Causes
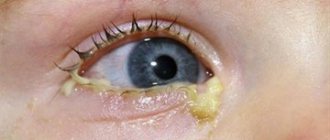
The most common cause of red eyes is conjunctivitis.
The causes of conjunctivitis may be:
- infectious (for example, viral, bacterial, chlamydial);
- non-infectious (eg, allergies, irritants).
Other common causes of red eyes and purulent discharge include:
- blepharitis,
- abrasion of the cornea,
- foreign body
- subconjunctival hemorrhage,
- keratitis,
- iritis,
- glaucoma, chemical burn,
- scleritis
You need to see a doctor. The doctor will ask questions about unilateral or bilateral eye damage, duration of symptoms, type and amount of discharge, visual changes, severity of pain, photophobia, previous treatments, allergies or systemic disease, and whether the person wears contact lenses. Then he will examine your eyes. Next, we will look at the various diseases that lead to red eye.
Prevention
Among the preventive measures are the following:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules is the best prevention. Many people use a handkerchief to wipe their eyes when they have a runny nose, thereby spreading the infection. After which inflammation and suppuration of the eyes occurs. Using someone else's towels, cosmetics, etc. may lead to infection.
- If contact lenses are used, they must be of high quality and from a trusted manufacturer. If inflammation occurs, you should stop wearing them for the duration of treatment.
- It is necessary to carefully monitor your health, to prevent vitamin deficiency and decreased immunity.
- It is necessary to master massage of the tear ducts. A qualified specialist will show you the technique, after which you can perform it yourself.
Don't touch your eyes with dirty hands
Viral conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis is usually very contagious. Especially caused by adenovirus. Conjunctivitis caused by infection with other viruses (such as herpes simplex virus) is less likely to spread. Viral conjunctivitis usually occurs through direct contact with contaminated fingers, medical instruments, pool water, or personal items. You can become infected from a person with an upper respiratory tract infection through coughing.
The clinical picture of viral conjunctivitis is usually mild with spontaneous remission after 1-2 weeks. Treatment is supportive and may include cold compresses, eye decongestants, and artificial tears. Antibiotics are not usually prescribed because secondary bacterial infections usually do not occur.
To prevent contracting viral conjunctivitis, you should wash your hands frequently and avoid sharing personal items. If the profession involves food processing and contact with people, then you should stop working until the discharge from the eyes completely disappears. Corticosteroid ointments are usually used. It is better not to treat yourself, but to consult an ophthalmologist.
Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is one of the diseases in which inflammation of the lacrimal sac is noted. After the infection appears, stagnation of tear fluid occurs in the organ of vision, which is why the disease appears. When the patency of the flow connecting the lacrimal sac with the nasal cavity is disrupted, fluid stagnation occurs.
Newborns may develop a congenital disorder in which an inflammatory process forms in the lacrimal apparatus. In adults, the disease appears for other reasons, mainly due to swelling of the tissues located near the tear duct. Dacryocystitis appears after the formation of several factors:
- presence of respiratory infections;
- chronic inflammation appeared on the nasal mucosa, as well as on the sinuses;
- after traumatic injuries.
A disease such as dacryocystitis has several types:
- viral form;
- microbial species;
- parasitic form.
Symptoms of this disease:
- Tears flow without stopping.
- There is a slight swelling in the area of the lacrimal sac.
- A mucopurulent secretion is released from the lacrimal canal.
- Hyperemia forms in the lacrimal caruncle.
- Conjunctivae appear on the eyelids, as well as on the semilunar folds.
- The chronic disease occurs with the presence of ectasia of the lacrimal sac.
- Blepharitis develops on the visual organs.
- In the chronic form of the disease, the corneas become covered with purulent ulcers, and keratitis or conjunctivitis forms on them.
- The acute stage of the disease is accompanied by a narrowing of the visual slit.
In addition to the listed factors, dacryocystitis is accompanied by the appearance of chills; a sick patient in the acute stage of the disease develops a headache, and a feverish state does not leave him.
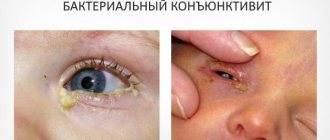
Bacterial conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis is highly contagious and is most often spread through direct contact with contaminated fingers.
Based on the duration and severity of signs and symptoms, bacterial conjunctivitis is classified into:
- fulminant;
- spicy;
- chronic.
Fulminant bacterial conjunctivitis is often caused by Yersinia gonorrhea in sexually active adults. The infection is characterized by sudden onset and rapid progression, leading to corneal perforation. In this case, there is abundant purulent discharge, pain and decreased vision. You need to urgently contact an ophthalmologist and begin treatment immediately.
Acute bacterial conjunctivitis is the most common form of bacterial conjunctivitis. Signs and symptoms last less than 3-4 weeks. Staphylococcus aureus infection often causes acute bacterial conjunctivitis in adults. The pathogens Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are most common in children.
Chronic bacterial conjunctivitis is characterized by signs and symptoms that persist for at least 4 weeks with frequent relapses. Patients with chronic bacterial conjunctivitis should be treated by an ophthalmologist.
Laboratory tests to identify bacteria and antibiotic susceptibility are performed only on patients with severe cases. Also, determination of the pathogen and sensitivity to antibiotics is recommended for patients with impaired immunity, people wearing contact lenses, and newborns. Also, a culture with an antibiogram is needed when initial treatment fails.
Typically, topical antibiotics are prescribed for the treatment of acute infectious conjunctivitis due to the difficulty of differentiating between bacterial and viral conjunctivitis.
The most commonly used antibiotics are:
- Azithromycin 1% (“Azasite”): 1 drop 2 times a day (with an interval of 8 to 12 hours) for 2 days, then 1 drop per day for 5 days.
- Besifloxacin 0.6% (“Bezivance”): 1 drop 3 times a day for 1 week.
- Ciprofloxacin 0.3% (“Siloxan”): 1 or 2 drops 4 times a day for 1 week. As an ointment: a pea-sized amount is applied to the conjunctival sac 3 times a day for 1 week.
- Erythromycin 0.5%. The ointment is applied 4 times a day for 1 week.
- Gatifloxacin 0.3% (Zymar) or Moxifloxacin 0.5% (Vigamox): 1 drop 3 times a day for 1 week.
- Gentamicin 0.3% (Gentac): 1 to 2 drops 4 times a day for 1 week. The ointment is applied 4 times a day for 1 week.
- Levofloxacin 1.5% (Iquix) or 0.5% (Quixin): 1 or 2 drops 4 times a day for 1 week.
- Ofloxacin 0.3% (“Ocuflox”): 1 or 2 drops 4 times a day for 1 week.
- Sulfacetamide 10% (“Bluff-10”): 1 or 2 drops every 2-3 hours for 1 week. The ointment is applied to the lower conjunctival sac 4 times a day and before bedtime for a week.
- Tobramycin 0.3% (Tobrex): 1 to 2 drops 4 times a day for 1 week. The ointment is applied to the conjunctival sac 3 times a day for 1 week.
- Trimethoprim, polymyxin B (“Polytrim”): 1 or 2 drops 4 times a day for 1 week.
The benefits of antibiotic treatment include faster recovery, earlier return to work or school, and prevention of further complications.
How to determine viral or bacterial conjunctivitis, watch the video:
Diagnostics
The patient describes the complaints in detail, the doctor evaluates the clinical manifestations, clarifies the anamnesis: contact with infected people, the presence of allergens, chronic diseases, etc. If conjunctivitis is suspected, a cytological examination, analysis for demodicosis, determination of antibody titer, nasal, allergic, conjunctival, sublingual tests are additionally prescribed . Additional consultations with an infectious disease specialist, venereologist, allergist, otolaryngologist, and phthisiatrician are possible.
If barley is suspected at the initial stage, an ophthalmoscopy is prescribed and mucus is taken for culture. This is necessary to determine the type of microbe and its sensitivity to antibiotics. Additionally, the doctor examines the immune system and takes blood to check glucose levels. Keratitis is examined using visometry, corneal scraping, biopsy, biomicroscopy, and fluorescein test. Trachoma in laboratory conditions is determined by examining mucus from the conjunctiva and epidemiological analysis.
Chlamydial conjunctivitis
Chlamydial conjunctivitis is diagnosed in sexually active patients who have typical signs and symptoms of a red eye and purulent discharge but do not respond to standard antibacterial treatment. Patients with chlamydial infection may also have chronic follicular conjunctivitis. A conjunctival scraping followed by PCR analysis can be done, but this is not usually required.
Treatment includes local therapy with eye ointment with Erythromycin and oral therapy with Azithromycin (Zithromax) with a single dose of 1 g. Doxycycline 100 mg 2 times a day for 14 days can also be cured. This regimen is used to eliminate genital infections. The patient's sexual partners should also receive treatment.
Trachoma
Trachoma stands out among severe infectious eye diseases. The disease often becomes chronic. The disease occurs from the penetration of chlamydia into the eye. If not treated immediately, the disease will lead to decreased vision. Nowadays, the disease occurs in rare cases.
The causative agent of trachoma can be found on hands, on personal items, as well as on clothes where purulent discharge is located. Sometimes the disease is caused by flies. The disease remains in the incubation period for 6-8 days. Two organs of vision are affected at once. At an early stage, the patient may notice redness of the conjunctiva. The late stage of the disease is accompanied by the formation of scars, the cornea becomes cloudy, and inversion is noted on the eyelids.
Trachoma is divided into several clinical stages:
- absence of symptoms, there is only a suspicion of the onset of the disease;
- presence of pretrachoma;
- infiltration appears on the conjunctiva along with hyperemia - this is prefollicular trachoma;
- the inflammatory process occurs with the appearance of large follicles, this is the beginning of the first stage;
- at the second stage, the splitting of the follicles is noticeable, then their fusion. This progresses to scarring;
- at the third stage of the disease, a progressive process forms in the conjunctiva;
- the fourth stage is accompanied by pronounced scar formation.
Allergic conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is often associated with atopic diseases such as allergic rhinitis (the most common), eczema and asthma. The eyes are involved in an allergic reaction in approximately 25% of the population. A typical manifestation is itchy eyes. Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis is the most common form. The appearance of symptoms is associated with seasonal allergens, such as flowering plants. Protracted allergic conjunctivitis worries throughout the year. Avoidance of allergens and the use of artificial tears are recommended. Antihistamines and vasoconstrictors are also indicated for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis.
The following drugs are recommended:
- Antagonists of histamine H1 receptors. Azelastine 0.05% (Optivar) – 1 drop 2 times a day. Emedastin 0.05% (“Emadin”) – 1 drop 4 times a day.
- Mast cell stabilizers. Cromolyn sodium 4% ("Krolom"). 1 or 2 drops every 4-6 hours.
- Lodoxamide 0.1% (“Alomid”). 1 or 2 drops 4 times a day. Nedocromil 2% (“Alocryl”). 1 or 2 drops 2 times a day.
- Mast cell stabilizers and H1 receptor antagonists. Ketotifen 0.025% (“Zaditor”). 1 drop every 8 to 12 hours. Olopatadine 0.1% (Patanol). 1 drop 2 times a day.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Ketorolac 0.5% (“Acular”). 1 drop 4 times a day.
- Vasoconstrictor and antihistamine. “Naphazoline”, “Pheniramine” – 1 or 2 drops up to 4 times a day.
The most effective option is a local 2nd generation histamine H1 receptor antagonist.
How to treat
Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor will recommend the necessary hygienic procedures to carry out the process of washing the inflamed eye canals and removing the pus that accumulates on the eyelids. In addition, for most infectious and viral diseases of the organs of vision, the ophthalmologist prescribes pharmacological agents:
- anti-inflammatory or antibacterial ointments;
- soothing, antiseptic or antibiotic drops;
- special saline solutions for washing.
Among eye ointments, tetracycline ointment has proven its effectiveness in the fight against conjunctivitis and other inflammations of the organs of vision. This is a powerful broad-spectrum antibiotic that helps with most eye diseases accompanied by pus. Placing tetracycline ointment under the eyelid three times a day helps to cope with the symptom of purulent discharge for 5 days.
During inflammation of the ocular mucous membrane, accompanied by the formation of pus, the procedure of washing the eyelids and eyeball is especially important, as it helps relieve inflammation, reduce irritation, and speed up the healing process. It is necessary to rinse your eyes when they turn sour; you can do this with a pipette or cotton pads. For rinsing with conjunctivitis of various types, doctors recommend using a solution of chloramphenicol, furatsilin or miramistin.
- Remedies for thrush - inexpensive and effective
- Cucumber and tomato salad for the winter
- Buckwheat diet with kefir - menu for 7 days. Reviews of those who have lost weight and the results of the buckwheat diet with photos
Eye drops
Drops should be instilled into inflamed eyes oozing pus to prevent them from turning sour. Doctors prescribe Albucid drops as an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agent. This is a universal remedy; when used, an allergic reaction rarely occurs; the drug can be used for antiseptic rinses. The feeling of discomfort and tingling when instilled is normal; Albucid should be instilled at least 3-5 times a day until the symptoms completely disappear.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of eye diseases accompanied by the discharge of pus should be used only as auxiliary methods in addition to drug therapy. For styes and other eye swelling, traditional healers recommend warming the eyeball with a warm boiled egg applied to the upper eyelid. For rinsing, you can use warm brewed green tea, since this plant has excellent antiseptic properties.
Calendula infusion and chamomile decoction are used as solutions for soothing lotions that soften inflamed mucous membranes. You should rinse your eyelids from pus with a solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin so that your eyes don’t turn sour, the pus stops flowing, and other symptoms begin to subside - redness, itching, burning. Some doctors recommend massage of the ocular ducts to speed up the process of suppuration and quick recovery.
Dry eye syndrome
Dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitis) is a common condition caused by decreased tear production or poor tear quality. Occurs due to increasing age, being female, taking medications (for example, anticholinergics) and certain diseases. The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on the clinical picture and diagnostic tests.
Tear osmolarity is the best diagnostic indicator for dry eye. Overall diagnostic accuracy increases when tear osmolarity is combined with assessment of tear turnover and evaporation rates. Some patients with dry eye may experience ocular discomfort on examination without disruption of the tear film. In such people, treatment for dry eye can be initiated based on signs and symptoms. If Sjögren's syndrome is suspected, autoantibody testing should be performed.
Treatment includes frequent application of artificial tears during the day and evening application of lubricants that reduce the rate of tear evaporation. Using humidifiers and well-fitting glasses with side shields can also reduce tear loss. If artificial tears cause itching or irritation, you may want to switch to a preservative-free form or alternative.
When inflammation is a major factor in dry eyes, Cyclosporine ophthalmic drops will help increase tear production. Taking Cyclosporine can continue for several months until there is visible improvement. Systemic omega-3 fatty acids are also beneficial. Topical corticosteroids have been shown to be effective in treating inflammation associated with dry eye. The goal of treatment is to prevent scarring and perforation of the cornea. An ophthalmologist is needed to prescribe a course of topical steroids or undergo surgery.
How to cure dry eye syndrome, watch the thematic video:
Why do an adult’s eyes fester and water?
The appearance of pus and lacrimation can be caused by various factors and diseases. An ophthalmologist, after an examination, will determine the root cause and select an alternative treatment. Most often, such discharge occurs:
- Due to mechanical damage to the eyes. It can also occur when a foreign body enters. After which an infection sets in and inflammation begins. Red sclera of the eyes are observed.
- Due to allergies. It can manifest itself in different ways in an adult. Most often, the eyes become watery, but pus can also appear as a result of prolonged contact with the allergen. The eyes may also become swollen and itchy.
- If infected during rehabilitation after eye surgery.
- For complications caused by ARVI, flu or colds.
In addition to the listed reasons, suppuration and tearing can appear in the presence of the most common eye diseases.
Tetracycline is an antibiotic for quickly treating a bacterial infection
Hemorrhage in the eyes - hemophthalmos.
Conjunctivitis
This disease is the most common, causing suppuration. It can have bacterial, acute and gonorrheal forms. If treated incorrectly, it can become chronic. In addition to suppuration, it may be accompanied by itching, burning, and copious discharge. In the gonorrheal form, blood may be present in the purulent discharge.
Depending on the form, conjunctivitis can occur as a result of improper compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards, due to incorrectly selected contact lenses, due to infection from another patient, or through contact with an allergen.
Will Heparin ointment help with swelling under the eyes? Find out here.
Signs of acute purulent conjunctivitis are pronounced
Hormonal therapy to eliminate non-infectious inflammation - Hydrocortisone ointment for the eyes.
Keratitis
Keratitis can cause a significant decrease in visual acuity. Its main symptom is the appearance of pus in the corners of the eyes. This is followed by unpleasant, painful sensations, fear of light and spasms of the eyelids. As the disease progresses, the cornea of the eye becomes noticeably cloudy and reddens. Long reading or computer work becomes impossible.
The disease occurs due to eye damage, injuries or burns, as well as due to the herpes virus. If the treatment was timely and correct, then vision may be completely restored and the clouding will disappear, otherwise blindness or the formation of a cataract may occur.
Redness of the sclera is the first sign of the development of keratitis
A remedy to eliminate the feeling of discomfort is Gilan Comfort eye drops.
Barley
Almost every person has encountered this unpleasant disease. In this case, the sebaceous glands located along the edges of the eyelid become inflamed, after which an abscess forms. During ripening it causes severe pain.
If a person has a strong enough immune system, the disease does not require treatment. The most common causative agents of the disease are demodicosis and staphylococcal bacteria. All purulent discharge must be carefully removed.
Under no circumstances should you try to squeeze out the abscess. Otherwise, the infection may spread to the entire eye.
What to do if you find hypermetropic astigmatism in children is described in the article.
A stye can cause more serious infection of surrounding tissues
Read here how to restore vision with mild hypermetropia.
Trachoma
The cause of development is chlamydia. After entering the body, the infectious process begins. The disease has several stages. At the very beginning, only the conjunctiva and epithelial cells of the cornea become inflamed, then the inflammation penetrates into the deeper tissues of the eye.
After which suppuration occurs, large ulcers form, and tissue scarring occurs. If drug therapy does not produce results, then surgical intervention is necessary.
Trachoma is a disease caused by chlamydia
Signs of a genetic abnormality in a child are hypertelorism.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammatory condition of the eyelid margins and is diagnosed based on symptoms and examination. The doctor examines patients for seborrheic dermatitis of the skin or face, redness and swelling of the nose or cheeks (rosacea). Therapy includes eyelid hygiene (cleansing with mild soap, diluted baby shampoo or eye cleansing solution). A light eyelid massage and warm compresses are recommended. These procedures should be done regularly.
Erythromycin or bacitracin ophthalmic ointment applied to the eyelids may be used in patients for whom hygiene procedures are insufficient. Azithromycin eye drops can also be used to treat blepharitis. In severe cases, long-term use of oral antibiotics (doxycycline or tetracycline) may be helpful. Steroids may be prescribed in severe cases.
Treatment methods
If the color and amount of mucous discharge from the eyes changes and they become red, it is recommended to consult a specialist. Treatment of pathologies can be carried out using various methods and means, including alternative medicine recipes.
Eye drops
Antibacterial drops can be used to treat eye pathologies that cause suppuration. With their help, it is possible to completely destroy the pathogen. The most effective among them are:
- Levofloxacin;
- Phloxal;
- Tsipromed;
- Tobramycin;
- Chloramphenicol.
Among sulfacyl-based antibacterial agents, the most popular are drops such as Albucid.
Antiseptic eye drops disinfect the surface of the mucous membrane and skin. You can get rid of unpleasant symptoms with the help of:
- Vitabakta;
- Okomistina;
- Miramistina;
- boric acid solution.
Eye drops with interferon have powerful antiviral, antitumor and immunostimulating activity.
Folk remedies
It is possible to eliminate unpleasant symptoms of eye pathologies using some folk remedies:
- It is necessary to pour 3 tablespoons of chamomile into a container and brew them with a glass of boiling water. The resulting mixture must be infused for at least 3 hours, then filtered. Soak cotton pads in this solution and apply them to sore eyes for a while. It is recommended to do 4-5 such procedures during the day.
- To prepare the decoction, you need to put a few rose hips in a bowl and pour a glass of boiling water over them. The mixture should be simmered over low heat for 3 hours, then cool and use the decoction for lotions. With the help of this rosehip-based remedy, it is possible to relieve inflammation and get rid of suppuration.
- You should pour a tablespoon of the plant into the container and pour 200 ml of boiling water over it. The mixture must be infused for several hours, then strained and made into a lotion based on the solution.
A solution of furatsilin can alleviate the patient's condition. In addition, purified water is suitable for washing the organs of vision. Children can use this method. It is impossible to get rid of the disease using this method; to eliminate the disease, you must definitely visit a doctor and use the anti-inflammatory treatment that he will prescribe.
You can independently prepare a decoction of chamomile, as well as calendula, and make compresses that will help an adult get rid of the disease. Unlike an adult patient, the sebaceous glands of the organs of vision of children are much smaller. To treat children's eyes, it is necessary to use special medications. Traditional methods will not help eliminate dacryocystitis and will not remove suppuration.
There are many antibacterial drugs that cope with infectious conjunctivitis. Among the medications are: Albucid, Gentamicin, as well as Cipromed and Ciprofloxacin. Children should not establish treatment on their own.
Sometimes an adult's eyes appear red and fester due to allergies, in which case it is necessary to get rid of the allergen. After this, treat the organs of vision with antihistamines. Adults use drugs such as Citrine, as well as Diazolin and L-cet. Young patients should be treated by an experienced ophthalmologist.
The disease - trachoma is treated with antibacterial medications, as well as sulfonamides.
All diseases that provoke redness of the organs of vision or cause suppuration must be treated by eliminating the pathogen. In addition, you need to get rid of the inflammatory process. Therapy includes the presence of drugs that have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect along with an antihistamine effect.
Corneal abrasion
Corneal abrasion is diagnosed based on clinical presentation and eye examination. If necessary, fast-acting local anesthetics can be used to facilitate eye examination. The doctor also conducts an examination under a Wood's lamp. The doctor finds an infection or abrasion. An infection involving the cornea requires initiation of therapy by an ophthalmologist within 1-2 days. Patients with corneal abrasion may have a foreign body under the upper eyelid.
Treatment includes:
- supportive care;
- cycloplegics: atropine, cyclopentolate (cyclogyl), hematropine, scopolamine and tropicamide;
- pain control: topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or oral analgesics.
The need for antibiotics for uncomplicated abrasions has not been demonstrated. Aminoglycosides should be avoided because they are toxic to the corneal epithelium. All steroid medications are contraindicated in patients with corneal abrasion.
For information about corneal pathologies, watch the video:
Medications
Basically, the treatment of diseases that cause suppuration is carried out with the help of antibacterial drugs, since their development is based on the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the eye tissue. In addition, it is recommended to wash the eyes with antiseptics, and for diseases of allergic etiology, use antihistamines, hormonal drops and ointments.
Eye drops
Table. The main drugs for suppuration.
| A drug | Features of the impact |
| "Albucid" | A drug based on sodium sulfacide, has a pronounced bactericidal effect, recommended for use in barley, blepharitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers and other infectious diseases |
| "Levomycetin" | The drug is available in the form of drops, ointments and tablets, and is effective against a number of pathogenic microorganisms, including those that are resistant to antibiotics. Indications for use include purulent and inflammatory processes (keratitis, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, etc.) |
| "Tobrex" | The active substance of the drug is tobramycin, which is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Destroys streptococci, staphylococci, Klebsiella, enterobacteria and other microorganisms that cause ophthalmic diseases. Can be used as a prophylactic agent to prevent complications after eye surgery |
| "Floxal" | An antibacterial agent based on a substance from the fluoroquinolone group, used for blepharitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis and other diseases, including chlamydial forms |
The list of antibiotics that are used to treat ophthalmic diseases is far from complete - the doctor can use their analogues or drugs based on other active substances.
Tetracycline ointment is the most effective remedy for eliminating suppuration in the eyes. The drug has an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect, which was caused by pathogenic microorganisms. The active ingredient of the ointment is tetracycline, but it also contains lanolin and medical petroleum jelly.
Tetracycline also has bacteriostatic properties, thanks to which it is able to destroy staphylococcal, streptococcal, chlamydial and many other types of pathogens that lead to eye inflammation.
Floxal is a remedy that is not inferior in its effectiveness to drugs containing tetracycline
The ointment has an antimicrobial effect, which is very important for the treatment of inflammatory processes in the eyes due to invasion of pathogenic microflora
It is indicated for suppuration of the eye due to blepharitis, barley, conjunctivitis, injuries, etc. Just like Tetracycline ointment, Floxal is applied behind the eyelid several times a day, but not more than 2 weeks.
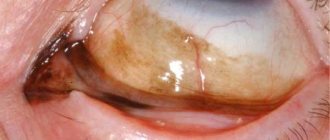
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
Subconjunctival hemorrhage is diagnosed clinically. It is not dangerous. The blood resolves within a few weeks and no special treatment is required. Warm compresses and ophthalmic lubricants such as hydroxypropylcellulose, methylcellulose, and artificial tears may relieve symptoms.
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
The doctor checks for corneal lesions or penetrating damage. Then urgent hospitalization to the ophthalmology department is needed. Recurrent bleeding may require evaluation for bleeding disorders. If the patient is taking Warfarin, the blood INR should be checked. To strengthen the vascular wall, Ascorutin is prescribed. For faster blood resorption, Emoxipin is recommended.
How to wash a festering eye
When the eyes are purulent, it is important to provide the patient with first aid. The result of treatment depends on this.
If the eyes are festered, the first step is to remove the accumulations of pus. All therapeutic procedures are done after thorough hand treatment. The eyes are washed with warm boiled water. Then you need to moisten the cotton wool with a solution of furatsilin and rinse the eye.
To improve the condition of the visual organs, compresses made from tea or chamomile decoction are used. These procedures help reduce the intensity of the eye inflammation.
Episcleritis
Episcleritis is a localized area of inflammation involving the superficial layers of the sclera. Lasts up to 3 weeks and is diagnosed by a doctor based on complaints and examination. Repeated episcleritis occurs with concomitant systemic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment includes supportive care and the use of artificial tears. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are not usually prescribed. Steroids may be prescribed in severe cases. If episcleritis recurs and symptoms increase, you should undergo a thorough examination by an ophthalmologist.
Red eye and purulent discharge are the main signs of inflammation. The condition is usually benign and can be treated by a primary care physician or family doctor. If severe pain is not relieved by local anesthetics, vision loss increases, and purulent discharge becomes abundant, then you should consult an ophthalmologist to clarify the diagnosis and correct treatment.
Localization of inflammation in the eyes
If the eye is inflamed, then this is understood as a complex adaptive reaction of the organ in response to the action of internal or external factors. It manifests itself as a complex of symptoms. The degree of their severity depends on the cause of inflammation of the eye mucosa. It is infectious or non-infectious in nature. The pathology affects the eyelids, conjunctiva or iris.
The eye has a very complex structure. It consists of several parts and fabrics, each of which has its own functions. Inflammation of the organs of vision is understood as the totality of their various inflammatory pathologies. They affect one or another part of the organ of vision. When the eyeball is inflamed, a pronounced vascular pattern is observed.
- conjunctiva;
- eye socket;
- cornea;
- iris;
- tear ducts;
- vessels.
It is worth distinguishing between inflammation itself and redness of the eye, which is caused by physical factors. These include dust, lenses, sand, bright light, wind, smoke and even headaches. Redness as a result of these factors is comparable to simple irritation, which most often goes away on its own.