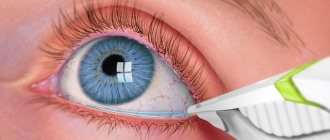
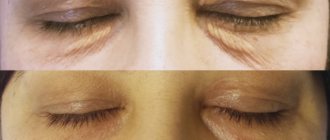
Causes of ectropion of the century
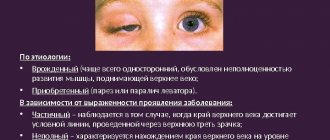
The development of pathology of ectropion of the eyelid can be congenital or acquired.
In the first case, the onset of the disease is associated with a violation of the muscular system during intrauterine development. Most often it is part of the clinical picture of Down syndrome. Acquired causes of ectropion of the eyelid may be the following:
- mechanical damage resulting from injuries and burns;
- cases of damage to the facial nerves (Bell's palsy);
- as a complication of dermatological diseases (contact dermatitis, malignant skin formations);
- scar changes as a result of unsuccessful blepharoplasty;
- inflammatory diseases leading to spasm of the periorbital muscle;
- pathological processes leading to failure of cerebral circulation;
- age-related changes that disrupt the structure of the cartilage tissue of the eyelid.
2. Reasons
Eversion of the eyelid can be congenital and, in this case, represents an anomaly in the intrauterine development of the visual organs. Cicatricial ectropion is a consequence of healing of wounds and other damage to the eyelid (for example, thermal or chemical burns). The paralytic version of inversion develops against the background of serious damage to the facial nerve and, in particular, paralysis of the orbicularis muscle. Spastic eversion sometimes accompanies inflammatory processes. In some cases, inversion is purely mechanical in nature and is associated with the growth of a neoplasm in the area of the ciliary edge of the eyelid.
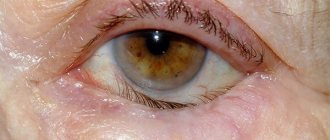
Finally, age-related (atonic) ectropion progresses with the natural aging of the body and the development of degenerative processes in the eyelid, which leads to a decrease in muscle tone and stretching of increasingly dehydrated tissues of the eyelid.
Visit our Microsurgery page
Classification of ectropion of the century
Based on the pathogenesis of the disease, the following classification of ectropion of the eyelid is distinguished:
- Congenital.
Pathology occurs infrequently. Violation of embryonic development causes shortening of the cartilaginous plate of the lower eyelid. For mild symptoms, no special treatment is required. Surgical therapy is performed in severe cases of deformity. - Spastic.
Occurs as a consequence of inflammation processes affecting the eyelid area and conjunctiva, which causes spastic contraction of the orbital orbital muscle. - Mechanical.
It is caused by displacement of the skin due to the impact of pressure on them during the growth of a malignant neoplasm. The problem can only be resolved surgically. - Scar.
It is formed as a result of a scar formed after an injury, burn or surgery. Severe cases of deformity can only be corrected by skin grafting. - Paralytic.
It is observed with a cut or paralysis of the facial nerve, since in this case the tone of the facial muscles decreases. - Age.
In the pathogenesis of this form, the main role is played by the loss of elasticity of the muscles and ligaments of the facial area, resulting in their drooping. With timely treatment, the pathology is eliminated by conservative treatment methods.
Types of eversion of the eyelid:
- Senile inversion of the eyelid - appears in older people; its cause is age-related weakening of muscles and stretching of the skin. The process is usually bilateral, the severity of eversion increases with age without treatment.
- Cicatricial eversion of the eyelid - occurs when the skin becomes scarred after injuries and burns, due to which the eyelid is pulled away from the eyeball by the scar. This type of eversion develops gradually, and its severity depends on the location and size of the scar.
- Paralytic eversion of the eyelid is observed with paralysis of the facial nerve, which regulates the functioning of many facial muscles, including the muscle that maintains the normal position of the eyelids.
- Mechanical eversion of the eyelid is a consequence of various eyelid tumors, which can be located in or near the edge of the eyelid. With the growth of such a tumor, the tissues of the eyelid gradually grow with tumor cells, and due to the mechanical action on the eyelid, it turns out.
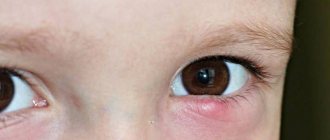
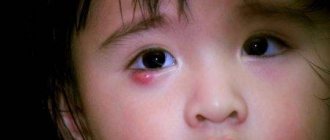
Symptoms of ectropion of the eyelid
Symptoms of the pathological condition of deformation with ectropion of the eyelid are primarily observed visually.
The patient has a lag of the ciliary edge, due to which the eyeball is not tightly closed by the eyelid. In addition, the following symptoms of clinical manifestations are noted:
- In the corners of the eyes, tear fluid accumulates due to a violation of its outflow. The patient experiences inconvenience and discomfort due to the fact that tears flow down the cheek.
- There is a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the visual organs. This symptom is accompanied by dryness of the mucous membrane of the eyeball, due to loss of moisture from the conjunctiva.
- Hyperemia of the white part of the eye appears. Upon visual examination, the severity of the capillary pattern is noted.
- The process of inflammation of the conjunctival membrane of the eye develops. This occurs due to insufficient cleansing of the eyeball from bacterial microflora and dust particles.
If for some reason adequate therapy is not provided, then in the future the patient experiences pain when blinking, clouding of the corneal layer of the eye occurs, and as a result, the acuity of visual perception decreases.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The most typical symptom of ectropion is constant intense lacrimation combined with hyperemia, irritation, inflammation, and swelling of the skin of the eyelid. Despite the abundance of tear fluid, the cornea dries out, and the conjunctiva, as a rule, becomes inflamed. Depending on the severity of the eversion, patients note varying degrees of discomfort (sensation of a foreign body in the eye, pain, burning). Chronic, long-term and untreated ectropion can result in clouding of the cornea and its inflammation (keratitis).
Eversion of the eyelid does not pose any difficulties in diagnosis and is detected during a standard ophthalmological examination.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Diagnosis of ectropion of the eyelid
Visual changes in the patient’s appearance and characteristic accompanying symptoms do not cause difficulties in diagnosing ectropion of the eyelid. In some cases, there is a need to differentiate with such a pathological condition as entropion, when the eyelid is wrapped with the ciliary edge towards the eyeball.
During a visual examination, the ophthalmologist pays attention to scar tissue changes and, if necessary, prescribes a consultation with related specialists (neurologist, dermatologist). In addition, diagnostic procedures are performed to confirm the diagnosis. In this case, the surface of the skin (in the middle of the eyelid) moves by 8 millimeters. The test is considered positive if the skin returns to its original state only after blinking the eye.
If necessary, microscopy of the eye is performed using a slit lamp. This allows you to assess the condition of the cornea of the visual organs, conjunctiva and tear film.
To establish the degree of neglect of the process, the acuity of visual perception and the boundaries of the field of view are determined. Bacterial culture and scraping for cytology are prescribed for the development of conjunctivitis or keratitis.
Treatment of ectropion of the eyelid
The correct tactics of the treatment process can eliminate the clinical manifestations of the disease.
But it is necessary to establish the cause and form of this pathology. In case of unexpressed deformation or when there are contraindications to surgical therapy, conservative methods of treating eyelid ectropion are used. In this case, the patient is recommended:
- Carry out a daily procedure for washing the visual organs with boiled water or pharmaceuticals (chamomile or calendula decoction);
- to moisturize the mucous membrane, relieve the feeling of dryness and redness, use Vizimax, Quinax or Restasis drops;
- in case of development of an inflammatory process in the conjunctiva, use Tobradex, Floxal or Norfloxacin.
Surgical intervention is a radical method that is used for the following indications:
- when scarring changes occur;
- if the patient is over 50 years of age;
- when diagnosing a congenital form of pathology;
- when drug therapy does not lead to the desired result.
The most commonly used surgical methods are:
- The Kunt-Szymanowski method involves partial truncation of the cartilage plate in a shape resembling a triangle. The same flap is simultaneously sewn into the lateral part of the palpebral fissure.
- Filatov's technique. The functionality and mobility of the ciliary edge of the eyelid is restored through transplantation. The required area of tissue is taken from the anterior abdominal wall of the patient being operated on, which eliminates rejection and creates favorable conditions for survival.
- Excision of a piece of skin in the required area using the Kurlov method involves subsequent engraftment of the mucous membrane taken from the patient’s lips.
Treatment of ectropion of the lower eyelid
About the disease
Eversion (ectropion) of the eyelid is characterized by an eversion or sagging of this part of the eye outward, opening the orbital septum. This part of the eye is designed to retain moisture so that the eyeball can move freely in the socket. So, when the eyelid sag outward, the orbital septum becomes dry, which causes irritation and makes it susceptible to various infections. Lack of hydration can also cause the eye to produce excessive tears and other types of fluids. If eyelid inversion is not treated in time, it can lead to damage to the cornea. Therefore, simple eye lubricants are not enough in the later stages of this disease.
Although eyelid inversion can be the result of some injuries or facial paralysis, the most common cause is age. Other risk factors include stroke, developing skin cancer, or a benign growth on the eyelid. Certain birth defects can also cause the eyelid to turn out. The most common of these is Down syndrome. People who have lost a significant amount of weight quickly may also suffer from ectropion as their facial muscles do not have time to adapt to the changes. Balanced and planned weight loss, however, is unlikely to cause this disease.
Although eye ectropion is very rare in people under 70 years of age, those who have a genetic predisposition to it or who have had facial surgery or trauma are at risk.
Symptoms
- Sagging eyelid
- Dry eyes
- Irritated eye
- Excessive tearing
- Redness
- Sensitivity to light
Diagnostics
- Typically, an ophthalmologist can diagnose ectropion simply by examining the patient.
- The eyelid is examined with a special device that measures the degree of sagging.
- The doctor will also look for signs of inflammation to rule out the possibility of infection.
Types of treatment
- Conservative measures such as moisturizing eye drops prepare the patient for surgery and relieve dryness and irritation.
- To protect the cornea, skin tape can be used to temporarily lift the lower eyelid and hold it in place.
- The operation usually solves problems associated with eversion of the eyelid. Part of the sagging lower eyelid is removed, and if there is tissue scarring, a skin graft is performed. Skin is removed from the upper eyelid or behind the ear and grafted onto the lower eyelid. After surgery, the patient must wear a special eye patch for several days. Antibiotics and steroid ointments may be prescribed to prevent infection during the healing process.
Author: Dr. Vadim Zhilyuk
Complications of ectropion of the eyelid
Incorrectly chosen tactics of the treatment process or insufficient therapy for inversion of the eyelid contributes to the development of frequent infectious processes (conjunctivitis, keratitis), which subsequently lead to partial or complete loss of visual acuity.
This can lead to the development of disability. Incorrectly performed surgical intervention can cause a number of the following complications with ectropion of the eyelid:
- Cicatricial changes and scars may appear at the sites where suture material is applied. Large fibrous lumps do not resolve on their own, which necessitates repeated surgery.
- An increase in intraocular pressure can provoke the development of bleeding.
- In the absence of proper care or non-compliance with medical instructions, the postoperative wound can become infected. In this case, therapy should be supplemented with antibacterial drugs.
- The lack of positive dynamics after surgery may be accompanied by the development of hematomas and the appearance of swelling. Areas of accumulated blood are removed surgically, followed by restoration of the integrity of the vessels.
- Insufficient production of tear fluid requires expansion of the tear ducts.
{banner_horizontalnyy3}
Prevention of ectropion of the eyelid
There is no specific prevention to reduce the primary risk of ectropion of the eyelid.
According to practicing specialists in the field of ophthalmology, a medical examination (once a year) will be sufficient. Early diagnosis followed by prescription of drug therapy will avoid surgical intervention. In order to prevent relapse of the pathology, the patient must adhere to the following rules and recommendations:
- perform daily hygienic care of the visual organs;
- when diagnosing infectious eye diseases, provide timely treatment, preventing the pathological condition from becoming chronic;
- minimize possible injuries to the eyeball;
- in the postoperative period, temporarily refrain from visiting the gym and swimming pool (limit physical activity to a minimum);
- impose a complete taboo on the consumption of alcohol and smoking;
- in sunny weather, use special cosmetics to protect against ultraviolet radiation or wear sunglasses.
Patients who have been diagnosed with ectropion of the eye need to know that the disease does not go away on its own. In some cases, even drug therapy does not have the desired effect. Particular care should be taken when using traditional healing methods, since they cannot prevent the pathological process, and superficial elimination of negative symptoms provokes the transition of the disease to an advanced form.