Is farsightedness a plus or a minus? Causes of farsightedness. Farsightedness due to age
We often hear questions from uninformed people about whether farsightedness is a plus or a minus.
In order to correctly answer these kinds of questions, it is necessary to understand the principle of operation of the human visual organs and study possible problems that may arise. The eye is one of the most complex organs in the human body. The interaction of the visual system with the cerebral cortex allows the transformation of light rays coming from the outside world into visual images. To understand how this happens, it is necessary to consider what the human eye is made of.
Structure of the eye
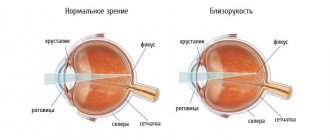
The eye is a very complex optical system that consists of many parts.
- Cornea. Through it, light waves enter the eye. It is an organic lens, with the help of which light signals diverging on the sides are focused.
- The sclera is the outer opaque layer of the eye, which does not actively participate in transmitting light.
- The iris is something like a camera diaphragm. This part regulates the flow of light particles and performs an aesthetic function by determining the color of a person’s eyes.
- The pupil is a hole in the iris that regulates the amount of light rays entering the eye, as well as filtering out curved, distorting rays.
- The lens is the second strongest lens in this human organ, located immediately behind the iris. Depending on the distance to the object, it changes its optical power. At a small distance it strengthens, at a large distance it weakens.
- The retina is a spherical surface onto which the surrounding world is projected. Moreover, the light, passing through two collecting lenses, hits the retina upside down. The information is then converted into electronic impulses.
- The macula is the central part of the retina that recognizes clear color images.
- The optic nerve is a transporter of information processed by the retina into nerve impulses to the brain.
Types of vision problems
Vision problems can appear at absolutely any age (they can even be congenital). The cause of some of them is a malfunction of the retina or optic nerve. However, most diseases of the visual system are caused by a violation of the refractive characteristics of the eye. The consequence of this is defocus, and the person loses the ability to see objects clearly. That is, human vision is impaired. “Plus” and “minus” indicate the degree of refraction of light (either the rays are not refracted enough, or they are refracted too much). There are several main types of visual impairment in humans.
Myopia is myopia
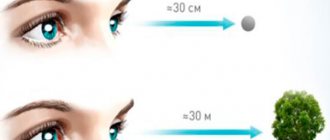
With myopia, a person cannot see objects that are at a great distance. Near vision is normal. With this disease, you can easily read a book, but you may no longer see the number of the house across the street.
Is farsightedness a plus or a minus?
Let's return to the main question. So, is farsightedness a plus or a minus? Farsightedness (also known as hypermetropia) is a visual impairment in which a person has difficulty distinguishing objects located nearby, but can clearly distinguish small details of distant objects.
Thus, the strength of glasses prescribed to a patient is measured in diopters. For farsightedness, glasses with a collecting effect are installed, which perform part of the functions of the lens. Such glasses are called positive, and therefore farsightedness is a “plus”. Or “minus”, for example, is used for myopia. Consequently, glasses with a scattering effect, which are called negative, are used in treatment.
Presbyopia – what is it?
In the medical community, age-related farsightedness is called presbyopia and occurs mainly in people over 40 years of age. This disease is caused by a loss of elasticity of the lens and is expressed by a loss of the ability to change the eye's focus when looking at objects at different distances.
Astigmatism
Visual impairment, characteristic of astigmatism, occurs as a result of changes in the curvature of the lens and is expressed in incorrect refraction of light rays. Because of this, the picture of the outside world looks somewhat distorted.
What is the cause of cataracts?
Cataracts are a very common disease that causes visual impairment. Most often it occurs in older people, but it can also be a consequence of a viral disease. A manifestation of this disease is clouding of the lens.
Within the framework of this article, I propose to consider in more detail issues related specifically to farsightedness.
Main causes of farsightedness
So, as already stated, farsightedness is an eye disease in which the image is focused behind the retina. The degree of development of hypermetropia depends on the eye’s ability to refract light rays and on accommodation (the ability of the lens to change its shape depending on the distance to the object):
- Weak (up to +2 diopters).
- Medium (from +2 to +5 diopters).
- Strong (more than +5 diopters).
There are two causes of farsightedness:
- The eyeball is too short, and therefore the longitudinal ocular axis is short. Most often, this visual disorder is hereditary.
- Insufficient refractive properties of the visual system. With age, the human lens loses elasticity and corresponding abilities.
There is also the possibility of a combination of these two reasons.
Symptoms of farsightedness
The main symptom is poor near vision. At the same time, the patient sees objects located in the distance well. However, over time, the pathology may intensify due to the loss of the accommodative properties of the lens.
The main symptoms, the presence of which prompts you to consult an ophthalmologist with suspected hypermetropia, include:
- Impaired near vision.
- Disturbance of “distant” vision.
- Increased eye fatigue when working.
- Visual fatigue when reading books.
- Frequent conjunctivitis and other inflammatory processes of the eyes.
- Strabismus in childhood.
Diagnosis of vision problems
As soon as you feel a decrease in visual acuity, you need to seek help from a specialist. The standard diagnostic procedure includes the following steps:
- Visual acuity study. For this purpose, a special vision table is used. Nowadays, Sivtsev, Golovin or Orlova tables are used (mainly in children).
- Examination of the fundus using a mirror and ultrasound.
3. Selection of lenses of the required power, carried out using a phoropter.
Treatment of farsightedness
In order to never be bothered by vision problems, you must be guided by the following principles:
- Observe lighting conditions.
- Alternate visual stress with physical relaxation.
- Train visual muscles both with the help of special gymnastics for the eyes and with the use of modern technologies (including computer and laser).
- Conduct early diagnosis and correct vision correction (includes mandatory periodic examination by an ophthalmologist).
- Perform general strengthening exercises, supported by proper nutritious nutrition.
Taking these preventive measures will help preserve your vision. Plus, of course, don’t forget to undergo periodic examinations with an ophthalmologist.
Vision correction is performed using glasses or eye contact lenses, which are prescribed to the patient in a special prescription after a full examination.
In addition, eye surgery is moving forward with huge strides and now allows a person to stop wondering whether farsightedness is a “plus” or a “minus”.
fb.ru
Determination of visual acuity
- In the CIS countries - fractions of one: 1.0 - normal vision, 0.9; 0.8, etc. up to 0.1 - determined by the number of lines starting from the top in the Sivtsev or Golovin table from a distance of 5 meters. Studies are carried out for each eye separately: first, the visual acuity of one eye is determined, then the other eye.
When examining visual acuity from a different distance (less than 0.1 - if a person from 5 meters does not recognize the signs of the top row), the person being tested is brought closer to the table and asked every 0.5 meters until he correctly names the signs of the top row. The value is calculated using the formula:
V=d/D
, Where
V - visual acuity;
d is the distance from which the study is carried out;
D is the distance at which a normal eye sees a given row.
But it is better to use Polyak optotypes to determine visual acuity less than 0.1 s 5 meters.
To determine visual acuity in children, the Orlova table is used.
The distance of 5 meters was chosen for a specific reason: with emmetropia, the point of clear vision is as if at infinity. It is generally accepted that for the human eye, infinity begins at a distance of 5 meters: when an object is located no closer than 5 meters, parallel rays are collected on the retina of an eye with emmetropia.
- In English-speaking countries, visual acuity is usually determined using the Snellen chart and is usually expressed as a simple fraction: the numerator is the distance from which the test is performed (usually 20 feet ~ 6 meters), and the denominator is the distance from which the emmetropic eye sees the sign. correctly read by the subject (20/20 - equivalent to 1.0; 20/200 ~ 0.1).
Simultaneously with determining visual acuity without refractive correction of the eye, visual acuity with the maximum possible correction is usually also determined (for emmetropia, the two values coincide).
The maximum possible correction is the minimum optical power of the corrective lens (dispersive - for people suffering from myopia; converging rays - for farsightedness), providing maximum quality of vision. It is determined by a subjective method by selecting lenses, according to tables for distance vision, gradually increasing the optical power of correction, for myopic refraction, until an increase in diopters no longer gives an increase in visual acuity, and for far-sighted refraction, until distance visual acuity begins to fall.
These are subjective methods
(that is, focused on the patient’s sensations).
Towards objective methods
diagnostics include:
- refractometry of the eye (measurement of refraction using special instruments - refractometers),
- skiascopy (observation of the movement of a light spot in the illuminated pupil during rotation of the ophthalmoscopic mirror).
Using these methods, it is possible to determine refraction regardless of the patient's testimony, which is very important when conducting examinations or studying very young children.
Thus, an entry in medical documents usually looks like (example):
- for myopia (myopia):
O.D.
(designation right eye - oculus dexter) 0.4 (right eye sees 4 lines from above) | -1.75D (the power of the corrective diverging lens, with which a person sees the tenth line from the top with his right eye - 1.0)
OS
(designation left eye - oculus sinister) 0.4 | -1.75D
If the values for each eye are the same, the entry can be (example)
OU
(designation both eyes - oculus uterque) 0.4 | -1.75D
Depending on the value of vision correction, there are 3 degrees of myopia:
I degree - weak - up to −3D
II degree - average - from −3D to −6D
III degree - high - over −6D
- for farsightedness (hypermetropia):
O.D.
+1.75D
OS
+1.75D
Depending on the value of vision correction, there are 3 degrees of hypermetropia:
I degree - weak - up to + 2D
II degree - average - from +2D to +5D
III degree - high - over +5D
For glasses and contact lenses, subdivisional diopter values that are multiples of 0.25 (-1.25D; −1.5D; −1.75D or +1.25D; +1.5D; +1.75D, etc.) can be used. ).
Note.
Only the second method also provides numerical expressions for weak and even moderate degrees of farsightedness (hyperopia). The first method cannot be used, since a person with such a refractive error (I-II degree), as a rule, from 5 meters sees all the symbols on the vision test tables without the help of lenses.
Admission to military service
Health requirements in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Belarus Names of diseases, degree of dysfunction Category of suitability for military service
The disease schedule provides for the health requirements for the following categories of citizens:
| |||
| column I | Count II | Count III | |
| Refractive errors and accommodation: | |||
| a) myopia or farsightedness in any eye in one of the meridians more than 12.0 diopters or astigmatism of any kind in any eye with a refractive difference in the two main meridians more than 6.0 diopters | NGI | NGI | |
| b) myopia or farsightedness in any eye in one of the meridians more than 8.0 diopters and up to 12.0 diopters or astigmatism of any kind in any eye with a difference in refraction in the two main meridians more than 4.0 diopters and up to 6.0 diopters | GPS | NGM GNS - IND | |
| c) myopia of any eye on one of the meridians is more than 6.0 diopters and up to 8.0 diopters | GPS | GO SS - IND | |
| d) myopia of any eye on one of the meridians more than 3.0 diopters and up to 6.0 diopters, farsightedness of any eye on one of the meridians more than 6.0 diopters and up to 8.0 diopters, or astigmatism of any kind in any eye with a refractive error difference of two main meridians more than 2.0 diopters and up to 4.0 diopters | GO | G SSO, SS - IND | |
| Blindness, low vision, color vision abnormalities: | |||
| a) visual acuity of one eye is 0.09 or lower, or blindness if the visual acuity of the other eye is 0.3 or lower, as well as the absence of an eyeball if the visual acuity of the other eye is 0.3 or lower, or the visual acuity of both eyes is 0.2 or lower | NGI | NGI | |
| b) visual acuity of one eye is 0.09 or lower, or its blindness if the visual acuity of the other eye is 0.4 or higher, as well as the absence of an eyeball if the visual acuity of the other eye is 0.4 or higher, or the visual acuity of one eye is 0.3 if visual acuity is vision of the other eye from 0.3 to 0.1 | GPS | NGM GNS - IND | |
| c) visual acuity of one eye is 0.4 with visual acuity of the other eye from 0.3 to 0.1 | GPS | GO | |
| d) dichromasia, color weakness II-III degree | GO | G | |
| Abbreviations : G - fit for military service; GO - fit for military service with minor restrictions; VN - temporarily unfit for military service; State Tax Service - fit for service outside the ranks in peacetime; GPS — unfit for military service in peacetime, limitedly fit for military service in wartime; NGI - unfit for military service with exclusion from military registration; IND — individually determined category of suitability for military service, military service in the form of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus, branch of the armed forces and military formation, suitability for a separate military specialty (hereinafter referred to as VUS), for admission to military educational institutions; NG — unfit for military service in the form of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus, branch of the armed forces and military formation, for individual military establishments, unfit for admission to military educational institutions and the educational institution “Minsk Suvorov Military School” (hereinafter referred to as MSVU); SS (special structures) - special structures; MTR — special operations forces; | |||
| Source Resolution of the Ministry of Defense of the Republic of Belarus, the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus dated December 20, 2010 N 51/170 “On approval of the Instruction on determining the requirements for the health status of citizens when assigned to conscription stations, conscription for military service, service in the reserve, military service of reserve officers , military and special training, enrollment in military service under a contract, in the educational institution “Minsk Suvorov Military School” and military educational institutions, military personnel, citizens in the reserve of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus" | |||
en.wikipedia.org
What does “minus 1” vision mean? What you need to know about preserving your vision
Our eyes give us 85% of the information about the world around us. Even though some of us have already learned more than once what vision problems are, we often leave our eyes without proper attention and care. Some people don’t even think about the fact that at one moment they could lose almost the most important thing in their life - the ability to see. We talked with ophthalmologists and received recommendations, which we will talk about now.
Don't self-medicate
If you have poor vision (myopia), do not forget to visit your ophthalmologist promptly. With high and moderate myopia, the volume of the eyeball increases and the retina stretches, which leads to its deformation. In the future, the deformation may cause a retinal tear. In this case, surgery cannot be avoided. It should also be noted that for the time being, changes at the bottom of the eyeball occur without any symptoms. Deformation can only be detected during a specialized examination in an ophthalmology clinic.
Comments from ophthalmologists
If you are concerned about itching, tearfulness, various types of discharge, pus from the eyes, you should not use the first remedy that comes to hand. The first thing you should do is see a doctor at the nearest clinic, and this should be done as soon as possible. The previously described symptoms may indicate the presence of a variety of diseases that cannot be detected at home. An incorrectly selected drug, at best, will not give any results, at worst, it can cause harm. If your red eyes are due to an allergic reaction, then antibacterial drops will only make your situation worse.
Often in medical practice there are patients who complain of foreign bodies behind the eyelid. There are usually no other symptoms of inflammation. In this case, it is necessary to urgently conduct a series of studies, as this may be a symptom of chronic, low-grade inflammation of the eyelid margins (blepharitis).
Myopia correction
One of the most ancient methods of correcting myopia is the use of glasses. Of course, with mild myopia, doctors do not impose wearing glasses. Vision correction in this way lasts quite a long time. You have to wear glasses only at certain times in order to restore your vision to its former sharpness. If the degree of myopia has reached the point where it is no longer possible to see without glasses, then they are prescribed for constant wearing. Then more complex glasses with cylindrical lenses are prescribed.
It should also be noted that most of these problems can be solved by contact lenses. However, this does not exclude the use of glasses for preventive purposes. Unlike glasses, a contact lens fits tightly to the surface of the eyeball.
One of the most advertised methods of combating myopia is laser vision correction. Yes, this method has its advantages. However, an operation is an operation. Its result cannot be completely predicted, which in some cases frightens patients.
Vision “minus 1”: what does such a diagnosis mean, is treatment necessary?
Today, there are two opposing opinions regarding whether treatment is necessary for visual acuity of minus 1. Some believe that this indicator does not interfere with a full life, while others, on the contrary, see this as a cause for concern.
Early correction methods
When you have “minus 1” vision, which means possible myopia, some people begin to self-medicate and do not always turn to doctors. But you shouldn’t worry so much; in such cases, patients are prescribed special vitamins and glasses that need to be worn for several hours a day. If glasses are not prescribed, you will be prescribed special exercises to strengthen the eye muscles. The disadvantage of glasses in this case is that the eyes will get used to being in this state and will stop fighting myopia.
Treatment methods for accommodative and anatomical myopia
If you are still tormented by the thought that you have minus 1 vision, what does such a statement mean, is it dangerous, then we hasten to reward you with irreplaceable information with which you will no longer have such questions.
Anatomical myopia
In this case, the eye is extended in the anterior-posterior direction, and the focus is in front of the retina. Accommodative muscles work normally. If after a course of therapeutic exercises (for example, retracting the eyes deep into the sockets) vision has fallen below “minus 1,” then additional manipulations need to be carried out, including surgical intervention.
Accommodative myopia
The eyes are not extended, and vision is “minus 1”. What does this symptom mean? In this case, there is weakness of the accommodative muscles. To improve vision, you need to pay attention to the accommodative muscles and train them. For this purpose, a system of eye gymnastics, special devices and drug therapy were developed. In this case, glasses are not prescribed, as they will cause the muscles to stop working. Accommodative myopia often develops due to spasm of the eye muscles.
Ultrasound examination will help determine the type of myopia. This way you can find out how long the eye is. If after treatment the vision is still “minus 1”, then this already indicates the presence of true myopia, which means glasses are needed. The downside of glasses is that they prevent your eyes from exercising in one way or another. However, properly selected glasses (less than minus 1) will allow the eye muscles to work. The ability to see needs to be trained and maintained.
Vision Test Chart
You can ask your ophthalmologist for this device to test your vision. How can we check our eyesight at home? The table is a regular set of block letters of different sizes. Eyes with 100% vision perfectly perceive the line V=1.0. The table also has a column “D=…” in the left corner, which indicates the distance from which you need to look at the letters. The distance is calculated for a person with 100% vision. The ophthalmologist's vision test chart looks similar. The only difference is that you see it not on a monitor screen, but on paper. It is also recommended to print it at home to get a more accurate result.
Ophthalmologist's advice
- When working at a computer, the distance between the monitor and your eyes should be at least 60 centimeters. If possible, the screen should be dimmed and have a flat surface. Be sure to take a break every half hour. You can simply avert your eyes to the window and look somewhere into the distance.
- Don't read in moving vehicles. Constant shaking and poor lighting have a bad effect on the eye muscles.
- Before going to bed, apply a compress to your eyes. Soak cotton pads in chamomile tea and place them on your eyes. Thus, you need to lie down for 10-15 minutes.
- Throughout the day, try to set aside time to close your eyes for 3-5 minutes. This will give them some rest.
- Try to blink more often. This movement stimulates the production of tears, which moisturize tired eyes.
- In the summer or when the sun is shining, try to wear sunglasses at all times. They should not be decorative, as such glasses will not protect you from retinal burns.
- If your place of work has air conditioning, then you cannot avoid dry air. It is better to consult a doctor so that he can select special moisturizing eye drops for you.
Foods that help improve vision
- First we will have blueberries. This is the most famous product for maintaining vision. In the summer you need to eat at least 10 glasses of this wonderful berry.
- Eggs contain lutein and amino acids that prevent the occurrence of cataracts.
- Be sure to include fish in your diet. Almost every type of it contains fatty acids, which have a positive effect not only on the eyes, but also on all organs.
- Greens (arugula, spinach and parsley). These products have special components that protect the retina from the negative effects of sunlight.
- Sesame, nuts and seeds are those products that contain a considerable amount of zinc. These products are suitable for those who have a computer-related job or those who simply spend a lot of time in front of a monitor.
- Meat, especially beef, is also rich in zinc.
- Carrots, sweet potatoes, mangoes, persimmons, apricots - they contain carotene, which protects the eyes from dryness. Freshly squeezed carrot juice is especially useful. It is best to cook it yourself.
- Eating these products will not save you from existing serious diseases, but will help prevent the development of new ones.
fb.ru
Prevention
You can prevent vision of minus 0.75 by maintaining eye hygiene and eliminating significant eye strain. It is important to minimize watching TV or sitting in front of a monitor. It is necessary to read or write so that the distance between objects and eyes is at least 30 centimeters, because in this position the load on the organ of vision is minimal and a person does not experience discomfort during prolonged work. Sufficient and non-irritating lighting is important. At the end of the working day, it is necessary to do eye exercises. This will help the extraocular muscles, the main one of which is the ciliary muscle, as well as relax and restore tone. You need to monitor your diet, saturate your diet with a sufficient amount of foods containing vitamin A, which is necessary for normal focusing.
Should I wear glasses at -0.75?
6 years ago they prescribed glasses at -0.75, I never wore them. Now I notice that my vision has become worse, I went to the ophthalmologist, nothing has changed as before -0.75, I’m afraid if I start wearing glasses, I’ll be without them later I can’t do it at all, what should I do?
Just katya
My vision is also -0.75. The ophthalmologist prescribed glasses. We decided not to buy. They thought that I didn’t see it that bad... Total -0.75. Then, over time, we consulted an ophthalmologist we knew. He said that even with such vision, glasses are needed. You've probably noticed that if you squint, you can see better. And so he told us that if I squint to see something, wrinkles will appear near my eyes at an early age. Therefore, to avoid squinting, you need to wear glasses. I've been wearing glasses for almost a year now. But not all day. The ophthalmologist should have told you that with such vision, wearing glasses, you only need to watch TV and look at the blackboard at school. Sitting at the computer without them, at home without them, and preferably on the street without them either. Here.. . Well, now I don’t always wear glasses to school, because it gets boring, I’ll tell you honestly... But sometimes I wear... Then it's up to you to decide).
Yulchik
My vision is also minus 0.75 in both eyes. The doctor said that watching TV with glasses is minus 0.75, and reading and working on a computer with glasses is plus 0.5, I was very surprised why plus, because I have a minus, and the doctor reassured me: this is for vision correction, so as not to overstrain my eyes , when working at a computer (I work 8-10 hours at a computer). She also prescribed Vitrum Vision for a month, Irifrin 2.5% eye drops in the morning or afternoon, Systane Ultra or Oxal drops at night, and also a massage of the cervical-collar area, as well as an appointment with an ophthalmologist every six months!
Should I worry?
During your next visit to the ophthalmologist, you heard a diagnosis of visual acuity of 0.75. What does it mean? In fact, this is a slight deviation from the norm, which can be corrected with simple eye exercises. If there are additional symptoms that affect the patient’s well-being, the ophthalmologist may prescribe wearing glasses. If vision is minus 0.75, the diagnosis means that the patient requires minor correction, as well as treatment for myopia. Although, myopia, like any other ailment, can be treated only if there are other aggravating symptoms. When diagnosing vision of 0.75 in a child, it is recommended to carry out only therapeutic exercises for the eyes, which allows you to correct a slight deviation from the norm without the use of medication.
Is +1 vision already farsighted?
exactly a plus
Elena
Farsightedness, or hypermetropia, is characterized by insufficient optical power of the eye. Rays of light, these conductors of visual information from the world around us, rarely converge when they approach the surface of the eye. As a rule, they diverge from their source in different directions, and in the best case they go like a bunch of parallel rays. And in order to get a clear image of an object on the retina, which is the basis of normal vision, the optics of the eye - the cornea and lens - need to strongly refract the light rays so that they all become converging. Moreover, they were so converging that after 23 millimeters of their journey inside the eye they converged at one point on the retina. Farsightedness most often occurs when the length of the eye is less than 23 millimeters, and light rays simply “do not have time” to focus on the retina. Instead of one clear point, a blurry spot of light is projected onto the retina. There is often a combination of insufficient optical power of the cornea and lens with a short eye length. Much less often, farsightedness occurs due only to weak optics with a normal length of the eyeball. Symptoms of Farsightedness Farsighted people usually have trouble seeing close up, but vision may also be blurry when looking at distant objects. Young, and even more so, young people with weak or moderate farsightedness often do not have vision problems, since their natural lens can adapt or accommodate to increase the optical power of the eye. However, with age, accommodation is gradually lost, and patients notice a progressive deterioration in near vision. So, the main signs of farsightedness: poor near vision poor distance vision (with high degrees of farsightedness) increased eye fatigue when reading eye strain during work (headaches, burning eyes) strabismus and “lazy” eyes in children (amblyopia) frequent inflammatory eye diseases (blepharitis, stye, chalazion, conjunctivitis) Diagnosis of farsightedness Hypermetropia is determined by testing vision using a phoropter or computer-assisted autorefractometry. The optical power of the cornea is measured by keratometry, and the length of the eye by echobiometry. Farsightedness in young patients is checked after pupil dilation, which relaxes accommodation and makes hidden farsightedness obvious. Treatment of farsightedness Correction of farsightedness depends on many factors, such as the age of the patient, his occupation, the degree of farsightedness, and the presence of concomitant pathology. In addition to classical spectacle or neoclassical (since the middle of the last century) contact correction, there are also more modern post-industrial technologies for correcting any degree of farsightedness. All methods for correcting hypermetropia are aimed at increasing the optical power of the eye in order to force light rays to focus on the retina. Currently, the most common methods of surgical correction of farsightedness are LTK, clear lens replacement, LASIK, positive lens implantation and TKA.
Adm lh
Yes, because 0 should be normal, but if, for example, it’s -1 or +2, then it’s either farsightedness or nearsightedness, I have nearsightedness, I’m lucky - almost -5, but those who are far unlucky have to wear glasses all the time.
What does it mean
During the diagnostic process, the ophthalmologist diagnosed vision plus 0.75. This means that the patient is able to read 7.5 letter lines in Sivtsev’s table. Considering that the table has only 10 rows, this result can be considered quite good. If this diagnosis is established for a child, there is no need to worry; in children, vision is never taken for granted. This means that vision of 0.75 is a good result. As you grow older, visual acuity increases and the indicators level out.