Signs of the disease
Adenoviral conjunctivitis flares up in spring and autumn. It is common in children's groups. The first symptoms observed in children are:
- headache;
- runny nose;
- a sore throat;
- cough;
- temperature increase;
- chills;
- abdominal pain;
- weakness.
After the primary symptoms inherent in acute respiratory infections, sore throat, and flu, secondary symptoms begin to appear:
- inflammatory process;
- development of conjunctivitis.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane has an incubation period that lasts from 7 to 8 days. Initially, nasopharyngitis develops, accompanied by fever, cough, runny nose, and sore throat. After the next increase in temperature, other symptoms appear. They initially affect one eye, then move to the second. The main signs of inflammation are noted:
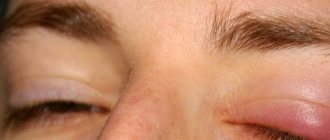
- swelling of the eyelids;
- development of photophobia;
- the formation of follicles on the inner region of the mucous membrane of the eyelid;
- redness;
- discharge of clear mucus;
- there is an increase in regional lymph nodes;
- decreased vision (disappears after treatment);
- the sensitivity of the cornea decreases.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis affects children and adults with the progression of respiratory tract diseases (sore throat), as well as viral diseases (measles, rubella, chickenpox). Treatment of the underlying disease is necessary, and adenoviral conjunctivitis may disappear on its own. It is very important to cure a runny nose, sore throat, cough that occurs with a sore throat, and acute respiratory infections. At the same time, inflamed mucous membranes are washed with herbal infusions.
Reasons for appearance
The spread of this type of inflammation is carried out by airborne droplets. After infection, damage to the eyes and nasopharynx is noted. Adenoviral conjunctivitis can occur in a preschool, school, or institute during epidemiological outbreaks.
The disease is mainly common in children and middle-aged adults. Its duration is within 1 – 3 weeks. The inflamed mucous membrane hurts, the throat, runny nose and other symptoms also bring a feeling of discomfort.
The causes of infection may also be:
- contact with infected people;
- dirty hands - when coming home a person could scratch or rub his eyes with dirty hands;
- household items previously used by an infected person;
- surgical intervention;
- severe hypothermia;
- eye injury;
- progression of respiratory diseases (flu, sore throat, acute respiratory infections).
Forms of the disease
Catarrhal is characterized by mild inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane. There is redness and some mucus. The disease progresses easily in a fairly short period of time (about a week).
Membranous is quite common. It occurs in 25% of cases. It is characterized by the formation of a thin film, which has a grayish-white color and is easily removed with cotton wool. Sometimes these thin films are firmly attached to the conjunctiva, on which bleeding ulcers form. With such symptoms, experts recommend being examined for the presence of diphtheria.
During recovery, there are no traces of the film on the mucous membrane. Rarely, minor scarring may be observed. Peculiar hemorrhages and infiltrates may appear in the conjunctiva. With complete recovery, nothing remains of these formations; they dissolve.
Follicular is characterized by the appearance of small vesicles, which in rare cases reach large sizes. The eye hurts and irritates the child.
The diagnosis of the disease is determined by a specialist after studying the clinical picture. The disease is also detected by smear and culture results.
Complications
Adenoviral conjunctivitis in children cannot be started. If you have a runny nose, cough, sore throat, accompanied by pain in the eyes, redness and inflammation, you should consult a specialist. The symptoms are by no means harmless. It is necessary to carry out timely treatment to eliminate the symptoms of sore throat and conjunctivitis. Otherwise, inflammation of the mucous membrane can cause complications in children and adults such as:
These complications arise due to viral damage to the tissues of the eyeball and cornea. There is cloudiness on the cornea, and a decrease in visual acuity can be observed.
Prevention
Adenoviral conjunctivitis in adults and children is not difficult to cure if treatment is started in a timely manner. The most common prevention methods are:
- wet cleaning in a room with a large team;
- frequent ventilation of the room;
- timely treatment of respiratory tract diseases (sore throat, flu, acute respiratory infections);
- timely isolation of an infected person;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules.
Treatment of mucosal inflammation
How long the treatment of this inflammation in children and adults will last depends on the degree of development of inflammation and the body’s immunity.
Treatment of this inflammation in adults and children involves the use of drops and ointments. Drops such as Albucid (sodium sulfacyl) are very effective. This remedy is considered universal for the treatment of this type of mucosal inflammation. It eliminates both mild and acute conjunctivitis.
Interferon-based drops are also very effective for treating this disease:
- Ophthalmeron. These drops have anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antiviral effects. Doctors recommend instillation 6 - 8 times a day in cases where conjunctivitis is acute. You only need 1-2 drops of the product. For mild inflammation, it is enough to perform the procedure 2 – 3 times a day.
- Aktipol. It is an inducer of endogenous interferon. These drops are characterized by strong antioxidant and regenerating properties. Has a very strong antiviral effect. Recommended dosage is 2 drops. It is necessary to instill the inflamed mucous membrane about 8 times a day. Treatment will last approximately 10 days.
- Poludan. These drops are based on a biosynthetic complex of endogenous interferons and cytokines. Recommended dosage – 1 – 2 drops. It is necessary to treat the inflamed mucous membrane 6 – 8 times a day.
Ointments are also used to treat inflammation in children and adults. They should also be used as prescribed by a doctor. Before applying, it is necessary to rinse the child’s eyes with a special infusion prepared from the following herbs: sage, chamomile, tea leaves. After washing the inflamed eye, drops are instilled.
After completing these procedures, you should wait half an hour and lubricate with ointment. Treatment of mucosal inflammation is possible with the following ointments:
- Tebrofen ointment. It effectively copes with various viral eye diseases. Tebroferon ointment should be applied to the inner edge of the eyelid. Lubrication should be done 3 – 4 times a day.
- Florenal. This ointment is for inflammation of the eye mucosa. It has a strong antiviral effect, inhibits adenoviruses, herpes viruses, and Varicella-zoster virus. It should be applied behind the lower eyelid 2 – 3 times a day. Treatment can last from 10 to 45 days.
To treat conjunctivitis in children, Dr. Komarovsky recommends rinsing the nasal cavity and eyes. For this purpose, a special saline solution is used. The use of such a remedy is very effective if a child has a viral infection. Preparation of the solution is very simple: 1 teaspoon of salt + 1 liter of water.
According to Dr. Komarovsky, any viral conjunctivitis will go away on its own only when the human body develops immunity to the infection. And he will be able to do this only after 5 - 7 days.
According to experts, you should consult a doctor in the following cases:
- child's age up to one year;
- manifestation of redness, photophobia in a child;
- Pain in the eyes;
- the appearance of a bubble in the upper eyelid.
Temperature abdominal pain conjunctivitis
. or: Pharyngoconjunctival fever
Forms
Acute respiratory disease is accompanied by various damage to organs and body systems:
- rhinopharyngitis (damage to the nasal passages and pharynx);
- rhinopharyngotonsillitis (damage to the nasal passages, pharynx and palatine tonsils);
- nasopharyngobronchitis (damage to the nasal passages, pharynx, bronchi);
- pharyngoconjunctivitis (pharyngoconjunctival fever) - damage to the pharynx in combination with damage to the mucous membrane of the eyes (conjunctiva);
- conjunctivitis and keratoconjunctivitis (damage to the mucous membrane of the eyes and cornea (transparent membrane) of the eye);
- pneumonia (lung damage);
- Another combination of organ damage is also possible.
Pharyngo-conjunctival fever by :
- increased body temperature;
- pharyngitis (inflammation of the mucous and lymphoid tissue of the pharynx);
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (accompanied by a sensation of a foreign body in the eye, burning);
- a whitish film may form on the surface of the eye and a white-yellow discharge in the corners of the eye;
- frequent dry cough, which turns into a wet cough with sputum on the 3-4th day.
Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis is accompanied by:
- burning sensation in the eyes;
- lacrimation;
- clouding of the cornea;
- erosion (destruction) of the cornea up to loss of vision;
- gastroenteritis (damage to the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by frequent bowel movements up to 5 times a day);
- sharp pain in the abdomen in the navel area.
Adenoviral atypical pneumonia is accompanied by pneumonia caused by the virus itself, and not as a result of the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, develops against a background of severely reduced immunity, and is characterized by a severe course.
Diagnostics
- Analysis of patient complaints: a characteristic combination of increased body temperature, runny nose, sore throat, redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes.
- Often in the anamnesis there are indications of contact with a patient (cold), outbreaks of infection in the team (for example, a large number of children with “colds” in the class).
- Examination of the patient: nasal breathing is difficult, mucous discharge from the nose; in the pharynx (throat) there is hyperemia (redness), the conjunctiva is swollen, red, etc.
- To identify the pathogen and confirm the diagnosis, ELISA (immunofluorescence analysis) and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) of a nasal swab are used.
- In most cases, studies to identify the pathogen (rhinovirus) are not carried out due to its mild course. The disease occurs with a general diagnosis - ARVI.
- It is also possible to consult an ophthalmologist.
Treatment of adenovirus infection
There is no specific therapy for adenoviral infection; treatment is symptomatic.
In mild cases the following are prescribed:
- eye drops, ointments (for eye damage) - strictly as prescribed by the doctor;
- nasal drops (vasoconstrictor, oil, etc.);
- immunomodulatory drugs - strictly as prescribed by the doctor;
- vitamin C (and products containing it: rosehip decoction, cranberry compote, etc.);
- drinking plenty of water;
- chamomile decoction.
In severe cases, treatment is carried out in a hospital. In addition to the above, they carry out:
- infusion therapy - solutions are administered intravenously to reduce intoxication of the body;
- antibacterial drugs (if a bacterial infection is attached).
Complications and consequences
In most cases, adenovirus infection occurs without complications and has no consequences.
The most common complications are:
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
- angina;
- sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses);
- otitis (inflammation in the ear cavity);
- swelling, necrosis (death of tissue areas) of the walls of the bronchi and alveoli;
- damage to the liver, kidneys, spleen;
- exacerbation of other existing chronic diseases.
Prevention of adenovirus infection
- Avoid visiting crowded places (theaters, shops, etc.) during an infection epidemic.
- If one of the family members becomes ill with an adenovirus infection, he must be isolated and given a separate towel and dishes. The patient must wear a medical mask.
- Hardening the body (carrying out procedures aimed at increasing the body’s resistance to the effects of low (cooling) and high (overheating) temperatures. For example, dousing with cold water).
- During the period of rising viral incidence (ARVI), take multivitamin preparations or vitamin C.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Taking interferon.
- Putting oxolinic ointment in the nose.
- Strict adherence to personal hygiene rules (regular hand washing after contact with objects on which the virus could remain).
- Disinfection of premises.
INFORMATION FOR REVIEW
Consultation with a doctor is required
“Children's infectious diseases”, V.N. Samarina, 2007. “Infectious diseases in children”, V.V. Ivanova, 2009. “Infectious diseases in children”, V.F. Uchaikin, 2011.
“Influenza and other acute respiratory diseases” Guidelines for the clinic, diagnosis, treatment and prevention in the armed forces of the Russian Federation. Moscow, 1998
What to do if you have an adenovirus infection?
- Choose a suitable therapist
- Get tested
- Get a treatment plan from your doctor
- Follow all recommendations
source
Fever and conjunctivitis: can this happen?
When a person observes sour eyes and a hot forehead in himself or his child, does he worry about whether there is a fever with conjunctivitis, or are these signs of a more serious pathology? Inflammation of the conjunctiva often occurs as a result of infection. To successfully fight germs, the body raises its temperature. This is a completely normal reaction of the immune system to an irritant.
Causes of fever with conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis with fever can occur as an independent disease or develop against the background of infectious inflammation of the respiratory tract: ARVI, rhinitis, bronchitis and others. Depending on the pathogen, the following types of conjunctivitis occur:
- Bacterial - appears due to infection with staphylococcus, streptococcus, pneumococcus, gonococcus. Transmitted through shared household items and close contact. Bacteria are often brought into the eyes by dirty hands or from stale towels or pillowcases. The spread of infection is likely due to sinusitis.
- Viral is the most common type of conjunctivitis. It is transmitted by airborne droplets and can develop against the background of acute respiratory viral infections or a runny nose.
- Adenoviral - characterized by simultaneous inflammation of the throat and conjunctiva. Another name is adenopharyngoconjunctival fever (AFCL). Infection occurs from an infected person. The peak of the disease occurs in the spring.
Symptoms
A high temperature during conjunctivitis in adults and children indicates an acute course of the disease. When the conjunctiva is infected, the average incubation period lasts from 2 to 7 days. The following symptoms are observed:
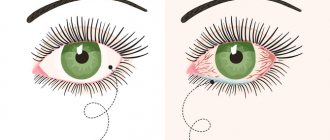
- Severe redness of the eyes, swelling of the eyelids. The phenomenon is accompanied by itching and a feeling of sand.
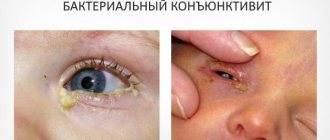
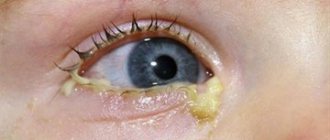
- Tear production increases. Discharge appears. The eyes turn sour during sleep, the patient has difficulty opening his eyelids in the morning. A viral infection produces clear, thick mucus, a bacterial infection produces pus, and an adenoviral infection produces pus with mucus.
- Increased sensitivity to light and wind.
- General malaise, loss of strength, loss of appetite.
- AFCL always occurs together with pharyngitis. The throat turns red and hurts, the voice becomes hoarse, and a dry cough appears. Adenovirus infection also provokes the formation of films on the eyes.
- The lymph nodes, usually the ones in the air, become enlarged.
It is not difficult for an ophthalmologist to diagnose infectious conjunctivitis based on these signs. Sometimes, to select medications, it is necessary to do an analysis of pus and mucus from the eyes to accurately determine the pathogen. Additional consultation with a therapist or pediatrician is recommended to identify concomitant ailments.
Treatment of conjunctivitis with fever
For adults, concomitant infections should be treated to make a full recovery. The following drugs are prescribed locally:
- For a bacterial infection, apply ointments under the lower eyelid at night, and antibacterial drops during the day.
- At temperatures above 38.5, antipyretics based on paracetamol and ibufen are used. Adults can take Aspirin. It will not only reduce the temperature, but also improve tissue nutrition by thinning the blood.
- Anti-inflammatory drops are used to reduce hyperemia and relieve itching. When the mucous membrane is dry, artificial tears are recommended.
- Local and general vitamin therapy is prescribed, including calciferol, ascorbic acid and B vitamins.
It is useful to wipe pus from your eyes during the day with diluted aloe juice, chamomile and calendula decoctions.
If all the doctor’s recommendations are followed and the disease progresses well, treatment takes from 7 to 15 days.
Features of the disease in children
If a child has a fever and his eyes are purulent, he needs to be seen urgently by a doctor, especially when the baby is less than a year old. In children, the spread of infection occurs much faster and the likelihood of complications is higher.
As first aid, the eyes are washed from pus with a swab of sterile gauze moistened with chamomile infusion or boiled water. If the temperature is above 38.5 degrees, it is brought down with Efferalgan, Paracetamol, Panadol. Albucid can be used topically. All other medications are used only as prescribed by a doctor .
Conjunctivitis and fever are common companions in children under 7 years of age. Often, every cold in a child occurs with inflammation of the conjunctiva, which goes away on its own after recovery. In this case, the eyes do not require separate treatment.
Prevention of conjunctivitis
In order not to guess whether conjunctivitis can cause a fever, you need to reduce the likelihood of the disease. This is done using simple recommendations:
- treat infectious diseases in a timely manner;
- during epidemics, appear less often in public places;
- replace contact lenses on time and keep them clean;
- touch eyes only with clean hands and tools;
- do not use other people’s hygiene items;
- monitor the cleanliness of towels and bed linen;
- when sick, sneeze and cough into your elbow or tissue;
- foreign bodies must be removed from the eyes with clean hands using a sterile bandage;
- wash your hands more often.
Source: https://sfmggu.ru/temperatura-boli-v-zhivote-konyuktivit/
What is adenoviral sore throat
Tonsillitis, which is caused by a virus, is much milder than bacterial tonsillitis. In some cases, the symptoms are mild and the disease is often diagnosed as a common cold. This type of sore throat affects young children and adults under 40 years of age. Sore throat due to adenovirus infection is seasonal. It is caused by adenoviruses, a family of DNA viruses. Depending on the pathogen, they also distinguish:
For proper treatment, it is necessary to identify the virus that caused the sore throat. To do this you need to undergo laboratory tests.
How does the adenovirus spread among adults and children? Routes of infection:
- contact with a patient or carrier - airborne;
- through the use of household items, dishes, toys - contact and household;
- through contaminated food or water - nutritional.
At risk are children from 3 to 7 years old attending kindergartens or schools. Parents often neglect the health of others by bringing their sick child to an educational institution.
Weakened immunity in an adult or child increases the chance of adenoviral tonsillitis. The following factors significantly increase the likelihood of the disease:
- poor ecology - air pollution;
- natural conditions - sudden changes in temperature and humidity;
- unhealthy diet, lack of vitamins;
- smoking;
- tonsil injuries;
- stress and emotional stress;
- hypothermia, eating cold foods and drinks.
The tonsillitis epidemic mainly occurs in the cold season. The adenovirus, which gets on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, causes the spread of infection and the appearance of symptoms.
Symptoms of adenovirus infection
According to Wikipedia, adenovirus infection is an infectious disease caused by adenoviruses. What are adenoviruses? These are DNA-containing viruses, sensitive to high temperatures and which are stored in the body for almost 2 months. Therefore, you can become infected with adenoviral sore throat from a person who has already had the disease. The incubation period lasts about a week. What are the main signs of a disease such as adenoviral tonsillitis:
- fever, acute;
- headache;
- lack of appetite;
- pain in the throat and when swallowing;
- general weakness,
- vomiting (mainly in young children);
- cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis;
- sometimes asthmatic syndrome is observed;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck;
- swelling and redness of the tonsils;
- stomach ache;
- diarrhea.
Conjunctivitis appears 1-3 days after the onset of the disease. Sometimes there is an enlargement of the liver and spleen. In some patients, there is a decrease in leukocytes in the blood. Elevated body temperature can last from 5 to 10 days.
Associated symptoms
Redness of the eyes is accompanied by other symptoms: fever, runny nose, cough. If conjunctivitis is diagnosed, the patient may still experience profuse tears, a feeling of a foreign body in the eyes, and a feeling of glued eyelashes in the morning. But there can also be complications. If the eye flu has damaged the cornea, there may be pain, twitching of the eye and severe fever, requiring more serious treatment.
ARVI is also characterized by symptoms:
- sore throat;
- redness and sore throat;
- dry, intermittent cough with sputum;
- feelings of general intoxication.
Redness of the eyes appears only if a bacterial infection is associated with the disease. With eye flu, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes (keratitis) may also occur. Severe forms of the disease are observed mainly only in the case of an epidemic of colds.
Soreness
During illness, the body is greatly weakened. The patient may feel lethargic, tired, and have sore eyes due to the spread of the virus in the body. Toxins even penetrate into the muscles of the body, weakening them. The mucous membrane of the nose swells, pain appears in the frontal part of the head and around the eyes.
Eye pain may include:
- like a sensation of a foreign body, sand;
- excessive dryness, causing itching;
- feeling of stickiness due to purulent discharge.
Migraines may worsen when turning or tilting the head. It is recommended to drink as much warm liquid as possible and take medications that reduce fever and treat a runny nose. During illness, pain may radiate to the head and some areas of the face (if the trigeminal nerve is affected).
Expert opinion
Kim Oksana Alexandrovna
Head of the ophthalmology clinic. Ophthalmologist with more than 10 years of experience.
In particularly difficult cases, headaches intensify with exacerbation of the disease and may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting. There may be dizziness and even loss of consciousness. The temperature during ARVI can rise to 38°C on the first day, but does not stay high for long.
Tearing
With ARVI, due to intoxication of the body, the eyes may water all the time. When moving the eyeballs, painful sensations, photophobia, and burning may occur. Tearfulness usually begins due to a severe runny nose and cough, when the nose is stuffy and the nasopharyngeal mucosa is swollen. Red and constantly watery eyes during ARVI lead to the fact that it becomes difficult to work at the computer or look at the light.
A complication can lead to epidemic keratoconjunctivitis. Not only uncontrollable tears occur, but also a sensation of a foreign body in the eyes, swelling of the eyelids, redness of the mucous membrane, eyelids, photophobia, and decreased clarity of vision. At first, all these symptoms may occur in one eye, and then move to the second.
Swelling
During a cold, swelling of the nasal mucosa with impaired nasal breathing is observed. The eyelids also swell and bruises appear under the eyes. With conjunctivitis of a viral and microbial nature, the eyes swell due to the accumulation of inflammatory fluid. Swelling of the eyelids can also occur if you frequently touch your eyes and wipe them with a tissue.
Swelling is observed:
- century;
- tonsils;
- mucous membrane of the nose or eye.
During ARVI, not only does capillary permeability increase and swelling of the mucous membrane and nasal turbinates develops, but breathing becomes difficult, nasal discharge and other unpleasant symptoms appear. When a cold worsens, an abscess occurs in the lacrimal sac and eyelid, and pus accumulates in the eyes. Swelling of the entire face may be observed, especially in case of impaired nasal breathing, and an increase in the size of the cervical lymph nodes.
Swelling of the nasal cavity during ARVI lasts throughout the entire period of the disease. Vasoconstrictors can minimize swelling and improve the flow of mucus from the paranasal sinuses. This is very important as it reduces the risk of sinusitis and other complications.
Swelling around the eyes can also occur for reasons unrelated to ARVI. The reason may be high salt intake, which retains water in the body, or high fluid intake at night. A separate topic: swelling due to kidney problems, when metabolism and moisture release through the kidneys and urinary tract are disrupted. In addition, swelling can be a manifestation of allergies.
Drug therapy
Treatment of adenoviral sore throat is carried out at home. Only in severe cases is the patient admitted to the hospital. Before starting treatment, you should visit a doctor and determine the nature of the sore throat. Antibiotics will not help in this case. They are attributed when sore throat is caused by a bacteriological infection. If you take them in the case of a viral form of sore throat, the drugs will disrupt the intestinal microflora and reduce the patient’s immunity, which will only worsen the situation. Therefore, antiviral medications are prescribed:
These medications are mainly taken in tablets. Only in severe cases are injections prescribed.
If your body temperature has risen above 38 °C, you need to take medications that bring down the temperature:
- Paracetamol;
- Nurofen;
- Panadol;
- ibuprofen-based drugs.
To increase the effect of antiviral drugs, take immunostimulating medications. Course of treatment 7-10 days:
For severe sore throat, lozenges or sprays are given:
To relieve nasal congestion and runny nose:
To eliminate swelling of the tonsils, antihistamines are prescribed:
If plaque appears on the tonsils, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics:
For conjunctivitis, special drops are used.
In addition to drug therapy, the patient must remain in bed, eat properly and drink a lot. The temperature of the food should not exceed 50 °C and should not be too hard, so as not to injure the sore tonsils. The patient should also gargle 3-4 times a day. For rinsing, you can use herbal decoctions, salt, soda or pharmaceutical preparations: hydrogen peroxide, Dimexide, Miramistin.
Treatment of pathology
Medications that the doctor selects based on the diagnosis will help get rid of inflammation and cure a sore throat. Antibiotics will help destroy the bacterial infection and stop the inflammatory process:
Augmentin must be taken to destroy pathogenic bacteria.
- "Flemoxin";
- "Amoxicillin";
- "Augmentin".
In addition to oral use, the antibiotic is used topically, using aerosols and sprays for irrigation of the mucous membrane. Well proven:
- "Ingalipt";
- "Hexoral";
- "Bioparox".
The rinsing procedure, which is recommended to be done in the morning, during the day and before bedtime, will help to cleanse the mucous membranes and rinse out ulcers in the throat. It is effective to gargle with solutions that contain the following medications:
Pleasant-tasting lozenges and lozenges that eliminate pain and sore throat help treat your throat. Well proven:
When should surgery be done?
If purulent plugs in the throat cannot be removed conservatively, the doctor decides to carry out surgical treatment, during which the inflamed tonsils are removed. Common types of surgery are:
- traditional resection;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser excision;
- radiofrequency ablation.
Return to contents
Unconventional methods
Folk remedies can be used as an addition to therapy after consultation with a doctor. Pus in the throat can be removed faster if you rinse the mucous membrane with an infusion prepared according to this recipe:
- Combine chamomile, St. John's wort and sage flowers in equal proportions.
- Separate 1 tbsp from the mixture. l. and pour 250 ml of boiling water over it.
- Use the medicine in the morning and evening after meals.
Return to contents
Treatment of infection with folk remedies
To speed up the healing process, you can use folk recipes. To remove toxins from the body, you need to drink a lot and often:
- tea with honey and lemon;
- compotes from viburnum, raspberries, rose hips;
- fruit drinks from berries and fruits;
- herbal decoctions.
This simple method will help avoid complications due to tonsillitis. You should also eat right. What foods should you avoid:
A good microclimate should be created in the room where the patient is located. Air that is too dry makes breathing difficult, so it needs to be humidified regularly. You can use a special device for humidification or hang wet towels in the room. It is necessary to regularly ventilate the room so that the virus does not linger in the air. It is also important to remember that with adenoviral sore throat you cannot do inhalations or any thermal procedures. The following recipes will be useful:
- Oat decoction. Pour 300 grams of thoroughly washed oats with a liter of hot milk. Cook the resulting mixture for 40-50 minutes. Add half a tablespoon of honey to the mixture. Drink in small portions up to 6 times a day.
- Aloe infusion. Pour 300 grams of crushed aloe leaves with a glass of honey and a glass of good red wine (preferably take Cahors). The product should be infused in a dark place for 10 days. Take a spoon three times a day.
- Egg yolk mixture. Separate the yolk from the white (3 pieces). Mix eggs with butter (3 tablespoons), honey and flour (1 teaspoon each). Take a tablespoon three times a day.
The patient should also avoid close contact with others. He must be provided with his own separate dishes and hygiene items.
How is the treatment carried out?
If a child or an adult’s visual organs become inflamed and begin to fester, they resort to the help of a medication called “Albucid”. With its help, it is possible to relieve swelling of the eyes, relieve the patient of pus and redness of the mucous membrane. Actipol and Oftalmoferon can also be prescribed. The first medication has a disinfecting effect. Preferably, instillation of the visual organs is prescribed about 7 times a day, 2 drops in each eye. As for Oftalmoferon, the scheme of its use does not differ from Aktipol.
Swollen eyes are also treated with anti-inflammatory medications for external use. Often they resort to Florenal ointment. The mechanism of operation of this medicine is based on the destruction of the virus that provoked the condition in which the eyes become inflamed and swollen. Antibacterial vitamin medications are also used, which help improve the immune system.
In addition to the therapy of the visual organs, treatment is also required to relieve allergy symptoms.
Possible complications
If the symptoms of the disease are ignored and timely medical assistance is not provided, the following complications may occur against the background of a sore throat:
- Otitis media - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear;
- purulent sinusitis - an inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses and sinuses;
- pneumonia;
- pleurisy - pathological inflammatory processes in the pleural membranes;
- Eustachian tube obstruction (mostly found in children);
- laryngospasm - spasm of the muscles of the larynx;
- kidney damage.
Conjunctivitis with tonsillitis is a rather dangerous symptom that can cause the following complications:
- transition to a chronic process,
- blurred vision;
- dry eyes;
- bacteriological conjunctivitis.
This symptom also requires separate treatment, but only with the permission of a doctor.
Treatment of “collective disease” in adults
If conjunctivitis is not advanced, it can be cured at home. Cool boric water is suitable for wiping your eyes. Drops are placed behind the eyelid and can be purchased at a pharmacy without a prescription. After the solution enters, the eyes are kept closed for several seconds. During the treatment of conjunctivitis, you should stop using cosmetics and wearing contact lenses. During illness, you should not overstrain your eyes; it is better to stop reading, watching TV and working at the computer for a while. Lotions are effective in the treatment of conjunctivitis and sore throat. Once a day, you can apply cotton pads or gauze soaked in dill juice to your eyelids for 15 minutes. Rosehip infusion is used in the same way. Two tablespoons of berries are poured into a glass of boiling water and infused. The strained solution is applied to the eyes. Herbal tinctures are effective - chamomile, sage, cornflower. Compresses are also made from aloe juice. It is diluted with cold boiled water in a one to one ratio. Soak gauze in the resulting liquid and keep it on the eyelids for 5-10 minutes 1-2 times a day. If there is no improvement 2-3 days after home treatment, you should consult a doctor.
Preventive actions
There are no vaccinations against adenoviruses, so to protect yourself from the disease, you need to adhere to general preventive rules:
- healthy and balanced diet;
- physical activity and regular sports;
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- stabbing;
- during epidemics, avoid large crowds of people.
- hygiene of the body, especially hands.
Fruits and vegetables should be washed thoroughly before consumption, and in the summer try not to swim in unfamiliar bodies of water. If there is a suspicion of adenoviral tonsillitis, the patient should be isolated from others and a doctor should be called. When in contact with a patient, you should wear a mask and provide him with certain household items.
Prevention of conjunctivitis and sore throat in adults and children
During seasonal epidemics, contact with sick people should be avoided. When returning from the street, the first thing you should do is wash your hands. The general recommendations are the same for people of any age. Bad habits, violation of work and rest schedules weaken the body. It is a known fact that people who smoke are more likely to get viral diseases. And, conversely, adults and children who play sports, spend a lot of time in the fresh air, and practice exercises get sick much less often. This is due to the fact that healthy procedures and healthy varied foods strengthen the immune system. In this case, the body's defenses are able to resist diseases.
What is Viral conjunctivitis -
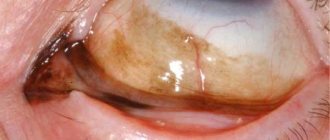
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the outer clear mucous membrane that covers the sclera and inner surface of the eyelids.
Viral conjunctivitis. most often associated with an upper respiratory tract infection (adenoviral or herpetic), and may appear with a common cold and/or sore throat.
Viral conjunctivitis has now become very common. They are very contagious and the disease in many cases becomes epidemic. Conjunctivitis is caused by a large number of viruses of different types.
Errors in diagnosis, especially when trying to independently distinguish pharyngitis from acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis), lead to uncontrolled use of antibiotics for the treatment of pharyngitis, and thus the formation of antibiotic-resistant microflora.
Subsequently, this becomes the cause of various inflammatory processes in the throat caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Treatment of such diseases is always long and complex.
And on the contrary, having a sore throat, patients try to get by with traditional methods of treatment. Such carelessness can be costly, as the disease often becomes more complicated. Almost all glomerulonephritis and rheumatic reactions are the result of self-medication for angina.
Sore throat (acute tonsillitis) is a disease of an infectious nature with a predominant lesion of the palatine tonsils. The main focus of inflammation is in the thickness of the tissue and mucous membrane of the tonsils. The vast majority of sore throats are caused by bacteria - streptococci, staphylococci and their associations.
Pharyngitis (inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa) has a varied etiology - infectious, allergic, traumatic. If we talk about infectious causes of the disease, pharyngitis in the vast majority of cases is caused by viruses. Fungi and bacteria rarely infect the pharyngeal mucosa.
Conjunctivitis may cause headaches
In ophthalmology, conjunctivitis refers to a group of ophthalmological diseases in which the conjunctiva of the mucous membrane of the eyeball is damaged. There are several types of disease, each of which is caused by a specific type of pathogen. Currently, viral conjunctivitis is quite common and is diagnosed in both adults and children.
Many people underestimate the complexity of the disease and, when it develops, often ignore the symptoms or try to self-medicate, which makes a big mistake, since the lack of therapeutic therapy can lead to a decrease in visual acuity, even to complete blindness.
Viral conjunctivitis is a fairly contagious disease, so a sick person puts not only his own health at risk, but also the health of those around him.
According to statistics, this disease occupies a leading position among all ophthalmological diseases and often reaches epidemic proportions, since it is quite easy to become infected with this disease. Symptoms of viral conjunctivitis are specific and directly depend on the type of pathogen, as well as the characteristics of the human body, concomitant diseases and other factors.
How does viral conjunctivitis develop?
The causative agent of viral conjunctivitis can be various viruses, but most often the disease is caused by adenovirus, enterovirus, herpes viruses, rubella or measles.
Infection with a viral infection can occur in any conditions, but most often infection occurs through household, contact or airborne droplets.
The pathogens are quite resistant to the external environment and can maintain their vital activity for a long time.
Once the virus has entered the mucous membrane of the eye, it begins to actively develop and within 2 to 5 days, pronounced symptoms of the disease appear. The disease has a pronounced clinical picture, which is characterized by redness of the conjunctiva of the eye.
Initially, viral conjunctivitis affects only one eye, but within 1–2 days, the virus will spread to the second eyeball. Basically, viral conjunctivitis is manifested not only by damage to the eyes, but also by other symptoms affecting the ENT organs and respiratory tract.
Inflammation often causes an increase in body temperature with subsequent intoxication of the whole organism.
Treating conjunctivitis is not at all difficult, but quick results from treatment can only be obtained in the early stages of the disease.
In cases where treatment is carried out incorrectly or is completely absent, the disease will progress, and its advanced forms often lead to damage to the deeper tissues of the eyeball, including the cornea.
When a viral infection affects the cornea, white spots (spots) appear on it, which impair vision and can remain for several months, or even years.
Causes
The main cause of viral conjunctivitis is viruses of various types, but in addition to this, there are a number of predisposing factors that increase the risk of infection:
- lack of personal hygiene rules;
- habit of rubbing your eyes with dirty hands;
- myopia;
- farsightedness;
- astigmatism;
- hypothermia of the eyes;
- improper use of contact lenses;
- prolonged and regular eye strain;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- vitamin deficiency;
- decreased immunity;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx.
Experts in the field of ophthalmology note that in 80% of cases, the disease is caused by adenoviruses, less often by coxsackieviruses or enteroviruses. Basically, viral conjunctivitis affects both eyes of an adult, and the signs of the disease are pronounced and require immediate treatment.
Symptoms and first signs
The incubation period of viral conjunctivitis is 2-12 days, it depends on the type of virus, as well as how close the person was in contact with the sick person or his things. With this disease, there is an increase and inflammation of blood vessels and nerve fibers, which leads to severe redness of the eyes, itching, and watery eyes.
Initially, the disease affects only 1 eye, but as it progresses, damage occurs to the second eyeball.
Pathological changes are observed not only in the mucous membrane of the eyes, but also in the general well-being of a person: body temperature rises, a runny nose appears, the cervical and pre-auricular lymph nodes enlarge, which become painful when palpated or when turning the head.
Basically, viral conjunctivitis manifests itself acutely, but still has its own characteristics, the symptoms of which directly depend on the type of virus, but in any case, the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- lacrimation;
- a burning sensation in the eyes.
- burning sensation in the eyes;
- photophobia;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- swelling of the conjunctiva;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- purulent discharge;
- gluing of eyelids.
In almost 60% of cases there is a runny nose, cough, headache, and fever. Sometimes, the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms, and is characterized only by redness of the conjunctiva, minor itching and burning in the eye area.
In ophthalmology, there are several types of viral conjunctivitis, each of which is caused by a certain type of pathogen and has characteristic symptoms that allow the doctor to make a primary diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment that will relieve inflammation, reduce and eliminate the vital activity of the virus.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis: symptoms
Adenoviral conjunctivitis, or the medical term pharyngoconjunctival fever, develops when adenovirus types 3, 4, 7, 10 enter the human body, in particular the mucous membrane of the eye.
This type of disease is highly contagious and spreads quite quickly among people. You can become infected by airborne droplets, through coughing, sneezing, or when the pathogen gets into the mucous membrane of the eyes or throat.
In the initial stages, the symptoms resemble a common cold, but within 1 – 2 days, the clinic is more pronounced and is characterized by the following signs:
- headache;
- rhinitis;
- feeling of weakness throughout the body;
- a sore throat;
- increased body temperature;
- cough;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- lacrimation with purulent or serous discharge;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- itching, burning in the eyes.
Source: https://cska-tir.ru/pri-konjunktivite-mozhet-bolet-golova/
Cause of diseases
Bacterial conjunctivitis develops after bacteria and viruses that cause acute respiratory infections, measles, and sore throat get on the mucous membranes. Conjunctivitis can accompany a cold and go away with it. They are easily transmitted from child to child during epidemics of colds in kindergartens and schools.
Gonococcal and chlamydial conjunctivitis are transmitted to the child from an infected mother during the passage of the birth canal.
The reasons why a person develops conjunctivitis. explain the classification of this disease.
The most common conjunctivitis is viral and bacterial. Staphylococci or streptococci enter the eyes through the hands, and viruses spread due to diseases such as herpes and chickenpox. sore throat, measles.
Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis are contagious and are easily transmitted from person to person through airborne droplets, as well as through shared objects.
Sore throat: caused mainly by pathogenic bacteria - streptococci, staphylococci and their associations.
Pharyngitis: the causative agent is most often a virus (influenza, rhinovirus, adenovirus, herpes, etc.), although it is worth considering that bacterial pharyngitis also happens. It can also be of an allergic and traumatic nature.
- various strains of viruses that cause ARVI.
- adenoviral infections. causing keratoconjunctivitis and conjunctival fever.
- enteroviral infections of the pickernavirus family, which are causative agents of epidemic and hemorrhagic diseases.
- activation of the herpes virus - Herpes simplex of the first two types, is the cause of herpetic conjunctivitis.
- The manifestation of follicular conjunctivitis is caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus. - novolat Molluscum.
Infection occurs through airborne contact, water and food.The undeformed lens and cornea have a smooth, spherical surface. Astigmatism leads to a violation of sphericity: the lens and cornea undergo pathological changes. As a result, light rays are fixed not at one point of the retina, but at several. Subsequently, the eye perceives objects indistinctly.
- ophthalmological operations;
- diseases associated with corneal opacities;
- dystrophic reactions in the organs of vision.
Astigmatism can be combined with myopia and farsightedness. There are mixed types of the disease (combined with signs of myopia and farsightedness). The mixed type of astigmatism is characterized by the fact that one area of the light beam is concentrated behind the retina, the other in front of it. Astigmatism is divided into several types.Cornea develops when the cornea has an irregular shape. This type of disease is common.
Distinctive diagnosis and treatment methods
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx; with tonsillitis, the tonsils are affected. Pharyngitis accompanies colds caused by viruses. The causative agents of acute pharyngitis in 70% are viruses, tonsillitis - bacterial flora.
Pharyngoscopy allows you to determine the localization of inflammation. In patients with pharyngitis, mucus flows down the reddened back wall of the pharynx (in acute form), there may be granulation (granular pharyngitis), thinning of the mucous membrane (atrophic pharyngitis).
When examining the throat of patients with tonsillitis, enlarged tonsils covered with purulent plaque are visible; the uvula and palatine arches may swell. The wall of the pharynx is not inflamed.
Main reasons
The discharge of pus from the mucous membrane indicates the progression of a bacterial complication, which develops against the background of advanced infectious and inflammatory pathologies. Common reasons why children and adults develop pustules in the pharynx and sinuses are:
- Acute tonsillitis. Characterized by inflammatory processes localized to the tonsils. With a sore throat, the throat becomes red, and hard purulent balls with an unpleasant odor appear on the tonsils, palatine arches and the back wall of the pharynx. The patient is bothered by a dry cough, mucus is difficult to cough up, and the patient complains of a feeling as if there is a stake in the throat.
- Chronic tonsillitis. It is a complication of acute sore throat, which is treated incorrectly or untimely. With this disease, the throat does not hurt so much; a bad-smelling discharge appears and then goes away. Relapse may occur without fever or with a slight increase in temperature.
- Sinusitis. A pathology that occurs in acute or chronic form, in which green pus collects in the nose. Constant inflammation leads to irritation and swelling of the mucous membrane. There is copious mucus secretion and a bacterial infection occurs. Due to congestion, it is impossible to breathe through the nose, and phlegm flows down the back wall of the throat.
- Diphtheria. A dangerous infectious pathology in which a yellow or white abscess forms on the palate and tonsils. If you try to remove the pus, a wound appears on the mucous membrane, the throat also hurts severely, and the disease occurs with a temperature of 38 °C and above.
- Laryngeal abscess. This is a dangerous complication, accompanied by necrotic changes in the pharyngeal mucosa, which causes the pus to turn black.
Return to contents
Other reasons
Yellow or white pustules in the throat can be a symptom of sinusitis. With this disease, inflammatory processes affect the maxillary sinuses, where pathological mucus accumulates. Pieces of purulent inclusions also accumulate between the nose and pharynx; when the infection spreads to neighboring structures, the eye festers and the ear becomes inflamed. During pregnancy, purulent lumps on the tonsils and palatine arch occur due to a decrease in the protective functions of the body. When immunity decreases, the tonsils begin to fight intensely against infection in the mouth, which become covered with a film and increase in size.
In a child, pus on the tonsils and a sore throat can cause a foreign body to enter the nasopharynx cavity. If the object is large and hard, it does not come out of the respiratory passage on its own. A small child sometimes cannot explain what happened to him, but parents should suspect a problem if pus and blood flow from the nose, the mouth smells bad, and green lumps are coughed up from the throat. If the foreign object does not come out on its own, the baby should be taken to the doctor.