Main causes of photophobia
The most common causes that can cause photophobia of the eyes in adults are:
- Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the ocular conjunctiva, accompanied by pain and pain in the eyes, redness of the whites of the eyes, and sometimes the formation of pus (if the disease is bacterial in nature);
- Iritis – inflammation of the iris of the visual organ;
- Keratitis – inflammation of the cornea;
- Mechanical damage to the cornea;
- Formation of ulcers or tumors in the eye area;
- Albinism is a disease in which light rays penetrate not only through the pupils, but also through the discolored iris;
- Frequent, prolonged migraines;
- Colds;
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight;
- Eye irritation resulting from violation of the rules of staying in a solarium;
- Congenital photophobia, accompanied by partial or complete absence of the pigment substance melanin;
- Drug treatment of various diseases;
- Daily long stay at the computer;
- Exposure of the eyes to prolonged exposure to bright light;
- Acute attack of glaucoma;
- Corneal erosion caused by a foreign object entering the eye cornea;
- Examination of the fundus followed by artificial dilation of the pupil;
- Viral and infectious diseases such as measles, rabies, botulism;
- Photophobia can also be a side effect of taking furosemide, quinine, doxycycline, belladonna, tetracycline, etc.;
- Retinal detachment;
- Thermal or sunburn of the eyes;
- Surgical interventions in the area of the visual organs (one or both);
- Spending a long time in a dark room, after which bright lighting suddenly appears (such changes lead to the fact that the pupil simply does not have time to adapt to new conditions; this is a completely normal phenomenon, so it should not be perceived as a deviation).
Photosensitivity is a fairly common anomaly in people wearing contact lenses. But such a deviation does not always occur, but only if they were incorrectly selected. In such a situation, irritation of the cornea occurs, which can also cause tearing and pain in the eyes.
There is no need to worry if photophobia occurs due to prolonged exposure to a dimly lit room. After the sudden appearance of bright light, the eye does not have time to adapt to the new conditions, which can cause pain, pain and black spots (or dots). A similar deviation is observed in people who are accustomed to reading or working at a computer for a long time, as well as after waking up. But if photophobia is a constant symptom that does not disappear over a long period of time, this should seriously alert the person and force him to consult an ophthalmologist.
Homeopathic treatment for photophobia
Homeopathic remedies help maintain the health of the visual organs, which is confirmed by many years of practice.
If at least once you have experienced how unpleasant increased light sensitivity of the organs of vision is, then your first aid kit must have the following medications:
For conjunctivitis, keratitis, glaucoma
- Mercurius solubilis (Mercurius solubilis) eliminates the problem at the initial stage, relieves the inflammatory process;
- Mercurius corrosives (Mercurius corrosivus) relieves inflammation, reduces lacrimation, helps with photosensitivity;
- Arsenicum iodatum (Arsenicum iodatum) is prescribed for inflammatory processes accompanied by edema;
- Apis (Apis) eliminates cutting sensations in the eyes, redness of the sclera, excessive tearing, photosensitivity;
- Ranunculus bulbosus (Ranunculus bulbosus) eliminates photophobia, lacrimation;
- Calendula (Calendula) will relieve pain, remove inflammation and redness.
For injuries
- Aconitum is taken to help with injuries to the visual organs and traumatic conjunctivitis;
- Graphites (Graphitis) - eliminates irritation as a result of photosensitivity;
- Acidum picrinicum is taken for mechanical damage to the sclera, traumatic conjunctivitis;
- Hepar sulfur is taken to eliminate pain;
- Hypericum (Hypericum) - alleviates the condition of the organs of vision in case of injury;
- Silica (Silica) – eliminates photophobia.
Homeopathy, if its traditions and principles are followed, carefully preserves visual function, eradicating the sources of problems both in diseases and injuries.
Treatment
When contacting a medical institution with a problem of photophobia, the ophthalmologist will definitely diagnose eye diseases. If photophobia is accompanied by fever, vomiting or allergic manifestations, you should also visit an infectious disease specialist or therapist to find out the cause.
Medically
It is useless to treat photophobia without identifying the cause and underlying pathology. Very often, this symptom goes away on its own when the irritating factor is eliminated or after recovery from the underlying disease. Photophobia can be reduced by wearing dark sunglasses and anti-inflammatory eye drops. Such measures will help reduce discomfort and lead a normal lifestyle during the treatment of the underlying disease.
Treatment of photophobia of the eyes depends on the reasons that cause it. If increased sensitivity to light has developed due to an inflammatory disease of any part of the eyeball, then after eliminating the source of inflammation, photophobia will go away on its own.
For purulent discharge, it is necessary to use drops with antiseptics or antibiotics, for example, Okomistin, Levomycetin drops, Tobradex, etc.
If photophobia occurs as a result of a bruise, injury or burn to the eye, urgent ophthalmological assistance will be required. You can first drip your eyes with antiseptic drops and apply a sterile bandage on top.
In the case when such a disorder is associated with the entry of a foreign body or contamination, then after eliminating the negative factor and rehabilitation of the injured organ, the disease can also go away on its own.
Sometimes photophobia is caused by the development of any infectious diseases that are not related to the functioning of the visual system and its normal functioning. In this case, treatment should be aimed at treating the underlying disease that provoked photophobia.
If photophobia is caused by taking certain medications, then the doctor will select an analogue that will not provoke such a reaction to light.
In cases of congenital photophobia or associated with environmental factors, the doctor may recommend wearing contact lenses that minimize negative reactions to light.
Folk remedies
Eye diseases can be treated not only with medications, but also with traditional methods. We offer several recipes that can eliminate or reduce discomfort, including the symptom of photophobia:
- Compress and infusion of Potentilla erecta. This plant helps cure many eye diseases, including eliminating photophobia, as well as improving vision. To prepare a compress, you will need 1 teaspoon of herb, which needs to be filled with 200 ml of water. The broth should be brought to a boil, then let it brew for 3 hours. You should rinse your eyes with this infusion before going to bed. A compress will also have a good effect. Soak sterile gauze wipes with the infusion and apply to your eyes for half an hour.
- Sweet clover compress. The flowering tops of this plant should be collected in July. Pour 40 g of sweet clover with 200 ml of water and boil over low heat for 15 minutes. Cool the product, strain and apply swabs soaked in it in the morning and evening for 30 minutes.
- Drops on “silver water”. Boil and cool water, pour into a glass jar. Place some silverware there (coins or cutlery). Leave the water for a week, during which time it will become enriched with silver ions. Then take 4 large aloe leaves (the plant must be over 3 years old) and place in the same container. Bring the water to a boil, remove from heat, and wrap the pan in a large towel and blanket. The remedy should be infused until the morning. Strain the broth in the morning, then add 2 teaspoons of natural honey and stir until completely dissolved. Place 2 drops in each eye 3 times a day. The course of treatment ranges from 1 week to six months. Such drops will relieve photophobia, eye inflammation, cataracts, and also improve vision. They need to be stored in the refrigerator.
- Sea buckthorn oil. It will help get rid of photophobia. The first two days you need to drop 1 drop of oil into the eye every 2 hours. And then 2 drops up to 3 times a day. It can also be used for compresses. Soak cotton pads in sea buckthorn oil and apply to eyelids for half an hour, 2 times a day.
- Calendula with chamomile. Mix calendula and chamomile flowers. Pour a spoonful of the mixture with boiling water (250 ml) and leave for 1 hour. Strain the infusion. Rinse your eyes several times a day or use the infusion for compresses. You can also drop the product into your eyes, 2 drops 3 times a day.
Symptom therapy
Treatment of photophobia is entirely based on the cause of this symptom. This requires ophthalmological diagnosis, since many eye diseases are similar to each other. To make a diagnosis, the following studies are needed:
- Ophthalmoscopy – examination of the fundus through a previously dilated pupil.
- Biomicroscopy - examination in a special slit lamp for changes in the vitreous body and areas of the fundus.
- Perimetry - checking visual fields.
- Tonometry is the measurement of intraocular pressure.
- Gonioscopy is an examination of the corner of the eye where the iris borders the cornea.
- Pachymetry is the measurement of corneal thickness.
- Ultrasound of the eye helps to examine the transparent media of the eye when it is impossible to perform ophthalmoscopy.
- Fluorescein angiography is a study of the patency of blood vessels that supply the structures of the eye.
- Optical coherence tomography - helps to identify changes in retinal tissue.
- Electroretinography - helps to carefully study the functioning of the retina.
- Sowing the discharge from the conjunctival sac for viruses (using the PCR method), bacteria and fungi.
If, according to the results of an ophthalmological examination, a person is healthy, an examination by a neurologist is necessary. This specialist also prescribes additional studies:
- MRI of the brain;
- electrocephalography;
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck, which are directed into the cranial cavity.
An ultrasound of the thyroid gland, determination of hormones produced by this gland in the blood, and radiography of the lungs are also prescribed. If signs of hyperthyroidism or diabetic retinopathy are detected, treatment is carried out by an endocrinologist. If there is evidence of a tuberculous process in the cornea and conjunctiva, therapy is prescribed by a phthisiatrician.
What can you do before consulting a specialist?
We do not recommend delaying contacting a doctor, as seemingly banal photophobia may hide a malignant brain tumor that is rapidly progressing. But while you're waiting for your appointment with a doctor or for a test, you don't have to suffer from daylight. To alleviate the condition, buy polarized sunglasses, which will make it possible to reduce the dose of ultraviolet radiation entering the eye. In addition you need:
- stop rubbing your eyes;
- reduce time spent sitting at the computer;
- use Vidisik drops containing artificial tears;
- for purulent discharge, use drops with antiseptics or antibiotics: “Okomistin”, “Levomycetin drops”, “Tobradex” and others. In this case, an examination by an ophthalmologist is mandatory, since the purulent process can affect the deeper parts of the eye, which the local antiseptic “does not reach”;
- If photophobia appears as a result of a bruise, injury or burn to the eye, emergency ophthalmological assistance is needed. First, apply antiseptic drops to your eyes, apply a sterile bandage on top, and call an ambulance.
Diagnosis of the disease and its prevention
To exclude all organic brain injuries (intracranial hematomas, tumors and hydrocephalus), the patient uses MRI
If you suspect complications when bearing a child, it is important to donate blood for a biochemical test (urea and creatine) and urine, in which protein can often be detected, which indicates disturbances in the normal functioning of the kidneys
The electroencephalogram is very important for assessing the rate of excitation of the cerebral cortex, determining the location of the ectopic lesion that causes epileptic seizures and fear of light. If a doctor diagnoses heleophobia, the patient visits a psychiatrist.
When conducting diagnostics, it is very important to exclude alcohol intoxication and drugs, as well as conduct tests for the presence of such substances in the patient’s blood. There is no need to suffer from bright daylight at all before going to the doctor.
To alleviate your general condition, you need to purchase special polarized sunglasses that will help reduce the amount of ultraviolet radiation reaching the retina. You also need:
There is no need to suffer from bright daylight at all before going to the doctor. To alleviate your general condition, you need to purchase special polarized sunglasses that will help reduce the amount of ultraviolet radiation reaching the retina. You also need:
- reduce the number of hours per day working at the computer;
- stop rubbing your eyes too much;
- use Vidixic drops, which are considered a good means of artificial tears;
- if there is purulent discharge in the eyes, it is best to use special drops with antibiotics or antiseptics Tobradex, Okomistin, chloramphenicol drops. With all this, the attending physician must carefully examine the patient, since purulent processes can also affect the deeper layers of the eye, to which the local agent simply will not reach;
- If photophobia appears due to a burn, bruise or injury to the eye, then the patient should be immediately provided with ophthalmological care. First, you should drip the eyeball with drops containing an antiseptic effect, and apply sterile gauze to the eye.
There is no need to wait long before seeking help from a treating specialist, otherwise such a seemingly insignificant reason can provoke the development of a malignant tumor in the brain, which will begin to progress rapidly.
Attention, TODAY only!
A symptom such as photophobia gives a person a lot of unpleasant sensations. In this case, any ray of light, daylight or artificial, on the area of the eyeball brings a feeling of discomfort, and sometimes even acute pain. Sometimes this manifestation is accompanied by lacrimation (or both at once) and redness of the eyes. What are the causes of photophobia? What to do in this case?
Causes
At times, photophobia can occur due to strain on the eyes. When exposed to light after being in a dark room or after spending a long time in front of a computer screen. In such cases, photophobia is short-lived and does not pose any threat.
But if the painful reaction continues for a long time, urgent medical examination is necessary, because in this case photophobia is the result of an illness or injury to the eyes.
List of diseases that can lead to photophobia:
Conjunctivitis. Iritis and other diseases in which any part of the eye becomes inflamed; Structural features and congenital pathologies of the visual organs - albinism or melanin deficiency; Mechanical damage to the eye or ingress of foreign bodies, irritation from contact lenses; Neoplasms in various parts of the eye; Diseases that affect the brain (rabies); Migraine; Mercury poisoning; Side effects of certain medications (quinine, tetracycline); Retinal detachment. chemical or sunburn.
As can be seen from the list above, photophobia can be a sign of a serious illness, so this pathology should not be ignored.
Since photophobia most often indicates the presence of another disease, treatment should be aimed at the disease that led to increased sensitivity of the eyes.
In the event that painful sensitivity to light is caused by congenital structural features of the eyes, or if the treatment of the pathology that caused photophobia is too long or not possible at all, it is necessary to take measures that can improve well-being.
First of all, you need to reduce the strain on your eyes: you need to darken your workplace and reduce the brightness on your computer monitor.
You should only be in the light with special glasses, which should completely protect your eyes from ultraviolet rays.
It would also be useful to wear a hat with a visor or wide brim.
If photophobia is caused by taking medications, you need to contact your doctor to change them.
Eye drops
When photophobia is episodic and not a symptom of any disease, eye drops can be used to reduce discomfort.
If this pathology is caused by excessive strain on the eyes, then you can use moisturizing drops that contain vitamins. And if photophobia occurs due to inflammatory processes, then anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drops should be used.
But do not forget that you can use any medications only with the permission of a specialist.
Causes
There are two main causes of the pathological condition. The first is a side effect of therapeutic treatment with pharmaceuticals.
List of medications that cause photophobia:
- products used in ophthalmic practice (eye drops, ointments);
- antibiotics – Tetracycline, Doxycycline;
- drugs to lower blood glucose levels in diabetes mellitus;
- statins - drugs for reducing cholesterol in the vascular walls and preventing cardiovascular diseases;
- NSAIDs – Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Ketoprofen.
The second common cause is diseases of various etiologies, in which photosensitivity is an accompanying symptom. These include the following diseases:
- conjunctivitis and keratitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane and cornea);
- infectious meningitis;
- ARVI and other viral diseases;
- neurological diseases;
- mental disorders - depression, hallucinations, sleep disturbances;
- chronic fatigue syndrome.
A temporary fear of light occurs when working at a computer for a long time, when going outside without protective glasses, when the sun is as bright as possible - both in summer and winter. If you stay in a dark room for several hours and then go outside, sunlight can trigger the development of non-pathological photophobia.
Unilateral photosensitivity of the eye appears when a foreign body enters the conjunctiva.
Eye diseases
Eye diseases
– various functional and organic lesions of the visual analyzer, which limit the ability to see.
Symptoms of eye disease
• sharp pain, redness of the eyes, discharge from the eyes and photophobia indicate the presence of an infectious eye disease;
• the likelihood of developing myopia exists if objects located nearby are clearly visible, but in order to see distant objects, you have to squint and strain;
• when the cornea is damaged, a sharp, acute pain is observed, attacks of which go away with closed eyes;
• decreased vision and the presence of a veil before the eyes indicate the presence of cataracts;
• symptoms of glaucoma: increased intraocular pressure, accompanied by headaches and reduced visual field.
Types of eye diseases
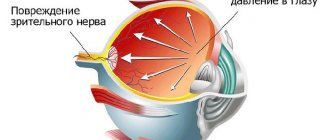
1. Glaucoma is the loss of the eye's ability to regulate its internal pressure, resulting in increased pressure. Glaucoma is the most dangerous eye disease.
2. Cataract is a disorder caused by clouding of the lens of the eye.
3. Blepharitis - diseases associated with inflammation of the edges of the eyelids.
4. Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of infectious origin.
5. Leukoma – the appearance of a white spot on the cornea.
6. Keratitis – inflammation of the cornea, redness, clouding.
Symptoms
A characteristic feature of the choroid is the absence of nerve endings, so uveitis can occur for a long time without obvious symptoms and is not accompanied by pain. Manifestations of the disease depend on the cause of uveitis, the extent of the lesion, the pathogenicity of microorganisms and the state of the patient’s immune system.
Anterior uveitis in the initial stage of the disease can manifest itself as a feeling of “veil”, a slight “fog” before the eyes, which is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the eye and a gradual decrease in visual acuity. If the patient does not consult a doctor, as the inflammation progresses, severe redness of the eye appears, vision continues to decline, heaviness and pain in the eye intensify, photophobia, lacrimation, and increased intraocular pressure join these symptoms. In severe advanced cases of uveitis, blindness may be a possible outcome of the disease.
Posterior uveitis is characterized by late onset of symptoms, absence of pain, and no redness of the eyes. There is a gradual progressive deterioration of vision, with the appearance of a “fogginess” or “spot” in front of the affected eye. As inflammation progresses, mild dull pain in the depths of the orbit may occur. Typically, this sign indicates involvement of the optic nerve in the inflammatory process.
Symptoms
A person suffering from photophobia, when exposed to an illuminated space, squints, closes his eyes, and tries to protect his eyes from the light with his hands. When wearing sunglasses the situation improves slightly. Increased photosensitivity may be accompanied by additional symptoms, such as:
- Headache;
- Pupil dilation;
- Redness of the eyes;
- Feeling of “sand” or “stinging” in the eyes;
- Impaired visual acuity;
- Unclear outlines of objects.
Photophobia of the eyes is a manifestation of a painful reaction of the visual organs to daylight. In medicine, this concept is called photophobia (fear of sunlight). The disease is characterized by unpleasant sensations and squinting of the eyes when natural or artificial light penetrates them.
When you are in the dark, the feeling of discomfort disappears. All this has its own causes and is also accompanied by certain symptoms.
Symptoms of photophobia
It’s easy to identify signs of photosensitivity yourself. As soon as streams of bright light hit the retina, unpleasant sensations and discomfort appear in the orbit. A man tries to squint his eyes. Even dim light can cause irritation.
In parallel, a spasm of the eyelids is observed. Some people's pupils dilate. The eyeballs become pink or deep red. The person involuntarily begins to blink frequently. Complains of a feeling of sand in the eyes. Some people experience a temporary decrease in the quality of their vision.
Reasons for the development of the lesion
The oculomotor nerve is designed to regulate the size of the pupil, thereby ensuring normal vision of surrounding objects at different degrees of illumination around.
The entry of light through the refractive system into the retina is limited by the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The action of the first can lead to a noticeable dilation of the pupil, and the second to its narrowing. In a dark room, the pupil begins to increase in diameter, and in light it becomes smaller. Photophobia is a sign that too much light enters the pupil from the external environment, which negatively affects the nervous system, causing the pupil to react with irritation. Bright rays can provoke headaches, epilepsy attacks, and other negative feelings.
Causes of photophobia:
- development of a migraine attack, increased level of intracranial pressure in epilepsy, hypertension, eclampsia in pregnant women;
- alcohol intoxication, drug intoxication, hangover;
- exposure to medications that significantly dilate the pupil;
- pathologies in the central nervous system due to traumatic brain injuries, tumors, neuroinfections, strokes and multiple sclerosis;
- allergic infections and respiratory diseases;
- albinism;
- : conjunctiva, iris or cornea;
- pathology in the circular muscle, which narrows the pupil after injuries and various tumors.
This list is far from complete; there are a large number of diseases that cause photophobia. Photophobia is more typical for attacks of epilepsy, traumatic brain injuries, encephalitis and other diseases that occur along with cerebral edema, eye damage and injuries that develop intolerance to bright sunlight.
Treatment
If meningitis or encephalitis is diagnosed, then antibacterial or glucocorticoid therapy is mandatory. If any problems with the eyes are determined, eye drops are prescribed, and, if necessary, tablets or injections.
An effective remedy for restoring vision without surgery or doctors, recommended by our readers!
Often, when leaving a dark room on a sunny day, tears begin to flow from your eyes. I really want to close them with my hands. This is the weakest manifestation of photophobia. In more severe pathologies, pain, pain, and lacrimation occur at the slightest ray of light. Photophobia is one of the most common ophthalmological diseases.
Prevention
Preventing the problem involves organizing the following activities;
- Low-intensity training;
- Hiking;
- Good nutrition;
- High-quality sleep that eliminates fatigue;
- Avoidance of stressful conditions;
- Elimination of habits harmful to health;
- Complete treatment of infections;
- Swimming;
- Limiting time in front of a monitor screen;
- Prevention of osteochondrosis;
- Timely moisturizing of the eyes;
- Regular blood pressure measurement (this is important after reaching the age of 40);
- You should definitely ventilate the room where a person stays for a long time.
If you carefully follow the recommendations given, you will be able to minimize the risk of developing most diseases.
What diseases can cause photophobia?
Photophobia is a symptom of various diseases. The causes of photophobia lie precisely in pathologies in the body associated with visual perception and its processing in the brain. If this chain is disrupted, a person begins to have vision problems and photophobia manifests itself.
The following diseases may be to blame:
- keratitis, conjunctivitis, glaucoma, iritis - eye diseases. When they occur, inflammatory processes occur that make the nerve endings in the eye area hypersensitive not only to light, but sometimes also to touch, cosmetics, etc. In this situation, photophobia is nothing more than a defensive reaction of the eye that occurs to preserve normal vision;
- Albinism is a hereditary structure of the visual organs. Albinism cannot be called a disease, but it is characterized by a lack of melanin, which can cause photophobia;
- viruses and infections (flu, ARVI, rabies, measles);
- eye injury;
- allergies to chemicals. Most often it occurs as a side effect of certain medications (Atropine, Tetracycline). Typically, stopping the medications that trigger the allergic reaction will help the photophobia go away;
- poisoning with substances containing mercury;
- foreign body entering the eye. Even a speck in the eye can cause short-term photophobia. This is due to interference in visual perception, while the eye protects itself, reacting sensitively to external influences, in particular to light;
- severe emotional disturbances, mental instability;
- diseases of the central nervous system
- a (tumors, cysts, traumatic brain injuries). In this case, the causes of photophobia are the loss of the ability to process information received by the eyes.
By the way, not only adults, but also children suffer from photophobia. In them, photophobia manifests itself as a symptom of diseases such as measles and rubella. This can be immediately recognized by the following sign: if one eye is sensitive to light, then the problem is a pathology of vision, the structure of the eye, or a foreign body. If both eyes cannot tolerate light, the cause is either infection or brain damage. Photophobia in a child manifests itself externally in the same way as in adults, but the temperature may still rise and chills may appear.
Causes of flashes in the eyes
The indicated flashes are a manifestation of internal problems. They do not arise on their own without reason.
Therefore, it is important to consider the main causes of symptoms:
Damage to the vitreous
It is located in the inner areas of the eye and occupies most of it. This is a very dense structure. However, with injuries or infections, the vitreous body can be seriously damaged. The resulting damage is expressed in flashes. A person sees them and perceives them as flashes. But in reality it is a display of damage.
| Cloudiness and other defects occur deep inside the eye. However, they also have an external manifestation, forming the effect of flashes. As a rule, this leads to the development of infection. Hemorrhages form inside the body. It is they who are perceived as flashes. |
Migraine
This condition occurs against a background of nervous exhaustion and extreme tension. Nervous activity leads to unbearable headaches. Against this background, it is very difficult for a person to perceive even quiet sounds. Pain is caused by any irritants - smells, normal walking. And its intensity is reflected in the form of a flashing effect.
Retina
This organ of the eye allows you to normally perceive surrounding objects. The retina can be damaged as a result of a burn, toxin poisoning, or shock. Any of these factors leads to the development of pathologies. They do not always appear instantly, but develop over a long period of time.
The effect described above becomes a tangible expression of such processes. In this case, outbreaks will not be accompanied by pain or inflammation of the eyes
But you need to pay attention to them if the effect has become regular.
Vessels
They permeate the entire eye organ. These are the smallest blood capillaries that react sharply to shock, poisoning, and infections. Any influence leads to injury to these vessels. They burst and the eye begins to hurt. If the damage is severe, it will be expressed in flashes. It is pain that leads to these manifestations;
Tumors
They are formed in the brain. Extremely dangerous as they can be fatal. It grows and inevitably begins to affect the organ of vision. This action manifests itself in an increase in pressure inside the eye and leads to a flashing effect;
Inflammatory processes
Inflammatory processes are caused by infection. This may be conjunctivitis, blepharitis, iritis, keratitis. In these situations, severe redness of the eyes is observed. This occurs due to damage to blood vessels - capillaries. Intense inflammation develops against a background of pain and suppuration.
| Such symptoms strain the eyes, which leads to flash effects. |
Consequences of injuries
Serious injuries result in damage to the eye organs. They can affect the retina, vitreous body, lens, and so on. With severe eye strain, injuries make themselves felt, manifesting themselves in a flash effect;
For cervical osteochondrosis
In this case, outbreaks are also characteristic of acute human conditions. Nerve endings are pinched. The person cannot turn his head normally because he is in severe pain. As a result, a flashing effect appears.
Why do my eyes hurt from light?
Some people experience eye pain and watery eyes when looking at bright sunlight or electric light. The pain appears due to increased light sensitivity of the retina, which occurs when there is a malfunction in the body.
Reasons why the failure occurs:
- You sit too long at the computer in the office or at home in front of the TV. As a result of prolonged stress, the mucous membrane dries out, the eyes begin to itch and therefore react painfully to light rays.
- You are taking medications with the side effect of light sensitivity in your eyes.
- You have been exposed to high levels of radiation which has affected the sensitivity of your retina.
Also, the eyes hurt from bright light with the following diseases:
- conjunctivitis - an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the eyes, acute or chronic;
- keratitis - inflammation of the cornea;
- Iritis is a disease in which the iris of the eye becomes inflamed.
Photophobia is also a characteristic of the natural aging process of the lens. Older people often complain that it hurts to look at the light.
My eyes hurt from the light and my head hurts
Eye pain and headache often accompany each other. The pain can “originate” first in the eye area and gradually move to the head, or it can arise somewhere in the back of the head and slowly spread to the organs of vision.
Doctors identify several diseases that cause these symptoms:
- Myopia (myopia) - severe tension in the eye muscles provokes a painful reaction of the nerves located in the head. Perhaps the diopters for your glasses were chosen incorrectly.
- Overfatigue - your eyes are constantly strained when you work for a long time at the computer, relax in front of the TV, or are mentally overstrained at work. This negatively affects the condition of the optic nerve, especially in a child who sits in front of a monitor for too long. The pain usually appears in both eyes in the afternoon.
- High blood pressure - eye pain with high blood pressure and visual disturbances, including light sensitivity.
- Head injuries - a sign of a concussion is headaches, which are reflected by pain in the eyes.
- Infectious lesion of the brain - pain is localized in the temples and eyes, moving to the occipital region. Additionally, dizziness, nausea, and weakness occur, which indicates symptoms of meningitis. The sooner you see a doctor, the lower the risk of death.
- Colds and flu are accompanied by pressing pain in the head and increased sensitivity to light.
- Migraine - occurs due to emotional and physical overload, weather changes, consumption of chocolate, cheese, nuts. The body begins to react in the form of throbbing pain in the temple area.
- Glaucoma - when the flow of fluid inside the eye is impaired, intraocular pressure increases. The disease is characterized not only by headache and eye pain. Patients often say: “I can’t look at the light, there’s something pressing on my eyes,” a colored halo appears around the light bulbs. If glaucoma is not diagnosed in time, the disease will lead to blindness.
In some cases, the eyes hurt from light and the head hurts due to a brain tumor, arteritis, Horton's syndrome, and trigeminal neuralgia.
Also, painful sensations in the eye and head area may indicate disturbances in the blood supply to the tissues around the eyes, when nutrients stop flowing to the visual organs due to vascular diseases. Pain in the eyes is sometimes provoked by disruptions of the vegetative-vascular system, sinusitis and sinusitis.
Eyes in the wind
How to reduce excessive eye sensitivity in spring? Do Botox and solarium affect visual acuity? Why do blood vessels burst in the eyes?
Svetlana Viktorovna Milova, candidate of medical sciences, ophthalmologist of the highest category, chief medical doctor in the town of Pushkino near Moscow, answers these and other questions from readers.
“I am very sensitive to sunlight. Even with partly cloudy conditions, the eyes seem to be “corroded” by the sun. And they immediately begin to cry. Please advise how to make your eyes more resilient?
Katerina Odintsova, Vladimir
Increased sensitivity to light indicates that the eye is tired for some reason. Perhaps you sleep little and work a lot on the computer. Also, the eyes can become “unaccustomed to the sun” during a long, cloudy winter. You need to strengthen the protective tear film of your eyes. Moisturizing drops, for example, Systane Ultra, Artelak Balance, are well suited for this. They protect the eyes from dryness and irritation. Provides them with long-lasting comfort throughout the day.
Such funds are not used constantly, but as needed. On bright sunny and windy days, when working at the computer for a long time. Before going to the sauna, if you are in a smoky, “smoky” room. Place 1-2 drops of the product into each eye and blink.
“My daughter became interested in colored lenses. And with their help he constantly changes his eye color. But I'm worried, will this fashion harm her eyesight? My daughter is 17 years old.”
N. Shapovalova, Astrakhan If the eyes perceive the lenses well - they do not hurt, do not turn red - then there will be no harm from them. 17 years is the age when many teenage girls are “looking for themselves,” their own style. They strive to express their inner world through changes in appearance. Within reasonable limits, such harmless experiments are not dangerous.
But if your eyes become irritated, begin to dry out or water, it is better to avoid contact lenses. At least for a while.
“In the summer I often ride a bike. And sometimes small flies fly into your eyes. After this, the eye becomes red and even inflamed. How to behave correctly in such a situation? What hygiene products should I use to prevent infection?
Lera Golubeva, via e - mail . In this situation, the eye may turn red not only due to small flies. Exposure to wind, which disrupts the integrity of the protective tear film of the eye, also plays a role. Therefore, when riding a bicycle, you must always use protective sports glasses. Thanks to their special streamlined shape, they protect the eyes well from all external influences - ultraviolet radiation, wind, dust, insects and debris.
If a foreign body does get into the eye, you need to rinse it with antiseptic drops. The drugs Okomistin or Vitabact are suitable for this purpose. They disinfect the eye, preventing inflammation. And then you need to apply moisturizing drops.
If eye irritation persists, you should see an ophthalmologist.
“A month ago, I injected Botox under my eyes so that wrinkles would not be visible when I smile. I feel that after this procedure my vision somehow became worse, as if there was fog before my eyes. What to do?"
Inna Pershina, St. Petersburg It is unlikely that a Botox injection could affect your vision. Unless you had a habit of squinting your eyes a little to see more clearly. And now, under the influence of the drug, the muscles are “frozen”, and you can no longer do this. However, after a few weeks, the effect of the injection will begin to gradually weaken, and the muscles will return to their previous mobility.
But in order not to worry, you should consult an ophthalmologist and have your visual acuity checked.
“Recently, blood vessels in my eyes have begun to burst. What health problems does this indicate and how to avoid this phenomenon?
Tatyana Porokhova, Kaluga Most often this is a problem of unstable blood pressure. Hemorrhages into the conjunctiva of the eye usually occur at night, when after a rise in pressure it sharply decreases.
In addition, a lack of vitamin C can lead to increased fragility of blood vessels. In this situation, taking the vitamin preparation ascorutin can help.
However, a more serious problem cannot be ruled out - developing diabetes mellitus. So you need to be examined by a therapist.
“Over the past six months, I have already suffered from conjunctivitis three times.
Moreover, traditional albucid no longer helps me. What powerful antibiotic drops should I use to finally get rid of this problem?
Elena Myachina, Saransk
In your case, there is no way to self-medicate, since the inflammation has already taken a chronic form. Here you need the help of an ophthalmologist and a competent search for the reasons that cause frequent relapses. Individual selection of drugs. And the treatment is under the supervision of a specialist.
It is incorrect to recommend antibiotic eye drops in absentia. You may have herpetic conjunctivitis, in which case antibacterial agents may make the condition worse. And antiviral and immunomodulating drops, for example, Ophthalmoferon, will be beneficial. And vice versa: with a bacterial infection, interferon products may be ineffective.
Therefore, for chronic conjunctivitis, we usually use drugs from different groups. And there are often situations when, after treatment with one medicine, you need to immediately start the next course. And without examining and assessing the reaction of the eye to the previous drops, this cannot be done. Sometimes, at the discretion of the attending physician, laboratory tests also have to be done.
“I have very pale skin, so I tan in a solarium a couple of times a month. But one day I heard on the radio that artificial tanning causes glaucoma. Is it really true? Is there any way to protect your eyes?”
Polina Eliseeva, Tambov . This is not entirely true. To protect your eyes in a solarium, it is enough to use special “caps”. They completely reflect ultraviolet radiation and thus protect your vision. But ordinary “outdoor” sunglasses will not provide such protection, since the artificial rays of a solarium are much more powerful than the sun. And, of course, it is not recommended to sunbathe in a solarium with your eyes simply closed.
But even if you take all precautions, you need to know when to stop when tanning. You should not go to the solarium regularly all 12 months of the year. And in order not to miss possible troubles with your eyes, you need to visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year.
“At the end of May, when the trees are in full bloom, I begin to experience allergic conjunctivitis. Can it be prevented in advance and how? Recommend some new drops or tablets.
Zhanna Lapshina, Murom It is better to ask an allergist about tablets. And drops for allergic conjunctivitis really exist. These are Lecrolin, Opatanol, Cromohexal and others, including hormonal ones based on dexamethasone. But it is advisable to use them only after consulting a doctor. After all, the main thing is not to do harm, since these drugs have side effects and contraindications.
Particular care should be taken when using dexamethasone drops. With its long-term use, cataracts and even glaucoma can develop.
“During the medical examination, I was diagnosed with increased intraocular pressure. They said that there is a risk of developing glaucoma, which without treatment leads to blindness. Strange, but no medications were prescribed. Is there any way to prevent this disease? Maybe some vascular medications or vitamins are needed? I wouldn’t want to waste time.”
Olga Zhilina, Izhevsk Apparently, the doctor is not entirely sure of the diagnosis yet and wants to examine you in more detail before prescribing lifelong treatment.
The diagnosis of glaucoma cannot be made based solely on the level of intraocular pressure. To clarify it, it is necessary to undergo modern ophthalmological diagnostics. First of all, the so-called optical coherence tomography of the optic nerve. This completely painless, non-contact examination provides the doctor with comprehensive information about all structures of the eye.
And the prevention of the development of glaucoma is, first of all, the normalization of venous and lymphatic outflow from the brain. As well as relieving excess tension in the muscles of the cervical-collar area. An osteopath or neurologist can help with this.
“They say that an experienced ophthalmologist can tell about all a person’s diseases based on the condition of the eyes. This is true? What kind of diagnostics and where should I go for this?”
N. Yurkova, Kostroma What you are asking about is called iridology. This is the recognition of human diseases by the pattern of his iris. To do this, you do not need to be an ophthalmologist, but you need to be an iridologist.
However, this study does not claim to be completely accurate.
At best, they will point you to an organ with which you may have problems.
And they will recommend a more detailed examination by a specialist on this issue. Polina ZABELINA