Danger
Acetone (dimethylketone) belongs to the group of low-toxic substances, which allows it to be used in the production of household products, including paints, cosmetics, and medicines. Nail polish remover containing acetone is very common in everyday life. The solvent is a volatile substance. Has the following properties:
- highly flammable;
- a certain concentration of accumulated vapors in the air can lead to an explosion;
- releases toxic gases when burned.
The use of the chemical requires caution. Poisoning occurs in the following cases:
- inhalation of large amounts of vapor;
- ingestion of a concentrated substance;
- contact with eyes or skin.
This chemical causes swelling of the mucous membranes of the organs of vision.
The substance is quickly absorbed into the blood. Under the influence of acetone, signs of intoxication, swelling of the mucous membranes, and drug intoxication appear, but without a threat to the life of the poisoned person. Death can occur from consuming a large amount of the chemical (more than 50 grams) at one time.
If acetone gets into the eyes, it causes a chemical burn, accompanied by severe pain, burning, and swelling of the mucous membranes. Difficulty occurs when opening the injured eye. During the healing process, a scar usually forms on the retina. In most cases, vision is significantly reduced. With severe damage, irreversible blindness occurs.
Types of solvents.
It is accepted that solvents are divided according to their degree of volatility. This indicator allows you to determine the rate of evaporation of liquid. The higher this value is, the more likely it is that solvent poisoning occurs through the respiratory tract during work even with a mildly toxic substance. Conversely, it is easier to protect yourself from a substance with a high toxicity index if it is a non-volatile liquid.
Non-volatile solvents: butanol (butyl alcohol), chlorobenzene, solvent naphtha, xylene.
Low-volatile solvents: nitroparaffins, tricresyl phosphate, decalin and tetralin.
Volatile solvents: chloroform, acetone, gasoline, diethyl ether, carbon tetrachloride, methyl and ethyl alcohols, benzene, toluene, dichloroethane, trichlorethylene.
The harm of the solvent lies in its effect on mucous membranes, skin, and internal organs if absorbed into the blood. If a solvent gets into your eyes, few people know what to do, but in this case you should react very quickly, because otherwise the person may lose his vision. Most organic solvents perfectly dissolve the lipids that make up the cell membrane. The nervous system, kidneys, liver and lungs react most strongly.
First aid
Any form of burn to the visual organ requires emergency contact with an ophthalmologist. First aid consists of immediate rinsing with water at room temperature. If acetone gets into the eye, then in the best cases, immediate rinsing of the damaged organ can help get rid of the development of vision problems and the need for further treatment.
It is better to perform the washing procedure using a syringe.
- It is not advisable to expose your face to the stream from the tap.
- It is recommended to collect water in a rubber bulb or a large syringe without a needle and direct a narrow stream into the eye.
- It is necessary to rinse continuously for at least 10-20 minutes.
In addition to washing the affected eye with water, it is not recommended to use ointments or make lotions, so as not to cause further harm.
How to provide first aid at home?
First aid consists of immediately washing the eyes with clean, warm water.
To avoid vision problems in the future, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Do not expose your face to the running tap. Strong pressure can damage the fragile eye capillaries. In addition, running water often contains chlorine, which can aggravate an already serious eye condition.
- Don't rub your eyelids. Your hands will instinctively reach out to rub your eyes, but under no circumstances should you do this. Rubbing only increases irritation and discomfort.
- Be sure to wash your hands. The eyes are very sensitive to bacterial exposure. Damage further weakens local immunity. Therefore, before working, be sure to wash your hands with antimicrobial soap.
- Use a rubber bulb or a large syringe without a needle. Fill the device with clean water and rinse the eye with a thin, weak stream in the direction from the outer corner to the inner one (towards the tear duct). If you are rinsing the eyes of a child or person experiencing acute pain, place it near a sink or in front of a basin so that the solution flows freely from the eyes.
- Use a sterile bandage or gauze. This is true if the above-mentioned washing accessories are not available. Soak a small piece of cloth in clean water and wipe from the eye towards the nose. The action must be repeated until the lacrimation subsides.
- The longer the better. Rinse the damaged eye for at least 10-20 minutes. This is necessary in order to get rid of residual traces of the chemical.
- Relieve inflammation with herbs . This item is not mandatory, but in some cases its implementation helps to get rid of swelling caused by a chemical burn. To make an anti-inflammatory solution, regular tea leaves, chamomile or nettle are suitable.
- Do not apply a cold or hot compress. You may feel that this relieves pain and makes you feel better. In part, this is true, but local temperature changes provoke dilation of blood vessels and accelerate the penetration of chemicals into the bloodstream.
If you wear contact lenses, you can try rinsing your eyes with a special solution or moisturizing drops.
If the solvent gets into your eye on the street, take care of disinfection. Rinse your eyelids with a strained solution of furatsilin or potassium permanganate.
Varieties
A chemical burn of the eyes is one of the types of injuries to the organs of vision that occurs as a result of exposure to the mucous membrane of aggressive chemicals in liquid, solid or vapor form. The substances listed below can act as a chemical agent.
Alkalis
They pose a serious danger to the organs of vision, affecting the deep-lying structures of the eye. The higher the pH level, the more severe the injury will be. Most often, alkali damage results from exposure to the following agents:
Acids
When the eyes are exposed to acidic agents, only the external structures are affected, so the consequences are less dangerous. However, such injuries severely damage the cornea, causing decreased vision. Chemical burns to the organs of vision can be caused by the following acids:
Chemical burns to the eyes can be of an industrial or household nature.
Symptoms
A chemical burn to the eye manifests itself with a clear clinical picture that cannot be ignored. When the conjunctiva is damaged by chemicals, severe pain occurs and the following symptoms are observed:
- burning, cutting;
- tearfulness;
- photophobia;
- swelling, hyperemia of the eyelids;
- swelling of the cornea;
- redness of the eyeball;
- blurred vision.
Possible consequences
A chemical burn to the eye is a serious injury that can cause blindness. The consequences of exposure to chemicals on the organs of vision can be very diverse and largely depend on the type of aggressive agent. An acid burn leads to severe pain that can provoke a painful shock, but with timely assistance there are no negative consequences. The most dangerous are alkaline injuries, as they change the structure of the eye and provoke tissue death, increasing ophthalmotonus.
Regardless of the type of aggressive substance, the following primary complications may occur as a result of injury:
- swelling of the cornea;
- conjunctivitis;
- perforation of the cornea;
- cataract;
- inflammatory processes;
- acute increase in ophthalmotonus.
A few days or weeks after a chemical burn, the following negative consequences may appear:
- secondary cataract or glaucoma;
- scarring of the conjunctiva;
- ulceration or vascularization of the cornea;
- phthisis.
With a chemical burn, visual acuity decreases and vision loss is possible.
Use special tools
If the two methods above did not help you deal with the problem, then try using special tools: tongs, pliers. There is no need to use too much force, because the massive tool can crush the bottle, which will lead to the varnish leaking out. Here are three methods with tools you can use if you don't know how to open polish:
- Take tongs, pinch the lid with them and turn it.
- Pliers and an adjustable wrench will help you. Use it as a lever to turn the lid.
- Turn the bottle upside down and secure the cap with a vice. Start turning the jar, but as soon as it opens slightly, turn it over immediately, otherwise the varnish will leak out.
Now you are armed and know how to open dried varnish with tools.
First aid
First aid should be provided immediately after the accident occurs. Immediately after the incident, it is necessary to carry out the following PMP algorithm for chemical eye burns:
- Rinse your eyes well with saline solution or plain clean water. It is recommended to do rinsing not under running water, but to fill a container with warm water, lower your face into it and blink vigorously. This action should be performed for at least 20 minutes.
- In case of a chemical burn with acid, it is recommended to use a soda solution or potassium permanganate for washing.
- The effect of an alkaline agent can be neutralized with a 2% acetic acid solution.
- If there are foreign particles in the eye, they must be carefully removed.
- To eliminate pain, you should take a painkiller.
After this, you need to apply a sterile bandage to the sore eye and send the victim to the doctor. In order for the ophthalmologist to select the most effective treatment, it is recommended to take with you a bottle of the damaging substance.
Solvent got into the eye.
Solvent getting into the eyes is quite rare, but it still happens. It doesn’t matter if white spirit, acetone, 650, 646 solvent got into your eyes, everyone needs to know how to rinse it. Rinse only with cool running water without stopping.
As soon as the solvent gets into the eye, you should immediately call a doctor and not rely on your own strength. The longer you wait, the more likely you are to lose your vision. After the doctor is called, while waiting, you only need to rinse the eye with water and nothing else. You should not apply anything cold or warm, and in general it is better not to touch the eye, since this can cause even more harm.
Drug treatment
What to do if your eyes are burned by chemicals? After first aid has been provided, it is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist, even if the condition has improved significantly. After a thorough diagnosis, the doctor will assess the severity of the injury and select the appropriate treatment. For chemical burns to the eyes, the following medications may be prescribed:
- antibiotics: Tsipromed, Floxal;
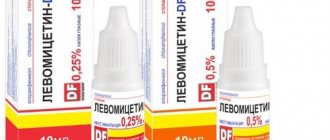
- disinfectant drops: Levomycetin, Sofradex;
- corticosteroids: Betamethasone, Maxitrol;
- analgesics: Alcaine, Inocaine;
- anti-inflammatory drugs: Indocollir, Dexamethasone;
- mydriatics: Cyclomed, Irifrin;
- corneoprotectors: Korneregel, Solcoseryl gel.
What not to do?
In case of chemical burns to the eyes, first aid should be provided to the victim as quickly as possible, and then contact an ophthalmologist. You cannot delay in providing pre-medical care, as the consequences of this can be extremely serious. In case of such an injury, it is strictly prohibited:
- rub your eyes;
- puncture blisters;
- use eye drops for chemical burns;
- apply healing agents without washing the eyes;
- treat damage with alcohol.
Fix the problem with regular rubber bands
To make it more convenient to unscrew the varnish cap, you can use regular rubber bands. After all, the lids are often quite thin and difficult to wrap your fingers around. How to open varnish using such a simple device? To solve this problem, put one or two rubber bands on the lid, wrap them quite tightly, this will help to fit the lid well. The rubber texture will make it easier for you to turn the cap.
Prevention
Chemical burns to the eye are most often of an industrial nature, so the main measure to prevent such a serious injury is compliance with safety precautions. When working with chemicals, be sure to wear safety glasses. At home, it is also necessary to protect your eyes when using hazardous chemicals and always study the instructions and composition in detail before you start using an aggressive product. If there are small children in the house, then all household chemicals should be stored out of their reach.
Main characteristics of injury
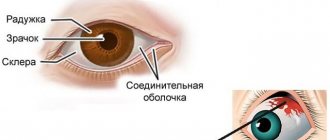
A chemical burn is an injury to the eye caused by exposure to aggressive chemicals. First of all, there is damage to the conjunctiva - a thin connective membrane that covers the outer surface of the eye and the back surface of the eyelid. It performs an important function because it releases a special liquid that lubricates the eye and prevents it from drying out. Its damage often leads to impairment and even loss of vision.
Damaging substances
Chemical burns of the conjunctiva are not uncommon these days. According to statistics, 10% of all eye burns are of chemical origin. Most often, damage occurs when aggressive substances come into contact with the ocular surface. Among them are:
Acids. Most often, burns occur with the following acids:
- hydrochloric acid (HCl);
- sulfuric (H2SO4);
- acetic (HC, COOH);
- hydrofluoric(HF).
An acid burn is similar to a thermal burn. It affects the conjunctiva and cornea without spreading into the eyeball. The degree of damage is influenced by the concentration of acids and the duration of their exposure. At the site of acid entry, a necrotic area appears, which is separated from healthy tissue (coagulation). In this case, a very strong pain syndrome appears, since the optic nerves are irritated.
Alkali. The most common alkalis that cause burns are:
- ammonia (ammonium hydroxide);
- caustic soda (sodium hydroxide);
- magnesium hydroxide;
- potassium hydroxide;
- slaked lime (calcium hydroxide).
Burns from alkaline substances are considered more dangerous because the damage extends deep into the eye, from where it is not easy to remove. At the same time, the time of negative impact increases.
This occurs due to the fact that alkali provokes liquefaction necrosis in the proteins, which leads to their melting (myomalacia) and spreading throughout the eye. In this case, the optic nerves are damaged by alkali, which leads to their loss of sensitivity. That is why a person with alkaline burns practically does not feel pain. This often leads to underestimation of damage.
Risk factors
How do chemical eye burns occur? This occurs through direct contact with acids or alkalis, when, due to carelessness or failure to comply with safety measures, these aggressive substances first enter the area of the conjunctiva of the eye, causing its necrosis (death). Among the risk factors contributing to the occurrence of such burns are:
- Construction or repair manipulations. These types of work often use chemicals that can cause burns.
- Using aggressive substances in everyday life without following safety rules. For example, improper or careless use of ammonia, household chemicals containing dangerous acids or alkalis. It is also risky to leave such substances within the reach of children.
Work involving frequent use of chemicals. This may be the production of concentrated acids and alkalis or other types of work where such substances are used.- Careless behavior with car batteries that contain sulfuric acid concentrate. This is especially true for car enthusiasts who do not have professional skills in working with cars.
- Alcohol abuse. In this state, very often people do not follow safety rules, which leads to unpleasant consequences.
Any type of burn is potentially dangerous. Therefore, first of all, a person needs emergency care for a chemical burn to the eyes.
The sooner it is provided, the more favorable the forecasts will be.
Useful video
From this video you will learn how to wash your eyes with folk remedies:
Solvents, regardless of their purpose, are highly toxic.
When it comes into contact with the epidermis, areas of hyperemia appear.
Intense pain is observed at the site of contact.
If the solvent gets into the eyes, complete loss of vision is possible.
Symptoms of a chemical burn when it comes into contact with the eyes are severe. Before providing first aid, you must immediately call an ambulance.
As a result of the solvent getting into the visual apparatus, the following symptoms are observed:
- intense pain in the contact area;
- strong closure of the eyelids;
- redness of the affected area;
- intense production of tears;
- burning;
- the appearance of a veil in front of the visual apparatus.
The intensity of symptoms depends on the time of contact of the caustic liquid with the mucous membranes or eyelids and the concentration of the reagent. The main rule in case of solvent ingress is timely and urgent assistance from medical personnel. If the visual apparatus comes into contact with the reagent, you must not get confused and provide quick first aid before the ambulance arrives. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate contact with the caustic substance and mucous membranes. The first steps for eye contact with a solvent are:
- Rinse eyes with plenty of running water.
- Immediately call an ambulance or take the patient to a medical facility yourself. Travel time should take a minimum amount of time.
It is prohibited to carry out additional manipulations, except for washing under running water:
- It is not recommended to rub the damaged area;
- It is unacceptable to apply a cold or warm compress;
- It is prohibited to lubricate the area of eye contact with the solvent with greasy ointments or sprinkle with starch;
- Do not wipe the solvent with towels or cotton swabs;
- first aid does not cancel calling an ambulance.
After the patient is admitted to a medical facility, the level of vision is diagnosed:
- determine the clarity of the picture;
- assess eyelid damage;
- study the degree of burn to the eyeball;
- the substance damaging the mucous membrane is removed.
To treat burns caused by solvent ingress, medications are prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- painkillers;
- antibiotics;
- drugs that accelerate the regeneration of the visual apparatus.
To prevent solvent from entering the visual apparatus, special protective glasses must be used. The caustic liquid, in contact with the eyeball, penetrates into the deep layers. To eliminate possible introduction of chemicals through your hands, you must work exclusively with gloves.
The consequences of contact of the visual apparatus with solvents are:
- reduced picture clarity;
- increased blood pressure in the eye cavity;
- formation of defects on the cornea;
- hyperemia and swelling of the conjunctiva, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process;
- blanching of the cornea;
- scarring in the conjunctival area;
- corneal perforation.
Working with solvents greatly simplifies everyday chores. However, when interacting with a caustic substance, it is necessary to take care in advance about the availability of special clothing that will prevent possible chemical liquid from entering the visual apparatus. In the event of unexpected contact with a caustic liquid on the mucous membrane, you must remain calm and adhere to the first aid steps.