Eyeball hurts: main causes
When the eyeball hurts only if you press, there is no reason to panic. This means that you have enough time to undergo a diagnosis and consider the proposed courses of treatment. It is much worse if you notice other symptoms of common ailments of the visual organ.
Glaucoma
A chronic disease characterized by high intraocular pressure. It provokes the accumulation of fluid and disruption of the structure of blood vessels, which leads to atrophy.
There is a high risk of occurrence in people in whose family someone also suffered from this disease. In addition to pain when pressing, the following symptoms are distinguished:
- the viewing angle narrows;
- spots, double vision of the image seen;
- decreased visual acuity at dusk.
Oncological diseases of the eye
Metastases and cancerous tumors, fortunately, occur in rare cases. In this case, the patient feels:
- aching pain during the day;
- lack of coordination;
- poor appetite;
- weakness throughout the body.
| If an unpleasant sensation in your eyes bothers you constantly and only gets worse with pressure, there is a reason to consult an oncologist. |
Vascular problems
There are several options for the development of the disease:
- atrophy of capillaries inside the eyeball;
- uveitis - inflammation of the vessels of the visual organ;
- a spasm that leads to blurring of what is seen.
All manifestations of disorders of the circulatory system are dangerous, since at the final stage of development they lead to complete loss of vision.
Entry of foreign bodies
If you feel that there is something in the eye, the white turns red, and pain is felt when pressing, there is a risk of a foreign body getting into the membrane. The likelihood increases if discomfort began after an impact, swimming in an open body of water, or a walk in windy weather. The problem is dangerous because the object can damage the organ and cause infection. Negative consequences are:
- retinal detachment;
- inflammation;
- visual impairment.
Return to contents
Possible reasons
Tingling under the eye may be a symptom of one of the following conditions::
- Sinusitis . The pathology is an inflammation of the nasal sinuses, which communicate with the lacrimal canals. With this disease, the maxillary sinuses, which are located under the eye sockets, become clogged with purulent discharge. The pathology in its advanced form can progress to the chronic stage, and inflammatory processes can spread to the upper respiratory tract. Treatment in this case is carried out by an otolaryngologist, who prescribes appropriate anti-inflammatory and, if necessary, antibacterial drugs.
- Osteomyelitis . A purulent-necrotic process in the bones, which can develop against the background of complications of dental diseases, when infectious processes from the teeth of the upper jaw spread to the infraorbital bones. Treatment consists of taking immunostimulating and antibacterial drugs, vitamins, and in severe cases, blood plasma transfusion to detoxify the body.
- Mechanical damage to the periocular area. Painful sensations in such cases require, first of all, symptomatic treatment and the use of painkillers. And with concomitant damage to the eyeball and penetrating wounds, antibacterial treatment and surgical intervention are necessary.
- Neuralgic pathologies. Such disorders are usually accompanied by a complex of symptoms, including disturbances in facial expressions, numbness of the facial, hypoglossal and pharyngeal nerves. Often the patient experiences tingling sensations in the temples, shoulders or neck.
- Disturbances in the activity of the vascular system of the organs of vision . In such cases, the patient may feel pain in the bone under the eye, but this syndrome only affects the blood vessels and soft tissues.
Only a specialist can determine what exactly causes such a symptom after conducting an appropriate examination.
Treatment is determined solely by the origin of the pathology and its severity.
Why the eyeball hurts: additional reasons
There are factors that are not so scary in nature. Some of them only indirectly relate to the organ of vision, others can be easily eliminated if you seek professional medical help in a timely manner.
There are also a number of natural causes of pain caused by cosmetic procedures:
- eyelash extensions;
- eyelid and eyebrow tattooing;
- face lifts.
Any of these procedures will inevitably lead to swelling, and violation of the rules can lead to infection.
But during pregnancy, general soreness is generally a relative norm, so any complaint should first of all be heard by the doctor leading the expectant mother. The main thing is to pay attention to cross-symptoms.
Damage due to trauma
When soft tissue ruptures or the integrity of the membrane is damaged, the eyeball constantly hurts. This is a very sensitive organ that reacts vividly to any irritation. The damage caused by damage depends on:
- affected areas;
- degrees;
- type of source: mechanical or chemical.
Return to contents
Sinusitis
The negative effects on the eyes are as follows:
- high risk of infection on the mucous membrane;
- increased pressure during edema due to the accumulation of pus;
- disruption of healthy blood circulation.
The unpleasant feeling and heaviness are felt more strongly on the back wall of the eye - in the place where a large number of receptors accumulate. Symptoms of the disease:
- pain in the forehead and nose on the left and right sides;
- thick discharge of green shades;
- breathing problems;
- ear and headache;
- chills.
Toothache
The likelihood of a symptom increases in the presence of edema with purulent content. The reason also lies in the pressure exerted on the eyes. Malocclusion also affects the bite - due to the anomaly, the muscles in the upper part of the face are overstrained, and discomfort occurs when pressing.
Return to contents
Headache
Tension pain. Accompanied by general physical ailments, such as drowsiness, apathy. Occurs due to overload of the eyes and the body as a whole:
- long-term work with papers and equipment;
- bad light;
- room temperature is too high or low;
- stress;
- fatigue.
Meteosensitivity. My head hurts when the weather and atmospheric pressure change. The organs of vision also react due to the rich vascular network. The eyes feel squeezing and heaviness.
By cluster type. Appears periodically and returns systemically after a long period of time. It is characterized by a high level of strength and a large set of accompanying symptoms:
- swelling of half the face;
- drooping eyelid of one eye;
- sweating
Return to contents
Arterial hypertension
With high blood pressure, the absorption of blood vessels decreases, and blood stagnates in the head area. The skull cannot physiologically expand, so the soft eyeballs suffer. They become elastic, and when you press on a closed eyelid, pain is felt.
Diffuse toxic goiter
The autoimmune disease hyperthyroidism leads to a negative effect of the body on the thyroid gland. The release of excess hormones affects the muscles that press on the eyeballs, pushing them out. A characteristic symptom is unpleasant sensations that intensify with eye movement. Other symptoms:
- redness of the vascular network on the protein;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- it hurts to blink;
- decreased visual acuity.
Infections from the body
It is important to localize the source: with some ailments the upper edge of the eye hurts, with others it hurts below, with others you feel all-round pressure.
An infection can get to the sensitive membrane if the functioning of certain organs is disrupted and from the environment:
- from the nasal cavity - the consequences of sinusitis and tonsillitis;
- from the mouth - with advanced caries;
- virally through the blood - herpes;
- from the outside - conjunctivitis.
Return to contents
Frozen chamomile decoction for pain relief
Freezing the cooled chamomile infusion does not require much time. Chamomile has a beneficial effect on skin condition. Strengthens metabolic processes. Helps remove toxins and poisons from the body.
The cooled broth should be poured into an ice tray. Place in the freezer. You can add a few spoons of milk to cleanse your skin.
During the procedure, the ice cube should not be left in one area for a long time. This can lead to stiffening of the nerves and worsening of the condition.
Due to the temperature difference, the blood vessels will narrow. Swelling and inflammation will decrease. The speed of skin restoration will increase. But before use, you need to make sure that the skin is not dry. Individual intolerance to chamomile is also a contraindication.
Diagnostics
As soon as you notice a recurrence of painful sensations or see a coincidence of symptoms, you should contact an ophthalmologist. The doctor first prescribes medications to relieve discomfort, swelling, and lacrimation. Further examination will require professionalism and efficient equipment.
| Remember that often eye pain cannot be eliminated without neutralizing the source of the disease. |
The video talks about common diseases and diagnostic methods:
What diseases cause eye pain?
Many people have eye pain due to ophthalmological and systemic diseases. The reason may be in the organs of vision or in other disorders. The choice of specialist and treatment depends on the cause of the pain; in order to identify it, laboratory and instrumental examination methods are prescribed.
There are a number of ophthalmological diseases and conditions that can affect soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerves located in the organs of vision.
They cause acute and chronic pain:
- Increased eye strain. It occurs in people who spend a long time in front of a computer, phone, TV, or tablet. Pain occurs when reading books frequently in poor conditions, for example, in low light.
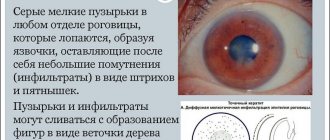
- Entry of a foreign body. It can penetrate the cornea due to strong winds, sparks from a welding machine, or for other reasons. Acute pain, redness, photophobia, increased sensitivity, and spasm of the eyelids occur.
- Conjunctivitis. It can be of an allergic, bacterial, viral nature. This is a disease in which the conjunctiva of the eye becomes inflamed. Redness, swelling, pain, and photophobia appear. With bacterial conjunctivitis, purulent exudate is released.
- Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. It can develop due to the proliferation of fungi, viruses, bacteria, parasites (eyelash mites). The eyelids swell and an abscess filled with fluid may form under the skin.
- Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea. The inflammatory process begins as a result of mechanical damage, burns, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. If the disease lasts a long time, the cornea becomes cloudy and visual acuity decreases.
- Glaucoma is an increase in intraocular pressure due to impaired outflow of secreted fluid. There are anterior and posterior chambers in the eyeball, and fluid constantly circulates inside them. If it accumulates but does not come out, the pressure increases. This can lead to damage to the optic nerve, retinal detachment, and blindness.
- Retinal diseases. They develop due to burns, mechanical damage, and malnutrition through blood vessels. If the retina detaches, the person goes blind.
- Diseases of the optic nerve. Light streams pass through the eyes, hitting the rods and cones of the retina. From them, information in the form of nerve impulses passes through the nerve, entering the brain. The nerve is damaged due to malnutrition through blood vessels, mechanical damage, and infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Strabismus, amblyopia. If both eyes see the picture in front of them incorrectly, this leads to increased strain. As a result, not only your eyes hurt, but also your head.
There are diseases that develop not in the eyes, but in peripheral organs; with their prolonged development, complications arise from the organs of vision, this also leads to pain:
- Diabetes. A large amount of glucose accumulates in the patient’s blood, which is not distributed to the tissues, but binds to cholesterol and forms plaques. They are transported through large and small vessels, including the microcirculation of the eyes. This leads to blockage, severe pain, decreased or complete absence of vision.
- Atherosclerosis. Cholesterol accumulates in the patient’s blood, which spreads through the vessels, clogging their lumen. The mechanism of the disease is the same as for diabetes mellitus.
- Arterial hypertension. Increased pressure puts stress on the endothelium. This leads to rupture of the vessel wall and hemorrhage inside the eyeball. With chronic hypertension, the function of the visual organs decreases, and constant headaches and eye pain occur.
- Ischemic disease. A person experiences spasm of peripheral vessels. If this happens in the eyes, nutrition is disrupted. Gradually, the organs of vision will fail to function. Severe spasm causes severe pain.
- Vasculitis, increased fragility of blood vessels. If the endothelium is fragile, this leads to hemorrhage in any part of the body. Painful sensations appear during spasms, which causes a decrease in vision function.
- Neuropathy. The inflammatory disease can spread to the optic nerve, this is dangerous because it connects to the brain. This causes a decrease in its functionality and constant pain.
For each disease, a separate treatment is determined. Therefore, diagnostics are initially carried out, identifying the nature of pain, decreased vision function and other symptoms.
What to do if the eyeball hurts: traditional treatment
Having undergone diagnostics in the clinic and having determined the root cause of the disease, you can safely begin treatment. The symptom itself is quite difficult to remove and restoring health to the eyes is possible only after eliminating the source of discomfort. Methods of dealing with it depend on the nature of its appearance and the degree of neglect.
Let's look at the most common medications and techniques used to solve problems of different categories.
1. Glaucoma:
- surgical intervention;
- pilocarpine relieves pain;
- as therapy - phosphacol.
2. Conjunctivitis:
- chloramphenicol;
- sodium sulfacyl;
- norsulfazole;
- sulfapyridazine.
3. Inflammatory processes:
- antibiotics;
- scopolamine;
- atropine sulfate.
Return to contents
What to do to eliminate pain
To stop the syndrome, you need to know the root cause of its occurrence. The patient must be aware of the full extent of responsibility for an incorrect decision. If caused by the presence of a neoplasm, then time is the decisive factor that will provide a chance of survival. The more advanced the stage, the less chance of recovery.
Temporary relief of symptoms can be achieved by taking an anesthetic. Common painkillers:
- Nurofen.
- Ketanov.
- Nise.
- Dexalgin.
- Diclofenac.
- Aspirin.
- Analgin.
- Paracetamol.
- Citramon.
There is a different drug for each person. It all depends on individual characteristics. But the painkiller gives a temporary effect. Visiting a doctor and following the recommendations received are a prerequisite for a complete recovery. Otherwise your eye will hurt.
To reduce inflammation, decoctions and compresses are used. To enhance the effect, the compress can be cooled or frozen.
Let's consider well-known tinctures of medicinal herbs
The positive influence of nature’s gifts is beneficially used in the treatment of many diseases, including eye diseases. Decoctions, compresses and tinctures help get rid of pain when pressed and relieve fatigue. The basic rule is to apply the substance only to clean skin and washed eyes.
Aloe decoction. The plant is a well-known biostimulant that activates metabolism, relieves inflammation and cloudiness in the eyes. There are cases where the use of a solution with natural aloe extract restored vision by 0.5-1. To prepare, peel the inside and boil in a small amount of water, cool. Apply generously to a cotton pad and wipe slightly open eyelids. Suitable for use every morning and evening.
Celandine compress. The cleansing properties of the plant are familiar to everyone. Recently, reviews have increasingly appeared about its positive effect on the organs of vision. To create compresses, stir two tablespoons of the herb in a glass of water, then pour into a ladle and boil. After cooling, add honey so that it does not lose its healing properties. Soak cotton pads in the mixture and apply to your eyes for 10-15 minutes, 2 times a day.
Combined tincture. You will need a mixture of plants: birch leaf, nettle, horsetail, string, lingonberry leaf, bird knotweed, plantain, St. John's wort and rose hips. The entire list or most of it is sold in pharmacies as a package. Some ingredients can be purchased or assembled separately. The herbs should be crushed, crushed berries should be added and boiling water should be poured over everything for 10-12 hours. After straining, apply the liquid to your eyes for a week.
Return to contents
Prevention of eye pain
To prevent pain in the eyeballs, use the following rules:
- daily hygiene procedures to help eliminate the risk of bacterial infection;
- lack of contact with infected people, especially viral diseases;
- temporary restrictions on interaction with electronic devices;
- daily gymnastics for eyeballs and eyelids;
- timely contact with an ophthalmologist and other doctors in the presence of illness;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases that cause eye complications;
- the use of contact lenses or glasses if visual acuity decreases, as their use eliminates eye strain;
- the use of multivitamin preparations that normalize vision function, for example, Blueberry Forte.
Prevention rules will not be able to completely eliminate the risk of deviations and diseases, but they will significantly reduce it. They are used daily to achieve effect.
Eye pain occurs with the development of a pathological condition. Normally it should not appear. If a person does not know the cause of the condition, consult an ophthalmologist or a doctor of another specialty. Only with the help of laboratory and instrumental examination methods can the cause be identified and eliminated.
Symptoms
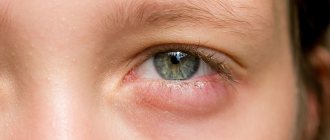
The nature of the symptoms accompanying eye swelling completely depend on the causes of the pathology itself. If we are talking about an infectious lesion, for example, blepharitis (in which the corners of the eyes become chronically inflamed), then the swelling will be accompanied by severe hyperemia (redness) and disturbing itching.
When diagnosing phlegmon or conjunctivitis, a sharp deterioration in vision is possible. If the injury site hurts and the eyes themselves are very itchy, this could be an allergic reaction to cosmetics.
After burns, peeling of the skin of the eyelids, as well as redness of the mucous membrane, is possible. After suffering bruises, as a rule, a painful hematoma or bruise appears. In case of serious injuries, swelling may be accompanied by temporary numbness of the eyelids and a feeling of a veil before the eyes. The patient himself may complain of increased lacrimation, burning and loss of eyelashes. The swollen area may hurt more when you try to touch it.