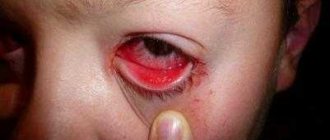
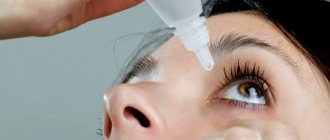
The effectiveness of Levomycetin for conjunctivitis
The main active ingredient of the drug is chloramphenicol. This is a remedy that has a wide range of effects on various bacteria. The solution is prescribed if the patient has developed resistance to the action of penicillin, streptomycin, or sulfonamide.
The action of the drug is carried out by suppressing protein synthesis inside the bacterium. They stop reproducing, their membrane is destroyed. Cells die.
Resistance in bacteria to the drug develops slowly. Therefore, doctors resort to prescribing a solution for a long course of treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis. The addiction does not form for a long time, so the doctor does not need to replace the drug with an analogue.
After instillation of the product, the active substance penetrates the vitreous body and sclera. After this, it is absorbed into the systemic circulation, so there is no effect on the lens. This reduces the number of side effects from the drug.
The effect of the drug after instillation occurs within 20 minutes. The maximum area of effect is observed in the anterior parts of the eye. Therefore, it is used for conjunctivitis and other bacterial formations on the mucous membrane and skin in the eye area.
Content
- Characteristics of chloramphenicol 0.25% dropper bottle 10ml eye drops
Composition: 10 ml bottle Chloramphenicol 2.
5 mg per 1 ml.
Pharmacological Action: Broad-spectrum antibiotic.
The mechanism of antimicrobial action is associated with a violation of the synthesis of microbial proteins.
Has a bacteriostatic effect.
Active against gram-positive bacteria: Staphylococcus spp.
, Streptococcus spp.
; gram-negative bacteria: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Salmonella spp.
, Shigella spp.
, Klebsiella spp.
, Serratia spp.
, Yersinia spp.
, Proteus spp.
, Rickettsia spp.
; also active against Spirochaetaceae and some large viruses.
Chloramphenicol is active against strains resistant to penicillin, streptomycin, and sulfonamides.
Resistance of microorganisms to chloramphenicol develops relatively slowly.
Indications for Use: For oral administration: infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to chloramphenicol, incl.
h.
: typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, dysentery, brucellosis, tularemia, whooping cough, typhus and other rickettsioses; trachoma, pneumonia, meningitis, sepsis, osteomyelitis.
For external use: purulent skin lesions, boils, long-term non-healing trophic ulcers, second and third degree burns, cracked nipples in nursing women.
For local use in ophthalmology: inflammatory eye diseases.
Method of Use: Levomycetin eye drops (DIA, Akri, AKOS, Ferein) are applied into the conjunctival sac of each eye, one 3-4 r.
/day
The course of treatment usually lasts from 5 to 15 days.
When using the drug, you should tilt your head back, gently pull the lower eyelid towards the cheek so that a cavity is formed between the skin and the surface of the eye, and, without touching the eyelid and the surface of the eye with the tip of the dropper bottle, add 1 drop of the medicine into it.
After instillation, press the outer corner of the eye with a finger and do not blink for 30 seconds.
If you cannot avoid blinking, you need to do this as carefully as possible so that the solution does not spill out of the eye.
For children during the neonatal period (the first 28 days after birth), the drug is used for health reasons.
For purulent otitis, the drug is injected into the ear 1-2 times.
/day
2-3 drops each.
If there is significant discharge from the ear canal that washes away the applied solution, Levomycetin can be used up to 4 times a day.
/day
For bacterial rhinitis, your doctor may recommend using nasal drops.
Interaction: With the simultaneous use of chloramphenicol with oral hypoglycemic drugs, an increase in the hypoglycemic effect is observed due to the suppression of the metabolism of these drugs in the liver and an increase in their concentration in the blood plasma.
When used simultaneously with drugs that inhibit bone marrow hematopoiesis, there is an increased inhibitory effect on the bone marrow.
When used simultaneously with erythromycin, clindamycin, lincomycin, a mutual weakening of the effect is observed due to the fact that chloramphenicol can displace these drugs from the bound state or prevent their binding to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes.
When used simultaneously with penicillins, chloramphenicol counteracts the bactericidal effect of penicillin.
Chloramphenicol suppresses the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, therefore, when used simultaneously with phenobarbital, phenytoin, warfarin, a weakening of the metabolism of these drugs, a slower elimination and an increase in their concentration in the blood plasma are observed.
Side Effects: From the hematopoietic system: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia.
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence.
From the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: peripheral neuritis, optic neuritis, headache, depression, confusion, delirium, visual and auditory hallucinations.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, urticaria, angioedema.
Local reactions: irritant (for external or local use).
Contraindications: Blood diseases, severe liver dysfunction, deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, skin diseases (psoriasis, eczema, fungal diseases), pregnancy, lactation, children under 4 weeks of age (newborns), hypersensitivity to chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol, azidamphenicol .
Use in children Chloramphenicol is not used in newborns, because
To.
the development of “gray syndrome” is possible (flatulence, nausea, hypothermia, gray-blue skin color, progressive cyanosis, dyspnea, cardiovascular failure).
Overdose: Severe complications from hematopoiesis are usually associated with long-term use of doses exceeding 3 g/day.
Symptoms of chronic intoxication: pale skin, hyperthermia, sore throat, hemorrhages and bleeding, fatigue or weakness.
Treatment with high doses of newborns can provoke the development of cardiovascular (“gray”) syndrome, the main signs of which are: - change in skin color to bluish-gray; - hypothermia; - bloating; - vomiting; - lack of nervous reactions; - respiratory rhythm disturbances. ;— acidosis;— circulatory collapse;— cardiovascular failure;— coma.
In 2 out of 5 cases the patient dies.
The cause of death is the accumulation of the drug in the body due to the immaturity of liver enzymes and the direct toxic effect of floramphenicol on the myocardium.
Cardiovascular syndrome occurs when plasma concentrations of chloramphenicol exceed 50 mcg/ml.
Special Instructions: Chloramphenicol is not used in newborns, because
To.
the development of “gray syndrome” is possible (flatulence, nausea, hypothermia, gray-blue skin color, progressive cyanosis, dyspnea, cardiovascular failure).
Use with caution in patients who have previously received treatment with cytotoxic drugs or radiation therapy.
With simultaneous intake of alcohol, a disulfiram-like reaction may develop (skin hyperemia, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, reflex cough, convulsions).
During treatment, systematic monitoring of peripheral blood patterns is necessary.
Features of application
Before prescribing the drug, the ophthalmologist should consult the patient about additional recommendations in the field of its use:
- The solution does not cause clouding or decreased visual acuity. Therefore, it can be used when driving a vehicle or working in an enterprise that requires increased concentration.
- The drug may cause allergic reactions. Therefore, if a patient has eczema or psoriasis, it is necessary to first consult a doctor. The drug is not contraindicated, but is used with caution so as not to cause an exacerbation of the disease.
- If the drug is used for persons after radiation exposure, the dosage is reduced. The active substance may inhibit the function of red bone marrow.
- If side effects occur, you cannot wait for the body to get used to it. The drug is immediately cancelled, consult a doctor.
Instructions for use
Levomycetin can be used for children from two years of age. The dosage for children and the duration of treatment for children are individually prescribed by the doctor. For severe diseases, chloramphenicol is prescribed to children under two years of age, but children under one year of age are recommended to use it only when it is not possible to cure the disease in any other way.
Dosage
Children under one year of age are recommended to drop one drop into the conjunctival sac into each eye 3-4 times a day. If a specialist has prescribed only 3 appointments, you should not add a 4th, no matter how much you want to speed up the baby’s recovery. Instructions and recommendations from a specialist are what you need to follow during treatment. The effect of the drug begins 2-3 hours after use.
Directions for use:
- Shake the bottle of medication;
- Place drops in a clean pipette;
- Gently move the child's head back and pull the lower eyelid down;
- Place the pipette over the eye socket, press lightly, drop a drop of medicine;
- After treating the eye, place your index finger to the inner corner of the child's eye. Hold for a few minutes, applying light pressure. Thus, the drops will remain in the eye for a long time.
Even if a child has one eye inflamed, it is imperative to drip the drug into the second to prevent the spread of viral conjunctivitis, keratoconjunctivitis, and other inflammatory eye diseases.
Levomycetin for conjunctivitis in adults
Before using the drug, wash your hands with bactericidal soap. This will prevent pathogenic microorganisms from entering the packaging and the eye area. Open the bottle, tilt your head back, and drop the product onto the area of the conjunctival sac. After this, do not close the eyes for several seconds so that the solution is distributed throughout the mucous membrane. This way the active agent will affect a wide area of eye tissue.
For adults, the dosage is 1 drop in each eye 3 times a day. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor individually for each patient after a general examination and tests.
How to take and dosage for children
For children over 3 years old, instillation of 1 drop into each eye cavity is prescribed 3-4 times a day. If the doctor has prescribed the child to use the drug 3 times a day, you should not drip 4 times; this will not speed up recovery, but it can cause increased side effects. The therapeutic effect is observed 2 hours after using the product.
Before putting drops into a child’s eyes, you need to familiarize yourself with the existing rules:
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap;
- shake the bottle with drops;
- pull down the child’s lower eyelid;
- press on the bottle and drip the product;
- After instillation, gently press with your index finger on the corner of the inner eyelid for 1-2 minutes.
You can use the medicine for no longer than 2 weeks, and if no positive dynamics are observed within a week, you need to contact an ophthalmologist to change the drug.
Levomycetin for conjunctivitis in children
Eye drops are recommended for use in children over two years of age. If the doctor decides that the solution will have a greater effect than side effects, it is used from 4 months. Parents should be careful when instilling the solution; do not exceed the prescribed dosage. The baby may experience nausea and vomiting.
The dosage for children is 1 drop in each eye 2 times a day. If the disease affects a large area of the eyes, the doctor may increase the dosage to 3 times a day.
Contraindications and possible side effects
Side effects when using Levomycetin eye drops in children may include:
- burning sensation in the eyes;
- redness of the eyelids and cornea;
- itching;
- increased tearfulness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- decrease in hemoglobin concentration in the blood.
Very rarely, with long courses of treatment, hematopoiesis may be impaired - thrombopenia, anemia, leukopenia. Therefore, Levomycetin eye drops should be used in children only after consultation with an ophthalmologist and strictly following the instructions.
As for contraindications, first of all it should be said about allergic reactions to the components that make up the product. In addition, potassium Levomycetin is not used in the following cases:
- acute renal or liver failure, as well as their chronic forms;
- porphyria;
- psoriasis, eczema, fungal skin infections;
- hematopoietic disorder;
- age up to 4 months, and preferably up to 3 years.
It is important to understand that Levomycetin can reduce the effect of other antibiotics:
- erythromycin;
- lincomycin;
- cephalosporin;
- penicillin and others.
With simultaneous radiation therapy, as well as when taking drugs that inhibit hematopoiesis, side effects may increase.
Side effects
Side effects develop when the dosage is selected incorrectly, self-medication, or the presence of contraindications. The most common symptoms that develop are:
- allergic reactions in the form of itching, burning, irritation, redness, swelling, inflammation;
- inhibition of hematopoietic function (rarely develops when using large dosages);
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, change in stool);
- the formation of a fungal infection;
- superinfection that is resistant to most drugs.
If side effects occur, the drug should be discontinued immediately. Contact a doctor. He can replace the product with an analogue that will not have a negative effect on the body.
Side effects
When using Levomycetin in the form of drops, the development of side effects is unlikely. In most cases, they manifest themselves in the form of local dermatoses, urticaria of epithelial tissues located around the organ of vision, itching, visual hallucinations, blurred vision, blurred vision, and headache.
In the first days of using eye drops, the child should be under the supervision of parents and medical personnel. If adverse reactions occur, further use of the drug should be discontinued immediately. To more quickly eliminate these symptoms, you may need to take antihistamines that stop the manifestation of allergies.
Contraindications
The following conditions and diseases are contraindications to the use of the solution:
- increased sensitivity of the body to one of the components of the product;
- liver and kidney disease;
- blood disease, bone marrow damage;
- pregnancy, lactation.
If there are contraindications, it is prohibited to use the drug. The patient's health may deteriorate sharply. Allergic reactions and dyspeptic disorders will appear.
Analogs
The drug is replaced with an analogue if there are contraindications, side effects, or lack of effect from its use. Chloramphenicol eye drops have the following substitutes:
- Tobrex or Tobradex;
- Albucid;
- Oftaquix;
- Tsipromed.
The above drugs have an antibacterial effect. They have their own contraindications and side effects. Therefore, only a doctor can replace the product with an analogue after examining the patient and conducting tests.
More details about analogues can be found here
Reviews from doctors
Eremina Daria, ophthalmologist: Patients with bacterial conjunctivitis often come to me. I prescribe topical chloramphenicol eye drops. The product has a low cost with a minimum of side effects. The action begins immediately after instillation of the drug. The next day, all manifestations of conjunctivitis should disappear.
Oleg Eroshkin, ophthalmologist: If a patient comes to me with bacterial conjunctivitis who has become resistant to many antibiotics, I prescribe Levomycetin eye drops. They can be used for a long time without developing resistance.
Consumer Reviews
Anastasia: Recently, purulent discharge appeared from my eyes. The doctor said it was bacterial conjunctivitis. He prescribed me Levomycetin. The very next day all the discharge disappeared. But I continued treatment for 1 week, as the doctor said that this would reduce the risk of relapse. Only within a week's course will the bacteria die.
Michael. I often get bacterial conjunctivitis. I have already tried many antibiotics. Some became addictive. The doctor prescribed me Levomycetin. He said that it can be used over a long course. So far there has been no addiction. The effect appeared quickly, all symptoms disappeared.