Facial swelling in a child is a fairly common manifestation of various pathological processes occurring in the child’s body. Methods for eliminating this problem directly depend on the etiology of the edema that appears. Therapy, including medication, in this case is aimed at relieving local symptoms and treating the primary disease that caused facial swelling in the child. Below are the most commonly diagnosed causes and recommended methods for eliminating them.
Common causes of the phenomenon
The first step is to rule out the most common cause. Facial swelling in a child most often occurs after crying for a long time. Little children love to cry for a long time without reason - this is the most common cause of swelling of the eyelids, lips and cheeks. An experienced parent will always recognize whether the face is swollen after crying or due to injury, or maybe the child drank too much soda?
But young parents, due to lack of experience in caring for children, cannot always distinguish the causes of facial swelling in a child.
- Kidney diseases of an inflammatory or infectious nature are most often accompanied by fluid retention in the body. Favorite places to store excess water are the face, area around the eyes, wrists and ankles. Please note: if you remove the socks, will there be a mark left on the baby’s feet from the elastic band. If so, then the swelling of the child's body and face is most likely caused by impaired kidney function.
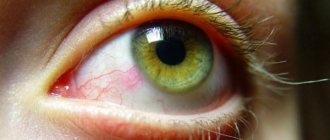
- Diseases of an allergic nature: urticaria, Quincke's edema, lacrimation, nasal discharge. If a child has swelling on one side of his face, then most likely this is a manifestation of an allergic reaction. Below is an algorithm for what to do and how to help your child in such a situation.
- The parotid salivary glands usually become inflamed due to mumps. People call this disease “mumps.” The pathology is most often observed in children over five years of age and under ten.
- Features of the formation, growth and development of the body, in some cases, can also provoke some swelling. Young parents can start to panic for any reason. But sometimes swelling of a child’s face after sleep can simply be associated with the incorrect position of the pillow and, accordingly, the child’s head.
- In infants, swelling of the face can be caused by teething. This process in some cases is accompanied not only by an increase in temperature and swelling of the gums. Sometimes a child's cheeks and even nose swell.
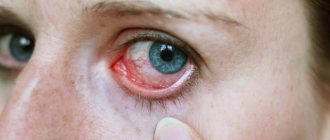
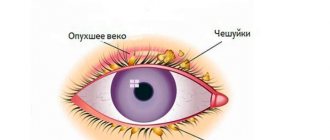
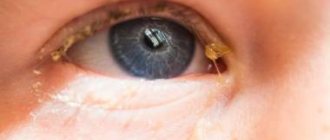
- Infectious eye diseases can cause swelling of the eyelids and area around the eyes. At the same time, the eyes are very itchy, pus remains on the eyelids in the morning, and painful tearing begins. Sinusitis, sinusitis, adenoiditis and other infectious diseases of the nasopharynx often have similar symptoms.
When swelling is not a symptom of the disease
Edema is the external manifestation of fluid accumulation in tissues. Children are mostly prone to short-term and painless swelling, provoked by physiological reasons. The most common type is swelling of the eyelids, swelling around the eyes.
Swelling of the face, particularly the eyelids, in infants may appear after prolonged screaming and/or crying. Also, swelling of the eyelids in young children often manifests itself as an inherited trait: it has been established that the structure of the eyelids in close relatives, which contributes to fluid retention, directly correlates with the presence of edema and can be inherited genetically.
Disturbances in daily routine and sleep at an early age are also often the cause of severe swelling of the eyelids. In infants, swelling of the face can be noticed if the body is in an incorrect position: if the child spends a lot of time lying down, with the head lower than the body, the outflow of fluid from the tissues of the facial part of the head will be difficult, which leads to the formation of swelling.
During teething, swelling of the lower part of the face, cheeks, and mouth area is associated with the reaction of the gums to the emerging tooth.
In children who start eating from a common table, edema is often caused by excess salt and spices in food, as well as excessive consumption of water and drinks in the evening.
Older children, who have already become accustomed to watching TV and playing games on a computer, tablet, or smartphone, are exposed to numerous risks if they do not adhere to safe screen time. One of the symptoms of trouble is redness of the sclera of the eyes and swelling of the eyelids.
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
When wearing contact lenses, which is also not uncommon for children, swelling of the eyelids can be a symptom of non-compliance with the rules for using lenses, traumatic, inflammatory processes or allergic reactions to the material.
Professional help: which doctor to contact
Being confused, parents cannot always figure out where to go to get help and accurately determine the cause of facial swelling in their child?
If the child himself reports that there has been an injury, you should go to the emergency room. There, if necessary, they will stitch the wound (if there is one) and check the child for the presence of traumatic brain injury. Note to parents: if there was a short-term loss of consciousness after a bruise or nausea and vomiting, most likely a closed craniocerebral injury occurred.
If a child has a fever and there is swelling not only on the face, but also on the body, you need to call an ambulance. Most likely, this is a manifestation of acute pyelonephritis. In some cases, such symptoms indicate an infectious process in the ureter or bladder. Severe swelling, accompanied by an increase in temperature, may indicate an inflammatory process in the lungs. Ambulance doctors will take the child to the hospital, where he will be provided with the necessary assistance and conduct research to identify an accurate diagnosis.
A swollen red face in a child is a serious symptom, and if parents are concerned about the baby’s well-being, they should not hesitate, it is better to immediately call the treating doctor. An independent visit to a nephrologist or allergist can take a lot of time and the disease will have time to develop into a chronic form.
Swelling caused by physical injury
Special attention should be paid to swelling resulting from various injuries and physical damage to tissues and organs. Children, due to their increased physical activity, are quite often prone to falls. The measures taken in this case to relieve swelling on the child’s face depend on the type of injury received, namely:
- When the nose is damaged, swelling of the face around the eyes is characteristic, which turns into hematomas. To relieve pain and relieve swelling, it is recommended to use Troxevasin, Troxerutin or heparin ointment.
- With general head contusions, swelling of the face may indicate a concussion, which in turn requires immediate hospitalization.
In addition to all of the above, rare causes of facial swelling in a child can be teething in infancy, an incorrect position adopted by the child during sleep, anemia, metabolic disorders, and liver diseases.
Pathologies of the urinary tract
Renal edema is a serious condition. They arise when the functioning of the kidneys is disrupted - not endocrine, not hematopoietic, but excretory, which is closely related to ion- and osmoregulatory.
If kidney function is impaired, edema can be of the following types:
- nephrotic - soft to the touch, extensive in area (start from the eyelids, go across the face, down the arms, hands and fingers swell). Such edema is a complication of membranous nephropathy, renal amyloidosis, glomerulosclerosis, and they are also typical for patients with diabetes.
- nephritic edema is characterized by the parallel development of pressure surges, the presence of blood in the urine, severe weakness and the inability to get out of bed. This condition requires emergency medical attention.
- Retention swelling of the face and body occurs most often in chronic renal failure and is characterized by the fact that it first appears on the face and then on the legs. There is practically no accumulation of fluid on the arms and torso.
Swelling of the face as a consequence of diseases of the internal organs
In contrast to manifestations of an inflammatory nature, such swelling is expressed in both eyes and often appears or intensifies after waking up, especially after a night's sleep. They can be a symptom of a number of diseases and dysfunctions of various organs and systems, a consequence of malnutrition, an unbalanced diet, low hemoglobin levels, circulatory disorders in the eyelid area caused by the anatomical structure of the facial part, cysts, tumor formations, and so on.
Such edema can be caused by pathological processes and disturbances in the functioning of the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system, lungs, as well as increased intracranial pressure.
Rare but common causes of swelling of the face and eyelids in children also include disturbances in metabolic processes, congenital deficiency of thyroid hormones, enlargement of the pharyngeal tonsil, which causes difficulty breathing and disrupts the normal functioning of the body, and urolithiasis.
Swelling of the face, which does not affect the area of the eye structure, also appears in diseases such as infectious mumps or mumps, diabetes mellitus, and also accompanies bacterial and viral diseases of the nasal sinuses, inflammation of the oral cavity, and carious processes.
Treatment methods and advice from nephrologists
The fastest and easiest method to rid a child of edema is to give him a diuretic, i.e. diuretic drug. The instructions for use for Furosemide tablets indicate that this drug is contraindicated for children under three years of age. It can relieve swelling in older children in a short time.
The use of diuretics affects the accumulation of fluid, promoting its rapid elimination. But it does not treat the cause of swelling - the inflammatory process in the organs of the urinary system does not go away, so literally the next day the child’s condition will worsen.
In addition, almost all diuretics for children have many contraindications. Side effects include dehydration and depression of the central nervous system. So it is better to refrain from taking diuretics or give them to your child only in emergency cases, on the recommendation of a doctor.
How to fix it?
What should I do if my child’s face is swollen for this reason? The usual way to relieve renal edema is to take diuretics, such as Furosemide. Such medications remove fluid from the body well, but when used to treat children they raise a lot of questions and doubts. Firstly, many diuretics are contraindicated for children under three years of age, and secondly, if the dosage is incorrectly selected, they can lead to dehydration. In addition, diuretics can relieve swelling only for a short time, but do not have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, or anti-infective therapeutic effects. Therefore, if adequate treatment is not started, the child’s swelling will return again.
What drugs are best to use
Here is a list of drugs with a diuretic effect that have an anti-inflammatory effect on kidney tissue:
- “Canephron” is a homeopathic drug, has a mild diuretic effect and promotes the removal of sand and stones (if any), effective as an independent remedy and as part of complex therapy for chronic and acute pyelonephritis and cystitis;
- "Renel" is a drug whose positive results are achieved through the action of plant components. It has a healing effect on the tissues of the kidneys and bladder, helps relieve swelling of the face and body due to its diuretic effect.
The desired result is achieved differently in all children. The swollen face will take its previous shape literally two to three days after proper drug therapy. In some cases, the child may require a course of antibiotics (in the case of an infection in the urinary system).
Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions (angioedema) and obstruction (blockage) of the superior vena cava cause local swelling of the face. This term means that one side or area of the body becomes swollen.
Swelling of the eyelid in children, or of the nose separately, or only of the cheek and one finger on the left side - all this indicates the allergic nature of the problem. Insect bites fall under this same heading, since the toxin injected under the skin by bees or mosquitoes provokes a local allergy.
Allergies most often do not pose a threat to life (except for some rare pathologies, for example, Quincke's edema). It is advisable to show the child to an allergist and conduct the necessary studies, so-called tests, to identify the exact allergen and check its sensitivity to pharmacological treatment.
If a child is prone to developing allergic reactions, it is worth visiting an immunologist for advice. Most often, an increased tendency to rashes and swelling due to substances foreign to the body appears due to a weakness of the immune system. Taking medications with immunomodulatory effects can help reduce the intensity of allergic reactions.
What to do?
If allergic edema is detected, the following measures must be taken:
- give the child one of any antihistamines (Fenistil, Diazolin, Pilpofen), you also need to use antiallergic eye drops and nasal drops;
- seek medical help and in the future it is recommended, in addition to an allergist, to consult an immunologist to correct the child’s immune system.
Treatment methods and advice from allergists
The most effective drugs for treating facial swelling in children caused by an allergic reaction:
- "Pilpofen" - is used to relieve allergy symptoms in children older than two months. Release form: injection solution, dragees, tablets. It has a number of contraindications; before use, parents must read the instructions.
- "Fenistil" is available in the form of drops, tablets and solution for injection. Approved for use by children aged one month and older. It is better for kids to take the product in the form of drops, for teenagers and adults - in the form of tablets.
- "Diazolin" is used to treat allergies in children one year of age and older. Release form: tablets. The drug has a number of contraindications; parents should read the instructions before use.
Infectious diseases
The following infectious diseases often lead to facial swelling in children:
- Measles is a serious disease, the virus of which, moving with air currents, can easily enter a child’s body. The disease has a fairly long incubation period - up to three weeks. At the same time, it will not manifest itself in any way, then symptoms similar to the flu will appear. In the first days, the temperature rises and conjunctivitis develops. Next, a rash occurs in the mouth. After a few hours, the rash may cover the entire face and gradually spread to the body.
- Scarlet fever is an infectious disease that is transmitted by airborne droplets. Symptoms: swelling of the eyelids and face, severe sore throat, temperature rises to forty degrees, painful enlarged tonsils, possible vomiting and a small rash on the body. The nasolabial triangle turns pale with scarlet fever.
- Meningitis is one of the most dangerous diseases of an infectious nature, in which swelling of the face and body of a child is observed. Meningitis is characterized by high fever, and hemorrhagic rashes appear on days 2-3. Small hematomas begin to appear under the skin. Bleeding, loss of consciousness, severe headaches are symptoms of meningitis. The child needs to be hospitalized urgently.
Face and head injuries
Children, due to their restlessness, often injure their faces. When the nose is bruised, severe swelling of the area around the eyes appears; after a day, a hematoma (bruise) usually develops in this place, i.e. accumulation of blood in the subcutaneous tissue.
For treatment, Heparin ointment, Troxevasin or Troxerutin gel are most often used. Even without special treatment, swelling and hematoma will subside in about ten days.
If you urgently need to get rid of swelling in the area around the eyes, you should use Veroshpiron (the dosage for edema in children is prescribed by the attending physician depending on the weight and height of the child) and Badyaga gel to prevent the appearance of hematomas on the face.
If a child has suffered a serious head injury, you need to take him to an emergency room for examination. There, if necessary, they will stitch the wound (if there is one) and check the child for the presence of a traumatic brain injury. If immediately after the impact there was a short-term loss of consciousness or severe nausea and vomiting, a closed head injury (CLT) most likely occurred. It is advisable to consult a neurologist and, if necessary, do an MRI of the brain.
Injuries as causes of facial swelling in a child
Traumatic swelling of the eye area appears not only as a result of bruises or violation of the integrity of the skin of the eyelid. Causes of such swelling also include insect bites, prolonged irritation from water, especially salty or contaminated water, foreign objects entering under the eyelid, as well as sunburn, which is not uncommon in infants due to the characteristics of the skin.
Swelling of the face and eyelids, therefore, depending on the location, severity, manifestations, can be both a normal phenomenon and a symptom of various diseases that require diagnosis and medical therapy. Prolonged swelling, suddenly developing swelling, severe discomfort, as well as almost all types of facial swelling in infants should definitely be a reason to visit a specialist.
Is it advisable to use diuretics?
Almost all pharmacological drugs are prohibited or partially limited for children. Diuretics are no exception.
Here is a list of diuretics that are approved for use in children (should be used with caution, as drug dependence may develop):
- "Furosemide". This drug is prescribed with caution. The instructions for use for Furosemide tablets contain a wide list of contraindications. However, there are situations when you cannot do without this medicine. Can be used both in the form of tablets and in the form of a solution for intramuscular injection. It is able to get rid of the accumulation of excess fluid in the body in just an hour; it will be released through the kidneys and bladder;
- “Diacarb” is a diuretic that is often prescribed to children by neurologists as part of complex therapy for the treatment of intracranial pressure. The tablets quickly and effectively help remove excess fluid from all parts of the body and from subcutaneous fat;
- "Hypothiazide" - tablets with a strong diuretic effect. Used for severe liver failure in children aged three years and older.
Side effects and contraindications to the use of diuretics in children:
- chronic renal failure;
- liver diseases of various etiologies;
- violation of water-salt balance in the body;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- taking cardiac glycosides;
- hypercalcemia;
- intolerance to sulfonamides.