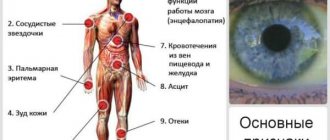
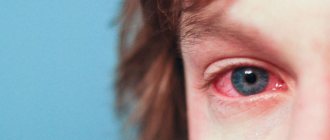
Causes of the unpleasant syndrome
Discharge from the eye becomes a protective reaction of the body to the effects of aggressive environmental factors. It could be an infection, an allergen, or mechanical damage. In most cases, they suggest that a person, and in particular his organs of vision, are affected by one or another ailment.
What diseases can discharge from the eye indicate:
- conjunctivitis (allergic, bacterial or viral);
- dacryocystitis;
- trachoma;
- blepharitis;
- keratitis.
Discharge is also possible when an infection penetrates into the organ of vision, weakened by surgery, during the rehabilitation period. Uncomfortable or dirty lenses can also cause an unpleasant symptom. Discharge from the eyes of a person can appear when exposed to chemicals and ultraviolet radiation, as a result of long work at the monitor due to dryness and fatigue of the visual organs.
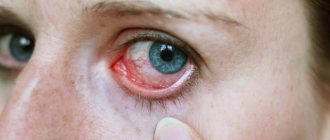
Inflammation of the conjunctiva most often causes a similar symptom. The cause may be infection of the organs of vision with pathological bacteria and viruses or a reaction to an allergic irritant. This disease can lead to serious consequences in the form of endophthalmitis or corneal ulcers. Inflammation of the lacrimal sac or dacryocystitis is caused by dysfunction of the nasolacrimal ducts, which provokes congestion in the eye. Trachoma, that is, a chronic inflammatory process in the conjunctiva and cornea, is caused by chlamydial infection. With keratitis, the cornea becomes inflamed for infectious reasons.
Blepharitis, manifested by inflammation of the ciliary edge of the eyelids, may have several causes:
- excessively oily skin;
- low-quality cosmetics;
- reaction to demodex dust mites;
- infections of neighboring organs or brought from contaminated objects.
Discharge from the eye is usually accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms:
- cloudiness, burning and itching in the organs of vision
- painful sensation and increased lacrimation;
- redness, swelling, photosensitivity.
With bacterial or viral lesions, cough, runny nose, aching sensations in the joints, and fever are also possible.
Discharge from the eyes accompanying a certain disease can lead to serious complications, including loss of vision. And if they do not go away quickly or are accompanied by severe itching and pain, you should definitely consult an ophthalmologist.
In newborns
The appearance of discharge from the eyes of a newborn is a common occurrence. In the first weeks after birth, the mother may notice yellow or white crusts in the corners of the baby’s eyes, which come off easily and do not cause much discomfort. Their appearance in newborns is an absolutely normal phenomenon, which is caused by the adaptation of the child’s body to the influence of the external environment.
In the womb, the baby's eyes are protected from exposure to UV radiation, dust, bacteria and infections. After birth, they immediately encounter all the negative factors, and therefore their body as a newborn child begins to turn on protective functions. But until he “understands” how to properly resist external factors, several weeks will pass. As soon as the body adapts, the crusts that accumulate in the corners of the eyes will disappear.
However, there are cases when babies accumulate pus in the corners of their eyes for a very long time. And if we talk about why this happens, then we should immediately talk about such a pathological condition as dacryocystitis. It is characterized by inflammation of the lacrimal ducts and develops against the background of the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the lacrimal organs.
With the development of dacryocystitis, a newborn child produces abundant pus from the eyes, the eyelashes become sticky and stick together. To combat this problem, many mothers on the forums advise washing their eyes with various aseptic solutions, but this cannot be done without a doctor’s recommendation. The point is that simple washings will help here.
To treat dacryocystitis, probing is used, followed by washing the lacrimal canals. If this procedure does not produce positive results, which also happens quite often, surgical treatment is resorted to.
However, speaking about why pus can be discharged from the eyes of children, one cannot help but say that children, just like adults, are susceptible to the diseases described above. Therefore, in order to prevent vision problems and other complications from occurring, the child must be shown to the doctor immediately after his eye has become infected.
Diagnosis of the disease that caused the discharge
Depending on the cause of the inflammatory process, discharge from the eyes may have different structures and shades.
Based on their appearance, it can be assumed that ailments should be treated. However, the diagnosis must still be made by a doctor, based on examination of the contents and other tests. What do different discharges from the eyes indicate:
| Structure and shade | Why do they arise? | Additional symptoms | Possible disease |
| Purulent - thick, viscous, yellow-gray, greenish or brownish in color. | Due to the accumulation of leukocytes as a reaction of the body to the activity of pathogenic bacteria. | They form hard crusts that make it difficult to open your eyes in the morning, or a film on the front of the eyeball. | Bacterial conjunctivitis, ocular herpes, trachoma, fungal keratitis. |
| Foamy structure, yellowish or green with the formation of crusts and scales. | The reasons are different: from a reaction to dust mites to infection with pathological microorganisms. | Swelling and itching of the eyelids appear, discharge usually occurs in the morning. | Blepharitis. |
| Mucous white | Due to exposure to viruses. | Redness, increased tearing, first there is discharge from one eye, then the second one joins. | Viral conjunctivitis, colds. |
| Abundant yellow | It is provoked by congestion in the organs of vision. | The component flows out strongly when pressed. | Dacryocystitis. |
| Transparent, liquid | The body's reaction to an irritant from the external environment: pollen, animal hair, etc., as well as severe eye fatigue. | Both eyes are affected at once. They disappear after eliminating the irritating factor. | Allergic conjunctivitis, dry eye syndrome. |
Thread-like discharge most often occurs with filamentous keratitis, rarely with allergic conjunctivitis.
The first disease is a type of chronic inflammation of the cornea that occurs due to dysfunction of the lacrimal glands. Such discharge from the eyes is accompanied by sensitivity to light, burning, and dryness of the nasopharynx. Thread-like keratitis is treated with emollient ointments, drops - analogues of human tears with vitamin and mineral complexes.
Treatment
If you or your child has purulent discharge in the corner of the eye, accompanied by pain, redness of the eyeball, increased tearing, etc., you need to go to an ophthalmologist. Only he will be able to establish the exact reason why pus appears from the eyes.
Self-medication is very dangerous, as it can lead to serious problems, including complete loss of vision. Therefore, if the eye festers and waters, you must immediately go to the doctor. Only correctly selected and timely treatment will quickly get rid of suppuration and prevent the occurrence of complications against it.
What is white discharge in the corners of the eyes?
The consistency and color of discharge from the eyes varies. A more common situation is when a person wakes up in the morning with his eyelids and eyelashes glued together. This occurs due to the discharge drying out overnight. In general, eye discharge is a thick or thin substance, sometimes mixed with mucus or pus. In some cases, discharge is an indicator of some kind of infection that has entered the tear ducts. As a result, the normal secretion of large sebaceous glands is disrupted, as indicated by profuse lacrimation. The discharge may have a different color:
- white;
- green;
- pale yellow.
In the latter case, it often has a mucus-like structure, which indicates a bacterial infection. Not too thick discharge indicates an allergy. They are abundant in orbital cellulite syndrome. The condition is often accompanied by a number of other symptoms, such as:
- sore eyes;
- lacrimation;
- blurred vision;
- burning and itching of the eyelids;
- photosensitivity;
- cough, fever, nasal congestion.
What to do if there is discharge from the eyes
The best thing to do if you find yourself in the situation described above is to wash your face with warm boiled water and immediately visit an ophthalmologist. Only a specialist can determine the cause that caused this pathology, and then prescribe adequate treatment.
If you find any kind of discharge from your eyes, you should not tempt fate and wait until the disease becomes chronic. Treating an advanced disease is always more difficult and expensive than acting in hot pursuit. It is urgent to see an ophthalmologist so that the doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
For any vision complaints, you can contact specialized ophthalmological clinics: doctors will quickly conduct a thorough eye examination using modern diagnostic equipment and, based on the results, prescribe the most effective treatment.
Discharge from the eyes is a protective reaction of the body. They differ in color and consistency. They may be a temporary phenomenon, or they may be permanent.
Let's look at the reasons why yellow, white and other discharge appears in the corners of the eyes:
- Diseases of the visual organ of inflammatory and non-inflammatory nature.
- Allergic reactions. Occurs when exposed to an allergen. This could be decorative cosmetics, eye creams, makeup remover. As well as other allergens: food, dust, industrial, etc.
- White discharge in the corners of the eyes in the morning can be caused by excess dust particles. They accumulate and are then released during sleep.
- High load on the visual organ. Symptoms appear as part of dry eye syndrome.
Possible diseases
By the nature of the discharge, one can determine the disease of the visual organ. Periodically appearing white discharge from the eyes in the morning, not accompanied by signs of inflammation, is normal. If they become regular and other complaints appear, then the development of an ophthalmological disease is likely.
- White mucous discharge from the eyes is characteristic of viral diseases (viral conjunctivitis), and is possible after an acute respiratory viral infection. Additionally, redness of the mucous membrane and sclera, lacrimation, photophobia, swelling, as well as signs of a cold (coughing, sneezing, elevated body temperature) are noted. When the virus first affects one visual organ, then the second one joins.
- Another reason is dry eye syndrome. It manifests itself as dryness and fatigue of the visual organ. Occurs after prolonged hard work at the computer or with small objects.
- Liquid transparent. This is a sign of an allergy (allergic conjunctivitis). The defeat is two-sided. Accompanied by severe itching. The eyelids turn red and swell. After eliminating the allergen, the symptoms subside.
- Transparent liquid discharge is possible when dust or foreign bodies enter the discharge. It is a protective reaction of the body. The goal is to remove foreign particles mechanically.
- Yellow abundant. Appear due to inflammation of the lacrimal sac - dacryocystitis. The discharge is copious and thick. It intensifies when massaging the affected area.
- Greenish or yellowish foamy discharge is most often found with blepharitis, an inflammation of the eyelid. Accompanied by itching, peeling, swelling of the eyelids. The discharge from the eyes is sticky, accumulates in the morning, sticks together the eyelashes, and forms dense scales and crusts. Other causes are eye infections, a reaction to a dust mite.
- Thick yellow, green with a gray or brown tint is a sign of inflammation, formed due to the accumulation of leukocytes. Characteristic of bacterial conjunctivitis, viral and fungal infections of the cornea, trachoma, opening of barley. Additionally, there is the formation of dense crusts that are difficult to remove. A film forms on the eye, which interferes with the clarity of vision. There are redness, swelling, lacrimation, and photophobia. In severe cases - pain in the eyeball, headache, increased body temperature.
- Thread-like discharge is characteristic of. This is a disease that occurs when the function of the lacrimal glands is reduced. It manifests itself as dryness, burning, thread-like discharge, redness of the sclera. Leads to dystrophic changes in the cornea.
Why does eye discharge accumulate in the corner? This is due to the anatomical structure of the organ of vision. The corner is somewhat recessed in the orbit relative to other structures. It is convenient for liquids to flow there. The outlet of the nasolacrimal duct is also located there. When it becomes inflamed, pus comes out in the corner.
Additionally, watch a video about discharge that accumulates in the morning. What are they and why are they needed?
Mucus accumulates in the corners of the eyes
So why do you constantly have discharge in the corners of your eyes, and it is always noticeable after waking up?
The thing is that during the day we constantly blink, and this washes away excess tear fluid.
But when we sleep, these secretions accumulate in the form of mucus in the corners of the eyes. Prolonged exposure to air causes these lumps to harden and dry crusts appear in the corners.
It is also worth knowing that there is a proper way to remove this mucus.
Most people use their fingers to pick out the mucus or scrape it with their nails, but this should not be done. First, you could scratch your eye or accidentally introduce bacteria into it, leading to an eye infection. Also, you will be surprised, but this is not the most effective way to remove discharge from the corners of the eyes.
For these purposes, a clean cloth is best suited, blot it in warm water and lightly press it to the corners of the eyes.
to soften the mucus. Once it softens, it is much easier to get rid of it, rinse with clean water or wipe with the same cloth.
A little mucus in the corners of the eyes is normal, but changes in color, consistency and amount of discharge should alert you. Our bodies constantly produce mucus to keep us hydrated, but the immune system can increase mucus in response to irritants to relieve you of what's bothering you.
So, what can mucus in the corners of your eyes tell you?
Drug therapy
Treatment with medications is aimed at removing and washing away germs, bacteria, as well as eliminating the mucous film and allergic reaction. To do this, use solutions, drops or ointments:
- Antibiotics - Levomycetin, Tobrosopt, erythromycin ointment, Fluconazole solution. Indicated for keratitis, blepharitis, conjunctivitis. They quickly penetrate the blood through the eyes. A small amount of the drug should be instilled directly into the area of the tear ducts or applied to cotton pads. They carefully wet each eye separately from the outer edge to the inner. It is imperative to treat both eyes, regardless of the severity of the symptoms of infection.
- Antiviral - Oftalmoferon, Virgan gel. For the treatment of keratitis and conjunctivitis of any etiology. Used in case of eye infection with herpes simplex virus. Povisep is used as a prophylactic agent before and after ophthalmological operations and is prescribed to newborns.
- Antibacterial - Sulfacyl sodium, Albucid, Oftaquix. The products are released in the form of drops. The active substance effectively copes with strains of microorganisms that cause bacterial conjunctivitis with sticky secretions.
- Antimicrobial - Okodek, Okatsin. Drops help with acute and chronic inflammation of the eyes, to prevent infection in adults and blenorrhea in children. The eyeballs may turn red. Drops are used to treat contact lenses.
- Antihistamines - Allergodil, Opatanol, Cromohexal. Relieves symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis in the acute stage. The drops prevent its development during seasonal exacerbations if the allergen is the smell of flowers or pollen.
It is not recommended to take medications on your own, especially for infants. The same applies to traditional methods. The drug, dosage regimen and duration are prescribed by the doctor after making an accurate diagnosis. Uncontrolled treatment reduces the sensitivity of pathogenic microflora, which develops immunity to the components.
Prevention
Prevention is always easier than cure, so let's look at some simple measures that can be taken to prevent discharge from occurring in the first place:
- Protect your eyes. Try to avoid injuring them and getting foreign substances into them as much as possible.
- Treat your body. Even a prolonged cold can provoke discharge, so be sure not to delay treatment of diseases.
- Limit eye strain. To prevent dry eye syndrome from developing, reduce your load.
Timely treatment of eye diseases allows for recovery without negative consequences for vision. The main methods of prevention include adherence to personal hygiene standards, timely treatment of respiratory tract diseases, dental and ENT diseases, anti-epidemic measures, proper rest and working conditions (good lighting, time limit for PC).
Treatment of white discharge in the corners of the eyes
If this unpleasant symptom persists for a long time or appears periodically, then this is a clear sign of infection, and not simple allergies or fatigue. You cannot diagnose yourself. Only a specialist can do this. Self-medication, especially if diagnosed incorrectly, can only worsen the situation. In general, therapy includes the following activities:
- Use of antibiotics. Prescribed in case of eye damage from a bacterial infection. Drugs in this group are prescribed in the form of tablets, eye ointments or drops. Doctors recommend drugs such as Albucid, Ciprofloxacin, Tetracycline and Ophthalmoferon.
- Massage the eyelids and rinse the tear ducts. They are additional procedures. To wash out purulent exudate, use a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Regular tea leaves will also work.
- Taking antihistamines. Prescribed to relieve inflammation due to allergies. These include Lecrolin and Opatanol.
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs of steroidal and non-steroidal nature. They help quickly eliminate inflammation, but have many side effects. Examples are Ibuprofen and Dexamethasone.
- Instillation of drops. In this case, special means are used to relieve tension and fatigue. These include Visin, Levomycetin, Maxitrol, Normax.
- Installations with a solution of dicaine 0.5% or trimecaine 3-5%. Prescribed for meibomitis.
- Surgical intervention. Indicated if there is a foreign object in the eye. Surgery is often performed when eyelashes grow into the eyelid.
Drug treatment
The basis is still medications in the form of tablets, ointments or drops. First of all, ophthalmologists advise removing the exudate itself from the eyelids. To do this, use a weak solution of the antiseptic Furacilin or potassium permanganate. A cotton swab is moistened in it, which is then used to wipe the eyes from the outer corner to the inner. If the discharge is very thick, it is necessary to perform a light massage of the eyelids. Among the medications used to eliminate the problem are:
- Visine. These are vasoconstrictor and decongestant drops based on tetrizoline. The substance is a sympathomimetic that stimulates alpha-adrenergic receptors. The effect of the drops lasts for 4-8 hours. They reduce redness and swelling of the conjunctiva. The advantage of the drug is that it is practically not absorbed into the systemic circulation. Visin is used for hyperemia of the conjunctiva when exposed to bright light, smoke, dust, chlorinated water and for swelling and redness due to seasonal allergies. These drops are contraindicated for angle-closure glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, age under 2 years, arterial hypertension, corneal dystrophy, pheochromocytoma. It is necessary to instill 1-2 drops 2-3 times a day. After the procedure, local reactions are possible: blurred vision, redness, burning and pain in the eyes, dilation of the pupil.
- Normax. The active ingredient of this drug, norfloxacin, is an antibiotic. The medicine is available in the form of drops and tablets. They are indicated for external and internal otitis, conjunctivitis, trachoma, keratitis, corneal ulcer, blepharitis. The dosage is determined by the disease. Contraindications include sensitivity to fluoroquinolones, pregnancy, and breastfeeding. Side effects include allergies, itching, and rash.
- Maxitrol. Contains neomycin and polymyxin, has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. Indications for use are blepharitis, keratitis, iridocyclitis, keratoconjunctivitis. It is necessary to instill 1-2 drops every 4-6 hours. Maxitrol should not be used for shingles, tuberculous or fungal eye infections, chicken pox, or the condition of the cornea after removal of a foreign body. After instillation, itching and swelling of the eyelids are possible.
- Levomycetin. Based on chloramphenicol, available in the form of drops and alcohol solution. Their action is antibacterial, so they are used for bacterial infections, including blepharitis, keratitis, scleritis, and conjunctivitis. One drop should be instilled into each conjunctival sac 3-4 times a day. Side effects and contraindications are numerous, so it is better to study them in detailed instructions.
Folk remedies
A number of folk remedies can be used against the background of drug treatment. Their recipes involve instilling medicinal decoctions into the eyes. They are also consumed orally or used for compresses. The following recipes are effective:
- Take 3 large spoons of chamomile or calendula flowers. Steam them with 200 ml of boiling water. After cooling, strain. Soak cotton pads in the broth and apply them to the eyelids for 15 minutes. Repeat up to 5 times a day.
- Add a couple of drops of fresh St. John's wort juice to the calendula decoction prepared according to the previous recipe. Next, pour the liquid into a container, where you then immerse your face for a few seconds. You can simply wipe your eyes with the same product.
- Mix plantain leaves, sage, hop cones, string and birch buds in proportions 3:3:2:3:2. Next, brew the herb collection with 0.5 liters of boiling water and let it stand for about an hour. Take the decoction orally, 100 ml 3 times throughout the day.
- Take a couple of elderberries and brew them like regular tea. Use the cooled rinse or lotion. It eliminates itching and inflammation well.
Causes of mucus from the eyes
1. Mucus with a crust
Dried mucus is a common occurrence in the morning, but if you feel more crusty than usual and feel irritated, blepharitis
- inflammation of the eyelid.
It could also be a manifestation of a common allergy
. During allergy season, the eyes begin to water more, the discharge hardens, and a crust forms.
Another reason could be dry eyes.
, due to which the tear film thickens and a crust appears on the eyelids.
2. Color of mucus from eyes
Yellow, green, or white discharge indicates an infection such as conjunctivitis
, especially if your eyes are itchy or red.
There are two types of conjunctivitis: bacterial and viral, and both are contagious. A viral infection spreads especially easily even after a normal handshake.
With a viral infection, one eye first becomes red, and after a day or two the irritation spreads to the other eye. Bacterial conjunctivitis usually appears in one eye.
Barley
, which appears due to infection of the eyelash follicles, also leads to yellow discharge and discomfort.
3. Eyes become watery
Watery eyes are most often caused by allergies.
, or is it a reaction to cold weather.
However, watery eyes can be a sign of dry eye
.
As surprising as it may sound, if you have dry eyes, your eyes may become watery because your eyes don't produce enough tears to moisturize. The eyes become irritated and the lacrimal gland begins to produce tears in large quantities.
4. Mucus is thick and sticky
A blocked tear duct can interfere with the normal flow of tears, causing dacryocystitis.
- inflammation of the lacrimal sac and thick and sticky mucus appears.
5. Mucus in the eyes when wearing contact lenses
When wearing contact lenses, the risk of infection increases significantly. If you notice a discharge that is accompanied by pain or changes in vision, this may indicate an eye infection. It's best to see a doctor rather than rely on it going away.
Bacterial and fungal keratitis
are two corneal infections that most commonly occur in contact lens wearers. Along with the discharge, you may also experience pain and sensitivity to light.
6. Mucus makes it difficult for you to see
If the discharge becomes so thick that it interferes with your vision, do not delay visiting your doctor. Corneal ulcers are purulent infections that can cause vision difficulties.
There are different reasons for the appearance of white discharge in the corners of the eyes. Some of them are not dangerous to health, but some conditions require mandatory consultation with a doctor. Inflammation can be infectious or non-infectious in nature. The cause is often conjunctivitis, eye fatigue, stye, sinusitis, or simply a weakened immune system. If white plaque in the corners of the eyes is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, then this is a clear sign of some disease. Timely diagnosis and treatment will help prevent the development of complications.