Floaters appear in the eyes of each of us from time to time. This can be due to a variety of reasons and is not always a sign of a serious illness. But there are also exceptions.
The flickering of black or white dots is especially noticeable when looking at smooth, well-lit surfaces. Examples include a white wall of a building, a ceiling in a room, or a cloudless sky. When we look there most often and spots appear in our eyes. The initial stage of cataracts sometimes manifests itself with just such a symptom, so you should not ignore it.
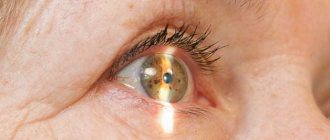
What do floaters look like before your eyes with cataracts?
Patients describe their sensations in different ways, but the essence remains the same - objects are seen as if through glasses stained with dirt. There is a constant flickering sensation in the eyes, which distracts and makes it difficult to concentrate. Most often, flies look like this:
- - black spots or spots
- - sinuous dark lines, sometimes smooth, sometimes broken
- - blurry spots that look like jellyfish
- - cobweb-like defects consisting of many intersecting threads
- - rounded rings
- - sparks that disappear when you want to focus your vision on them.
In addition, the floaters in the eyes at the initial stage of cataracts can be of different colors - gray, black, white or yellowish. Usually they move when the pupil moves, but sometimes they are not mobile.
Causes
The most common cause of floaters before the eyes is pathological changes in the vitreous body. The vitreous humor is the whitish-colorless substance inside the eye. It has a gel-like consistency and is located between the lens of the eye and the retina. In youth, the vitreous body is absolutely transparent, but with age (by the age of 45-50), small opacities appear in it, which appear as flying dots or floaters before the eyes.
Among the factors that provoke the appearance of flying spots before the eyes, experts identify the following:
Destruction of the vitreous body . Physiological aging of the vitreous body together with the body leads to destructive changes in it. In this case, some of the cells become cloudy and gather into clumps, visible to a person when streams of light enter the eye.
Eye injuries . Serious eye injuries may be accompanied by intraocular bleeding, which causes blood to enter the vitreous. It causes a violation of the transparency of the vitreous body. In this case, a person sees black or brown spots in front of his eyes and feels a significant decrease in visual acuity.
Inflammatory processes of the eyes. In some cases, inflammatory processes in the eye media also lead to clouding of the vitreous, which causes floaters to appear before the eyes.
Additionally, eye floaters can be a result of high myopia, changes caused by diabetic retinopathy, tumors inside the eye, and migraines or ocular migraines.
If floaters suddenly appear before your eyes due to a head or eye injury and at the same time pain appears in the eye, it turns red and your vision becomes worse, you should immediately seek emergency medical help.
When to see a doctor.
Floaters in front of the eyes themselves are not dangerous. They are often temporary and associated with excessive stress, vascular dystonia, or simply with age. They can go away on their own, and if they remain, the person gets used to them and does not experience any discomfort. But in order not to miss a truly serious pathology, including cataracts, with the following manifestations, you should definitely visit an ophthalmologist:
- 1) Sudden and unexpected appearance of flies
- 2) This symptom is accompanied by pain or discomfort in the eye
- 3) Other signs of early stage cataracts are observed
- 4) The number of spots and interference increases
- 5) Visual acuity decreases, myopia or farsightedness occurs
Complications and prognosis
The process of removing cataracts is called phacoemulsification. The doctor replaces the clouded lens of the eye with an artificial one. Many people do not realize how important it is to follow the rules of the rehabilitation period.
Complications after surgery to replace the lens of the eye for cataracts arise due to many factors. If vision has not been restored or other adverse consequences have developed after surgery, the person makes an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
Floaters before eyes
Cataracts are differentiated as primary and secondary. The second form appears after the first and has characteristic mechanisms of occurrence. The reasons for the development of such a complication after cataract phacoemulsification include:
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- unusual cell reaction, applies to people with systemic diseases;
- formation of a dense film at the back of the lens capsule.
Secondary cataracts are detected only by examining the structure of the visual organ using special equipment.
Intraocular pressure
The increased intraocular pressure in the early postoperative period after phacoemulsification is explained by:
- disruption of the natural outflow of aqueous fluid from the posterior chamber of the orbit;
- accumulation in the drainage system of viscoelastics, viscous drugs that are used during phacoemulsification to protect the structural surface of the visual organ;
- development of the inflammatory process or sedimentation of particles of the removed lens.
If there is such a complication after cataract removal, eye drops are prescribed. In special cases, another surgical procedure is performed - puncture of the anterior part of the chamber and cleansing.
Why do my eyes water and hurt?
If the eye itches and waters after surgery, this indicates the development of an inflammatory process after cataract removal. The appearance of symptoms is explained by the penetration of infection into the cells during the operation.
Additional symptoms include:
- severe pain;
- profuse lacrimation;
- the occurrence of swelling and swelling of the eyes;
- purulent discharge;
- the eye partially or completely does not see.
For diagnosis, if the eye hurts and festeres after cataract surgery, an analysis of tear fluid and vitreous particles is used. Next, therapeutic therapy is prescribed. In severe cases, additional surgery is performed to remove the pus.
Fog in the eyes, or Irvine Gass syndrome
Blurred vision, or Irvine Gass syndrome, appears one month after cataract surgery. Fluid accumulates in the central part of the retina, causing the macula to swell. Symptoms of the development of Irvine Gass disease include:
- pinkish fog appearing before the eyes;
- distortion of objects;
- fear of light.
To identify the disease, the fundus of the eye is examined using a microscope and an optical tomograph. People with this complication are prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs in tablet or injection form. If treatment fails, a surgical procedure is prescribed.
Corneal edema
When removing mature cataracts, which have a hard structure, the risk of complications due to ultrasound exposure increases. Therefore, a film forms on the cornea after surgery. But the symptom cannot be treated.
If air bubbles appear in the cornea, solutions, ointments and lenses are prescribed. In especially severe cases, the cornea is changed surgically.
Astigmatism, nearsightedness or farsightedness
If the surgical process for removing cataracts and replacing the lens of the eye is disrupted, a complication appears - myopia, farsightedness or astigmatism. This happens for several reasons:
- use of low-quality tools;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- seam overtension.
Diagnosis of the complication is carried out if a person’s vision sharply deteriorates after cataract removal. An ophthalmologist examines the eyelid with a special instrument. Treatment involves wearing lenses or glasses if a person, after cataract surgery, cannot see near or far.
Lens displacement
The ligaments and capsules of the optic organ are torn when the surgeon performs incorrect actions. Therefore, a complication appears after cataract surgery—displacement of the lens.
The following symptoms are characteristic of this defect:
- there is something in the eye that is disturbed and double;
- bright flashes;
- swelling, tumors;
- pain;
- darkness before the eyes.
As a diagnostic measure, fundus examination is prescribed. The complication is treated surgically. During the procedure, the doctor lifts and fixes the lens in its proper place.
Retinal disinsertion
If black spots appear in the eyes after cataract surgery, this indicates the development of retinal detachment. More often, people with myopia are susceptible to this complication. In addition to black dots, flashes and a veil may appear, blocking the view.
To diagnose pathology, several studies are used, intraocular pressure is measured. The defect is corrected through a surgical procedure.
Bleeding
A large artery is located in the choroid of the optic organ. After cataract removal, the occurrence of a rupture of this artery is explained by the presence of the following diseases:
- diabetes;
- glaucoma;
- impaired functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- atherosclerosis.
Sometimes bleeding occurs during a surgical procedure. This is considered a serious complication and requires prompt sealing of the wound.
When bleeding occurs, a person's eyelid becomes red and capillaries are visible. The mucous membrane of the organ swells.
Are floaters really a sign of cataracts?
Floaters in the eyes may simply be a manifestation of autonomic disorders or a short-term increase in pressure. But in some cases, floaters in the eyes are actually the first sign of the initial stage of cataracts. It is worth conducting an examination and, if you have been diagnosed with lens opacity, treatment. In our clinic, cataracts are removed by phacoemulsification using multifocal lenses or conventional intraocular lenses. The operations are performed using modern equipment by an ophthalmologist with 25 years of experience.
Prevention
To prevent complications in the eye after cataract surgery, you must follow the recommendations of the specialist who replaced the lens. The postoperative period includes the following preventive measures:
- Elimination of visual and physical stress.
- Applying a tight bandage to the eyelid for the first 5 days after replacing the lens.
- Instillation of drops to promote tissue healing. For example, drugs such as Vitabact and Diclof are used.
- When there is no longer double vision and vision has been restored, it is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of the visual organ and wear glasses as recommended by a doctor.
Almost all people with cataracts removed do not experience any visual impairment. The recovery period lasts several months.
Additionally, we invite you to watch a video where an ophthalmologist will talk about complications and their prevention:
New treatment methods and computer equipment help to perform phacoemulsification with minimal risks of subsequent complications. But at the first signs of a developing defect, you need to visit an ophthalmologist.
Comment on the article and tell us and other readers about your experience. Share the article with your friends by reposting it. Be healthy.
Secondary cataract
Secondary cataract is called clouding of the posterior capsule of the lens in the late postoperative period. This causes a decrease in the quality of vision and a visit to an ophthalmologist. The appearance of secondary cataracts is rather a physiological process and is not a complication of the operation.
Symptoms of secondary cataracts
The main complaints are blurred vision. Characteristic manifestations of secondary cataracts:
progressive deterioration in the clarity of visual perception;
difficulty reading, working on a PC, or working with small parts;
surrounding objects are not clearly visible, as if through frosted glass or cellophane;
change in color rendering - colors lose their brightness and acquire a dirty tint.
Symptoms of visual impairment are constant, progressive and are not accompanied by pain or redness of the eye.
Secondary cataracts are accompanied by subjective symptoms that can also occur with other eye diseases; for an accurate diagnosis, an examination by an ophthalmologist is required.
The timing of the manifestation of signs of secondary cataracts varies from person to person. The younger the patient, the greater the chance of developing it during the first year after surgery.
Causes of secondary cataracts
To understand the processes that lead to secondary cataracts, let us recall the essence of the operation to replace the lens. During phacoemulsification or extracapsular extraction, ophthalmic surgeons remove the anterior capsule and “clean out” the clouded lens masses. An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is implanted into the posterior capsule (or bursa). For the majority of those operated on, the optical structure remains transparent for decades.
In 3 out of 10 patients, the posterior bag of the lens undergoes changes - the appearance of Elschnig balls or fibrosis, this is called secondary cataract.
The structure of the posterior bursa is such that its cells continue to grow and form defective lens fibers. The latter have a round, spherical shape and are similar to salmon eggs; they are also called Adamyuk-Elschnig balls. Arranged in dense rows, they lead to a decrease in the transparency of optical media and incorrect refraction of light. As a result, the image quality becomes unclear, and patients think that the cataract has returned. This scenario for the development of secondary cataracts is typical for young people.
| Secondary cataracts occur only once after lens removal. |
In older people, a degenerative process - fibrosis - is more often observed. In some cases, an excessively dense, fibrously altered posterior wall of the lens is determined during surgery. During postoperative examinations, the ophthalmic surgeon focuses the patient’s attention on the possible deterioration of vision in the next 3-6 months.
Cataracts can develop again at any time after surgery. Most often this happens within 6-18 months.
Diagnosis of secondary cataracts
To accurately determine the causes of deterioration in visual function, the doctor conducts a full examination of all parts of the eyeball.
Diagnostic examination for suspected secondary cataracts includes:
testing visual acuity and refraction;
tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure);
examination of the anterior segment of the eye in transmitted light and at a slit lamp (biomicroscopy);
examination of the retina (with pupil dilation).
If concomitant diseases appear, the list of diagnostic measures can be expanded.
Removal of secondary cataracts
There is an expression among patients: “They removed the film from me” or “They cleaned my lens.” Ophthalmologists call the procedure for removing secondary cataracts laser discission.
The intervention is performed using a YAG laser machine. Features of the procedure:
does not require preliminary preparation and collection of general clinical tests;
low-painful - only flashes of bright light cause discomfort;
short-term – takes a few minutes.
In the laser room, before the operation, intraocular pressure is measured and the pupil is dilated. After reaching maximum mydriasis (about 60 minutes), the patient is instilled with anesthetic drops.
Removal of secondary cataracts is carried out in a sitting position, placing a goniolens on the surface of the eye. Through it, a laser beam is focused on the surface of the posterior bag and a rounded hole is formed - a “window” in the optical zone. The operation takes a few minutes. A prerequisite is immobility during the operation - you cannot move your head or eye, or fidget in the chair.
Laser dissection of secondary cataracts. Contraindications
There are contraindications for surgical intervention.
The operation will not be performed in the following cases:
if the main cause of poor vision is other diseases - for example, retinal dystrophy or optic nerve atrophy;
IOL dislocation – its displacement relative to the visual
pathology of the anterior segment of the eye. These can be acute inflammatory reactions in the cornea - keratitis, iris - iridocyclitis, etc.;
decreased transparency of the optics of the anterior segment of the eye - scars or corneal dystrophy, swelling, etc.;
increased intraocular pressure.
Some contraindications are relative. After stopping the acute inflammatory reaction or drug reduction of intraocular pressure, objections are removed and treatment is carried out.
Postoperative period
Vision after surgery is restored as the pupil narrows - on average within 4-6 hours.
The main complaints of patients after removal of secondary cataracts are “spots” or black dots in the field of vision, visible against a light background.
This is caused by remnants of the posterior capsule floating in the vitreous humor of the eye and casting a shadow on the retina. The interference disappears within 2-3 months and does not require special therapy.
After removal of a secondary cataract, the rehabilitation period takes 2 weeks. During this period, it is necessary to instill drops prescribed by the doctor. Visual stress is not limited, physical activity should be moderate until the end of the period of instillation of drops. General overheating or hypothermia of the body should be avoided.
Control examinations are carried out the next day after surgery and 2 weeks later.
More than half of all congenital pathologies of the visual organs are cataracts. This disease is a clouding of the lens, which leads to a sharp deterioration in vision.
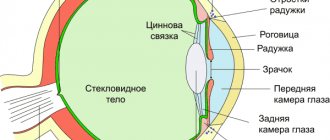
The lens is an optically transparent structure located behind the iris, in front of the vitreous body and retina. The shape, clarity, and refractive index of a natural lens allow it to focus light on the retina.
A fairly large percentage of ophthalmic diseases is cataract, which is essentially a progressive clouding of the lens. Surgical treatment of cataracts is currently the only effective treatment for this pathology.
Cataract is a disease caused by clouding of the lens inside the eye, resulting in decreased vision. It is a common cause of blindness and can be successfully treated surgically. Loss of vision.
ARTICLES ON THE TOPIC: Cataracts at 87 years old Cataracts: can you go blind Kalanchoe cataracts Vision after cataracts What can be the consequences after cataract surgery