This treatment method is designed to prevent a serious complication of dystrophy - retinal detachment and prevent vision loss. The laser allows you to provide a targeted effect without damaging healthy tissue. During the manipulation, the damaged areas are cauterized to the desired areas of the eye to the specified depth.
Surgery
Whether it is possible to do without surgical intervention is determined by the doctor after a comprehensive examination of the patient. Retinal dystrophy is treated surgically most often in cases where the disease was diagnosed late and when it no longer makes sense to hope that eye injections will help.
To improve metabolic processes and normalize blood supply, patients undergo vasoreconstructive surgery. When the wet form is diagnosed, treatment of macular degeneration of the retina is aimed at preventing the accumulation of fluid in the retinal tissue. To prevent retinal destruction, the following surgical methods are used:
- Vasoreconstruction, which is based on the use of transplants;
- Revascularization results in an increase in the lumen of functioning vessels.
Physiotherapy
For retinal dystrophy, physiotherapy is prescribed in the initial stages of the disease to strengthen the eye muscles and the retina itself. Several methods of physiotherapy exist and are used:
- ultrasound therapy;
- phonophoresis;
- electrophoresis;
- microwave therapy;
- laser irradiation of blood (intravenously).
Drug treatment
Retinal dystrophy can be treated with medications only at the earliest stages of the disease. In other situations, the positive effect of such conservative treatment alone is impossible. The following medications are indicated for patients:
- vitamins E and A;
- angioprotectors;
- corticosteroids;
- products with lutein;
- agents that strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- local acting vasodilators;
- antioxidants;
- general action vasodilators.
Forms of the disease
- Dry - 85-90% of cases of dystrophy. In the area of the macula, drusen are formed - non-split formations containing the pigment lipofuscin. Such formations impair the metabolism of the retina, causing the macula to atrophy, leading to a decrease in the quality of vision.
- Wet - 10-15% of cases of dystrophy. It is characterized by the formation of pathological capillaries in the choroid - with them the body compensates for the deterioration of retinal trophism. New vessels are very fragile, this leads to local hemorrhages with subsequent formation of scar tissue. Vision deterioration in this form progresses faster than in the dry form.
Treatment of dystrophy
Treatment tactics for retinal dystrophy depend on its form and stage. The treatment method must be comprehensive and prescribed individually. The goal of treating wet dystrophy is to suppress the formation of pathological vessels.
The progression of the disease can be controlled with drugs and therapeutic procedures, but they do not provide a stable effect. The operation to treat retinal dystrophy is called laser coagulation. This is a method in the complex treatment of wet macular degeneration, which allows you to stop the progression of the disease.
How is laser coagulation performed?
A laser beam with specified parameters acts precisely on thin areas of the retina. Next, the retina is strengthened and glued to the adjacent tissues of the choroid. Laser coagulation lasts only 15-20 minutes. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. A three-mirror Goldmann lens is placed on the patient’s eye; it allows the laser beam to be focused on any part of the fundus of the eye.
Next, laser coagulates are created on problem areas of the retina. The operation is completely bloodless: under the influence of the high temperature of the laser beam, coagulates appear on problem areas of the retina. As a result of such cauterization, the patient does not experience hemorrhages.
A strong adhesion of the retina to nearby tissues is formed 10-14 days after surgery. Upon completion of the procedure, the patient does not need to undergo a long period of rehabilitation. On the same day, after rest and examination by a doctor, the patient can leave the clinic.
After the operation, the patient is not recommended to lift weights or do other physical activities, or visit baths, saunas and swimming pools. In extremely rare cases, laser coagulation is accompanied by minor complications.
Prevention
As preventive measures, those who are at risk for eye diseases are recommended:
- spend less time under sunlight;
- perform eye exercises;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- take vitamin complexes;
- give your eyes a chance to rest;
- good workplace lighting;
- lack of heavy physical activity;
- periodic medical examination by an ophthalmologist.
Treatment with traditional recipes
As an additional therapy and an integrated approach to the treatment of dystrophy, treatment with folk remedies can be used.
Pine decoction. To prepare you will need:
- 1 l. water;
- 4 tsp each crushed rose hips and onion peels;
- 10 tsp. pine needles.
Preparation:
- Connect all components.
- Fill with warm water.
- Cook for 10 minutes over low heat.
- Cool.
- Strain.
- Take throughout the day, distributing evenly.
The course is 30 days.
Garlic drops
To prepare you will need:
- 1 l. vodka;
- 1 kg garlic.
Preparation:
- Pour vodka over garlic in a jar.
- Close the container tightly with a lid.
- Place in a warm place.
- Leave for 2 weeks, stirring the contents periodically.
- Strain.
- Take 13 K before meals three times a day.
The course of treatment is 60 days, then a break for 1.5 weeks.
Serum drops
For preparation you will need: 2 tsp. water and the same amount of fresh goat whey.
Preparation: mix the ingredients.
Application: Drop 1 drop into the eyes. Blindfold your eyes with a cloth. Lie down for 30 minutes. without moving your eyes.
Course - 7 days.
Treatment at home should be carried out after consultation with an ophthalmologist.