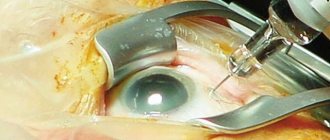
Pneumotonometry is a non-contact technique for determining the level of intraocular pressure. The method is based on the principle of directing a dosed air flow onto the surface of the open eye. Depending on the degree of corneal deformation, the level of intraocular pressure in mmHg is determined.
With non-contact tonometry, 16-21 mm Hg is considered normal. An important advantage of the technique is its non-contact nature, resulting in virtually no risk of infection of the eye or injury to its surface.
The disadvantage of pneumotonometry is the accuracy of the measurement. The amount of pressure may be influenced by individual anatomical features, including the thickness and elasticity of the cornea. Also, if the eye muscles are tense during the pressure measurement process, the resulting value of intraocular pressure can increase. In this regard, when determining an abnormal level of intraocular pressure during pneumotonometry, it is recommended to re-examine the patient using the Maklakov technique.
Concept of IOP
Intraocular pressure is the force with which the eyeball exerts force on the walls of the visual organ. This force normally regulates the amount of necessary nutrients and creates the correct shape of the eye.
The following factors influence pressure indicators:
- The degree of filling of the capillaries, which are located in the choroid of the ciliary body, and their sensitivity.
- Tone of the cornea and sclera.
- Pupil dilation.
- The activity of secretion of internal moisture and its outflow.
If vision is not impaired, mutual and clear regulation of these elements can be observed. A slight fluctuation in pressure in the eyes throughout the day is considered normal. Vascular and muscle tone is usually higher in the morning. However, the observed fluctuations are not too significant; they do not affect a person’s well-being.
When IOP changes in adults or pediatric patients under the influence of negative factors, functional impairment of the eyes occurs, which leads to the development of serious diseases. Pressure surges are the result of pathological changes in the visual apparatus, disruption of the functioning of other systems and organs.
Important! The normal level of pressure in the eyes does not depend on age-related changes. An average is considered to be an indicator ranging from 10 to 25 mm Hg. Art., it all depends on the testing apparatus.
In what cases is non-contact eye tonometry necessary?
This method is based on the reaction of the cornea of the eye. Air pressure is created on it. Non-contact tonometry is carried out only by specialists - an optometrist or ophthalmologist. Because this method is painless, there is no need to use local anesthetic drops during the procedure.
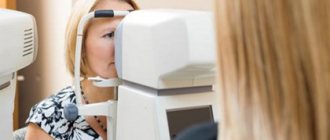
Non-contact ocular tonometry is a quick and simple process for measuring eye pressure. First, the patient places his chin on a special stand and looks into the slit lamp. A doctor sits in front of him and shines a bright light. Using special equipment, he delivers a small air blow to the patient's eye.
If necessary, the doctor can repeat this procedure several times for each eye.
Non-contact tonometry is often used to check intraocular pressure in children and LASIK patients. It should be recalled that this method has no complications and is easily tolerated by patients.
This procedure is prescribed in the following situations:
- for disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, cardiovascular diseases;
- retinal detachment;
- the appearance of complications in the eyes after surgical interventions;
- glaucoma.
Even in the absence of obvious vision pathologies, ophthalmologists advise all people after 40 years to undergo tonometry. At this age, irreversible atrophic changes begin to occur in the ocular structures, which can lead to the development of glaucoma. This risk is especially high in people with a high degree of myopia.
This is a safe and modern way to study the visual organs, with the help of which IOP indicators are determined. The process eliminates the risk of damage to eye tissue and accidental infection of the mucous membrane. There is also no need for anesthesia or coloring solutions. This method is suitable for people with highly sensitive eyes, children and allergy sufferers.
The non-contact tonometry procedure is carried out as follows: portions of air of a certain strength are directed to the patient’s eye. Under its influence, applanation (or flattening) of the cornea occurs - it bends slightly inward, but this is counteracted by intraocular pressure. Sensors in the tonometer record the degree of deflection of the cornea.
It is on the basis of these data that the value of ophthalmotonus is calculated. If the production and outflow of intraocular fluid are in balance, then ophthalmotonus is considered normal. However, when there is a failure in the outflow, the amount of fluid begins to increase, and accordingly, the pressure inside the eyeball increases. This is the first and obvious sign of glaucoma, although sometimes an imbalance can be observed in other pathological processes in the eyes or body.
Methods for determining IOP
During an eye examination, eye tonometry is usually used. This procedure involves detecting elasticity in the eyeball, namely: determining the degree of its deformation under the influence of an external factor created by a tonometer.
It is customary to distinguish two ways to change the corneal shape:
- Applanation, which involves flattening.
- Impression carried out by indentation.
Tonometers known and used in ophthalmology for determining IOP are usually divided into impression and applanation. The first device of the impression type appeared in 1862. Graefe is considered its creator, but the device itself was not entirely accurate, difficult to use and quite crude.
The Schiotz tonometer turned out to be improved and quickly found wide application. As for the applanation technique, it appeared with the creation of the Maklakov device in 1884.
Eye pressure is measured in several ways, including:
- The palpation method is usually called indicative.
- Contactless.
- Contact, during which a tonometer is used that does not touch the organ being examined.
Why is IOP measured?
IOP measurement is a mandatory procedure that every patient undergoes with suspected certain ophthalmological diseases, for example, glaucoma, retinal detachment, uveitis. Thanks to an examination using a tonometer, the doctor receives the necessary information about the condition of the eyes, which gives him the opportunity to establish an accurate diagnosis and subsequently monitor during treatment.
An increase or decrease in IOP occurs as a result of an imbalance in the production and removal of intraocular fluid from the organs of vision.
Such violations can be caused by the following factors:
- Clogging of channels intended for drainage of liquid.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Damage to the eyeball.
The most severe and common ophthalmological disease is glaucoma, in which, due to increased pressure, the eyeball begins to put strong pressure on the optic nerve. This causes disruption of its function or complete death. It is impossible to restore a damaged optic nerve using even the most modern treatment methods. In some forms of glaucoma, a decrease in IOP is observed, which can also lead to the development of blindness.
However, timely detection of pathology and the use of special drugs or surgery can prevent the development of the pathological process. That is why, if a patient develops suspicious symptoms, it is very important to undergo a thorough examination of the visual organs, which must include IOP measurement.
Features of the palpation method
During this examination, an approximate assessment of the condition of the visual apparatus is established. The patient takes a sitting position, with closed eyelids, looking down.
The ophthalmologist places his fingers on the upper eyelid and presses lightly on it. This determines the approximate density of the eyeball. When it is soft, the condition is normal; with strong density and hardness, we can talk about IOP. The compliance of the sclera indicates the level of pressure. The result is announced using the Bowman three-point system.
Important! This method is applicable in cases where it is impossible to use instrumental measurements, for example, after surgery as a result of injury. In any other case, ocular tonometry is indicated.
Methodology for performing pneumotonometry
The duration of the procedure is only a few seconds. It is carried out in an automated mode. To do this, the head of the subject is fixed in a special apparatus, while the patient must keep his eyes wide open and fix his gaze on the burning point. Air is supplied from the pressure measuring device, which is felt as popping. As a result, the shape of the cornea changes, which is recorded in the computer. After processing the information received, the program produces survey data in the form of a printout.
Features of the applanation method
A striking example of such an examination will be a device for measuring eye pressure according to Maklakov. The tonometer is accurate and extremely easy to use; its undeniable advantage is its affordable price. Among the disadvantages, it is necessary to note the likelihood of infection of the diseased eye, since the device part comes into contact with it.
The principle of the described examination is to use weights that differ in weight. The device is presented in the form of a metal cylinder, hollow inside. The edges of the tonometer are equipped with frosted glass (special polished plates with a diameter of 1 mm).
The examination of the visual apparatus is as follows:
- Parts of the product that will come into contact with the eye are disinfected, after which a small layer of dye is applied to them using a stamp. Excess paint is removed.
- The patient is in a horizontal position, the doctor is located at his head. Next, an anesthetic, usually a solution of Dicaine, is instilled into the conjunctival canal. The procedure is performed in two approaches with an interval of several minutes. After this, the doctor carefully spreads the eyelids, and a weight of 10 g is placed on the cornea. A separate procedure is carried out with each eye.
- The weight has an effect on the cornea, which flattens slightly. On the device, at the moment of contact with the body, the coloring substance is erased, accordingly, a white imprint in the form of a disk is created. The resulting print is transferred to a sheet of paper pre-treated with alcohol. The next step is to measure the diameter of the spot with a ruler with mm Hg divisions. Art. Low ophthalmotonus is indicated by the softness of the eyeball (large contact area).
- At the final stage of measurement, the eyes are treated with an antiseptic drug to prevent the possibility of infection.
Important! Determining IOP in this way is more accurate compared to the finger method. The pressure norm should not go beyond the intervals of 18 - 25 mm Hg. Art.
Eye tonometry: two main methods
In modern ophthalmology, intraocular pressure is measured contact and non-contact. The first method, the earlier one, is contact, which is carried out using local anesthesia and a special dye. In this case, the so-called Schiotz impression tonometer or Maklakov and Goldman applanation devices are used.
- pathological condition of the cornea after ophthalmic surgery;
- eye diseases of bacteriological or viral etiology;
- high myopia;
- traumatic damage to the eye shell.
Contact tonometry is also carried out for children from 3 years of age or for overly restless children aged 4-6 years. They are put into deep physiological sleep, which allows the procedure to be carried out correctly. Before the examination, the doctor can also use the finger method for a preliminary assessment: he alternately presses the upper eyelid with his fingertips, thus determining the strength of the eyeball tension.
Non-contact tonometry is the most advanced way to calculate intraocular pressure in humans. It is based on the rate and degree of change in the surface of the cornea in response to air flow directed at it. In this case, there is no direct contact with the tissues of the eyes. The method is the safest, eliminating the risk of accidental eye infection.
Maklakov method
Tonometry according to Maklakov is the most common method of measuring IOP in the medical practice of Russian doctors.
How does the procedure work?
Before tonometry is performed, the patient must lie on his back, after which the nurse instills anesthetic drops. The procedure is carried out using a small metal cylinder, onto the contact surfaces of which a thin layer of dye is applied. Then the tonometer, alternately with each side, is vertically installed on the central part of the cornea. The resulting prints are transferred to paper moistened with alcohol, which are subsequently measured with a special ruler.
You should visit an ophthalmologist for preventive purposes annually. At the same time, measuring intraocular pressure in Smolensk is necessary for patients:
- over 40 years old;
- with diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- those suffering from endocrine pathology;
- having neurological diseases;
- with developmental anomalies of the eyeball;
- having blood relatives suffering from glaucoma.
For patients who have already been diagnosed with elevated IOP, repeated measurements of intraocular pressure are performed quarterly.
An unscheduled inspection will be needed if:
- visual acuity decreased;
- fields of vision narrowed;
- headache appeared, accompanied by pain in the eyes;
- the eye looks sunken compared to the other;
- the pupil is deformed.
– non-contact tonometry;
– finger tonometry;
– tonometry according to Maklakov.
Some tonometry methods are quite simple, while others, in turn, require the use of expensive equipment.
Ocular tonometry according to Maklakov is considered a more accurate method of measuring eye pressure. But often you have to use other methods. For example, in case of a large flow of patients or in cases where direct contact with the eye is prohibited due to indications, non-contact eye tonometry is performed.
Intraocular pressure is measured by several methods.
- Palpation through the eyelids makes it possible to estimate the pressure approximately and understand whether there are currently significant deviations from the norm. The result of palpation is determined depending on the tone according to the degree of hardness of the eye.
- More accurate results using the instrumental method. There are several fundamentally different types of tonometers that use contact and non-contact methods for measuring intraocular pressure. Any hardware tonometry uses the principle of the relationship between the force applied to deform the cornea by pressing and V.D. The difference lies in the methods of applying force and the way results are measured.
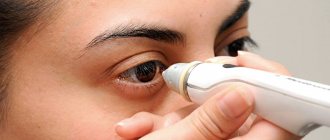
Non-contact tonometry is a computer measurement, the principle of which is based on the reaction of the cornea under the influence of air flow. This takes into account the degree and rate of change in the cornea. The non-contact method is the most gentle and non-traumatic, there is no direct contact with the eye and no painful effect for the patient, and there is no risk of infection. The procedure takes a few seconds, no preparation of the patient is required, and he does not feel any discomfort.
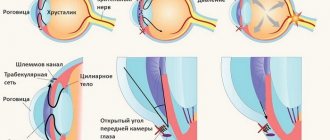
Applanation tonometry is a measurement of intraocular pressure based on the Amber-Fick law. According to this law, internal pressure is defined as the ratio of external force and the size of the area of influence.
Impression tonometry - indentation of the cornea with a rod with a rounded end. The method is mainly used for increased V.D. and for measuring pressure when the surface of the cornea is curved, when it is impossible to capture a large area.
Dynamic contour tonometry is a contact tonometry method based on measuring intraocular pressure along the contour of the cornea. A probe with an integrated pressure sensor based on integral sensitive elements made of single crystals is placed in the central part of the cornea. The force of pressure of the probe on the cornea is constant. The sensor records eye resistance and receives up to 100 results/sec. Based on these data, the measurement result is displayed.
Normal true intraocular pressure is approx. 16.2 mmHg Art. Readings from 10 to 21 are not considered a deviation from the norm. During the day, its level changes slightly, after waking up it is higher, and then begins to decrease slightly. Daily fluctuations can range from 1 to 5 mmHg.
Maklakov’s tonometers do not show true V.D., but the so-called tonometric one. The readings are somewhat inflated due to the squeezing out of a certain amount of fluid from the eye chambers. Therefore, the norm for tonometric pressure according to the Maklakov method was adopted in the range of 12-25 mmHg.
It is also necessary to take into account when measuring V.d. the fact that each method and type of instrument produces slightly different data. It makes no sense to compare readings - this is a feature of each measurement method. Therefore, if it is necessary to monitor the dynamics of the patient’s eye condition, then the check must be carried out using the same method. Only in this case can we compare the results and draw a conclusion. In particular, this is very important for patients with glaucoma.
The results of measurements using non-invasive methods are influenced by the thickness of the cornea. With a dense and thick cornea, the likelihood increases that the data obtained will be slightly higher than the true V.D. With a thin cornea, the opposite picture is observed.
Eye tonometry is a general concept that includes several diagnostic techniques carried out to measure the pressure directly inside the eyeball. Using a special device, a tonometer, changes occurring inside the eye when exposed to its cornea are studied.
In a healthy eye, no deformation of the eye is observed. At the same time, deviation of the device in one direction or another indicates the presence of some pathology of the organ of vision. This procedure is performed to prevent eye diseases such as glaucoma, a progressive pathology leading to complete loss of vision.
Before performing a diagnostic procedure, regardless of the method chosen by the ophthalmologist, the patient must remove contact lenses (if any) and stop using them within two hours after tonometry.
In addition, you should loosen a tight collar, remove a tie and other accessories that are squeezing your throat. An increase in pressure in the blood vessels caused by items of clothing can distort the result of the study. It is also necessary to refrain from taking large volumes of liquids for 2–3 hours. Alcohol should be avoided at least 12 hours before the proposed test.
Depending on what goal the specialist is pursuing, different research options are carried out. When tonometry of the eye, an anesthetic solution is almost always used, which is instilled into the eye of the subject. This is done to reduce the subjective feeling of discomfort. For the non-contact method, local anesthesia is not needed.
| Method | Description | Image |
| Finger | With this type of tonometry, no specific equipment is required. With the patient's eyes closed, the ophthalmologist uses his fingertips to make light pressing movements in the area of his upper eyelids. This seemingly simple study allows us to judge changes in eye pressure | |
| Non-contact (pneumotonometry) | The choice of a non-contact technique does not require direct contact of the tonometer with the eyeball. The measurement principle is based on studying the effect of the force of an air jet on the eyeball. Air jet tonometry is an insufficiently accurate research method, but a fast and technically simple screening method. It can detect elevated intraocular pressure in patients at risk, especially children and other groups of recalcitrant patients. Pneumotonometry is painless since there is no tactile contact between the equipment and the surface of the eye. When conducting non-contact tonometry, the head of the subject is fixed, after which the patient is asked to hold his gaze at a certain point, with his eyes wide open. Under the influence of a jet of air of a certain force, the shape of the eyeball briefly changes. After processing the received data, the computer draws a conclusion | |
| Contact | ||
| It is carried out with direct contact of the equipment with the surface of the organ of vision. Since the procedure is painful and can cause discomfort to the patient, it is necessary to use local anesthetic solutions | ||
| Applanation | In ophthalmology, this method is the most accurate, therefore applanation tonometry has become widespread in the practice of ophthalmologists. The study is carried out using force (applant), under the influence of which a flat area of the cornea of the eye is temporarily formed | |
| According to Goldman | A Goldmann tonometer is used as special equipment. The first step in carrying out this diagnostic method should be considered anesthesia. After the ophthalmologist drops an anesthetic solution onto the surface of the eyeball, the patient is placed in a horizontal position on the couch. Goldmann IOP measurement is the “gold standard” in ophthalmology. Using a tonometer of the same name and special colored plates, the colored semicircles of the eye are examined | |
| According to Maklakov | When using Maklakov weights, the doctor carefully widens the palpebral fissure and places a weight on the central surface of the cornea, after which some flattening of the area under study is observed. The bottom of the weight is painted with special paint. The resulting circle is compared with diagnostic models to determine normal or pathological values | |
| Impressive | With this method, the degree of depression of the cornea under the influence of a weight of a certain weight is assessed. The indentation of the weight is noticeably lower in the case of increased intraocular pressure. Since the method is painless and causes virtually no discomfort, impression tonometry has become widespread for diagnosing increased IOP in children. |
Modern ophthalmological techniques
Transpalpebral examination is improved, which, unlike Maklakov’s technology, is quick and painless and shows the most accurate results. Measuring the elasticity of the cornea is carried out by mechanical action on the eye through the closed eyelid.
An equally successful modern method of applanation tonometry, which measures IOP, is carried out using a Goldmann tonometer. The principle of operation is to use a slit lamp and a prism, which is in contact with the cornea. An anesthetic substance and a fluorescent solution are necessarily instilled into the eye.
Under strong illumination, the prism allows you to track the tear menisci, which take the shape of two half rings against the background of the refraction of the light beam. The cornea is then flattened under controlled pressure from the prism until the rings converge at one point.
Pneumotonometry of the eye: what is it?
Along with a number of other methods, pneumotonometry is a non-contact diagnostic method that allows you to determine the patient’s IOP. It has found wide application in modern ophthalmology and is one of the most common and accessible methods.
It is based on the pulsed direction of the air flow to the surface of the mucosa and the determination of IOP parameters by recording its deformation due to such an impact.
In the process of non-contact measurement of intraocular pressure, the pneumotonometer records the resulting ophthalmic tone. To do this, he uses a special pneumatic sensor, the design of which includes a piston “floating” on a bearing with an air film, which forms a gap between its elements.
These features make it possible to carry out a procedure in which, bypassing the piston, the air flow passes through an opening located in the membrane at the end of the sensor. By placing it in front of the cornea, they create pressure, and therefore resistance, from the mucous membrane. The balance of air flow and resistance affects the movement of the piston, which allows you to calculate IOP indicators.
IOP is determined by combining the production and drainage of aqueous humor of the eye. With normal intraocular pressure, all processes are stable and capable of providing the required level of metabolism. However, if there are disturbances in the ratio of produced and drained aqueous humor, the balance is disturbed. Most often, such manifestations are characterized by glaucoma, but there are a number of other pathologies, one of the symptoms of which is IOP disorders.
Impression pneumotonometry
There are cases when the cornea has become curved under the influence of external factors, and there is no possibility of covering a large area of it. For such situations, an examination according to the Schiotz principle is usually used.
Pressure is applied to the eyeball with a special rod having a constant mass. Anesthesia is mandatory; the specialist initially sets the amount of indentation in linear quantities. Next, the latter are converted to mm Hg. Art. through the corresponding normograms.
What indicators are normal for pneumotonometry?
Pneumotonometry does not always provide accurate results: they change during the day under the influence of various factors. In addition, their reliability may be affected by the tension of the eye muscles during the procedure. That is why, most often, this technique is combined with other, more reliable ones. It is important to understand that the normal values of pneumotonometry of the eye in such cases will be different.
Thus, the norm for pneumotonometry is indicators from 15 to 22 millimeters of mercury - however, during the day the indicators may change. Moreover, for patients of different ages, certain deviations from the established range are allowed. If we add to this the insufficient accuracy of the technique, we can conclude that small deviations do not necessarily signal the development of pathology.
That is why, if the indicators vary in the range from 10 to 20 millimeters of mercury, and other studies have not revealed any abnormalities and there are no clinical manifestations of the disease, this can be considered normal.