An abscess is a purulent inflammation of the skin of the eyelid, an extensive abscess. It all starts with swelling of the skin of the eyelids, then the process worsens and spreads to a large surface of the skin and an abscess of the eyelid occurs. Since an abscess is a cavity with purulent contents, the cause of its occurrence is infection entering the tissue. Let's consider the issue of treatment and prevention of inflammation of the eyelids.
More about pathology
An eye abscess develops as a result of the penetration of microorganisms.
Routes of infection:
- Through damaged tissue. Infection can occur when bacteria from inflammatory elements (barley, boil, etc.) enter.
- Hematogenously (through blood). This route of infection is typical for people with reduced immunity (severe illnesses, immunodeficiency).
Eyelid abscess is classified according to stages:
- Infiltrative – the initial stage, characterized by the appearance of redness and thickening.
- Purulent-necrotic – stage of cavity formation with the formation of pus.
- The healing stage is the final stage. With large lesions, scars remain after healing; with small lesions, no traces remain.
What causes suppuration?
The active activity of pathogenic microorganisms, such as streptococci and staphylococci, contributes to the development of the disease.
An abscess of the eyelid is a rapid process that often develops against the background of other ophthalmological ailments. For example, it may be preceded by a stye on the eye or blepharitis. In addition, an eyelid abscess can occur if a person is in a very dusty place and does not use protective equipment.
In advanced cases and in the presence of provoking factors, the purulent process spreads to adjacent tissues and leads to dangerous consequences.
Symptoms
At the initial stage of the disease (infiltrative stage), an abscess forms. The person experiences general weakness, a burning sensation at the site of the abscess, developing into pain.
Gradually, the lesion increases in size, and a cavity with purulent contents is formed. Clinical manifestations of the purulent-necrotic stage are characteristic:
- redness and swelling of the eyelid;
- drooping eyelid;
- impaired eyelid mobility;
- swelling, dilation of conjunctival vessels;
- throbbing pain in the area of the abscess;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness;
- headache.
At this stage, the eyelid is sharply painful and tight when touched, and the skin is hot to the touch. Instinctively, a person limits movement with the eyelid due to increasing pain. There is increased body temperature, weakness, and headache.
During the healing stage, all symptoms quickly subside. The person notes an improvement in his general condition.
Photo
The photo shows abscesses of the upper and lower eyelids.
Abscess of the lower eyelid
The appearance of an abscess in the lower eyelid area is due to its more delicate structure compared to the upper skin fold. In this case, suppuration is usually preceded by infection of the ducts of the sebaceous glands or lacrimal canal.
As swelling increases, the eyes may lose the ability to open and close completely. Against the background of swelling, the mobility of the eyelid decreases, and ptosis often occurs. The development of an abscess is accompanied by painful sensations in the eye area. The use of non-steroidal analgesics helps reduce their intensity. However, the effect of most of these drugs is short-term.
Only opening the abscess will allow you to achieve a stable improvement in your condition. But it is strictly forbidden to interfere with the process of emptying a festering cavity on your own. This can aggravate the problem and cause the infection to spread to the brain.
Only an ophthalmologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. A doctor can easily identify a superficial eyelid abscess, but a deep one is much more difficult to diagnose. In the latter case, after interviewing the patient and visual examination, the patient will have to undergo a number of diagnostic measures, including:
- palpation;
- biomicroscopy;
- blood and urine tests;
- ultrasonography;
- CT or MRI;
- X-ray of the sinuses.
Depending on the indications, the patient may need to consult an otolaryngologist or dentist.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis can be made based on examination. The doctor sees a large, sharply painful formation on the eyelid. A person complains of general malaise and fever. The ophthalmologist additionally examines the eye using a slit lamp.
Biochemical and general blood tests are required to assess the degree of the inflammatory process. To determine the source of infection, X-rays are taken and the condition of the orbit and paranasal sinuses are assessed.
Symptoms
According to the international classification of diseases, pathology has its own code. An abscess of the upper eyelid according to ICD-10, as already mentioned, is assigned code H00.0.
The symptoms of this pathology are clear:
- Inflammation develops rapidly, as a result of which a person begins to feel general weakness.
- His body temperature rises.
- The eye swells and festeres.
Treatment
People with an abscess of any location are subject to mandatory hospitalization in a hospital. It is necessary to begin treatment of eyelid abscess as early as possible. This will avoid the development of complications and shorten the period of illness.
It is imperative to determine the cause and exclude it. If the cause of purulent formation is diseases of the ENT organs, oral cavity, and other organs, then for treatment they resort to consultation with relevant specialists.
The basis of treatment is removal of the eyelid abscess. But the operation can only be performed if a cavity has formed. Treatment tactics depend on the stage of the process.
Infiltrative
A semi-alcohol compress and dry heat are applied to the area of the abscess. These procedures accelerate the maturation of the abscess. At this stage, opening the lesion is strictly prohibited.
Purulent-necrotic
When a purulent cavity has formed, you can begin surgery. The operation to remove an abscess consists of opening the lesion, aspirating the purulent contents, and washing the cavity with antiseptic solutions. To improve the outflow of new portions of pus, bandages with hypertonic saline are used.
The wound is sutured when pus stops forming. The timing of suturing is determined by the doctor, approximately no later than 5–7 days.
At the same time, drug therapy is prescribed. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed intramuscularly or intravenously, painkillers are prescribed intramuscularly or for oral administration. If there are signs of intoxication, detoxification therapy is carried out.
Healing
During the healing stage, a course of antibiotic therapy continues. Duration 10–14 days. To reduce inflammatory manifestations, eye drops with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects are prescribed.
- Anti-inflammatory drops "Diclofenac", "Indocollir".
- Antibacterial drops "Albucid", ointment "Tetracycline".
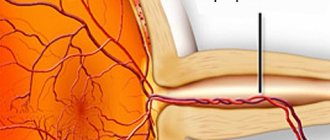
Orbital abscess - pathological anatomy
An abscess forms in dead tissues in which microchemical processes of autolysis occur (during injury, vascular thrombosis), or in large-scale infected living tissues. In the initial period of abscess development, a limited area of tissue is infiltrated with leukocytes, connective tissue cells and exudate. Under the influence of enzymes, the tissues gradually melt, resulting in the formation of purulent exudate, around which granulation tissue, enriched with new capillary vessels, actively develops (due to the endothelium of destroyed capillaries, fibroblasts, macrophages). Initially, the walls of the abscess are covered with purulent-necrotic layers. Over time, demarcation inflammation occurs along its periphery. Gradually, the granulation tissue matures and two layers are formed in the purulent membrane: the inner layer is granulation (vascular) and the outer layer is mature connective tissue.
An abscess may result in spontaneous rupture outward, into a body cavity, into a hollow organ, or by scarring. Very rarely the abscess is encapsulated. In this case, the pus thickens, cholesterol crystals fall out of it, and a thick scar capsule forms at the border of the abscess.
Prevention
You can avoid the formation of an abscess by maintaining eye hygiene and supporting your immune system. Prevention measures:
- do not rub your eyelids;
- avoid skin trauma;
- care for contact lenses;
- do not squeeze out ulcers;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Consult a doctor if tumors appear on the eyelids.
The disease lasts on average about 2 weeks. The prognosis is favorable if treatment is carried out correctly. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances or squeeze out purulent formations. This will inevitably lead to the spread of infection.
Share the article with your friends on social networks so that they know how to act in case of eyelid abscess. Tell us about your experience in the comments. Take care of your eyes. Be healthy.
Possible complications
Such symptoms should prompt the patient to immediately seek medical help. If this is not done, complications will soon begin, the most dangerous among them are:
- meningitis;
- phlegmon;
- thrombophlebitis of the veins of the eye.
At the initial stage of the disease, the eyelid becomes swollen and the tissues on it become denser. Many people confuse an abscess of the upper eyelid and a phlegmon, which means it’s worth mentioning their differences. With an abscess, pus is localized in one place, and with phlegmon, purulent contents spread over adjacent tissues.
There are also noticeable differences between an abscess and stye: in the latter case, the process of suppuration develops much faster (since the photo of an eyelid abscess is unaesthetic, we will not post it in the article).
What is a boil on the eyelid
Boils appear where hair grows. The eyelid is not the only place where a painful boil forms. A boil that has popped up between the eyebrows or a boil above the eye is also a common occurrence.
An abscess located mainly in the eyelid area is called stye. It occurs on the upper and lower eyelids with equal frequency. These boils, including boils under the eyebrow, are external boils when the hair follicle and sebaceous gland are affected.
If an abscess appears on the inside of the eyelid, bacteria enter the glands that moisturize the eyeball. The affected area is clearly visible when the doctor everts and pulls the eyelid during examination.
A cone-shaped, reddened swelling with a white-yellow dot in the middle is often confused with a pimple. However, unlike a pimple, inflammation with a boil nests deep in the skin. Through the thinned skin in the center of the abscess, only the head of the boil is visible. The necrotic core is hidden deeper.
This pathology also has a second name - barley. Many people have encountered this phenomenon. The inflammatory process begins after bacterial cells enter the hair follicles of the eyelashes. A boil under the eye is not only unpleasant, but also unsightly in appearance. A boil on the eye is a fairly common phenomenon, but not everyone suspects that this may indicate the presence of infectious diseases or other problems in the body
Important. The causative agent of this disease is Staphylococcus aureus, so treatment is simply necessary so as not to provoke more serious complications.
This pathology also has a second name - barley. Many people have encountered this phenomenon. The inflammatory process begins after bacterial cells enter the hair follicles of the eyelashes. A boil under the eye is not only unpleasant, but also unsightly in appearance.
A boil on the eye is a fairly common phenomenon, but not everyone suspects that this may indicate the presence of infectious diseases or other problems in the body
A formation that occurs due to an inflammatory process in the hair follicles of the eyelashes or eyebrows, or in the sebaceous glands located near them, is called a boil. Inflammation, as a rule, is accompanied by suppuration and increased activity of pathogenic microflora. The location of the boil, also called a boil, can be the eyebrow or the space under it, the lower or upper eyelid.
When an infectious agent enters the hair follicles of the eyebrows, a boil forms above the eye. An abscess on the eyelid (lower or upper) is popularly called “stye” and occurs due to inflammation of the eyelash follicles. Bacteria that actively multiply inside the neoplasm can, in case of improper treatment and complications, have a negative impact on the functioning of the organs of vision; the pathology can spread to the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx.
Traditional medicine recipes for boils
Experts do not advise self-medication, but traditional methods can speed up recovery. They are used in conjunction with classical therapy.
Calendula flowers have anti-inflammatory properties. They are brewed in boiling water, infused and the resulting liquid is used for compresses. Strong tea has similar properties. Not only does it promote healing, but it also soothes sore eyes.
Aloe is also a powerful agent with anti-inflammatory, bactericidal and wound-healing properties. The aloe leaf should be finely chopped and poured with a glass of warm boiled water. Leave for about an hour and then use as a compress.
At the same time, you should strengthen your immune system. A boil will not cause complications if the body is protected from the inside. Therefore, it is necessary to drink natural fruit drinks, rosehip decoction, linden tea with honey, currant and cranberry juice more often.
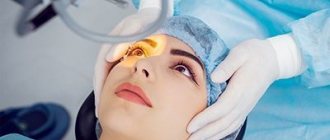
When is surgery necessary?
In the early stages, treatment of a boil on the eyelid is carried out using traditional methods. If the boil does not decrease or recurs, the general condition worsens, surgery is prescribed to quickly rid the patient of the abscess without serious consequences.
Surgical intervention on a boil takes place according to the following treatment plan:
- The patient is positioned and taken to the operating room.
- The head is covered with a cloth, leaving only the working surface where the boil is located free.
- The surgical site around the eye is treated with antiseptics.
- Anesthesia is injected into the treatment area.
- The surgeon puts a special clamp on the eyelid with a boil to prevent it from moving. If surgery is planned on the inner eyelid, it is turned outward. The clamp helps prevent bleeding.
- The formation on the eye is opened with a scalpel or laser, the purulent-necrotic rod is removed, and washed.
- The wound is sutured and stitched.
- Treat with an antiseptic, apply a compress with antibacterial ointment and cover with an aseptic bandage.
The rehabilitation period after treatment of a boil lasts no more than a week and usually does not cause complications.
Traditional medicine recipes for boils
In the early stages, you can treat a boil on the eye at home. The following recipes are suitable for this:
- Brew strong tea and cool it to room temperature. Dip a cotton pad into the infusion and apply it to the boil. Hold for 15-20 minutes. You can add a tea bag. Repeat the procedure 5-6 times a day;
- Boil the egg, cool it until it becomes warm. Apply to the abscess near the eye and hold until it cools down. Repeat treatment 3-4 times a day;
- garlic compress. Grate the garlic, wrap it in a piece of gauze, and apply it to the boil for half an hour. Repeat the procedure 4 times a day;
- carrot ointment. Mix carrot juice with sea buckthorn oil 1:1. The resulting product should be smeared on the abscess 3 times a day.
Effective folk remedies will help you quickly get rid of an abscess on the eye. Treat daily until signs of the boil disappear.