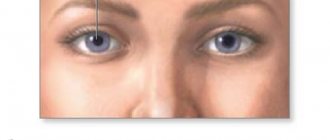
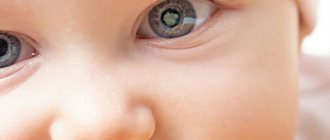
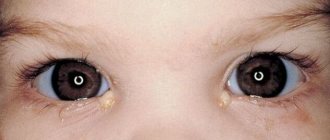
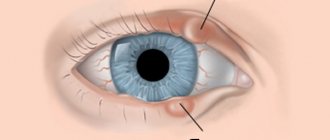
Choroidal nevus is a benign formation of choroidal tissue. It occurs in 5 - 10% of people with white skin, very rarely in dark-skinned people. A nevus is a pigmented formation - a focal accumulation of cells containing pigment (melanocytes).
In most cases, this is a congenital feature of the eye, but noticeable pigmentation does not appear immediately, but until the person reaches the prepubertal period. Therefore, as a rule, nevi are detected in adults, equally often in women and men.
The location of the choroidal nevus is usually on the fundus in its posterior part behind the equator of the eye. But sometimes another localization occurs: in the preequatorial or directly in the equatorial zone. At the first stages of development, the formation does not go beyond the superficial layers of the choroid; later it begins to spread deeper.
Types of birthmarks
Nevi that form before the eyes are divided into two types based on their location. In accordance with this, if necessary, diagnosis and treatment are prescribed:
- A mole that appears on the front wall of the eye is called a conjunctival nevus. In this case, research procedures will not be needed, since the formation is detected visually without additional medical equipment.
- If a mole appears on the fundus, it is called a choroidal nevus. To identify such a pigment spot, it is necessary to use special tools.
You need to know that any type of such formation does not pose a great threat to human health. But, like other moles, eye moles also require control. If it begins to transform, you need to undergo an examination immediately, otherwise melanoma may develop.
Formation on the conjunctiva
The human eye is surrounded by a thin layer of mucous membrane, called conjunctival mucosa in medicine. It is so thin that the white of the eye and blood vessels can be seen through it. A person may develop a nevus at this site. Based on the findings of scientists, 5% of the entire earth's population faces such a problem.
It should be noted that the formation can appear not only on the outside of the conjunctiva, but also on the inside . There are several types of such nevus:
- Vascular. It is formed from a collection of capillaries that are contained in the mucous membrane of the eye. This nevus will be red or pink in color.
- Pigment formations. Melanin cells are concentrated in them. Such formations come in different colors, including black, they look like dots.
- Cystic nevus. In this case, the appearance of a mole was provoked by lymphatic vessels. It is noticeably different from other neoplasms; it looks like a bubble filled with liquid. If the cyst-like formation is greatly enlarged, then its surface resembles a honeycomb.
A formed nevus on the eye does not interfere with a person’s vision and does not cause discomfort. Even if it is located very close to the pupil, it does not block the light and does not affect the quality of vision. Treatment will be prescribed only if the neoplasm shows symptoms of malignant degeneration. According to the degree of development, a nevus on the conjunctiva can be stationary and progressive:
- The stationary one does not change its shape and location. It is absolutely safe.
- A progressive nevus changes its shape, size, and can quickly degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Such education needs to be given special attention and supervision. Medicine recommends getting rid of progressive moles using laser therapy.
Localization and features
nevus choroid of the eye
As a rule, a nevus forms behind the widest part of the eyeball. It forms much less frequently in the equator region. A typical type of tumor is characterized by the following features:
- Clear or feathery outlines;
- Flat shape;
- Diameter no more than 6 millimeters;
- Gray-green or gray color;
- No changes in the underlying retina;
- It is possible that on the surface of the neoplasm there may be waste products of the retina - drusen;
- There is no visual impairment.
The following types of nevi are classified as atypical:
- No pigment;
- Having areas of degeneration;
- Surrounded by lighter choroid;
- Nevi, during histological examination of which degenerative changes in the cells are detected.
The following signs are characteristic of a progressive nevus:
- Height;
- Compression of blood vessels;
- Color change;
- Formation of a yellow halo around the tumor;
- Unclear boundaries;
- There is deterioration in vision.
If a neoplasm is just discovered and has signs characteristic of progression, it is considered suspicious.
Moles on the choroid
Such formations form inside the eye, and therefore are invisible to others. Choroidal nevus is formed from accumulations of vessels or pigment located on the inner surface of the eyeball, at the junction of the iris and the vessels. It can only be discovered through research. According to statistics, choroidal nevus is found in 2% of the population. Typically, such moles appear in adolescents subject to hormonal changes.
Choroidal nevi are small, dark or black in color. Very rarely they are colorless. In this case, it is impossible to recognize the birthmark until a certain point. Choroidal formation is usually progressive. As the nevus grows, it can impair vision. In addition, a person has complaints of pain in the eye, a feeling of the presence of a foreign object. If such symptoms appear, you should definitely consult an ophthalmologist.
The treatment prescribed by the doctor should be taken very seriously. He will choose the most effective methods, taking into account the condition of the nevus on the eyeball. Often in such cases, eye microsurgery is prescribed.
Reasons for appearance
The etiology of the formation of a mole on the pupil or eyeball is always of the same origin. A mole in the eye means that the cells of the organ are oversaturated with a large amount of pigment - melanin. There are provoking reasons for the formation of a benign spot in the form of a nevus:
- Labor activity. Daily exposure to environmental factors during professional activities affects the pigmentation of any part of the organ of vision. Typically, an acquired benign nevus is found in hot shop workers - welders and metallurgists. In this case, the mucous membrane of the eye comes into contact with heated air and a bright source.
- Ultra-violet rays. Tanners who spend a lot of time in direct sunlight and do not wear sunglasses may develop excess pigmentation in the eyeball. This is how the body reacts to ultraviolet radiation, which has a negative effect on vision.
- Hereditary predisposition. Birthmarks are passed from parents to children with information in the DNA. In most cases, the dermatological defect passes through the male line, so the female half of the population almost does not suffer from this pathology.
- Frequent visits to the solarium. Artificial ultraviolet rays have a negative effect not only on the pupil, but also on the entire visual organ. Although protective glasses are used, the procedures may result in the formation of a benign mole.
- Chronic inflammatory processes caused by fungal or viral microorganisms can also lead to the appearance of a nevus. This provoking factor is the most dangerous, since a mole that arises due to chronic inflammation can transform into a malignant formation.
- Adolescence. During adolescence, the child's hormonal system is restructured. Increased secretion of hormones leads to excess accumulation of melanin both throughout the body and in the cells of the eye.
Causes and mechanisms of formation of choroidal nevus
“Choroid” is the choroid located under the sclera.
It is what nourishes the retina and also maintains intraocular pressure at the same level. Since there are no nerve endings in the choroid, all processes occurring in it do not cause pain. The choroid includes several layers, each of which contains pigment cells. The formation of a nevus occurs in the supravascular part of the choroid. In the future, it can spread to deeper sections.
Choroidal nevus usually forms at the birth of a child, but it is almost impossible to notice it initially.
In people aged 10-12 years, pigmentation of this formation begins, this process is repeated after 30 years.
Also, increased pigmentation can occur during pregnancy. It is worth noting that this tumor is not pigmented in everyone, but only in 10% of cases. It is known that this neoplasm is more common in people of the Caucasian race, regardless of gender, most often in one eye.
As in the case of moles, the reason for the formation of nevi is an increase in the concentration of melanin. This can happen due to the following factors:
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Infection;
- Stress;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Genetic factors;
- Use of hormonal contraceptives.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The signs of a choroidal and conjunctival mole are almost the same. Their existence is usually not accompanied by any manifestations. Changes are detected only during an ophthalmological examination and then completely by accident. A nevus is dangerous in the eye when it degenerates into a malignant formation, then the following symptoms occur:
- the quality of vision deteriorates;
- the shapes of objects are distorted;
- sensation of a foreign body in the eye;
- limited field of view.
If such symptoms occur, you must follow all doctor’s recommendations to prevent dangerous consequences. The doctor gets acquainted with the medical history, clarifies the time of occurrence of the mole in the eye, and finds out about the presence of discomfort. Then he examines the mucous membrane of the organ and carries out diagnostic measures:
- Ophthalmoscopy. This procedure allows you to assess the condition of the retinal vessels and optic nerve using an ophthalmoscope. Using a red filter, you can easily detect a tumor. Using green, the doctor examines pathological changes in the structure of the eye that begin to progress as the nevus transforms.
- Echography. This diagnostic measure allows you to identify the focus of pigmentation.
- Ultrasound of the eye. The procedure examines the deep structures of the eyeball, which is necessary to monitor the development of a nevus.
- Fluorescein angiography. This test is designed to identify retinal angioma. The procedure is carried out by injecting a contrast agent (fluorescein), which illuminates the affected areas of the eye.
Usually, the presence of a mole in the eye can be detected independently if it is located on the outer layer of the mucous membrane. But it happens that the patient does not even suspect the existence of a nevus for quite a long period of time until symptoms arise. In this case, diagnosis of a mole is carried out only using comprehensive studies.
Results and discussion
Patients with a stationary nevus were under observation, during which one patient showed signs of progression of the formation, namely an increase in its size, redness, thickening and a slight increase in color intensity. No pigment sputtering was observed. Like other patients with progressive nevus, he underwent surgery to remove the tumor. During 5 years of observation, we did not observe a single relapse among the operated patients. In the first weeks of the postoperative period, hyperemia was observed with the formation of a delicate conjunctival scar. There were also no changes in refraction in patients. The diagnosis of patients with nevus and conjunctival melanoma was histologically verified in all cases. In histological specimens of nevi, proliferating melanocytes were found that formed cell nests in the basal layer of the conjunctival epithelium (Fig. 6). In preparations of removed melanomas, spindle cell and polygonal cells were present, limited by the conjunctival epithelium (Fig. 7). The tumor resection margins are intact in all preparations. In the postoperative period, patients received interferon α2-β for 5 weeks in the form of subconjunctival injections once a week, as well as in the form of daily three-time instillations. The drug was used to enhance local cellular immunity. As a result, 2 patients experienced a short-term increase in temperature and general malaise, which was easily eliminated by the use of oral anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs. For one year after surgery, patients with melanoma were required to undergo an ultrasound of internal organs every 3 months, a study of the level of liver enzymes in the blood in order to timely identify possible metastases, as well as chest radiography once every 6 months. Over the next 4 years, patients were transferred to dispensary registration once every 6 months. It should be noted that these patients are registered at the dispensary for life. During the observation period, which was 4 years, we did not notice any relapses or distant metastases in them. Recurrence of the nevus occurs when it is not completely removed. Histological studies have shown that remaining nevus cells induce proliferation of dendritic melanocytes to form typical nevus nests [5, 6]. Prognostically important factors for melanoma are the localization of the tumor, the thickness of the tumor, the depth of melanoma invasion of the subconjunctival layer or lacrimal caruncle, high mitotic activity, the absence of lymphoid infiltration, and the rare occurrence of small polygonal cells [7, 8]. A more favorable course of the disease is observed when melanoma is localized in the limbus [9]. The absence of relapses in our patients is explained by radical removal of the tumor, which was confirmed histologically [10]. Localization of the tumor only on the bulbar conjunctiva and limbus, lack of spread to the sclera and fornix also improved the vital prognosis [11]. Malignant melanoma occurs more often in adults and the elderly. Melanoma can occur de novo
or against the background of previous melanosis or nevus. Particularly dangerous in this regard are progressive nevus and primary acquired nevus with gross atypia of small spindle-shaped or epithelioid cells. Melanoma arises from a nevus in 20–30% of cases [12]. No malignant variants of blue nevus have been described in the literature [1]. An important point in the course of our observations is that all 3 patients with conjunctival melanoma and 1 patient with a history of melanoma of the lacrimal caruncle, which did not bother them for many years. It is known that melanomas of the lacrimal caruncle are characterized by extremely high malignancy [13]. Therefore, its banal removal, even within healthy tissue, can result in serious consequences for the patient. The treatment method for melanomas of the lacrimal caruncle is exenteration or proton therapy [14]. Considering the high visual acuity and the absence of spread into the orbit, the patient was offered proton therapy, for which she was sent to the Research Institute of Eye Diseases named after. Helmholtz in Moscow. The most significant feature of melanomas is high metastatic activity [8, 14]. Moreover, they can be detected both during the diagnosis of the primary lesion and years after the diagnosis has been established. Therefore, all patients with melanoma are monitored for life.
Rice. 6. Histological preparation of conjunctival nevus.
Rice. 7. Histological preparation for conjunctival melanoma.
Treatment methods
If the mole is benign and does not cause inconvenience to its owner, treatment is not carried out. But the progressive formation should be under constant supervision. Control visits to a specialist are carried out twice a year. If the development of formation is detected, treatment is prescribed. The therapeutic complex is selected in accordance with the location of the spot and its size.
The developing form of pathology requires mandatory surgical intervention. First of all, an atypical mole is treated, since it has a high risk of transformation into a malignant form and a large cell nevus located in the area of the optic nerve. In medicine, there are several methods for surgical removal of moles on the eye organ:
- Electroexcision. The nevus is removed using an electric scalpel. This method is applicable for large malignant tumors with subsequent plastic surgery.
- Laser treatment. The mole is removed using a laser beam, which is effectively used to perform manipulations in hard-to-reach places.
- Cryodestruction is a frequently used method for removing a birthmark using liquid nitrogen.
- Brachytherapy. This method of nevus removal is considered simple and safe. Within an hour, the patient gets rid of a mole in the eye. Here, radio waves of various frequencies are used, with the help of which they not only remove the tumor, but also force the tissue of the eyeball to regenerate. Brachytherapy is used as the main procedure, but is also part of a treatment complex.
It is important to follow preventive recommendations to reduce the likelihood of developing a mole in the eye area. To avoid pathological changes in the eyes, it is necessary to eliminate infectious foci in the body. If there are hormonal imbalances during pregnancy or menopause, you should consult a doctor to restore hormone levels, if necessary. It should not be forgotten that the eyes should always be protected from the negative effects of ultraviolet rays, which contribute to the development of nevi.