Most of us know what blood pressure is and why it needs to be controlled. We can also feel when it is high or when its numbers are low. Unfortunately, not everyone can say this about eye pressure, since it is measured quite rarely. After all, it is impossible to do this on your own at home.
Considering that people rarely come to an ophthalmologist for an annual preventive examination, especially if there is no need for it. Consequently, not everyone measures internal ocular pressure (IOP).
What eye pressure is considered normal for glaucoma?
In normal conditions, IOP readings should be in the region of 9-21 mmHg. Art. But even these values are not fixed, since as a result of the influence of a number of factors, a slight deviation from these figures is possible. Thus, ophthalmotonus can change depending on the time of day, with age, in the presence of certain diseases, and also with the season.
Normal intraocular pressure is necessary for the proper functioning of the retina.
The normal eye pressure for glaucoma is practically the same depending on gender and age. A slight increase in ophthalmotonus is observed in older people. Normal intraocular pressure is necessary for the proper functioning of the retina. Pathology is any indicator that is 5 mm Hg. Art. and more deviate from the normal limit. Normal values may also vary depending on how eye pressure is measured. But if the IOP value is more than 25 mm Hg. Art., then you need to urgently visit an ophthalmologist, as this means the beginning of the development of glaucoma.
How to understand the meaning of pneumotonometry results: deciphering the research results
The ophthalmologist interprets tonometry values using a table of standard indicators. Normally, the IOP of an adult is 15-24 mm.
The representativeness (purity) of the result may be influenced by side factors. For example, when the procedure is performed on tired eyes or in the dark. This causes a deviation of 10-20 units, and when such a result is obtained, the procedure is repeated. Therefore, it is necessary to come for the study in the daytime in a relatively healthy state, and the day before, do not overstrain your eyes and do not use specific substances.
If the result significantly deviates from normal indicators, and concomitant negative symptoms are observed, they speak of pathological conditions.
- High values may indicate glaucoma, the development of which is typical for patients older than middle age.
- Underestimated indicators, as a rule, indicate incorrect conduct of the study. Then the test is repeated, taking a control sample.
Due to the fact that the procedure is considered not accurate enough, it is usually prescribed in combination with other diagnostic tests. Pneumotonometry can tell the specialist what additional tests need to be prescribed for the patient, as well as identify the prerequisites for the development of the disease.
How to regulate blood pressure
In a healthy person, eye pressure should average 15-16 mmHg. Art. But sometimes, under the influence of a number of factors, intraocular fluid stagnates, resulting in increased pressure on the walls of the eyeball. The more advanced the pathological process, the greater the tension and the worse the vision. If the disease is at the beginning of its development, then IOP regulation occurs by instilling special eye drops.
How to reduce eye pressure with glaucoma
For people with glaucoma, Xalatan, Pilocarpine or Betaxolol drops are usually recommended. In more advanced cases, in addition to drops, adrenomimetics, osmotics, as well as intravenous administration of Urea or Mannitol are prescribed. In addition to drug therapy, to regulate IOP it is necessary to change lifestyle, wear special glasses and do special eye exercises. Sometimes a doctor may recommend a herb that restores blood pressure. In the most difficult cases, surgery is performed.
Treatment of intraocular pressure
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to avoid various complications of increased and decreased eye pressure - atrophy of eye tissue, glaucoma, etc. Doctors strongly recommend measuring eye pressure at least once every three years (for patients over 40 years old).
Treatment of ophthalmotonus depends on the causes that provoked it. If the cause is a certain disease, then only if it is completely cured can the eye pressure be brought back to normal. If the cause is any eye pathology, then an ophthalmologist will deal with the treatment, prescribing the necessary eye drops.
For glaucoma, the doctor prescribes medications designed to reduce eye pressure (pilocarpine, travaprost, Fotil, etc.). Often, during treatment, the ophthalmologist changes the medications used.
When diagnosing inflammatory eye diseases, antibacterial drops are prescribed.
If the cause of the increase in ophthalmotonus was the computer, the so-called. computer vision syndrome, then the doctor prescribes drops that moisturize the eyes (Visine, Ophtolic, etc.). They relieve dryness and fatigue from the eyes. Independent use of such drugs is allowed.
Additionally, eye gymnastics and vitamins necessary for vision are prescribed (blueberry forte, complivit, okuvait, ophthalmo, etc.).
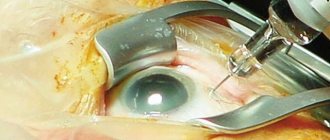
If treatment with medications does not give positive dynamics, then they resort to laser pressure correction or microsurgery.
Drops for eye pressure
Such drugs quite effectively normalize intraocular pressure. They nourish the tissues of the entire eye and remove excess fluid from the eyeball.
In this article you will find out the causes and methods of treatment for pain in the eyes.
Here you will find out what symptoms appear with stye of the eye.
Are you worried about nervous eye tics? Find out the main reasons -
In general, IOP drops are divided into several types:
- Prostaglandins – increase the discharge of intraocular fluid (Tafluprost, Xalatan, Travatan). They are quite effective: after instillation, blood pressure noticeably decreases within a couple of hours. Unfortunately, they also have side effects: the color of the iris changes, redness of the eyes, and rapid growth of eyelashes are observed.
- Cholinomimetics – contract the eye muscles and constrict the pupil, which significantly increases the amount of outflow of intraocular fluid (Carbocholine, Pilokartin, etc.). They also have side effects: the pupil becomes narrow, which significantly limits the visual field, and also provokes pain in the temples, eyebrows and forehead.
- Beta blockers are designed to reduce the amount of fluid produced in the eyeball. The action begins half an hour after instillation (okumed, okumol, timolol, okupress, arutimol, etc.). Side effects of these drugs manifest themselves in the form of: bronchospasm, decreased heart contractions. But there are beta blockers such as Betoptik-s and Betoptik, which have a much less pronounced effect on the heart and respiratory organs.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - designed to reduce the amount of intraocular fluid produced (Trusopt, Azopt, etc.). Such medications do not have a negative effect on the functioning of the heart and respiratory system, but patients with kidney diseases should use them with extreme caution and only as prescribed by a doctor.
Drug treatment of intraocular pressure can be supplemented with traditional medicine. She offers many different decoctions, compresses, lotions and infusions. The main thing is not to forget about eye hygiene and the treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Problems with eye pressure can lead to serious vision problems or even blindness. Therefore, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist in a timely manner at the slightest deviation in the functioning of the visual organs. Timely treatment and modern diagnostic methods will help return vision to normal.
Why is high blood pressure dangerous?
Increased eye pressure is a dangerous condition that disrupts the structure of the visual organs and impairs their functioning, negatively affecting vision. In the absence of adequate therapy, as glaucoma develops, the pressure becomes higher and higher, and the quality of vision becomes worse, which ultimately provokes the development of such serious consequences:
- acute migraines;
- nausea and vomiting;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- narrowing of the field of view.
If ophthalmotonus is not stabilized in time, the optic nerve may die, causing complete blindness.
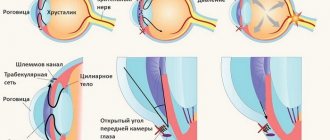
How does glaucoma develop?
Glaucoma, which occurs as a result of increased ophthalmotonus, has its own standard development pattern. It consists of the following main stages in the development of this disease:
- the first stage – the outflow of aqueous humor from the eyeball (namely from its cavity) worsens;
- the second stage - ophthalmotonus increases to a level above tolerable (that is, above the established standards);
- the third stage – the blood circulation processes in the eye tissues are disrupted;
- fourth stage – hypoxia develops, which is expressed in a lack of oxygen, followed by tissue ischemia in the area where the optic nerve exits the eye;
- the fifth stage is compression of the nerve fibers, called compression in the place where they exit the eyeball (and this can lead not only to improper functioning, but also to their death);
- sixth stage - dystrophy begins to develop, followed by destruction and atrophy of the optic fibers;
- the seventh stage is the disintegration of maternal retinal ganglion cells;
- the eighth stage – doctors ascertain optical neuropathy due to glaucoma;
- the ninth stage is the death of the optic nerve.
At various stages of glaucoma development, the nerve fibers of the optic nerve gradually atrophy. But there remains a part of these nerve fibers that can be in a state of “sleep” - parabiosis. They can be restored if effective treatment is started in a timely manner.
IOP during the development of glaucoma
Glaucoma of the eye is an ophthalmological disease accompanied by increased eye pressure. IOP indicators may differ depending on the stage of the pathological process:
- Initial stage. There are no symptoms, IOP is 22-26 mm Hg. Art.
- Second degree. Visual functions are impaired, the viewing angle decreases, IOP is 27-33 mm Hg. Art.
- Advanced stage. Fluid stagnation occurs, causing severe visual impairment. IOP indicators are no more than 35 mm Hg. Art.
- Final stage. At this stage, immediate surgical intervention is necessary. IOP exceeds 35 mmHg. Art.
Fluctuations in intraocular pressure are acceptable, but only by 3 units.
Acute increase in IOP
Typically, intraocular pressure during glaucoma rises gradually, and no sharp deterioration in vision is observed. But in the acute form of the pathology, a sharp jump in indicators is possible, which can be caused by the following factors:
- oxygen deficiency of the optic nerve;
- drinking excessive amounts of water;
- ocular circulatory disorders;
- severe stressful situation;
- long, identical work with the head tilted;
- excessive physical or psycho-emotional stress;
- being in the dark for a long time, when you have to strain your eyes, trying to see something.
A sudden jump in IOP can occur during surgery, accompanied by an increase in pupil size. In advanced forms of glaucoma, these factors can provoke an acute increase in pressure, accompanied by severe pain and loss of vision. The critical level is 60 mmHg. Art.
Read in a separate article: Open-angle glaucoma of 1 and 2 degrees: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Forms of glaucoma
Primary (chronic) open-angle glaucoma is the most common form of glaucoma. Initially, the disease is asymptomatic; only in an advanced stage can loss of visual fields be detected. Treatment begins with topical medications (eye drops), then, depending on the general condition of the patient and the side effects of the drugs, oral medications, laser surgery, or fistulizing surgery may be necessary.
Angle-closure glaucoma usually develops with farsightedness. Without treatment, an acute attack of glaucoma can lead to blindness due to severe damage to the optic nerve. The primary goal of treatment is to reduce intraocular pressure as quickly as possible; in this situation, immediate contact with an ophthalmologist is required.
Causes of IOP violation
If intraocular pressure readings deviate from the norm, then the causes of this pathological phenomenon may be different. Increased ophthalmotonus (ocular hypertension) is a common phenomenon that is mainly observed in elderly people suffering from the following diseases:
- chemical poisoning;
- VSD;
- thyroid dysfunction;;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- hypertensive crisis;
- heart defects, heart failure;
- ophthalmological diseases;
- obesity.
The following factors can provoke a decrease in eye pressure:
- diabetes;
- liver failure;
- pathologies of an infectious nature;
- inflammation of the eyeball;
- retinal detachment;
- low blood pressure;
- damage to the eyeball.
Ocular hypotension can develop due to complications after surgery on the organs of vision. If a deviation from the norm has been identified, then the first step is to determine the cause of this pathological phenomenon, and then select treatment.
Symptoms of high IOP
An increase in intraocular pressure occurs due to a violation of the outflow of fluid inside the eye and increased production of ocular secretion. This causes deformation of blood vessels and optic nerve atrophy. Glaucoma is always asymptomatic at first, but as the pathology develops, the following symptoms begin to appear:
- feeling of pain;
- hyperemia of the eye shell;
- feeling of discomfort;
- blurred image;
- pain in the area of the eyes, eyebrows, temples;
- fatigue, heaviness in the eyes in the evening;
- light halos when looking at the light;
- decreased visual acuity;
- poor visibility at night;
- decreasing viewing angle.
With glaucoma accompanied by increased IOP, the patient quickly gets tired and complains of discomfort in the eyes even after a short period of work at the computer. Sometimes there are sudden attacks of tearing.
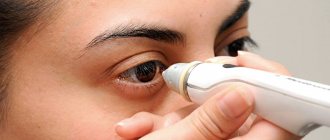
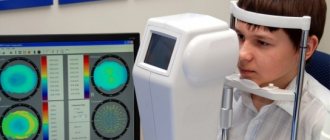
IOP measurement methods
At first, the pathological process is often asymptomatic, which makes timely diagnosis of the problem difficult. Therefore, it is recommended to measure the pressure inside the eye at least once a year for every person over 40 years of age. To diagnose glaucoma, doctors usually use the following methods to measure IOP:
- Palpation. A highly trained ophthalmologist can determine eye pressure by palpating through the eyelid. If it is increased, then the density of the eyeball increases, and if it is decreased, it decreases.
- Tonometry according to Maklakov . The cornea of the eye is treated with an antiseptic, after which a small weight weighing 5-10 grams is placed on the anesthetized cornea. After a few seconds, the weight is removed and transferred to a special sheet of paper, where an imprint appears indicating the amount of ophthalmotonus.
- Pneumotonometry. The essence of this method is similar to the principle of tonometry according to Maklakov, only instead of a load, the cornea is exposed to a stream of compressed air. But the accuracy of such measurements is low.
- Electronography. This is the most modern method of measuring IOP, in which there is no effect on the cornea. With the help of special equipment, the outflow of intraocular fluid is stimulated and accelerated, during which ophthalmotonus is assessed and abnormalities are diagnosed.
When measuring ophthalmotonus, one should take into account the fact that IOP changes throughout the day. In the morning its value will be highest, and then throughout the day the pressure decreases, reaching minimum levels at night.
After the level of eye pressure has been identified, the nature and stage of the pathology is determined.
How to reduce eye pressure without using drops
IOP is measured in several ways:
- Finger tonometry. This is the simplest technique that does not require special tools. Most often used in emergency situations, such as a traffic accident. The measurement is carried out by a qualified doctor. The specialist, by pressing his fingers on the patient’s closed eyelids, determines the density of the eyeballs and judges by his own feelings whether the pressure is increased or decreased.
- Maklakov's technique. This method is more common than others. The pressure measurement procedure is carried out using a special weight. The doctor instills pain-relieving drops into the patient and then places this weight on the eye. By the deflection of the eyeball, the specialist judges the increase in pressure.
- Goldman's technique. To measure IOP using this method, 2 instruments are required - a special slit lamp and an ophthalmic probe. Before the procedure begins, the patient is instilled with anesthetic drops, then the doctor carries out the necessary manipulations with the instruments and analyzes the information received.
- Impression tonometry. An eye tonometer is used to measure intraocular pressure, so the procedure is performed in a hospital setting. The tonometer operates in automatic mode. All measurements are visible on the monitor. This method is most effective when examining patients in whom elevated IOP is suspected.
- Pneumotonometry. This is the most painless method. The examination is carried out using a special tonometer that does not come into contact with the eye. The compressed air released by the device hits the cornea and deforms it. The extent of this deformation determines how high or low the pressure is.
The doctor is responsible for choosing a method for measuring blood pressure. The specialist takes into account the patient’s health status, individual characteristics of the body and the technical equipment of the medical institution. If a woman’s eye pressure is not normal at the age of 55, the doctor continues the examination to identify the cause of this condition and clarify the diagnosis.
Both low and high scores are considered a deviation from the norm. An increase in eye pressure in women after 50 years of age is observed much more often than a decrease.
Increased IOP is divided into 3 types:
- Transistor. With it, a deviation from normal indicators is observed for a short time. In this case, there is no need for treatment.
- Labile. With it, an abrupt IOP is observed, i.e. It then increases, then suddenly becomes normal. This does not happen once, but regularly.
- Stable. Constant high blood pressure is the main symptom of existing glaucoma or its precursor.
When IOP increases, the patient complains of pain in the eyes and headache. His field of vision is reduced, which also worsens sharply. A person also experiences other unpleasant sensations: midges flash before the eyes or multi-colored circles appear, but more often these symptoms are present simultaneously.
A decrease in IOP is observed in people suffering from low blood pressure. The development of infectious and inflammatory diseases, retinal detachment, endocrine and kidney diseases are also the cause of a downward deviation of the pressure inside the eyes.
A person with low IOP complains of eye pain. They become red, severe dryness is felt, and irritation appears. There is often a feeling that there is something foreign in the eyes that is interfering with vision.
A patient who is at risk for IOP should visit a doctor 1-2 times a year in order to notice the development of the disease in time.
The reasons for deviation of IOP from normal in women over sixty years of age are as follows:
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels cause an increase not only in blood pressure, but also in the eye;
- complications developing after serious illnesses;
- stress, psycho-emotional stress;
- increased physical and mental stress;
- farsightedness and atherosclerosis, incl. in the anamnesis.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor finds out the causes of the pathology. If the deviation from the norm was caused by some kind of disease, then it must first be cured.
IOP therapy begins with drugs produced in the form of drops. They are instilled into the eyes, as a result of which the production of intraocular fluid is reduced and its outflow is accelerated. Such medications include Timolol, Fotil, Pilocarpine, Betoptik. They are used under the supervision of a physician.
Other drugs are also prescribed in combination with drops:
- Omega-3 fatty acids have a positive effect on the condition of the retina and also help normalize blood pressure;
- Diuretics, having the ability to remove unnecessary fluid from the body, promote the outflow of intraocular fluid.
DETAILS: Which suppositories for hemorrhoids are best for men - Website about hemorrhoids
Traditional medicine also offers recipes for preparing home remedies that can normalize intraocular pressure. A good remedy is an infusion prepared from wild pear shoots (20 g), nettle (10 g), sleep herb (5 g) and boiling water (200 ml). The ingredients are mixed and infused for 15 minutes.
Traditional treatment involves the use of natural ingredients, but it can also cause harm, so before starting the procedure you should consult a doctor.
Giving up bad habits, healthy, full sleep, proper nutrition, and an active lifestyle will help prevent high blood pressure. We must try to avoid stress and monitor our psycho-emotional state, avoid physical and mental overstrain, sit less at the computer and limit watching television programs.
It should be remembered that it is easier to treat a disease that is in the initial stages of development, so when the first unpleasant symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
Glaucoma (in translation from Greek - “azure”, “color of sea water”) is a severe damage to the organ of vision, which received its name due to the greenish color that the dilated and motionless pupil acquires in the stage of an acute attack of the disease. This is also where the second name of this pathology comes from – “green cataract”.
Today, glaucoma is understood as a chronic eye disease characterized by a constant or periodic increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) with the development of trophic disorders in the outflow tract of intraocular fluid, in the retina and in the optic nerve, which lead to the appearance of typical defects in the visual field and the development of a marginal depression of the optic disc nerve.
Features and symptoms of glaucoma:
- Increased intraocular pressure;
- A characteristic lesion of the optic nerve fibers is glaucomatous optic neuropathy, which leads to its atrophy.
What are the most common causes and symptoms of low and high intraocular pressure?
One of the main preventive measures is regular visits to the ophthalmologist, who will measure eye pressure.
Normally, intraocular pressure ranges from 18 to 30 mmHg. Art. The highest numbers are recorded in the morning, after waking up. This is due to a long stay in a horizontal position and the predominance of the parasympathetic nervous system. In the evening, the readings decrease, the difference can be up to 2 mm Hg. Art.
This figure is the same for children, adults - women and men under 40 years of age.
- With age, the indicators decrease; after 40, the normal pressure is 10-22 mm Hg. Art.;
- After 50-60 to 70 years, ophthalmologists consider normal pressure to be 22-25 mm Hg. Art.;
- After 70, a slight increase is allowed, up to 23–26 mm, but the older a person gets, the more carefully the indicators need to be monitored and undergo a preventive examination at least once every six months. High blood pressure may indicate developing glaucoma.
The reasons for increased intraocular pressure may be:
- Arterial hypertension and increased intracranial pressure;
- Eye fatigue after working at the computer for a long time, when performing small precise actions;
- Stress, excessive psychological tension;
- Hormonal disorders, endocrine diseases (thyroid dysfunction);
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system and kidneys;
- Menopause;
- Intoxication with chemicals and drugs.
An increase in intraocular pressure can serve as a secondary symptom of malignant neoplasms that compress the eye from the inside and disrupt the inflow and outflow of fluid; inflammation and eye injuries.
See also on the blog: Vitamins for the eyes: a list of drugs to improve vision
However, the main cause of constantly increased intraocular pressure is glaucoma, as a result of which vision is greatly reduced, up to complete blindness.
Symptoms of increased ophthalmotonus:
- Headache, most often localized in the temple area;
- Steadily progressive decrease in visual acuity;
- Bright spots, concentric circles, dots and spots before the eyes;
- Impaired night vision;
- Reduction of visual angle.
A decrease in intraocular pressure is observed with:
- Reducing blood pressure;
- Injuries and damage to the eyes;
- Inflammatory eye diseases;
- Retinal detachment;
- General dehydration of the body;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Serious liver pathologies.
Age is not the only cause of ocular hypertension (increased IOP). The pathological condition is caused by:
- eye fatigue due to regular eye strain;
- atherosclerotic changes, arterial hypertension, VSD;
- stressful situations that last for a long time, psycho-emotional overload;
- sports exercises associated with strength physical activity;
- medications used locally;
- frequent consumption of drinks that contain caffeine;
- anatomical structure of the eye and heredity;
- frequent intoxication of the body, traumatic brain injury, diabetes of any type;
- inflammation occurring in the organs of vision.
Prevention of glaucoma
You can prevent an increase in intraocular pressure and the development of ocular glaucoma if you follow the following preventive measures:
- limit your time working at the computer;
- eat properly, balanced;
- stop drinking, smoking;
- avoid physical or emotional stress;
- drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- do eye exercises regularly;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- prevent eye fatigue;
- do not read or work at the computer in the dark.
An important point in the prevention of glaucoma is periodic visits to an ophthalmologist, regular measurement of intraocular pressure, as well as timely treatment of ophthalmological pathologies.
Author of the article: Kvasha Anastasia Pavlovna, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
Prevention of eye pressure abnormalities
A lowered head position increases IOP, so avoid such positions. When cleaning, use a mop, when working in the garden, use gardening tools, and when sleeping, use a high pillow.
Normal pressure inside the eye is promoted by following general recommendations:
- Fortified food. Reduce your consumption of sweets, salty foods, tea, coffee, and alcoholic beverages.
- Walks in the open air.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Avoid heavy physical activity.
- Reducing the time spent behind the monitor.
- Performing eye exercises while the organ of vision is working hard.
- Visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year.
- Treatment of chronic diseases.
If your eyes hurt from high blood pressure, contact an ophthalmologist immediately. A single increase in IOP is not dangerous. A persistent increase is a sign of glaucoma and treatment is required to prevent vision loss. The doctor will detect changes in the fundus in the early stages and select medications that you can use at home.
Tell us about your experience in the comments. Share what treatments helped you. Share the article with your friends. Be healthy.
The main ways to prevent deviations in eye pressure:
- Daily exercise for the eyes.
- Regular exercise.
- Quality rest.
- Complete nutrition.
- Taking vitamin complexes.
- It is necessary to rest your eyes and not strain your eyesight too much.
- Moderate consumption of drinks with high caffeine content.
- Complete abstinence from alcohol.
Ophthalmologist
Doctor with more than ten years of experience. Provides treatment for eye diseases such as myopia, astigmatism, blepharitis, retinal degeneration. Also provides assistance in removing a foreign body from the eye.