Strabismus
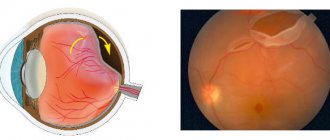
in children and adults, this is a deviation of one or both eyes from the central position, which leads to a person’s lack of binocular (stereoscopic) vision. The eyes may deviate from the visual axis towards the nose, inwards, or towards the temples, outwards. Strabismus causes not only physiological discomfort and is associated with decreased vision, but also creates various emotional and psychological inconveniences that can lower self-esteem.
Today, strabismus can be corrected using various methods. The doctor chooses the treatment method individually and adjusts it depending on the patient’s age, form of strabismus, concomitant diseases, etc.
Main types of strabismus:
- Periodic
- Permanent
- Unilateral or monolateral or monocular (squints one specific eye)
- Alternating or alternating (both eyes are involved)
- Converging (converging) - the visual axis moves away from the point of fixation towards the nose
- Divergent (divergent) - the visual axis moves towards the temple
- Vertical strabismus - supervergent (deviation of one axis upward) or infravergent (deviation of one of the axes downward).
Often, children under one year of age are diagnosed with imaginary strabismus, when there are skin folds in the cornea of the eye. The fold can cover a small part of the eye and thus create a visual illusion: it seems as if the child's eyes are directed in different directions. With age, this feature disappears and does not manifest itself in any way in the future.
Up to three months of a child’s life, periodic convergent and divergent strabismus is an acceptable norm.
Characteristics of the disease
If the functioning of the visual organs is impaired, displacement of the eyeballs may occur. A pathology that causes such physiological and moral discomfort is called strabismus. The disease is characterized by the lack of synchronous ability of the visual organs to look at one point.
It can be diagnosed independently without the help of an ophthalmologist. Eyeballs directed towards the nose, temples or upward will exclude the ability to concentrate on the object of attention. The disease is not a life-threatening disease for adults or children and can be eliminated at any age.
Timely treatment of strabismus in adults at home will help avoid deterioration of vision and eliminate aesthetic defects.
Causes
Source: aif.ru
Strabismus can appear as a consequence of congenital or acquired pathologies. The most common causes of strabismus are:
- myopia, astigmatism or farsightedness of high or moderate degree;
- sharp deterioration of vision in one eye;
- stress;
- injuries;
- central nervous system diseases (cerebral palsy);
- congenital abnormalities of the extraocular muscles;
- paresis or paralysis;
- infectious diseases (flu, measles, meningitis, etc.);
- mental trauma (fear);
- somatic diseases.
Displacement of the eyeballs from the joint point of fixation is not a fatal illness. Self-diagnosis of strabismus and treatment at home is not very difficult.
Symptoms
Source: farmakosha.com
Among the signs of pathology, it is necessary to highlight:
- displacement of the eyeballs in different directions;
- doubling of images recorded by the visual organs from the surrounding space;
- sudden closing of the eyes in bright light;
- constant search for head position for better focusing of vision;
- headaches of varying intensity;
- rapid fatigue of the visual organs;
- doubling of pictures obtained after perceiving the surrounding reality;
- constant desire for concentration to perceive the outside world;
- the need to control movements and actions.
With strabismus, the image from each eyeball cannot be focused into the overall picture, and there is no complete perception of the depth of objects from the surrounding space. At the same time, the possibility of perceiving the world on a par with ordinary people is excluded, and viewing is carried out only through one pupil.
Symptoms of pathology with a slight deviation of the visual axis of the eye from the joint point of fixation can be periodic in nature against the background of constant fatigue.
People with this pathology should have information on how to get rid of strabismus at home and immediately carry out all health procedures to prevent irreparable consequences.
If there is no desire to carry out timely treatment, blindness may occur, the world around you may plunge into darkness, and nervous disorders will become constant companions.
A timely response to a vision problem, including treatment of strabismus at home in adults and children, is the key to obtaining a positive result.
Indication for surgery
Surgical intervention is most effective in childhood. If it is acquired, the optimal age is 4-6 years. In congenital forms, the operation is performed somewhat earlier - at 2-3 years. In adults, it can be performed at any age in the absence of general contraindications.
Surgery to correct strabismus is recommended in the following cases:
- A person’s desire to eliminate a cosmetic defect in himself or a child.
- The entire arsenal of conservative methods was used, but the achieved improvement in binocular vision was not maximum.
The doctor believes that it is advisable to create conditions for restoring vision through surgery. That is, surgery is prescribed first, and then additional correction using conservative methods. This appointment is possible in case of too severe strabismus.
The purpose of the operation: to eliminate the asymmetrical arrangement of the visual organs. After the intervention, positive visual changes are observed. If the patient also has vision problems, additional intervention will be required, since conventional surgery to correct strabismus does not improve vision.
Diagnostics
Source: diagnos-online.ru
Strabismus is easy to notice visually: the child does not focus his gaze, one eye deviates and looks in the other direction.
Also, mild strabismus, difficult to detect visually, can be noted by the fact that the child does not look straight ahead and relaxed, but tilts his head, looks askance, squints, somehow turns his head unnaturally - and does this constantly, repeating the algorithm that helps him ok to see.
If you suspect a mild form of strabismus, you should definitely consult with an ophthalmologist to begin solving this problem as early as possible.
Prevention
Measures to prevent strabismus are simple. These include:
- Regular visits to the ophthalmologist.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Alternate eye strain with rest.
- Performing strengthening exercises for the eyes.
- Limiting time spent at the computer.
- Compliance with the rules of visual hygiene while reading and writing.
- Blood pressure control.
- Wearing sunglasses in bright environments.
- Compliance with the principles of healthy eating.
- Elimination of bad habits.
When should a child be examined?
Source: detki.co.il
The first examination is advisable immediately after birth. It must be said that in maternity hospitals, all babies without exception are not examined by an ophthalmologist. A neonatologist at the maternity hospital or a local pediatrician may classify the baby as a risk group, and then he will be prescribed a consultation with an ophthalmologist already in the maternity hospital or immediately after discharge.
The risk group includes children with a family history of eye diseases (if their parents have any), premature newborns, children born during abnormal births, as well as children whose parents have bad habits (alcoholism, smoking).
Further, an examination by an ophthalmologist is necessary for the baby at the age of two months, at six months and at the age of one year. During this time, all children are referred to an ophthalmologist.
The specialist will identify the presence or absence of farsightedness (myopia) in the child, the acuity and nature of vision, the angle of strabismus and, if necessary, refer for consultation to other specialists, for example, a neurologist. Only after a thorough examination can complex treatment of strabismus be started, including conservative therapy and surgical treatment.
Divergent strabismus in children
Divergent strabismus in children is morphologically similar to convergent strabismus, while at the same time differing from it. One of the child’s eyes deviates from the central axis of vision in the same way, only now the direction of deviation is the opposite: to the periphery, closer to the temple, the eyeball seems to stretch to the outer corner of the eye.
Divergent strabismus in children, unlike convergent strabismus, is often combined with myopia, thus being its complication. The causes of divergent strabismus in children may be the same as those of convergent strabismus, and in this situation, it is again necessary to consult a doctor to clarify the nuances of the condition and choose the correct treatment tactics.
Treatment methods for divergent strabismus in a child include the following options:
- Therapeutic treatment;
- Hardware treatment;
- Surgery.
The earlier this condition is diagnosed, the higher the likelihood that the child will respond to conservative therapeutic measures in the form of a set of physical exercises for the eyes, training the eye muscles with special glasses with one glass sealed. However, it often happens that parents, due to their own frivolity, the incompetence of the treating specialists, or for a number of other reasons, do not seek qualified help in a timely manner, and then strabismus can only be treated with a device or surgical treatment, without reacting in any way to the conservative therapy being carried out.
Divergent strabismus in children must be treated as early as possible and, if necessary, radically, because the consequences of this condition can be catastrophic for the child’s body. In the absence of strabismus, the image from both eyes is transmitted to the brain without difficulty, since it is “broadcast” from symmetrical areas of the retina. When a child suffers from strabismus, such processing of the image coming through the optic nerves to the visual center is impossible. In order to cope with such complexity of perception, the child’s brain acts more simply, “turning off” the squinting eye.
Thus, the body of a squinting child is unfamiliar with the concept of a binocular image, because in the cortical part of the visual analyzer the merging of two pictures does not occur. Until the body has adapted, the child constantly sees a “double” picture, and from constant tension he develops headaches, eye pain, nervousness, fatigue, even to the point of physical and mental developmental lag from his peers. When the brain “turns off” the second eye, the child sees a flat image. In this case, the squinting eye sees only if the other one is covered. A condition called “amblyopia” or “lazy eye” occurs, in which visual acuity in the squinting eye progressively decreases.
Types of strabismus
Source: uglaznogo.ru
As already mentioned, strabismus can be a congenital or acquired pathology. Depending on the nature of the deviation of the eyes from the visual axis, the following are distinguished:
- Convergent strabismus (synonymous with esotropia), in which the squinting eye deviates towards the bridge of the nose. Pathology usually appears at an early age. Often occurs with moderate or high farsightedness.
- Divergent strabismus (synonymous with exotropia), in which the squinting eye deviates towards the temple. The cause of this type of strabismus can be moderate or high myopia, especially in early childhood, trauma, infectious diseases, or fear.
- Vertical strabismus, in which the eye squints upward or downward.
- Atypical and combined types of strabismus are rare forms of the disease associated with genetic disorders (such as Down syndrome, Mobius syndrome, Crouzon syndrome, etc.).
Strabismus can be permanent or appear from time to time under certain conditions; only one eye can deviate from the normal position (monolateral strabismus) or both eyes alternately (alternating strabismus).
By origin, experts divide strabismus into two types: paralytic and concomitant. Concomitant strabismus often occurs in individuals with a high degree of farsightedness (predominantly convergent strabismus) or myopia (predominantly divergent strabismus).
With this form of strabismus, both eyes can deviate alternately, while the angle of deviation of the optical axis (deviation amount) remains the same, eye mobility in all directions is preserved.
Important!
Paralytic strabismus can appear at any age; it is usually preceded by trauma, poisoning, or toxicosis. The cause of paralytic strabismus can also be infectious diseases, tumors, hematomas or vascular diseases.
The pathology is one-sided, characterized by restriction or impossibility of movement of the squinting eye towards the altered extraocular muscle. Characteristic signs are double vision, dizziness, forced position of the head when looking at an object (to compensate for double vision).
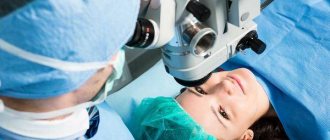
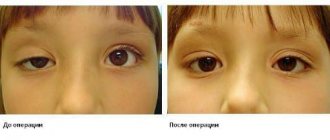
Surgical treatment of strabismus in children
Surgical treatment of strabismus in children is another treatment method successfully practiced at the Svyatoslav Fedorov Children's Medical Center. As a rule, the treatment of strabismus in children with surgery is used when the drug treatment in combination with gymnastics does not bring any effect. Surgical treatment of strabismus in children is the most radical method, however, it is successfully carried out daily by ophthalmologists and microsurgeons at the Children's Center named after. S. Fedorov.
Treatment of strabismus in children with surgery is best performed in preschool age, since 3-6 years is the most favorable age for treatment. The postoperative period will not take a long time, and the operation itself will be tolerated by the child without any difficulties. Before the operation, the child must undergo an examination, during which the surgeon will simulate the future position of the eyes. Surgical treatment of strabismus in children involves weakening or tightening, depending on the type of strabismus, the eye muscle that is involved in the formation of the pathological condition. Complex cases require staged treatment, where surgical interventions are complemented by gymnastics and wearing special glasses.
Surgical treatment of strabismus in children requires hospitalization of the child, but the recovery period after surgery is usually only 7 days. For children, mild local anesthesia is used. Squint correction surgery not only helps the child preserve his vision, but also restore psychological comfort. Take care of your child's health today and help him see the world correctly with the help of highly qualified specialists from the Svyatoslav Fedorov Children's Medical Center!
Treatment
There are more than 20 different types of strabismus. Outwardly, all of them are manifested by deviation of the visual axis from the point of fixation, but in their causative factors and development mechanism, as well as in the depth of the disturbances, they differ greatly from each other. Each type of strabismus requires an individual approach.
Unfortunately, even among doctors there is an opinion that until the age of 6, a child with strabismus does not need to do anything and everything will go away on its own. This is the greatest misconception. Any deviation of the eye at any age should be considered the beginning of the disease.
If no measures are taken, loss of visual acuity may occur, and then treatment will require much more effort and time, and in some cases the changes become irreversible.
Sometimes strabismus is imaginary: due to the wide bridge of the newborn’s nose, parents suspect the presence of this vision defect, but in fact it does not exist; it is just an illusion. In newborns, the eyes are set very close, and the bridge of the nose, due to the peculiarity of their facial skeleton, is wide.
As the facial skeleton develops, the distance between the eyes increases and the width of the bridge of the nose decreases. It is precisely in this case that everything really goes away with age and nothing needs to be corrected, but only a doctor can determine whether it is an imaginary strabismus or a real one.
Any suspicion of a deviation from the norm should alert parents and prompt them to visit a pediatric ophthalmologist as soon as possible. Timing of preventive visits to an ophthalmologist in the first year of a child’s life.
Occlusion and glasses
In children, the ability to concentrate on a specific place with both eyes develops before the 7th year of life. In this case, the technique of image perception of the information received will be processed until approximately the 12th year of life.
If congenital strabismus is present, during which the makings of binocular vision are absent, the main task of doctors will not be to correct strabismus, but to develop in the child the correct ability to visualize the world.
This is carried out in several stages, which are:
- Optical, existing errors in the structure of the eye can be corrected using glasses. However, it is worth understanding that such a method will be useful only in those moments when accommodation is present. If there is already partially accommodative strabismus, surgical intervention is required.
- The pleoptic method makes it possible not only to improve a person’s vision, but also helps to learn how to correctly focus the gaze on individual objects. This method includes several components.
- Treatment with medical devices.
- Occlusion, it can be used not only in the presence of vision problems, but also in their absence. The essence of this method is to put a special bandage on the whole eye and thereby remove its vision. Due to this, the main visual load will fall on the damaged organ, which will result in improved coordination of communication between it and the brain.
The development of strabismus often occurs against the background of farsightedness, in some cases there is hyperopia, so this is always taken into account during treatment.
Hardware
First of all, hardware treatment of strabismus involves the use of a monobinoscope. The principle of operation of such a device is to use light rays to irritate the retina located in the armhole.
To do this, the patient's head is fixed in a stationary state, after which the fundus of the eye is examined, as well as the ability to focus on a separate object is improved.
Based on many different factors, ranging from age to the stage of the disease, different methods can be used to get rid of strabismus:
- Avetisov method. Due to the short period of use, a similar procedure is prescribed to treat strabismus, which has an initial stage in children. The main tool is the LED.
- Using laser light. Most often, domestically produced medical equipment is used for such procedures. Even private clinics use domestic, but modernized devices.
- Various hardware exercises. They are used as one of a set of remedies to cure strabismus. A very common remedy is the synoptophore. It can be used in cases of large strabismus angles in those episodes where it is necessary to use many areas of the pathological eye simultaneously. Used in the presence of sensory strabismus (this can be either convergent or divergent).
- Postoperative hardware treatment. The main role in this treatment is given to lenses, due to which a specific double effect is created in the eyes. It is necessary to consolidate the achieved result.
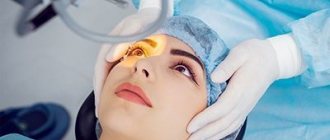
Surgical intervention
Surgery is one of the stages of treatment, the place and time of which depend on the type of strabismus and the depth of damage to the visual system. Before and after surgical treatment, conservative therapeutic measures should be carried out aimed at increasing visual acuity; to restore communication between the eyes and stereoscopic three-dimensional visual perception, this is achieved with the help of special exercises.
Techniques are used to improve the functional state of the visual part of the cerebral cortex, to force the visual cells of the cortex to work in normal mode and thereby ensure correct and clear visual perception. These techniques are stimulating in nature.
Classes are conducted on special devices on an outpatient basis in courses of 2-3 weeks several times a year.
During treatment, at a certain stage, in the presence of high visual acuity, restoration of the ability to merge two images from the left and right eyes into a single visual image, in the presence of eye deviation, surgical intervention is performed on the eye muscles.
The operation is aimed at restoring the correct balance between the muscles that move the eyeballs (oculomotor muscles). It is important to understand that surgery does not replace therapeutic techniques, but solves a specific problem that cannot be solved conservatively.
To decide the timing of surgical intervention, it is important that the patient has sufficient visual acuity. The sooner you put your eyes in a symmetrical position with direct gaze, the better. There are no special age restrictions.
Important!
In case of congenital strabismus, it is important to complete the surgical stage no later than 3 years, with the acquired, depending on the timing of treatment, achieving good visual acuity at the conservative stage and restoring the potential ability to merge images from both eyes into a single visual image.
Surgical treatment tactics are developed depending on the type of strabismus. From a surgical point of view, treating a permanent form of strabismus with a large squint angle, when the eye is significantly deviated, is not very difficult.
The effect of such operations is obvious to the patient. But for surgeons with certain qualifications it will not be difficult. It is difficult to operate on strabismus with unstable and small angles.
Currently, technologies have been developed for making an incision without the use of a cutting device (scissors, scalpel, laser beams). The tissues are not cut, but rather moved apart by a high-frequency stream of radio waves, providing bloodless exposure of the surgical field.
The technique of operations for strabismus is microsurgical; general anesthesia with specific anesthesia is used, which allows you to completely relax the oculomotor muscles. Depending on the volume of the operation, its duration ranges from 20 minutes to one and a half hours.
Surgery to correct strabismus
Strabismus is an ophthalmic pathology in which the focus of one or both eyes is offset from the center due to an imbalance in the muscles that support the eyeball. This problem is far from just aesthetic: the pictures that each eye transmits to the brain can differ significantly with severe strabismus.
Therefore, over time, the visual analyzer begins to ignore the data of the squinting eye, and in addition to strabismus (strabismus), the person also receives amblyopia - a decrease in visual acuity that is not corrected by glasses.
Important
When deciding to undergo surgery for strabismus, you need to know that such a surgical intervention allows you to get rid of the external manifestations of strabismus, but does not always return the ability to see well.
There are two types of operations for strabismus: strengthening and weakening. During weakening surgery, the attachment site of the muscle is changed and it is transplanted further from the cornea. That is, the action of a strong muscle (the one towards which the eye is deviated) weakens.
During augmentation surgery, the muscle is shortened by removing part of it, but the attachment site of the muscle to the eyeball remains the same. That is, the action of the weak, opposite muscle is enhanced.
As a result, such surgical intervention allows you to restore the correct muscle balance, strengthen or weaken one of the muscles that move the eyeball.
The type of operation is determined by the surgeon directly on the operating table, since with such a surgical intervention it is necessary to take into account many features: the angle of strabismus, the location of the muscles in a particular person, the condition of the oculomotor system, the age of the patient.
Typically, several muscles are operated on. Sometimes both eyes are operated on at once; in some types of strabismus, only one eye is operated on. There are cases when an ophthalmic surgeon performs a combined operation on both eyes, both on strong and weak muscles.
Indications
- Age - strabismus surgery is performed for adults at any age, for children - from 6 years old. In some cases, a pediatric ophthalmologist may decide on the need for surgical treatment for severe strabismus at an earlier age.
- Impaired binocular vision (strabismus is the cause of impaired binocular vision).
- Inability to correct strabismus using conservative methods - the doctor must confirm that the problem cannot be solved without surgery.
Elimination of pathology using traditional methods
Source: bezmorshchin.ru
Treatment of strabismus in adults at home is based on the use of traditional medicine recipes. The following remedies are recommended to strengthen the eye muscles:
- Dark dark chocolate with a cocoa content of at least 60% is a tasty and pleasant way to solve the problem of strabismus. Along with eliminating the displacement of the eyeballs, the health of the entire body as a whole is ensured. This pleasant way to strengthen the muscles of the visual organs also includes treating strabismus in children at home. To achieve a positive effect, you need to eat about four pieces of delicious chocolate twice a day, an hour after meals, for a month.
- An infusion of calamus roots, prepared from 250 cm³ of boiling water and 100 g of calamus, is recommended to be taken three times a day 30 minutes before meals. The volume of product used must be at least 80 cm³.
- It is recommended to consume cabbage leaves boiled in water up to 4 times a day, washing them down with the same decoction.
- A decoction of 100 g of rose hips in one liter of water after infusion for five hours, it is recommended to consume one glass before meals. Adding a teaspoon of honey to the drink after straining it will enhance its healing properties.
- An infusion of pine needles is also included in the list of effective remedies for eliminating strabismus, and knowing how to treat it at home, you can achieve a positive result in the shortest possible time. To prepare an effective product, it is recommended to pour boiling water over 100 g of raw material, keep it in a water bath for 30 minutes, and consume the strained infusion one tablespoon after meals. The period of its use is determined by the time to achieve the expected result.
- An infusion of clover leaves, prepared from 12 g of dry crushed raw materials and 500 cm³ of boiling water, is recommended to be consumed after meals at least twice a day.
- A drink made from 5 g of black currant leaves, brewed with boiling water, after straining, is recommended to be consumed at the most convenient time instead of tea.
- It is recommended to drink 500 cm³ of fresh juice made from equal parts of beets, carrots and cucumbers per day.
- A tincture of 500 cm³ of vodka and 100 g of lemongrass after ten days of infusion and daily shaking effectively solves the problem of strabismus. It is recommended to take it with water, to which you need to add 20 drops, twice a day, 30 minutes before meals.
Thus, having the knowledge of how to remove strabismus at home, you can always independently solve the problem of eyeball displacement and avoid irreparable complications.
Convergent strabismus in children
Convergent strabismus in children is often combined with farsightedness, which means it can occur against the background of long-term uncompensated farsightedness. The causes of convergent strabismus in children are determined individually, and for a correct diagnosis, a complete examination of the child’s visual apparatus and nervous system is necessary. Normally, children are born with some farsightedness compared to adults, and 3.0 Diopters, critical for an adult, is the norm for a child. However, some children have visual strength that exceeds this indicator.
In cases where the reading is above three diopters, the child has to make an effort to focus the image normally on the retina, which creates excessive strain on individual eye muscles. Prolonged presence of the muscles of the eyeball in a similar state often entails convergent strabismus in children, and therefore the presence of this refractive error necessarily requires treatment. This type of strabismus is also called accommodative, as it occurs more often by the age of three to five - just at the age when the child masters accommodation, learns to look at pictures, read and focus his gaze on one object in particular for a long time.
Here it should be noted how important it is to teach a child reading hygiene, which becomes a kind of prevention and helps to avoid such a condition as convergent strabismus. Treatment of convergent strabismus in children begins with therapeutic measures, which include long-term training of the eye muscles. The eye muscles are taught to contract and relax at the right time through special exercises, as well as wearing glasses that train the eye muscles.
Gymnastics for strabismus
Source: ozrenii.ru
As already mentioned, to correct the defect at home, you can start doing a special set of exercises.
Correctly performed eye gymnastics will work as follows:
- relaxes the muscles, which allows the eyeballs to move together;
- will force you to focus your gaze on one point;
- will force the eyes to combine two pictures that the individual usually sees separately.
It is believed that if, while doing eye exercises, an individual manages to connect two pictures together, then this is a very good result.
Exercises for kids
If an eye defect is detected in a small child, then parents are obliged to make every effort to help their child. The first rule that mothers and fathers should remember when performing gymnastics with their baby is to teach him to relax his eye muscles as much as possible, focusing his gaze on an object.
Since young children still have little understanding of why eye exercises are needed, all exercises should be presented in a playful way.
Let's consider an effective complex for kids:
- The first exercise is reminiscent of the game “find 10 differences”. To do this, you will need sheets with bright pictures that correspond to the age and interests of the child. The images should be identical, but one of them will be missing some details. The essence of the lesson is that after studying the pictures the child must point out the missing elements;
- For the second task you will need a special board with holes and a string. You can replace the board with a sheet of thick cardboard by making holes in it. Now the child should be given the task of threading the lace through the holes, following a certain sequence. Experts recommend doing the exercise from right to left;
- Take a landscape sheet and draw several squares of equal size on it. In each, draw some simple image. It should be repeated in several squares. Now give the prepared sheet to the child, he must highlight the repeating pairs of images;
- Play policeman with your child: give him a stick that resembles a baton and ask him to wave it in the air, imitating various objects. At the same time, tell the child that his eyes should be focused on the tip of the rod. It is important;
- Ask your child to throw back his head and imagine that there is a fly on his nose, at the very tip. To see an insect, a child must put his eyes together, that is, squint them towards his nose. This is the exercise;
- Ask your child to place their palms over one and the other eye. Now name various objects to the baby, and he must, without opening his eyes, describe the shape of the named thing. For example, you say the word “orange”, the baby should draw an imaginary circle with the help of his eyes, but without opening them.
All parents should know that strabismus is normal in babies under six months of age. But if even after 6 months the baby is mowing, then it’s worth visiting an ophthalmologist.
The doctor will give the necessary recommendations for correcting the defect and tell you in detail about eye exercises. It will be useful and effective for the baby, and will strengthen the muscles.
A set of exercises for adults
Each exercise described below should be performed daily, at least 15 repetitions at a time. The complex will be as follows:
- Raise either hand forward and extend your index finger, focusing your gaze on it. Gradually bring your finger to the bridge of your nose, but you cannot look away. Do the same exercise, moving your finger down and up;
- Using your eyes, draw an infinity sign in the air;
- Move your gaze from objects nearby to things in the distance. For example, first look out the window at the street, and then look at something in the room;
- Take a position with your back to the sun. Cover your healthy eye, for example the left one, with your palm. Now, slowly, without sudden movements or jerks, turn your head to the right side (towards the healthy eye) until you can see the slanting rays of the sun;
- If your left eye is sore, and it looks inward, at the bridge of your nose, then do this exercise. Place your right leg forward, and with the opposite hand begin to reach towards your lower limb. Then, changing the position of your torso, reach your hand towards the sun. Those whose eyes look not to the nose, but to the temple, should put their left leg forward and use their right hand.
Doctors also say that with strabismus it is useful to follow an object that is either moving away or approaching. For example, a table tennis game is suitable for this purpose. Moreover, the patient can not only watch the game, but also participate in the process. There will be no less benefits.
By performing exercises for strabismus, you can improve your condition and, possibly, make the defect less noticeable. The main thing is not to be lazy and do everything carefully. Love yourself and everything will work out, good luck!
Examination for childhood strabismus
Any medical examination, including ophthalmological, begins with the collection of anamnestic information. Parents should be prepared to inform the doctor about how pregnancy and childbirth proceeded, what diseases the child suffered during life, when strabismus was noticed and what its nature was - permanent or episodic, in one eye or both, whether the visible degree of strabismus depends on the external situations, whether the child (if he is of the appropriate age and is able to formulate sensations) complains of headaches, double or blurred vision, dizziness, etc. There will certainly be questions about ophthalmological heredity, about the injuries and infections the child has experienced, about the treatment received at different times and its effectiveness.
As a rule, the first scheduled consultation with an ophthalmologist is scheduled when the child turns 3 months old. After collecting anamnesis, the doctor performs a visual examination: the eyelids, the width and shape of the palpebral fissures, the position and size of the eyeballs are examined. It is necessary to exclude structural anomalies and/or insufficient transparency of the cornea, pupils, lens, vitreous body, and pathology of the fundus. For this purpose, conventional ophthalmoscopic instruments are used. To clarify the angle of strabismus, the Hirschberg method is used: when looking at a bright light bulb, its reflection (reflex) appears on the cornea, which normally falls in the center of the pupil. The degree of strabismus is judged by the shift of the light reflex in one direction or another. The standard pupil width is 3-3.5 millimeters; with convergent strabismus, the reflected ray is shifted to the outer corner of the eye, with divergent strabismus - to the inner, with vertical - down or up.
But for infant patients, it is extremely difficult to establish a final and confirmed diagnosis. The Hirshberg method is the only accessible and more or less reliable method, not counting direct observation of the movement of the eyeballs and the position of the pupils. Equally inaccessible is the exact measurement of refractive indices: pronounced impairments in the acuity of “near” or “far” vision can provoke the development of strabismus in the future, however, in children, an approximate assessment of refraction is possible only using the skiascopic method (“shadow method”, based on the movement of the reflected beam when turning mirrors).
If there are any doubts or suspicions, the ophthalmologist definitely recommends that parents closely monitor the development of ocular motility in the coming weeks; A follow-up consultation is scheduled at 6 months of age. Of course, you shouldn’t neglect these appointments.
In a six-month-old child, eye movements are usually already completely coordinated and adequate to surrounding objects, moving and stationary. Transient infantile strabismus at this age, as a rule, is no longer observed; if signs or at least individual episodes of strabismus remain, a more thorough examination and clarification of the specifics of strabismus (divergent, convergent, vertical; concomitant or paralytic; independent or accompanied by a refractive defect; angles of displacement of the eyeball positions, etc.) is necessary. It is important to understand that strabismus can be caused by a number of reasons that are completely different in nature; in some cases it is an independent problem, in others it is a consequence or symptom of more general diseases.
Thus, with paralysis of one of the muscles responsible for the mobility of the eyeball, turning the eye in the direction of this muscle is impossible or significantly limited. This condition is called paralytic strabismus .
As a rule, paralytic strabismus develops against the background of a disease of the central or peripheral nervous system (such a pathology can be either congenital or acquired); Possible causes also include tumors of muscle tissue, trauma, and infectious processes. Paralytic strabismus is stable and persistent. If it occurs in the first weeks after birth or is congenital, the visual functions of the affected eye cannot fully develop - so-called amblyopia, or “lazy eye syndrome,” is formed. Amblyopia cannot be corrected by glasses or contact lenses; Congenital or infant refractive error of this type may remain forever, despite the best efforts of doctors and parents. If signs of paralytic strabismus (and, as a consequence, amblyopia) appear at the stage of fully formed vision, the prognosis is more optimistic: in many cases it is possible to restore visual characteristics partially or even completely. The need to prevent the development of amblyopia through early diagnosis of paralytic strabismus is one of the most important reasons for constant monitoring of the child’s eye condition, i.e. Preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist should be regular and mandatory.
The degree and nature of eyeball mobility in children can be assessed using a simple technique that is available to parents in normal home conditions. It is enough to sit the child on your lap and hold the head in one position (if the child is older and able to understand the instructions, ask him not to turn), then place some bright or shiny object in the field of view and, moving it, observe the child’s ocular mobility. The “target” should be 30-40 cm, at the height of the baby’s eyes, right in front of the face. The focusing object is smoothly moved towards one ear, then returned to the central axis and the movement is repeated towards the other ear. When the eye is moved to the extreme side, the outer edge of the iris should touch the outer corner of the eye, and when the eye is turned towards the nose, the edge of the iris slightly does not reach the inner corner of the eye - such mobility is normal. If these boundaries are not reached by the iris, you should know that this is a characteristic symptom of paralytic strabismus. In the event that the test is performed quite normatively, but strabismus is nevertheless present, an in-depth examination is required to clarify its specifics and establish a diagnosis, possibly with the involvement of related specialists (pediatric neurologists, endocrinologists, etc.).
There are also cases of so-called false, imaginary strabismus. As a rule, the illusory feeling that the child is squinting a little occurs when there is a “Mongoloid” skin fold in the corner of the eye (epicanthus), the bridge of the nose is too wide, or other individual anatomical features of the structure of the craniofacial structures. Often, “observed” but in reality non-existent strabismus disappears as the child grows, mature tissues form and the relative position of organs.