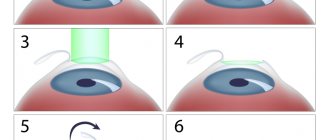
In case of visual impairment, the image does not focus on the necessary points of the retina, so it turns out blurry. The task of laser correction is to change the shape of the cornea and the refractive power of the eye in such a way as to correctly “collect” light rays and deliver them to the retina at the correct points. How is laser surgery performed?
If you have visual impairments, you have to use glasses or contact lenses. However, they only provide good vision while you are wearing them. After laser surgery, you can enjoy clear vision at any time without additional devices. During correction, the effect occurs on the cornea, which is a convex-concave lens. The laser evaporates micron layers of tissue from its surface, modeling the desired shape so that the light rays are clearly recorded on the retina.
How is laser surgery performed?
Before a patient is allowed to undergo laser surgery, he must undergo a comprehensive examination of the visual system, as well as some general tests as prescribed by the therapist. If no restrictions for vision correction are identified, you can proceed with the procedure.
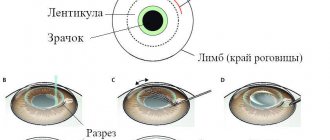
The operation lasts from 1 to 2 minutes, preparation for it takes from 10 to 15 minutes. After administering local anesthesia and instilling drops that dilate the pupils, the specialist makes a microscopic incision, bends the cornea and directs a beam of laser beams to a selected location (determined using computer diagnostics), which eliminate the affected parts of the eye tissue. After the process is completed, the corneal flap returns to its original position.
As a rule, corneal tissue regenerates within a few hours, however, for some patients it may take a day. When performing laser vision surgery, as well as during the rehabilitation period, a person does not experience any discomfort, since it is absolutely not traumatic.
Types of laser surgery to improve vision
In ophthalmic practice, there are a number of methods for performing the procedure with a laser device. In most cases, the patient chooses one of them for himself, after a detailed consultation with the doctor. So, these include:
- PRK. LASIK - during the operation, the outer layer of the cornea is not involved. Evaporation of moisture occurs when the eyelid is folded back; the laser device acts exclusively on the middle layers of the cornea. During the procedure, a minimum number of professional tools are used. The doctor takes a specialized device, grasping the edges of the eyelid and lifting it to the desired height, in order to bend it back and release the middle area of the cornea. After this, a laser is used: the rays are directed to an area predetermined by the computer.
- LASEK - this operation is necessary to eliminate visual pathologies in patients with too thin cornea of the eye. This procedure is an alternative and safety is guaranteed. With this laser vision surgery, the ophthalmologist acts on the epithelial layer, and an additional epithelial flap is placed on the upper part of the cornea. Despite the maximum safety of this method, the recovery period is slightly longer.
- Epi-LASIK is intended for those people who were previously refused LASIK due to a number of contraindications. During the procedure, a certain layer of epithelial tissue is completely removed from the surface of the cornea, after which it is exposed. The main goal of vision correction surgery is the dissection and partial separation of the epithelial flap. After using this method, the patient may experience minor discomfort, but rehabilitation occurs quite quickly.
- SUPER-LASIK - laser vision surgery is distinguished by the fact that it uses ultra-precise ophthalmological devices. During it, the cornea is polished, and every action of the doctor is dictated by conclusions based on information received from a special analyzer. The fact is that in the human visual system, with a high degree of refractive error, there are always certain distortions. The device allows you to precisely direct the position of the laser beams and adjust the required area. The method is usually used for severe forms of pathologies.
- FEMTO-LASIK - the method involves creating a corneal flap using a special femtosecond laser. In this case, there is no need to use a mechanical catheter or blades. Therefore, such vision surgery is considered the least traumatic.
Contraindications
Despite its versatility and high effectiveness, laser stimulation of the retina is contraindicated for:
- systemic blood diseases;
- acute inflammatory eye diseases (active period);
- oncological diseases;
- decompensated glaucoma;
- severe forms of epilepsy;
- eye injuries (acute period).
- hypertension;
- stroke;
- acute heart attack;
- diencephalic syndrome;
- acute mental disorders;
- rehabilitation after radio- or chemotherapy;
- pregnancy.
Advantages of laser vision surgery
In order to make a clear decision about whether to undergo a vision correction procedure, the patient needs to know its pros and cons.
Positive aspects include:
- Getting excellent results in the shortest possible time without a difficult physical and psychological recovery period.
- High precision of the procedure and minimal trauma to the eye tissue, since during laser vision surgery the beams of the device are under the full control of a specialist, whose actions are determined by a computer.
- The impact of the procedure is only on the cornea (its outer or middle layers), without touching or injuring other important elements of the visual system.
- Low invasiveness of the procedure: the process involves small incisions without sutures, the operation is bloodless.
- Individual approach to each patient and the ability to eliminate even severe refractive errors (myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism);
- The most effective operation in modern ophthalmology that provides lasting results in improving vision indicators with minimal risk of complications.
- A short and painless recovery period, after which, if the doctor’s recommendations are followed, repeated surgery is not required.
- Laser surgery can be performed on one or both visual organs at the same time.
- Democratic price. For minor visual impairments, almost anyone can afford this procedure. In difficult cases, the price becomes significantly higher.
Diabetic retinopathy
This vascular eye disease occurs as a complication of diabetes mellitus and is manifested by serious damage to the retina. The walls of the capillaries become thinner, deformed, become very fragile and begin to let the liquid part of the blood pass through. Because of this, the retina swells and hemorrhages occur. As a result of impaired functioning of the blood vessels, the eyes do not receive enough oxygen, and the formation of pathological capillaries leads to the appearance of scars. The more diabetic retinopathy progresses, the more the risk of retinal detachment increases, which in turn can lead to vision loss. Modern technologies make it possible to treat this disease using laser coagulation. During the procedure, the ophthalmologist “glues” the vessels, strengthens their walls, and prevents the process of pathological neovascularization. Timely laser coagulation can protect against blindness.
Cons of laser vision correction
There are much fewer negative aspects that hinder the operation; specialists warn patients about them in advance. Thus, it is important to understand that the procedure will not be able to eliminate the cause-and-effect relationships associated with significant visual impairment. If the nature of the problem is not identified in a timely manner, the pathology will progress, which will reduce the effectiveness of the previously performed operation.
Among other things, if the patient does not follow the recommendations of the ophthalmologist, and also continuously puts heavy strain on his vision, his visual acuity may decrease. As a result, the effectiveness of the operation may decrease to zero. There are also cases when the ophthalmologist performs the operation too quickly, and the result is not completely satisfactory to the patient. Unfortunately, this situation can only be corrected by repeated laser vision correction after a certain period of time.
Glaucoma
Frequent signs accompanying this disease are increased pressure inside the eyes and poor drainage of fluid. Glaucoma is one of the most dangerous ophthalmological diseases that lead to irreversible loss of vision, because with this pathology atrophy of the optic nerve occurs. Laser therapy is sometimes used to treat glaucoma. The goal of such treatment is to normalize and stabilize the outflow of fluid from the eyes, reduce intraocular pressure to normal levels and stop the progression of the pathology.
Restrictions on the operation
Surgery to improve visual ability using the laser method cannot be performed on all patients. There are a number of restrictions, which include:
- Detection of severe myopia (myopia) in a person.
- A significant difference in the refractive indices of each of the visual organs (the vision parameters of the eyes should not differ by more than 2.5 diopters).
- Progression of visual pathologies that are the result of diagnosed forms of disease.
- Presence of keratoconus. The disease is characterized by leakage of the cornea and changes in its contours.
- Age less than 18 years, which is associated with the formation of the visual system and jumps in vision indicators in children.
- The period of pregnancy and lactation, when the female body is subject to significant hormonal changes.
- The presence of pathologies that are chronic, allergic and infectious in nature (for example, AIDS, psoriasis, neurodermatitis, eczema, etc.).
- Endocrine disorders in the body.
- Mental disorders.
- Cataracts and glaucoma, especially severe ones, as surgery may worsen symptoms.
- Predisposition to the formation of keloid-type scar tissue, since the procedure can lead to a decrease in visual ability.
Ophthalmologists say that it is better to perform laser vision correction between the ages of 18 and 40 years. After the last age limit it can be dangerous, however, this is decided on an individual basis.
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK, Trans-PRK)
This is the oldest method of laser vision correction, which, however, has not lost its relevance today. Of course, modern PRK is significantly different from that used since 1985, at the dawn of excimer laser ophthalmic technology. And yet its essence remains the same.
The PRK operation consists of two stages. At the first stage, the top layer of the cornea - the epithelium - is removed to access the stroma, on which the correction is carried out. In outdated PRKs, this stage was performed by scarification - mechanical scraping. Today, the mechanical process has been replaced by laser action. The second stage of the operation is ablation (laser evaporation) of the corneal tissue until the required geometry of the natural lens is achieved. Both in the early method and now, it is performed with an excimer laser, however, modern laser systems have made it possible to transform a two-stage operation into a one-step operation, which has returned the relevance of an already outdated technology.
Today's methods of photorefractive keratectomy have received the prefix “trans” and have gotten rid of half of their former “disadvantages”. But the modified Trans-PRK is suitable only for people with a slight or moderate degree of myopia (up to -6 diopters), is accompanied by severe pain and discomfort in the first days after surgery and has a long period until complete restoration of vision (one month). In addition, scars on the cornea obtained during surgery can cause haze phenomena.
Among its undeniable advantages are:
- speed of operation;
- the possibility of vision correction for people with thin corneas and orbital features;
- no restrictions on active lifestyle in patients in the long-term period.
Possible consequences
In some cases, after the procedure, a person may experience prolonged healing of the epithelial tissue, which is accompanied by minor pain; to speed up rehabilitation, doctors prescribe special eye drops.
Various color and light anomalies may also occur due to poor lighting or reflection from mirror surfaces. After a while, if vision decreases significantly after laser surgery, the patient will again have to use contact lenses or glasses.
Laser eye stimulation for children
During a therapy session, laser radiation acts on the retina, which triggers chemical reactions, reduces inflammation, and helps restore damaged visual structures.
Laser eye therapy is performed from the age of three. The treatment regimen and mode of exposure are selected by the doctor, taking into account the type and severity of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies, the age and individual characteristics of the child. If necessary, during therapy he makes adjustments depending on the results obtained.
Laser eye stimulation for children provides more pronounced and lasting results than for adults.
Results
Laser correction is the most optimal procedure for improving vision today (the pros and cons are given above). With its help, patients will be able to forget about glasses and contact lenses and lead an active lifestyle without experiencing discomfort.
Remember that the procedure is absolutely painless, non-traumatic, and does not require large financial investments if you do not have serious visual abnormalities that require a special approach. But before you decide on it, you need to consult with a competent specialist and subsequently follow all the necessary recommendations.