Ectropion or eversion of the eyelid is a pathology of the adnexal apparatus of the eye, which leads to a disruption of the physiological location of the ciliary edge of the eyelid.
The disease can cause damage to the upper and lower eyelid, as a result it ceases to adhere to the eyeball, and it turns outward.
Ectropion is more common in older patients.
The following degrees of development of the disease are distinguished:
- light form. A slight lag of the eyelid from the eyeball is characteristic;
- severe form. Causes the eyelid to turn completely outward. The pathology often leads to the development of inflammation of the conjunctiva and mucous membrane of the eyelid, and a decrease in visual acuity. A noticeable cosmetic defect develops.
NON-INFLAMMATORY EDEMA OF THE EYELIDS.
Occurs in diseases of the cardiovascular system and kidneys. Its peculiarity is the absence of redness of the eyelids. The skin of the eyelids is pale, painful, and tense with severe swelling. The swelling is usually pronounced in the morning, bilateral, and is often combined in such patients with swelling in the legs. It should be remembered that swelling of the eyelids may be the first symptom of a general disease and the patient should be referred for a thorough examination to specialists.
ALLERGIC EDEMA OF THE EYELIDS.
The disease manifests itself in the form of Quincke's edema. Its signs: sudden appearance and equally sudden disappearance. Most often, swelling appears in one eye, mainly the upper eyelid swells. Edema occurs in persons with allergies to foods (eggs, chocolate, strawberries, fish, citrus fruits), medications, household chemicals (powders, varnishes, etc.). Help for such patients consists of eliminating the effect of the allergen (prescribing a special diet, avoiding contact with household allergens) and prescribing desensitizing agents (diphenhydramine, suprastin, tavegil, etc.).
In the summer, allergic swelling may occur after an insect bite. Upon external examination, the bite site is almost always visible. Treatment and care for these patients are the same as for allergic edema of other origins (see allergy).
TRAUMATIC EDEMA OF THE EYELIDS.
Edema can develop due to injury to the eyelids, eyeball, orbit, or skull. It is often combined with deep damage. Such patients should be carefully examined by ophthalmologists. Hemorrhage under the mucous membrane of the eyeball may occur with a significant increase in arterial and intracranial pressure (with severe coughing, vomiting, epileptic seizure, etc.). With traumatic compression of the chest and fracture of the bones of the base of the skull, hemorrhages are observed in the thickness of the eyelids of both eyes, reminiscent of “glasses”. Maximum caution is required when transporting such patients.
The injury may be accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the inner wall of the orbit, and air from the paranasal sinuses (due to the lack of fat in the subcutaneous tissue of the eyelid) easily spreads under the skin of the eyelids. As a result, emphysema of the eyelids occurs, which is characterized by crepitus (crunching) when pressing on the eyelid.
If air enters the orbit, exophthalmos is noted. In such cases, it is recommended to apply a pressure bandage to the eye, which promotes faster resorption of air. Consultation with an otolaryngologist is necessary.
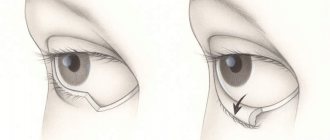
Blepharoplasty for the treatment of ectropion
The intervention takes from one to three hours, the duration depends on the form of the disease and the type of technique used. In addition to correcting the cosmetic defect, the process of tear drainage is corrected and the visible consequences of dislocation (hernia, excess epidermis) are eliminated.
Excision is carried out in places where natural folds of the skin form; special sutures are used, so the scars after surgery are practically invisible. Swelling and bruising persist for several weeks. To reduce negative symptoms, it is recommended to use cooling compresses.
The patient is left in the hospital for a day so that the doctor can monitor his condition. After discharge, you must visit the doctor on the specified days, he will monitor the process of tissue regeneration.
Contraindications for surgery
Surgical intervention has a number of limitations. Very often, correction is not possible in elderly patients. Also contraindications to blepharoplasty are:
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- High blood pressure with frequent crises;
- Severe diabetes mellitus;
- Thyroid pathologies;
- Detachment of the retina;
- Dry eye syndrome.
If contraindications are identified, doctors select an alternative treatment option. Return to contents
Postoperative complications
In some cases, even surgery will not help to completely get rid of the inversion. After correction, a slight gap remains between the eyeball and the edge of the eyelid. This maintains the risk of developing ectropion again.
Patients may also encounter a number of negative manifestations after blepharoplasty:
- Penetration of infection into the wound;
- Seams coming apart;
- Formation of cysts in the skin area;
- Impaired functioning of the lacrimal glands;
- Drooping of the upper eyelid;
- Inability to completely close the eye;
- Bleeding from a postoperative wound.
In most cases, repeated surgery is required to eliminate complications.
Memo for the patient after ectropion surgery
To eliminate the risk of developing negative consequences during the rehabilitation period, it is important to follow some rules:
- Avoid visiting baths, saunas and other thermal procedures on your face for two weeks after surgery. This will help reduce swelling and bruising;
- Limit physical activity and bending for one month. Necessary for favorable resorption of swelling and tissue regeneration;
- Avoid direct contact of the organ of vision and sunlight for six months. It is also prohibited to visit the solarium. This will help eliminate the risk of pigmentation on the eye.
| Do a set of exercises regularly and do not wear contact lenses. You also need to give up alcoholic drinks and cigarettes. |
Causes of symptoms
The eyelid is swollen, painful and causes severe discomfort. The upper eyelid is swollen and hurts: there is more than one reason for this:
- Inflammation of the eyelid, which is red and swollen, swollen. No pain is felt on palpation. The inflammatory process may be accompanied by barley and boils.
- Drinking too much fluid.
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, kidney diseases.
- Overwork or hypothermia. If you are overworked, if the eyelid is swollen, it is recommended to do a lymphatic drainage massage, in which not only the eyelids are massaged, but also the area around them. In this case, it is worth using special soothing gels that relieve fatigue.
- Vitamin deficiency, violation of sanitation and hygiene regime.
- Injury to the eyes, eyelids, mechanical damage. This reason may be accompanied by cyanosis of the eye.
- A bite of an insect.
- Allergy to external irritants. Swelling appears sharply and painlessly. This is how Quincke's edema may manifest itself.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol and salty foods.
- Disturbance in sleep and wakefulness.
- The initial stage of ARVI or influenza, infectious eye diseases.
- Some gynecological diseases in women.
About help with eye injury and tumor >>
INFLAMMATORY EDEMA OF THE EYELIDS.
It is characterized by pronounced redness of the skin, the skin becomes hot to the touch. Most often, inflammatory edema occurs in one eye, being a symptom of a local inflammatory process. When you feel the eyelid, you can often detect a local place of inflammation and pain.
Edema occurs as a result of inflammatory processes in the eyelid itself (styre, abscess, insect bite), the conjunctiva of the eyelids (it can be combined with chemosis, i.e. swelling of the conjunctiva of the eyeball), in the area of the lacrimal sac or lacrimal gland, the eye (inflammation of the iris , infected wounds of the eye, inflammation of all membranes of the eye - panophthalmitis), in the orbit, air sinuses and tissues surrounding the eye. The very fact of the existence of inflammatory edema of the eyelids requires careful research to establish the possible cause of its occurrence, and, depending on the cause, appropriate treatment.
Clinical picture
At the initial stages of the disease, patients have no unpleasant symptoms.
However, as the inversion increases, the following signs of the disease develop:
- Tearing. Normally, tear fluid constantly washes the conjunctiva of the eye, flowing into the lacrimal punctum along the lower eyelid. With the development of eversion, this becomes impossible. As a result, fluid accumulates between the eyelid and the eyeball, overflowing;
- Swelling and maceration of the eyelid. Watery eyes cause swelling of the eyelid skin, reducing its strength and elasticity;
- Sensation of a foreign body or sand due to dryness and irritation of the mucous membranes of the eye;
- Infection of the unclosed eyelid due to disruption of the natural cleansing of the eye from particles of dirt and microorganisms;
- Development of signs of keratitis. In the absence of therapy, clouding of the cornea, development of ulcers and decreased visual acuity are observed.
Treatment of the inflammatory process
Remember: if there is pus, then the disease is bacterial in nature. But bacteria can only be fought with antibiotics.
How is treatment carried out when the upper eyelid of the eye becomes inflamed?
- For bacterial inflammation, antibacterial therapy using antibiotics is used.
- In case of viral etiology of the disease, the eyes are treated with a solution of furatsilin or drugs such as Ciprofloxacin, Dexamethasone, etc., which are prescribed by the doctor.
- If the pain in the eyelid and eyes is of an allergic nature, then treatment will be carried out with antihistamines, such as Allergodil, Ketotifen, etc.
Swelling of the eyelids
Treatment
Treatment of ectropion always depends on its type and severity.
Paralytic
It may go away on its own when the cause that caused it – facial neuritis – is eliminated.
Eversion of the eyelid in a man due to paralysis of the nerve endings on the face
Mechanical ectropion
Treatment begins with the tumor, and then possibly surgery.
Senile and cicatricial ectropions
It can only be cured with surgery (blepharoplasty). The important point here is to restore the natural contact of the eyelid with the surface of the eyeball.
Pronounced eversion of the eyelid (ectropion) in an elderly patient before blepharoplasty
With a timely, adequate course of treatment, in most cases it is possible to prevent negative consequences for the eyes. In particularly severe cases, eyelid inversion after blepharoplasty cannot be completely eliminated.
ABSCESS OF THE CENTURY.
It develops most often after infected eyelid injuries or local purulent inflammations (stye, boil, ulcerative blepharitis). Inflammation can occur metastatically with septic foci in other organs. The abscess develops acutely with increasing diffuse compaction of the subcutaneous tissue of the eyelid. The eyelid is swollen, the skin is tense, hyperemic, hot to the touch. Palpation is sharply painful. In the stage of necrosis, fluctuation joins the melting of tissues; in this place, yellowish pus can be visible through the skin.
Emergency first aid.
- Prescribe 1 g of sulfadimethoxine, sulfapyridazine a or another sulfonamide drug orally.
- An intramuscular injection of 500,000 units of benzylpenicillin or a single dose of another antibiotic is performed.
- The patient is immediately sent for inpatient treatment to the eye department of the hospital, where the abscess must be opened.
Treatment.
- At the beginning of the disease, in the infiltrate stage, dry heat and ultra-high-frequency therapy are prescribed.
- A 30% sodium sulfacyl at least 5-6 times a day.
- It is necessary to prescribe sulfonamide drugs orally and intramuscular antibiotics.
- When fluctuations occur, the doctor or paramedic opens the abscess, drains the cavity, applies bandages with hypertonic sodium chloride solution , and rinses the cavity with antibiotics.
Lumps on the eyelid and their causes
Often, lumps and swellings of varying sizes are found that do not hurt, but bother the person. Usually these are harmless formations:
- Xanthelasma. Has a yellowish tint and may appear on the eyelids or other areas of the face. A common occurrence for women with diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and other disorders. The bumps almost always appear in large numbers, the main reason being a violation of lipid metabolism, which becomes the cause of the underlying disease.
- Milia are small, harmless formations. This is more of a cosmetic problem, and their removal should be done by a specialist. If you try to eliminate the bumps yourself, you can get an infection with the most dire consequences. Proper nutrition, pore-opening cosmetic procedures and masks will help prevent the appearance of such seals.
- Papillomas that appear as a result of the corresponding virus. They can appear on the inside or outside of the eyelid. The growth is not painful and resembles a wart in appearance. It causes concern due to its unaesthetic quality and can only be eliminated by highly specialized specialists through drug treatment or coagulation.
Complications
You should not be afraid of surgical intervention to eliminate eyelid inversion. For an experienced surgeon, the procedure is not particularly difficult. The correction takes place quickly and if the patient follows all the recommendations of the recovery period, then the risk of complications is minimal.
But attempts to get rid of the disease on your own are fraught with serious consequences. Firstly, you are unlikely to achieve a positive result. Secondly, such actions can cause serious harm to the health of the organ of vision. Return to contents
BLEPHARITIS.
This inflammation of the eyelid margins is one of the most common and extremely persistent eye diseases, which can continue for many years in the form of a scaly simple and ulcerative form.
This persistent course is associated with a variety of causes that cause it. These may be diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, gastric ulcer, pathology of the biliary tract), endocrine and metabolic disorders (diabetes, etc.), allergies, helminthic infestation, vitamin deficiency. Blepharitis is supported by pathological processes in the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis), dental caries, uncorrected refractive errors (astigmatism, farsightedness), and staying in a polluted, dusty room.
Scaly blepharitis may manifest as moderate redness of the eyelid margins. Patients complain of itching, a feeling of blockage in the eyes, rapid blinking with the appearance of an acrid foamy discharge in the corners of the palpebral fissure, eye fatigue during visual stress, especially in the evening under artificial lighting. With a pronounced clinical picture, the edges of the eyelids look constantly red and thickened. The skin at the roots of the eyelashes is covered with small dry or grayish-white pityriasis scales, reminiscent of dandruff on the head. If these scales are removed, sharply hyperemic, thinned skin is exposed underneath. Patients complain of constant painful itching in the eyelids, sensitivity of the eyes to dust and artificial light. Patients find it difficult to read, especially in the evenings.
Ulcerative blepharitis is the most severe, persistent form. Purulent crusts accumulate at the edges of the eyelids, the eyelashes are glued together, after the crusts fall off, bleeding ulcers remain along the edges of the eyelids, and the eyelashes fall out. At the edges of the eyelids, areas appear where eyelashes grow incorrectly (towards the eyeball, in tufts) - trichiasis or do not grow at all - medarosis. After the ulcers heal, scars remain, the edges of the eyelids become deformed, and inversion or inversion of the eyelid may develop.
Treatment.
Blepharitis therapy requires persistence and thoroughness in performing all procedures.
- First of all, it is necessary to identify the cause of the disease and eliminate it. Diabetes, helminthic infestation, diseases of the stomach and intestines should be excluded, refraction should be checked and, if necessary, glasses should be prescribed.
- Of great importance are general strengthening treatment, as well as measures that increase the body's resistance: normalization of the gastrointestinal tract, deworming, treatment of chronic infections, tonsillitis, rhinitis, sanitation of the oral cavity, desensitizing treatment and a number of other measures.
- It is mandatory to maintain hygienic conditions at home and at work, and a balanced diet using a diet rich in vitamins.
- When treating ulcerative blepharitis, first carefully remove all crusts. To soften them, the edges of the eyelids are lubricated with fish oil, petroleum jelly or any sulfonamide ointment.
- For the first 2-3 days, ulceration sites are extinguished with alcohol, a 1% alcohol solution of brilliant green , or a 5% solution of silver nitrate.
- The phenomena of inflammation are quickly relieved by applying cotton strips to the edges of the eyelids, moistened with solutions of one of the antibiotics, for example penicillin, erythromycin or neomycin (100,000 - 250,000 units in 1 ml of solution). Tampons are applied for 10-15 minutes up to 4 times a day.
- At night, the edges of the eyelids are lubricated with one of the ointments listed above. Some people may have increased sensitivity to antibiotics. In these cases, ointments made from sulfonamide drugs . If purulent crusts no longer form, it can be recommended to lubricate the edges of the eyelids with corticosteroid ointments (0.5-1% hydrocortisone ointment).
- If the disease persists, vitamins are prescribed ( ingestion of yeast drinks, vitamin tablets, injections of vitamins B1, B6, etc.).
- Autohemotherapy is carried out (prescribed and controlled by a doctor) in the form of intramuscular injections of autologous blood.
Prevention.
Due to the variety of causes causing blepharitis, careful sanitation of the entire body and elimination of etiological factors are necessary: timely detection and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, metabolic diseases, checking refraction and prescribing corrective glasses, sanitation of the oral cavity and other foci of chronic infection, general health and hygienic measures (eye protection when working in a dusty room, eyelid skin care, etc.).
It should be noted that it is more difficult to treat scaly and especially ulcerative blepharitis. Therefore, when signs of scaly blepharitis appear, the patient must be carefully examined and given a full course of treatment in order to prevent transition to its more severe clinical forms.
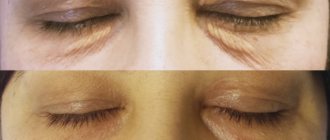
Ptosis of the upper eyelid after Botox and its treatment
Ptosis of the upper eyelid after Botox
Ptosis of the upper eyelid is one of the complications after the Botox injection procedure by unqualified specialists. Botox is a very popular product in cosmetology. This is a drug botulinum toxin (purified protein of natural origin), which is used to block the transmission of nerve impulses in the muscles, which allows you to remove facial wrinkles.
Injecting too much Botox causes it to penetrate into the upper eyelid, causing drooping (ptosis)
Ptosis can also develop due to the fault of the patient himself, who did not follow all the doctor’s instructions: after the injections, you need to be in an upright position for several hours, you should not lift heavy objects or bend over.
Symptoms:
- Drooping of one or both eyelids
- The head is thrown back
- Sleepy face
- Rapid eye fatigue
- Double vision
- The eyelids close completely only with additional force.
- Severe eye irritation that can lead to infection
Treatment
Typically, eyelid ptosis that occurs after using Botox goes away on its own within a month. For faster elimination of the drug, additional treatment can be carried out:
- Conservative treatment, the goal of which is to restore the functions of the damaged nerve. This includes: facial massage; UHF therapy; patch; galvanotherapy and electrophoresis.
- Surgical treatment is used if eyelid ptosis becomes severe. The operation takes about 50 minutes and leaves no scars on the skin. Analgesics are usually not used because the wound does not cause severe pain. After the operation, a sterile dressing is applied to it for several hours.
There are the following types of operations:
- The Eversbush operation is the most common type, involving the formation of a fold on the tendon.
- The Hess operation is used in cases of paralysis of the levator and superior rectus muscles. Hemming is carried out by transferring the levator function to the frontalis muscle.
- Mote. This technique is considered the most complex operation, which not every cosmetology clinic will undertake. It consists of activating the functions of the levator with the help of the non-paralyzed upper muscle.
To avoid all the unpleasant moments after using Botox injections, it must be carried out only under the supervision of highly qualified specialists and in trusted clinics. Treatment of pathology should begin at the earliest stages of its development in order to avoid serious complications in the future.
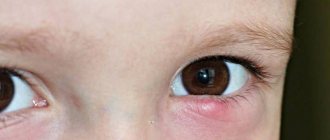
OUTSIDE BARLEY.
This is an acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle or sebaceous gland at the root of the eyelash. The disease is most often caused by staphylococci.
Redness with painful swelling appears in a limited area near the edge of the eyelid. The inflammatory infiltrate increases quite quickly, accompanied by swelling of the eyelid, and sometimes of the conjunctiva of the eyeball. On the 2-3rd day, the infiltrate purulently melts, the tip of the swelling becomes yellowish. On the 3-4th day, the head of the barley breaks out with the release of pus and necrotic tissue, after which the pain immediately decreases, the inflammatory phenomena subside. Swelling and hyperemia of the skin disappear approximately by the end of the week. Sometimes barley is accompanied by headache, increased body temperature, and swelling of regional lymph nodes.
INNER BARLEY.
It occurs with purulent inflammation of the glands of the cartilage of the eyelid, so the inflammation is more pronounced on the side of the conjunctiva, and the contents of the stye break out there. Barley is dangerous due to its complications that arise from improper patient care and treatment. It is unacceptable to try to squeeze out pus from an abscessed stye. This can lead to the spread of a purulent process through the vessels into the depths of the tissues of the orbit and cause such life-threatening complications as orbital phlegmon, thrombophlebitis, cavernous sinus thrombosis, and purulent meningitis.
No immediate first aid is required.
Treatment.
- At the beginning of inflammation, the skin of the eyelid is lubricated with antiseptic solutions and ointments (70% alcohol, 1% yellow mercury ointment, 1% brilliant green solution).
- are prescribed . You cannot apply compresses or lotions, as they cause swelling of the eyelids and lead to the spread of inflammation.
- 15-30% solutions of sodium sulfacyl are instilled into the eye 6-8 times a day.
- With an increase in temperature, severe swelling of the eyelids, enlargement of regional lymph nodes, as well as persistent styes, antibiotics and sulfa drugs should be prescribed orally.
- If the stye begins to abscess, that is, a purulent core appears, thermal procedures are canceled. In the event of a recurrent course of barley, the patient’s blood must be examined for sterility , for the sugar content in it, and an examination must be carried out to identify foci of chronic infection.
- For recurrent barley, general strengthening treatment is carried out (prescription of brewer's yeast, injections and pills of vitamins B, C, autohemotherapy).
Prevention of styes includes sanitation of foci of chronic infection (oral cavity, paranasal sinuses, etc.), eye protection when working in a dusty room and general health measures (food rich in vitamins, hardening of the body).
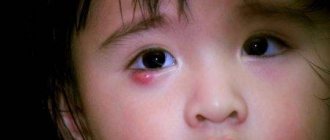
CHALAZION OR HAILDOWN.
This is a chronic proliferative inflammation of the glands of the cartilage of the eyelid. This process is almost painless. A compaction appears in the thickness of the cartilage of the eyelid, which increases in size to a large pea. A local bulge of the eyelid is visible, the color of the skin above it is not changed, the skin is mobile. From the side of the conjunctiva, the whitish-yellow contents of the chalazion are visible.
Treatment.
- For small-sized and short-lived chalazions, you can use drugs that have a resolving effect (1% yellow mercury ointment topically). Thermal procedures are contraindicated; they can stimulate the growth of chalazion.
- For large or long-standing chalazions, the patient is referred to an ophthalmologist for surgical excision on an outpatient basis. The chalazion is removed from the conjunctiva.
- Care for patients in the postoperative period includes washing the conjunctival cavity with a solution of furatsilin 1:5000, installation of 15-30% solutions of sulfacyl sodium.
Help at home
When a stye or boil appears, the doctor prescribes antimicrobial drops and ointments. To relieve inflammation and prevent possible consequences of complications, medicinal formulations are used.
After some time, the abscess opens and its contents come out. If this does not happen, it is possible to open the growth in a day hospital. In difficult cases, tableted antibacterial drugs are used.
It is strictly forbidden to open a boil or stye yourself, or pierce it with a needle or pin at home.
Inflammation of the eyes is relieved with drops; as mentioned above, if the disease is viral in nature, antiviral drugs are prescribed. In cases where the disease is complicated by a bacterial infection, the doctor prescribes medications that fight germs and bacteria.
If there is a skull injury, the eye hurts under the upper eyelid, it hurts to blink - it is important to consult an ophthalmologist
Features of therapy
The treatment method for ectropion is determined by the stage and form of development of the pathology.
Conservative treatment
For mild cases of the disease, it is enough to use warm compresses and antibacterial ointments. To reduce the risk of infection of the inverted eyelid, it can be glued in a physiological state using a patch. However, this is only a temporary measure, which is often prescribed in preparation for surgery.
If the eyelids do not close completely, it is recommended to moisturize the eyes with drops every evening. Ophthalmologists also advise covering the sore eye with a bandage at home and wearing glasses during the day. In case of infection of the eye, it is necessary to carry out a timely course of antibiotic therapy.
Surgical therapy
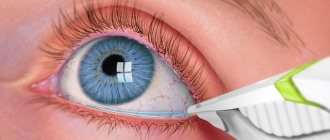
In severe cases, surgical treatment – blepharoplasty – is indicated. Depending on the form of the disease and the severity of symptoms, the surgical procedure is determined:
- Kunta-Szymanowski technique. It involves cutting out a triangular conjunctival-cartilaginous plate from the eyelid; a similar piece of skin is excised at the lateral canthus. The listed fabrics are tightened and stitched;
- Blaškowicz method. Surgery involves shortening the muscle and removing the cartilage of the upper eyelid;
- Imre's method. The physiological shape and mobility of the eyelid is restored with a small piece of skin from the infraorbital area;
- Filatov's method. The defect is restored by transplanting a piece of tissue from the abdominal area.
Adequate and timely treatment in most cases helps prevent the development of negative consequences for the eyes.
Blepharoplasty only in severe cases does not completely eliminate ectropion, which leads to a change in the anatomical shape of the eye shape.
If the doctor made mistakes during the operation, the following complications may develop:
- scar development;
- bleeding;
- infection of postoperative sutures;
- development of hematomas;
- seam divergence;
- dysfunction of the lacrimal glands;
- itching at the surgical incision site;
- development of the “hot eyes” effect.
Features of the rehabilitation period
After blepharoplasty, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- instill moisturizers and antiseptics;
- wear special sunglasses;
- use sunscreen cosmetics;
- regularly perform gymnastics for the eye muscles;
- stop using contact lenses;
- visiting a sauna, solarium, bathhouse is contraindicated;
- It is forbidden to sleep on a high pillow;
- exclude alcohol, coffee and smoking;
- limit physical activity.
The above recommendations should be followed for 2 months.
Molluscus contagiosum.
This disease is transmitted by contact, therefore a child in a children's group who is diagnosed with molluscum contagiosum is subject to quarantine until cured.
The disease is characterized by the appearance of yellowish-white nodules up to 2 mm in size with an oval edge and a small depression in the center. They are most often located in the area of the inner corner of the lower eyelid, closer to the eyelash edge, and sometimes several nodules form right on the edge of the eyelid. When the process is localized at the edge of the eyelids, maceration of the nodules occurs and a pasty mass is released into the conjunctival cavity. In such cases, the connective membrane becomes irritated and conjunctivitis occurs. There is reason to consider molluscum contagiosum a viral disease, but the causative agent has not yet been identified.
Treatment includes the following activities:
- squeezing out the contents of the nodule followed by cauterization with a 1% alcohol solution of brilliant green, Lugol's solution, 5% silver nitrate solution, 5% tincture of iodine, lapis pencil , etc. The manipulation is carried out on an outpatient basis.
EVERION OF THE EYELIDS.
Occurs with paralysis of the facial nerve, after injuries, burns of the eyelids, leading to scar deformation, against the background of chronic blepharitis, conjunctivitis, as well as in the elderly. The eyelid hangs down, moves away from the eyeball, and its conjunctiva is exposed. Eversion of the eyelid can lead to lacrimation, hypertrophy of the conjunctiva of the eyelids, and the eyeball.
Treatment of inversion is surgical.
Care for patients with ectropion includes:
- Treatment of the conjunctival sac (instillation of antiseptic solutions), application of vitamin ointments at night.
- Older adults should be taught how to properly wipe away tears during initial eversion. You cannot wipe the tear from the eye down (this stretches the eyelid even more), you need to slightly blot the lower eyelid with a handkerchief or cotton wool, pressing it to the eye.
Symptoms
Eversion of the eyelid is almost impossible to confuse with another disease. Usually the patient himself notes that the skin lags behind the eyeball. In addition to external manifestations, the anomaly is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of a “pocket” between the eyeball and the edge of the eyelid. The inner surface of the mucosa becomes visible from the outside. It is a thin edging of bright red color;
- It is impossible to completely close the palpebral fissure. The deviation causes discomfort when blinking;
- Increased and uncontrollable lacrimation. The reason lies in the loss of contact between the eyelid and the eyeball. As a result, the tear stream is not able to penetrate the lacrimal punctum. As a result, liquid accumulates in the area between the eyelid and the eye, pouring out;
- Irritation of the skin of the affected eyelid. It is caused by continuous lacrimation and mechanical irritation of the conjunctiva. The complication is associated with regular wiping of accumulated fluid and swelling of the eyelid;
- Feeling of a foreign object or sand in the eye. The lower eyelid does not cover the cornea during blinking, which causes it to dry out;
- Redness of the organ of vision due to inflammation of the conjunctiva. When ectropion develops, the mucous membrane becomes open and the natural process of self-cleaning of the eyes fails. As a result, the conjunctiva dries out and begins to thicken.
Return to contents
Features of the eversion of the upper eyelid
It is less prone to developing ectropion because it has thick cartilage that provides excellent protection against deformation. If an inversion of the upper eyelid occurs, the ciliary edge changes. This anomaly is usually diagnosed in elderly patients, as the eye muscles weaken.
| The person experiences discomfort. It seems to him that sand or a foreign object has gotten into his eye. The organ of vision becomes red and irritated, the eyelid swells, and there is constant and severe lacrimation. |
When the upper eyelid is everted, the sharpness of the eyes decreases, objects become blurred. If the pathology progresses, then keratitis (inflammation) appears, which can provoke clouding of the cornea.
Features of lower eyelid inversion
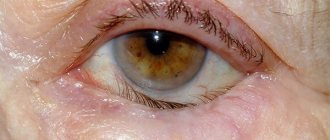
Ophthalmologists use the concept of “ectropion” exclusively to define pathology affecting the lower eyelid. Due to its anatomical structure, it is this element of the organ of vision that is most often affected by illness.
Eversion of the lower eyelid comes in two forms:
- Easy. The defect is insignificant, the lag from the eye is minimal. Approximately 1/6 of the entire eyelid is damaged;
- Heavy. Ectropion is visible to the naked eye. The mucous membrane of the visual apparatus is turned outward. In some cases, the defect extends to the entire eyelid.
| In severe forms of the disease, doctors usually diagnose “spastic eversion.” The anomaly is accompanied by inflammation of the conjunctiva and a decrease in visual acuity. |
Causes
Swelling of the upper eyelid often occurs due to inflammatory processes occurring in the body. Blepharitis, being one of the causes of this manifestation, represents a group of different eye pathologies. They are united by chronic inflammation of the eyelids. In addition to this significant reason, other frequently occurring factors should be noted:
- Allergy. Plant pollen often provokes such a manifestation as a drooping eyelid. This reaction is often caused by animal hair, low-quality cosmetics and certain products. A drooping eyelid is accompanied by symptoms of eye redness and runny nose.
- Infections. Common representatives of this category are stye and, of course, conjunctivitis. Infection occurs due to the introduction of bacteria, fungi or viruses into the eyes or under the protective folds. Pathologies are accompanied by redness of the eyes. Pain and itching appear. The eyes begin to water, and a mucous or purulent discharge appears. Photophobia occurs. A pimple that appears (a subcutaneous lump when palpated) above the eyelid contributes to the appearance of swelling.
- Excessive load on the organs of vision combined with lack of sleep. Insufficient rest and fatigue lead to redness and swelling.
- Drink a large amount of liquid at night. The morning, due to the habit of eating watermelon or drinking a few cups of tea before bed, begins with the fear of looking in the mirror. It is impossible to see oneself through the slits left by the cut of the eyes.
- Excessive love for salty foods retains fluid in the body. In the morning, the upper eyelids, and often the face, become swollen. If the person is elderly, then the problem becomes very pressing.
- Swelling occurs in lovers of beer and other “hot” drinks.
- Injury. A blow to the eye area or a bruise leads to an unnatural color of the eyelid, swelling and pain.
- Pathologies of internal organs. These are diseases of the heart, kidneys or gall bladder. This also includes endocrine syndrome (long-term existence of hormonal imbalances).
- An insect bite is one of the causes of swelling of the upper eyelid of one eye. The “predator” can be a midge or a mosquito. When bitten, an allergic reaction occurs.
- Foreign body getting into the eye. An eyelash trapped under the eyelid can lead to inflammation, causing injury to the inner surface of the protective fold of the eye. To remove it, you can try to blink frequently or perform a simple exercise - roll your eyes. You need to understand that these actions are possible in the absence of severe pain. A newborn baby reacts especially acutely to the ingress of a foreign body.
- Eyelash extensions, permanent makeup, otherwise called tattooing, or subcutaneous use of Dysport and Botox to eliminate expression lines can also be a factor that causes swelling of the upper eyelid. If used incorrectly, a seizure may occur.
Don't indulge in alcoholic beverages. This can lead to swelling of the eyelids.
What to do if the upper eyelid is swollen can be decided after identifying the main factor. It needs to be removed, but only the examination performed can indicate the possibility of using certain treatment methods. It must be taken into account that swelling can also be caused by inflammation of the bone tissue in the eye area.
TURN OF THE CENTURY. (usually the lower one).
This is a condition in which the anterior ciliary margin of the eyelid turns toward the eyeball. At the same time, the eyelashes, like a brush, rub the cornea, causing damage and even ulceration. Entropion of the eyelid occurs in newborns, the elderly and people suffering from inflammatory diseases of the eye and its auxiliary apparatus.
Treatment for entropion consists of identifying and eliminating its cause. In severe cases, volvulus is eliminated promptly. In mild cases and before surgery, the eyelid is pulled back with a strip of adhesive tape.
Care for patients with entropion consists of:
- In the toilet of the conjunctival sac (installation of antiseptic solutions), prevention of the affected cornea (laying in antiseptic and vitamin ointments), as well as in caring for the skin of the eyelid and cheek (if it is irritated with adhesive tape).
- It is necessary to apply the adhesive plaster correctly to retract the lower eyelid. Since during a spastic inversion, the skin of the lower eyelid is abundantly wetted with tears, when trying to pull the eyelid back, the finger slides over the skin and the inversion cannot be eliminated - the adhesive plaster will not stick to the skin and will not hold the eyelid. Therefore, before retracting the eyelid, you need to thoroughly dry the skin with a gauze pad.
- Sometimes the spasm of the eyelid muscles is so strong that it is possible to put the rolled eyelid in the correct position only when one or two layers of gauze are placed under the finger used to pull the eyelid down to prevent the finger from slipping.
- In case of mild inversion, it is enough to lubricate the skin of the lower eyelid with collodion. With severe inversion, this does not help and, in order to keep the lower eyelid in the correct position, you have to pull it down with one or two strips of adhesive tape.
How to perform the procedure
To examine the conjunctiva of the lower eyelids, the doctor pulls them down. He examines the structures and compares the mucous membrane of each eye. The upper eyelid can be turned out with the fingers of both hands. For this, glass rods or an eyelid lifter are used. Such devices make inspection easier.
During the procedure, the patient must look down. After this, he lifts the eyelid with his left thumb and pulls it forward a little. The doctor grabs the ciliary edge of the eyelid with the thumb and index finger of his right hand to pull it down and forward relative to the organ of vision. Removing his left hand, he pushes the eyelid down and forward.
The left thumb creates a skin fold. The doctor presses it on the upper cartilaginous edge of the eyelid, and with his right hand lifts the lower edge of the eyelid upward. After this, the left thumb holds the eyelid motionless.
To better examine the upper transitional fold, the doctor applies pressure to the eye through the lower eyelid. For this purpose, it is recommended to use an eyelid lifter. Its edge is placed on the skin of the eyelid slightly pulled down at the upper cartilaginous edge. The handle of the device is lowered down. The doctor supports and pulls back the ciliary edge of the eyelid with the other hand. After this, he turns the handle of the eyelid lifter upward and everts the conjunctival side of the eyelid.
Inversion of the eyelid step by step
LAGOPHTHALMOS.
Lagophthalmos - incomplete closure of the eyelids (the so-called hare's eye) - occurs with paralysis of the facial nerve. It is also observed with congenital shortening of the eyelids and scars of the eyelids after traumatic injuries. With this disease, the palpebral fissure on the affected side is always wider, the lower eyelid is atonic, does not adhere to the eyeball, and lacrimation is noted.
When trying to close the eyelids, the palpebral fissure remains open. The eye is open during sleep. Due to non-closure of the palpebral fissure, the eyeball becomes dry, constantly irritated, and the phenomena of conjunctivitis and inflammation of the cornea occur.
Treatment.
Facial nerve paralysis is usually treated by neurologists; in severe cases, ophthalmic surgery is indicated.
Caring for patients with lagophthalmos involves protecting the eye from excessive drying and infection. To do this, a 30% sodium sulfacyl solution, sterile petroleum jelly or ointments containing sulfonamide drugs or antibiotics are instilled into the conjunctival sac several times a day.
Main types of treatment
Surgical method
Surgical method for treating ptosis
The most common type of treatment for this pathology is blepharoplasty. This surgical method for correcting ptosis of the upper eyelid is a plastic surgery consisting of the following stages:
- Complete examination of the patient and identification of contraindications.
- Application of local anesthesia to the tissue of the upper eyelid. General anesthesia may be used (optional).
- An incision is made along the skin fold to remove excess fat tissue.
This method gives the most reliable and noticeable effect, which is why it is most often recommended by specialists. The following complications may occur after blepharoplasty: conjunctivitis, fear of light, tearing, eyelid asymmetry (goes away after complete recovery) and eyelid inversion (extremely rare).
It is important to remember that the pathology itself will not disappear; on the contrary, it will only worsen over time. Attention! The surgical method of treating ptosis of the upper eyelid is contraindicated in children under 3 years of age, since their eyelid and palpebral fissure are at the stage of formation.
Conservative treatment methods
- Local UHF therapy
- The use of drugs that provide adequate nutrition to damaged tissue
- Galvanotherapy
- Massage
- Special gymnastics
Home treatment
Home treatment for ptosis
In this case, you must remember that the effect of self-treatment will be less noticeable than after salon procedures. However, this method is safer and has fewer side effects. There are several home treatment options .
Folk remedies:
- Rubbing with ice cubes from a decoction of medicinal herbs 2 times a day
- Compresses with infusions of chamomile, birch, parsley and potatoes
- Firming masks made from eggs, potatoes and cottage cheese
Massage:
- Wash your hands and remove makeup from your eyes
- Apply oil to eyelids
- Easy to stroke your eyelids along the massage lines
- Lightly tap your eyelids
- Press on the eyelids (do not touch the eyeball)
- Apply a compress to your eyelids
Gymnastics helps to quickly tighten muscles:
- Fix your gaze straight ahead, slowly move your gaze to the left - up - right - down. Do the exercise 5 times.
- Close your eyelids for 3 seconds, then open your eyes very wide (5 times).
- Look up at the ceiling, open your mouth and blink.
- Open your eyes, place your fingertips on your temples (slightly pulling the skin), quickly close and open your eyes.
- Close your eyelids, holding the skin on the outside of your eyes with your fingers, and lift your upper eyelids as high as possible, overcoming the pressure.
- With your head tilted back, lower your eyelids down.
Home exercises do not provide such complete treatment as a specialist, but they allow you to restore clarity and beauty to your eyes.
What to do for pain in the eyelids
At the first signs of pain in the upper eyelid, you should contact a doctor as soon as possible, especially if the pain is accompanied by swelling or purulent discharge, or elevated body temperature. If there is no purulent discharge, or there is a feeling as if something has got into the eye, you can try to remove the symptoms yourself. If your child’s eye hurts, do not delay seeing a doctor. The first thing to do if you have eye pain:
- Prepare a cold compress from strong tea leaves; medicinal herbs are suitable instead of tea. The preparation process consists of preparing a tea or herbal decoction, then moisten it with a cotton swab, squeeze it out and apply it to the problem eye.
- It is possible to take antihistamines if, in addition to pain, itching or swelling is present. The best anti-allergy drugs: Tavegil, Suprastin.
- Eye drops. For mild inflammation, you can use eye drops that contain antibiotics, the best drugs: Albucid (Sodium Sulfacyl), Levomycetin, Ciprofloxacin. It is prohibited to abuse these drugs; according to the rules, these drugs cannot be used without the instructions of a doctor.
- Reduce the load on the inflamed eye, try to move it and blink as little as possible.
The above tips will not cure the disease, but will only temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition. Therefore, if the pain does not go away the next day, you need to contact an ophthalmologist who can determine the cause of the problem, prescribe effective medications, give useful advice and monitor the treatment process.
PTOSIS.
Ptosis is drooping of the upper eyelid. This disease can be congenital or acquired (after injury, with damage to the oculomotor nerve).
Ptosis can be unilateral or bilateral. Depending on how much the eyelid covers the pupil, ptosis can be complete or partial. The danger of complete congenital ptosis is that the eyelid does not allow light to pass through the pupil to the retina, and vision is reduced (amblyopia).
Treatment.
Ptosis is eliminated surgically. For children with congenital ptosis, surgery is performed at the age of 2-3 years. Care for children with congenital complete ptosis involves suspending the upper eyelid with strips of adhesive tape to the skin of the forehead. This procedure is prescribed while the child is awake to prevent amblyopia.
Diagnosis of ptosis
Diagnosis of ptosis by a specialist
Before treating ptosis of the upper eyelid, a diagnosis is required to identify the causes of its occurrence and determine the method of treatment:
- Consultation with the patient to determine heredity and the presence of possible diseases.
- Ophthalmological examination to determine visual acuity and intraocular pressure levels.
- If there is a suspicion of brain disease, MRI and CT are used.