Not everyone can boast of 100% vision these days. According to some reports, more than 25% of the female population suffers from myopia, and this number is growing rapidly and increasing every year. There are many reasons for this, and almost every woman tries to find an answer to the question of whether pregnancy and the process of childbirth affect vision, because very often you can hear that after childbirth, visual acuity decreases. Is this really so, and if so, why? And most importantly: how to prevent and prevent it? In this article we will answer exciting questions related to the postpartum drop in visual acuity.
Why does vision decrease after childbirth?
Possible vision problems after the birth of a child begin during pregnancy. They can be caused by natural physiological processes or emerging complications. In order for a woman to bear a healthy child, her hormonal levels are adjusted during pregnancy. Such changes often lead to disturbances in the condition and functioning of the visual organs. In particular, an increase in the level of the female hormone estrogen promotes the accumulation of fluid in the eye lens, which changes its size and refractive properties. The physical properties of the sclera and cornea also change, and the eye muscles become weaker.
If pregnancy proceeds with disturbances, the risk of vision deterioration after childbirth increases many times over. Toxicosis and gestosis, especially in severe form, can lead to disruption of the normal state of the choroid, which, in turn, can result in hemorrhage in the eyes or retinal detachment.
Sometimes vision decreases during pregnancy due to a lack of nutrients. An unbalanced diet, a small amount of fruits, vegetables, and cereals in a pregnant woman’s diet can lead to an imbalance in the vitamin and mineral balance of the body.
A lack of vitamins can contribute to damage to eye tissue and, as a result, a decrease in visual acuity.
Inflammatory processes in the retina, which often occur in pregnant women, also negatively affect vision. Anti-inflammatory drugs are usually used for treatment, but only a doctor can prescribe them. Childbirth itself is also a serious stress for the body and requires enormous physical effort from the woman. If a woman in labor breathes incorrectly during contractions and attempts, severe tension of the eye muscles occurs, IOP increases, which can result in hemorrhage.
As doctors note, even those births that took place without complications can lead to a physiological decrease in vision by several diopters. Subsequently, visual sharpness and clarity return gradually, over several weeks or even months. If the birth was complicated, then visual problems may be more serious and will require long-term treatment by an ophthalmologist.
How can an osteopath help?
One of the best recovery methods is to visit an osteopath. It is this specialist who is able to improve the functioning of internal organs, help the spine recover, and also reduce the negative impact of scar-adhesive changes after operations.
And if the birth was complicated and required surgical intervention, then you definitely cannot do without an osteopath. Previous gynecological operations can disrupt the outflow of blood from the pelvis, and venous congestion leads to chronic pelvic pain.
The same condition is observed with adhesions that can form due to epidural anesthesia. Osteopaths know how to create a new healthy balance in the pelvis, reduce adhesions, and remove venous stagnation. And after 3-4 sessions the pain goes away forever.
After childbirth, vision decreases: what to do?
If you notice that your vision has deteriorated after childbirth, the first thing you should do is consult an ophthalmologist. The specialist will determine how serious the disorder is and select the optimal treatment. Taking special multivitamin complexes for nursing women will help maintain eye health during the postpartum period. They contain a large amount of vitamins and minerals that affect visual function. Taking such medications in consultation with a doctor can stop the decline in vision and improve a woman’s overall well-being.
It is also necessary to monitor your diet and try to eat a variety of foods rich in carotene, B vitamins, antioxidants and other beneficial substances.
It is recommended to perform gymnastics several times every day, which helps to train the eye muscles, the accommodation apparatus, and relieve eye tension and fatigue.
The complex may include rotations and movements from side to side, squinting, shifting the gaze from distant objects to near ones, gentle massage through closed eyelids and a number of other exercises. Sometimes diabetes mellitus is the cause of vision impairment, in which case it is important to control blood glucose levels to avoid progression of the problems.
If an ophthalmologist has diagnosed myopia, astigmatism or another refractive error, then it is important to use optical correction means - glasses or contact lenses. They will help restore clear vision and can prevent its further deterioration.
Wearing contact lenses after childbirth is not prohibited, but it is better to discuss the choice of the appropriate model (Acuvue, BioTrue, Air Optix, PureVision, etc.) with your doctor.
If vision deteriorates after childbirth, then in some cases doctors recommend LASIK surgery. It can be used to correct myopia and other refractive errors. However, laser vision correction is recommended after breastfeeding has ended and hormonal levels have normalized.
What else can you do?
Physical activity can begin as early as the 3rd month after birth. But in order to create a good outflow of venous blood from the pelvic cavity, and prevent the abdominal press and pelvic diaphragm from weakening, the “vacuum” exercise will be the best help. Perform while lying on your back with bent legs: 1. Take a deep breath through your nose. 2. Exhale actively through your mouth, emptying your lungs. 3. Extend your ribs outward, allowing your belly to tuck under your ribs. Don't tense your abdominal muscles! Hold for 5-10 seconds. 4. Relax and breathe calmly.
It is recommended to visit an osteopath even for preventive purposes during the recovery period: to check the condition of bones, muscles, and ligaments. A pleasant bonus of this treatment is that osteopaths are able to erase the “memory” of the anesthesia from the body.
Is natural childbirth possible after laser vision correction?
Many women with myopia would like to correct this defect before pregnancy. But there is a myth that after laser surgery you will not be able to give birth naturally. For this reason, many people refuse LASIK.
Ophthalmic surgeons explain that laser vision correction performed before pregnancy in most cases is not a contraindication to natural childbirth.
That is, by improving your vision in this way, you will not have to give birth only by cesarean section. Surgical delivery is usually prescribed for other indications, including retinal detachment and serious eye pathologies.
A few words about our clinic
There is little that can surprise a modern person. Perhaps only excellent health. After all, everything depends on him: quality of life, family relationships, financial situation, etc.
The main goal of our “Quality of Life” clinic is to improve the patient’s quality of life, to give the opportunity to enjoy every day that comes, this is especially necessary for young mothers.
Children are the most important thing in the lives of many families. And women sometimes take unnecessary risks to have a baby. In almost 100% of cases, pregnancy leaves its mark on the life and health of the mother. That's why we strive to help you recover properly so that you can enjoy motherhood calmly and worry-free. A healthy mother means a happy baby. Restoring your figure after childbirth is certainly important, but not right away. But don’t waste time in fitness clubs, don’t exhaust yourself with hours of training, don’t put yourself on a strict diet in order to quickly get into your prenatal size, don’t look at yourself in the mirror with a dejected expression on your face, but don’t give up on yourself either. You are MOM! And now you are EVERYTHING for your baby. YOU are an example! It is YOU who bears all the responsibility and daily hassles. If pelvic pain and other pain syndromes appear, do not tolerate it. At the “Quality of Life” restorative medicine clinic, professional osteopaths and rehabilitation specialists are always ready to help you. Enjoy every day, give yourself and your body time to recover, and the results will not be long in coming.
- Directions
- Specialists
- For visitors
- Articles and videos
How to preserve vision after childbirth: preventive measures
Often the best way to preserve vision during the postpartum period is early prevention, begun during pregnancy or in preparation for it.
A woman who cares about her health should register with an ophthalmologist from the first weeks of pregnancy and undergo regular examinations. During such examinations, the doctor will examine the fundus of the eye, monitor visual acuity and other indicators.
It is useful to attend childbirth preparation courses during pregnancy, where they teach you how to breathe correctly and push while pushing. By learning to breathe and behave correctly during one of the most crucial moments of her life, a woman will minimize the risk of retinal damage and hemorrhage in the eyes.
Many girls have myopia and other vision problems even before giving birth. To maintain eye health, it is sometimes important to have a planned cesarean section as an alternative to a natural birth. The doctor must determine whether there are indications for the surgical method of delivery. Sometimes this is the only possible way to preserve vision after the birth of a child.
Now you know how to properly prepare for childbirth in order to minimize the risks to eye health, and what to do if your vision suddenly decreases. The birth of a child is not a reason to give up your own health, so we recommend that you carefully follow the recommendations of ophthalmologists. Regular examinations by your doctor and strict adherence to his advice will help protect your vision after childbirth.
Vision and childbirth: myths and reality
The topic of pregnancy and childbirth with poor vision is perhaps the most fertile ground for all sorts of speculation, myths and fears. Moreover, for the most part, they are completely groundless: among the many options for visual impairment, only two pathologies really make doctors think about the method of delivery, and even in these cases, cesarean section is not the only way out of the situation. But fear, as we know, has big eyes - and as a result, some expectant mothers, frightened by the prospect of “going blind in childbirth,” demand from the antenatal clinic doctor a referral for a planned operation, while others, dreaming of a natural birth and trying to hide the problems in order to achieve this goal with vision problems, they go to see a gynecologist without glasses.
In fact, neither myopia (myopia) nor hypermetropia (farsightedness) - the main reasons that force an expectant mother to wear glasses or contact lenses - are in themselves indications for surgical delivery. The so-called vision limitations for vaginal delivery are associated with other vision pathologies - increased fundus pressure and retinal pathologies, in which visual acuity, that is, the ability to see clearly without glasses, may well be normal. In these conditions, ophthalmologists can indeed give special recommendations to obstetricians for the management of childbirth, but in most cases they sound completely different from what future parents imagine. Contrary to popular belief, the ophthalmologist rarely pronounces the verdict “operative delivery” - only in cases of serious damage to the retina or fundus of the eye. In other cases, if minor violations are detected, it is recommended to “exclude the period of pushing,” that is, to minimize the tension of the mother’s press when moving the fetus along the birth canal, and for this in modern obstetrics there are much less radical methods that allow childbirth through the natural birth canal, without putting mother and baby at risk.
In order to dispel fears and speculation, let's try to understand the essence of the problem: what is the connection between pregnancy, the various stages of childbirth and the state of the pregnant woman's vision? To understand this, let's consider how the eye works and what can affect the structure and function of its structures.
Vision and childbirth: what you need to know about the structure of the eye
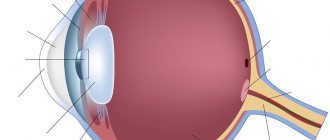
In medicine, the eye is called the “eyeball”. This name is due to the special spherical shape of the human organ of vision. The most important part of the structure of the eyeball is its three shells - the outer, vascular and reticular.
The outer surface of the eyeball is formed by the outer membrane. It consists of two parts: the front, shiny, which we see from the outside and through which the eye contacts the environment, and the back, invisible without examination. The front part is called the cornea. It is transparent and acts as a window to the outside world for the eye - after all, it is through it that rays of light enter the eyeball. However, this window is not simple, but with a secret: after all, the eyeball is convex, and the cornea, covering it, also has a convex shape - therefore, for penetrating light, it becomes not just glass, but a lens capable of refracting rays. The rest of the outer shell of the eyeball, covering it from the inside, is opaque and white. It's called the sclera and looks like the white of a hard-boiled chicken egg.
The next important layer of the eyeball consists of a network of tiny blood vessels, which is why it is called choroid. The vascular network of the choroid supplies the human eye with oxygen and nutrients necessary for visual function. This shell is also divided into several parts: anterior, middle and posterior. The anterior part of the choroid is called the iris; it secretes a pigment that determines the color of the eye. In the very center of the iris is the pupil - a round hole, the diameter of which depends on the amount of light. In bright light the pupil appears very small, but in the dark it dilates noticeably. The middle part of the choroid of the eye is called the “ciliary body” and produces intraocular fluid that washes all the structures of the eyeball. In addition, this part of the choroid has another important function: in its thickness there is an accommodative muscle, with the help of which the shape of the eye lens is regulated. The choroid - the most posterior part of the choroid - is adjacent to the third layer of the eye - the retina, providing it with nutrition.
The retina (or retina) is the third and probably the most important of the eye layers: in fact, it provides the ability to see. This happens as follows. This membrane lines the inside of the eyeball and consists of nerve cells. The retina is based on two types of photoreceptor cells: rods and cones. With their participation, the light energy entering the retina is converted into electrical energy. Rods help determine the outlines of objects in the dark, while cones are responsible for clarity of perception in light. In addition, cones help us distinguish colors and shades and the smallest details of visible objects. The retina displays everything we see. And then the information about the picture is transmitted along the optic nerve to the brain.
A feature of the retina is its weak and incomplete adherence to the choroid. This anatomical feature often provokes retinal detachment when certain eye diseases occur.
The inner part of the eye consists of the anterior and posterior chambers filled with intraocular fluid, the lens and the vitreous body. The lens has the shape of a biconvex lens. Like the cornea, it transmits and refracts light rays, focusing the image on the retina. The vitreous body has the consistency of jelly and separates the lens from the fundus of the eye.
Pregnancy, childbirth and vision: what are the risks?
During pregnancy, due to hormonal changes, the growth of the baby and the increase in the size of the uterus, the expectant mother experiences an increase in intra-abdominal and, as a consequence, intracranial pressure. In addition, the pressure, viscosity (thickness) and speed of blood flow in the vessels of the circulatory system changes. These factors can affect intraocular pressure and blood supply to the organ of vision, increasing the risk of retinal detachment in expectant mothers who already developed “weak spots” in this eye structure before pregnancy. Here it is important to understand that retinal pathology is not necessarily and not always associated with a clear deterioration in vision, which the expectant mother herself can notice - often visual acuity does not change at all. On the contrary, initially poor vision (a big minus and plus, the need to wear glasses) does not necessarily promise problems with the retina or increased fundus pressure. Therefore, doctors recommend being examined by an ophthalmologist several times during pregnancy: it is this specialist who determines the degree of risks, prescribes additional tests and treatment, and most importantly, determines the optimal method of delivery.
The risk of retinal detachment in women with pathology of the retina and changes in the fundus is associated with pressure changes in the woman in labor during labor and especially with repeated increases in intracranial pressure during the pushing stage, when the expectant mother strains her abs, pushing the baby out of the birth canal immediately in front of her. birth.
In modern ophthalmology, prophylactic laser coagulation is performed to prevent degenerative changes in the retina and the risk of retinal detachment. The coagulation technique is very simple, does not require hospitalization or anesthesia and takes literally a few minutes. The laser beam strengthens the retina, protecting it from stretching and detachment. The need for this procedure is determined by an ophthalmologist in the first and second trimester of pregnancy. Peripheral preventive laser coagulation can be done up to the 35th week of pregnancy - and as a result of timely examination and treatment, the expectant mother will be able to give birth naturally.
Childbirth and vision: we will be examined on time
When examining an expectant mother, the ophthalmologist’s task is to identify so-called vision limitations for vaginal delivery. Such diseases include increased fundus pressure and retinal pathologies. The main causes of the development of retinal pathology are increased arterial and intracranial pressure, diabetes, eye injuries, and vision correction operations. Pathologies of the retina include focal dystrophy (malnutrition of any part of it), increased tension of the retina (threat of its rupture), retinal rupture and failure of the suture on the retina after surgery to improve visual acuity.
Increased intraocular pressure is more often observed in patients with hypertension (high blood pressure), with gestational diabetes (impaired absorption of sugar in the body during pregnancy), gestosis (late toxicosis of pregnant women, characterized by increased pressure, increasing edema and the appearance of protein in the urine) and against the background increased intracranial pressure (with brain tumors, after traumatic brain injuries, with some neurological diseases). In these conditions, doctors recommend excluding the period of pushing, that is, not pushing while the fetus moves along the birth canal. Tension during pushing in pregnant women with pathologies of the fundus and retina can lead to a significant decrease and even loss of vision after childbirth.
These vision pathologies are easily identified during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist. A method that allows you to assess the condition of the fundus of the eye, identify retinal defects and assess the risk of their rupture during childbirth is called ophthalmoscopy. Usually, for the first time during pregnancy, such an examination is carried out already in the first trimester, that is, up to 12 weeks. If vision problems are detected during the examination, the woman is advised to come for repeat examinations in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Based on the results of the last examination, the ophthalmologist issues a written report for obstetricians with a recommendation on the method of delivery - even if high eye pressure or problems with the retina are detected, surgery is not always performed.
Why is a fundus examination necessary?
The fundus is the inner surface of the eyeball visible during ophthalmoscopy, including the optic disc, retina with vessels and choroid. An examination of the fundus by an ophthalmologist includes studying the degree of refraction, identifying pathological changes in the condition of the fundus, dystrophy of the retinal vessels, as well as the presence of retinal stretching, ruptures and detachments. To do this, various options for the ophthalmoscopy procedure are used, including the use of drops that dilate the pupil. Changes in the fundus during pregnancy may appear in the last stages, even if everything was fine in the first two trimesters. Symptoms such as false myopia or “floaters” in front of the eyes may indicate this problem. Pathology detected in time can be corrected, which will help prevent more serious consequences in the form of further thinning of the retina.
Problems and solutions: options for assistance in childbirth with poor vision
If changes in the retina or fundus are minor and no deterioration has occurred during pregnancy, the ophthalmologist may recommend vaginal delivery using epidural anesthesia in the second stage of labor. This method of pain relief allows you to create conditions under which the woman in labor does not feel any effort and practically does not participate in the advancement of the fetus through the birth canal. With the advent of epidural anesthesia in obstetrics, the number of caesarean sections “by sight” decreased by five times. However, with significant damage to the retina or progressive fundus hypertension, even minor efforts by a woman at the time of birth can lead to loss of vision. Therefore, if during pregnancy the situation worsens from examination to examination, the ophthalmologist recommends surgical delivery by cesarean section.
The listed vision pathologies are sometimes combined with myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism and other obvious vision problems. However, there is no clear connection between these conditions. Therefore, a change in visual acuity in itself, without more serious concomitant pathology, is never an indication for a cesarean section. You shouldn’t believe rumors, be tormented by vain doubts and hide alarming symptoms from the doctor - a timely examination by a specialist will resolve all doubts and choose the best option for your vision to help with the birth of your baby!