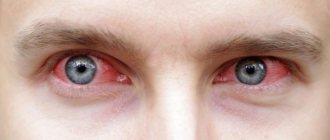
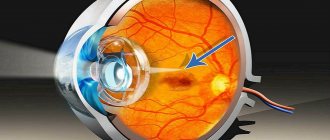
Photophobia of the eyes causes
The pathology may be congenital or acquired. In the first case, the increased sensitivity of the eyes to light is hidden in a malfunction of the body's functionality, which is accompanied by a decrease or complete cessation of the production of the hormone melanin.
In most cases, photophobia is characterized by pain when looking at a natural or artificial light source. It is often the primary sign of the development of the following anomalies:
- Keratitis;
- Wear of the lens;
- Benign or malignant tumor on the cornea;
- Iritis;
- Detachment of the retina;
- Conjunctivitis of any type;
- Corneal ulcer.
External factors can also cause eye pain:
- Burns to the retina when looking at the light and while working with welding without protective equipment;
- Use of contact lenses for irritation of the cornea;
- Use of certain medications;
- Spending a long time in front of a PC screen.
| If you stay at the computer for several hours and do not take breaks, the mucous membrane dries out. The tear film does not fully perform its “work” and does not protect the eyeball from harmful radiation. |
Symptoms
The main symptoms of photophobia include:
- discomfort, pain, itching, sensation of a foreign body, veils and pain in the eyes, forcing you to squint, close your eyes, or there is a constant desire to wear sunglasses or curtain the windows;
- redness of the eyes;
- blurred eyes;
- increased intraocular pressure ;
- tearing and various types of discharge - mucous, purulent, etc.;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- decreased visual acuity;
- negative emotional reactions and migraines when entering a space where there is bright sunlight, which promotes a closed lifestyle and forces one to avoid open spaces in the future, provoking agoraphobia ;
- increased discomfort in the eyes caused by other diseases.
Hypersensitivity to light rays can be accompanied by other mental disorders - depression, anxiety and other types of disorders .
Photophobia symptoms
Light sensitivity in the eyes may spread to one or both eyes. Finding himself in bright lighting conditions, a sick person begins to squint and reflexively covers the visual apparatus with his hand or closes his eyes completely. This is an instinctive reaction of the body that tries to protect the eyes from further contact with the irritant. When using tinted glasses, symptoms are less pronounced.
Photophobia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Blurry outline of objects;
- Decrease in visual acuity;
- Cut;
- Feeling of sand in the eyes;
- Increase in pupil size;
- Increased lacrimation;
- Strong headache;
- Filling of the mucous membranes of the eye with blood.
However, most often photophobia is not an independent disease, but a manifestation of various ophthalmological ailments. In this case, the anomaly is additionally accompanied by such signs as swelling of the eyelids, the formation of pus in the corners of the eyes and redness of the sclera.
If such symptoms do not appear, then most likely the anomaly is of neurological origin. To find out what caused photophobia, it is necessary to accurately establish the clinical picture. Return to contents
General information
Photophobia of the eyes, or otherwise photophobia, is a painful sensitivity of the organ of vision to light and refers to subjective visual disorders. Contact with even the slightest rays can cause quite unpleasant sensations in a person, including pain and discomfort in the eyes, spasm of the eyelids, severe lacrimation, resulting in an urgent need to squint the eyes.
The cause of photophobia usually lies in various eye diseases, but it can also be caused by measles , rubella , meningitis , encephalitis , epilepsy , pathologies of the cornea and conjunctiva, which could be caused by erosive processes and superficial inflammation. In addition, there is a possibility of developing photophobia when using eye drops to dilate the pupils.
The most famous people with photophobia were Hannelore Kohl, Lyubov Orlova, Anna Wintour.
Photophobia as a symptom of diseases
Intolerance to bright light signals the development of a number of ophthalmological abnormalities, which, in the absence of correct and timely treatment, lead to serious complications.
Conjunctivitis
Inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the organ of vision can be caused by viruses, fungi or bacteria. Treatment of the disease includes blocking pain with an anesthetic, which is eye drops (Lidocaine, Trimecaine).
Rinsing with antiseptic solutions will help cleanse the damaged organ of vision. Depending on the origin of the disease, antibacterial, antihistamine or antiviral drugs are used. Anti-inflammatory medications are used to eliminate the abscess.
Glaucoma
Increased intraocular pressure causes a decrease in visual acuity and the appearance of scotomas. The main manifestation of glaucoma is a change in the shade of the pupil, it becomes emerald or azure. The reason for the development of the pathology is hidden in the disruption of the free circulation of intraocular fluid.
| Glaucoma can also be caused by stress, intoxication, or taking hormonal medications for a long time. The risk group includes people over sixty years of age. |
Migraine
This is a chronic abnormality of neurological origin. A characteristic manifestation of the disease is unbearable pain in one part of the head. Impaired blood circulation, high blood pressure, and nervous system disorders can lead to migraines.
When there is bright light or loud noises, the throbbing pain increases. Massage, washing your hair, and a contrast shower will help you get rid of the attack. Try to avoid emotional and psychological stress. Remember that the key to health lies in a healthy lifestyle.
Fear of light during a cold
With viral abnormalities, body temperature rises. Many patients experience light intolerance. The reason lies in intoxication of the body as a result of the proliferation of pathogenic microbes and the penetration of their metabolic products into the circulatory system and muscles. Also, the person’s eyes become red, burning and pain appear.
If “pests” affect the structures of the organ of vision and lead to the development of conjunctivitis, then purulent or mucous discharge from the eyes is observed, and the eyelids swell. Less commonly, optic neuritis develops against the background of a cold; it has almost identical symptoms.
Photophobia with meningitis
A dangerous disease that causes inflammatory processes in the spinal cord and brain, is accompanied not only by photophobia, but also by unbearable headaches. The pathology is also characterized by an increase in body temperature, intolerance to loud sounds and the appearance of a rash on the skin.
Due to increased intracranial pressure, damage to the vessels of the visual system is possible. The disease develops rapidly and requires urgent hospitalization of the patient. Return to contents
Photophobia with measles
The disease rarely affects an adult. However, if it was not possible to protect yourself from the infection, it is very difficult to tolerate it. The disease invariably causes photophobia and increased lacrimation. The patient also feels a loss of strength, body temperature rises, and a rash appears on the skin.
| The cause of photophobia in measles is due to the fact that inflammatory processes affect the mucous membrane of the eye. |
Photophobia – cataracts
The pathology is most often encountered by women in old age. The cause of the development of the disease is a decrease in the degree of transparency of the lens, its complete or partial clouding. The main symptoms of the disease are blurred contours of objects, diplopia, and impaired color vision.
Many patients diagnosed with cataracts experience intolerance to bright light. Moreover, photophobia intensifies in the evening, and in the dark, visual acuity completely decreases. In addition, the appearance of luminous halos around the light source (lamps, lanterns) is observed. The reason lies in the fact that light pulses, hitting the clouded lens, are scattered and do not reach the retina.
Symptoms of photophobia
Light phobia is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Dry eyes;
- Feeling of “sand” in the eyes;
- Tearing;
- The desire to squint, close your eyelids periodically or constantly;
- Frequent headaches.
The presence of several symptoms immediately requires contacting a specialist to identify or exclude pathologies. First, visit an ophthalmologist, he will give other directions.
Over time, a person begins to experience general discomfort due to being in a brightly lit room; his appearance in the open sun causes tearfulness, a desire to hide in the shadows, or better yet, in a dark room. The longer a person is inactive, the more his health and mental state deteriorate.
If you suspect photophobia, you should consult an ophthalmologist
If it hurts to look at the light and your head hurts
A migraine that appears or intensifies when looking at a light source signals the development of the following ailments:
- Meningitis;
- Stroke;
- Encephalitis;
- Damage to brain tissue as a result of trauma;
- Formation of a tumor in the main organ of the central nervous system.
If a headache is accompanied by light intolerance, first of all you need to go to an appointment not with an ophthalmologist, but with a neurologist. Since such symptoms are a sign of neurological disorders.
Causes and symptoms of the disease fear of light
Photophobia is the most popular among those described above.
It can be associated with emotional disorders, mental disorders, and diseases of internal organs, including the visual apparatus. So, the main reasons for fear of light are as follows:
- psychosomatic disorders in which the patient feels panic fear when in the light;
- acute respiratory diseases, against the background of which severe intoxication of the body occurs, and it is difficult for a person to look at the light;
- after waking up, suddenly turning on the light in a dark room, or going out into the sun after a long stay in the dark. Fearfulness of lighting develops as a result of the fact that the pupil does not have time to narrow to the required size;
- cataract. Due to clouding of the cornea of the eye, light reaches the pupil poorly and gradually it reduces its transmission capacity, which manifests itself as discomfort;
- glaucoma. Due to increased intracranial pressure and disruption of impulses from the visual organ to the brain, the eye becomes sensitive and a fear of daylight develops.
If we talk about the causes of Gunther's disease, then we will talk about a congenital pathology, the signs of which appear already in the first year of life.
As an exception - at 4-5 years. The cause of fengophobia is a previous severe illness of the eyes and brain. As a result, exposure to light causes physical and mental suffering, discomfort and painful sensations in the eyes.
The cause of heliophobia is a strong emotional experience, anxiety. For example, an impressionable person saw a fire victim or a sunburn victim.
Symptoms of the disease fear of sunlight differ depending on the cause and type of phobia. As a rule, it manifests itself:
- increased sensitivity of the eyes and skin to light, especially sunlight. The skin turns red, becomes covered in a rash, and feels itchy. Your eyes burn, you feel pain, you want to close them;
- nausea, vomiting, increased body temperature. This is typical for illnesses caused by acute respiratory infections, meningitis, measles and other infectious diseases;
- attacks of panic at the mere thought of light and sun;
- increased heart rate.
Depending on the type of phobia and the severity of its occurrence, the symptoms differ in the intensity of their manifestation. By which symptoms are more pronounced, you can determine which symptoms of disease are characteristic of fear of light and photosensitivity.
Why does a child's eyes hurt from light?
The organ of vision of babies is not much more sensitive than that of adults. But this is enough for the development of photophobia. The following reasons can cause it:
- Ophthalmic ailments (retinal detachment, keratitis or glaucoma, uveitis, corneal ulcer);
- Neurological disorders (inflammatory processes in the brain, migraine);
- A number of infectious diseases (botulism, meningitis, encephalitis).
According to statistics, children most often visit an ophthalmologist due to photophobia due to the development of conjunctivitis, optic nerve palsy or lack of melanin.
| Also, doctors in practice often encounter such a manifestation as snow ophthalmia. This is a retinal burn that appears if you look at snow-white snow in bright light for a long time. |
Return to contents
Diagnosis and clinical picture
If the first signs of light intolerance appear, consult a doctor immediately. To make an accurate diagnosis, the ophthalmologist will prescribe a number of diagnostic examinations:
- Ophthalmoscopy. Using a unique technique, the doctor analyzes the condition of the fundus;
- Perimetry. Conducted to test visual fields and detect dark spots;
- Biomicroscopy. The ophthalmologist's main tool for this examination is the slit lamp. With its help, the doctor can detect pathological processes in the fundus and vitreous body;
- Tonometry. It is carried out to measure intraocular pressure;
- Gonioscopy. During the examination, the iris is in close proximity to the cornea;
- Ultrasound. It is prescribed if ophthalmoscopy cannot be performed. Conducted to analyze the degree of transparency of the internal environment of the eye;
- Pachymetry. Measuring the thickness of the cornea;
- Fluorescein angiography. Study of the patency of blood vessels in the visual apparatus;
- Optical coherence tomography. Helps identify destructive processes in retinal tissue;
- Exudate from the conjunctival sac is sent for bacteriological examination to determine the type of pathogenic organisms or viruses.
If, after a detailed diagnosis, it is revealed that there are no disturbances in the functioning of the visual apparatus, then the patient is sent for a consultation with a neurologist. He may order additional examinations:
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- Electroencephalography;
- Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland.
If necessary, blood is taken for biochemical analysis. If signs of tuberculosis infection are detected, then further therapy will be carried out by a phthisiatrician.
Photophobia of the eyes treatment
It is pointless to start treatment for photophobia without finding out the reasons for its occurrence. In some cases, the symptoms go away on their own; it is enough to eliminate the irritant or simply cure the concomitant disease. Darkened sunglasses and anti-inflammatory eye drops can help reduce the severity of photophobia.
Treatment for the anomaly depends on the cause that provoked its appearance. If photophobia is caused due to inflammatory processes in the eyeball, then after eliminating the source of infection, the symptom will go away on its own.
If there is purulent exudate, antiseptics or antibiotics are prescribed, for example, Okomistin eye drops. If the cause of photophobia lies in mechanical damage to the organ of vision or a burn of the mucous membrane, urgent medical attention is required. You can first use antiseptic drops and apply a sterile bandage to the damaged eye.
If the pathology has developed as a result of a foreign body or dirt getting into the eye, then after eliminating the source of the “problem” the symptom will go away on its own. In some cases, light intolerance appears due to an infectious pathology that has nothing to do with the visual apparatus and its functioning. In such situations, therapy is aimed at combating the underlying disease.
| If the cause of an unpleasant symptom lies in taking medications, tell your doctor. He will select an analogue of the drug that will not cause such a reaction. |
Congenital photophobia is corrected with special contact lenses, which minimize negative symptoms. Return to contents
I have increased eye sensitivity to bright light.
8
I always squint from bright daylight, and in winter from white snow. It’s very uncomfortable, and the eyes become very strained and tired... Tell me, are there any remedies to reduce the sensitivity of the eyes to light? And isn't this sign a cause for concern?
visionophthalmologyhealth
Added: September 16, 2011 at 09:59 Leah Level: 15
Comment..
Subscribe
0
If the best advice is not chosen for a problem, then the price for the best advice increases every minute. If the council has already been elected, this does not mean that your council cannot become the best (the best council may change if yours gets more votes). If there is a tie in votes for advice, the one given first wins. The advice must contain unique information relative to other advice already given. If you mostly agree with the advice already given, then simply vote for it and add unique information in the comments. The system itself determines how many votes the council needs to get to become the best (this indicator depends on the current level of activity on the project) Report on the last payment
Statistics on current payout
Tips: 3
3
You need to see a specialist, since eye sensitivity in some cases can be symptoms of a disease, I don’t want to scare you, perhaps this is just a feature of your body. But nevertheless, see a doctor, only he will be able to correctly answer this question. In general, you can buy glasses with simple chameleon lenses, one of my friends did just that after they sprayed a gas canister into his eyes at a disco, and his sensitivity also increased. But don’t put off visiting the doctor!
Added: September 16, 2011 at 11:45 Manechka Level: 13
Comment..
2
Almost all people squint from bright light in winter. This is how the body limits the bright stream of light entering the pupil, because constriction of the pupil is a natural reaction to bright light; it is not enough. In winter, with clean snow, this occurs from an excess flow of light waves reflected from the white surface of the snow, exactly the same phenomenon occurs when a person is near a large open surface of water, so tanning in snow-capped mountains and near water is much more intense. Under these conditions, it is normal for a person to squint reflexively to protect the retina from being burned. And if this phenomenon (squinting) occurs in normal lighting, it is photophobia. Photophobia (photophobia) is a painful sensitivity of the eye to light, in which exposure to light causes unpleasant sensations in the eyes and causes the person to squint their eyes. Usually caused by some kind of eye disease. Photophobia can develop as a result of dilated pupils after instilling various eye drops. Also possible due to measles, rubella, meningitis, diseases of the conjunctiva and cornea (erosion, conjunctivitis). Photophobia occurs when you spend a long time in the dark or twilight. Many years of daily computer abuse also leads to this condition. Photophobia in one eye, accompanied by pain, can be caused by the presence of a foreign body on the cornea. In healthy eyes, photophobia occurs when too much light enters the eye, such as when the light is too bright. For photophobia, wearing sunglasses is recommended, with mandatory treatment of the underlying disease.
Added: September 16, 2011 at 12:03 Alexander Level: 10
Comment..
1
I have the same problem) there is no reason to worry, but it creates some inconvenience, so in the summer it is more convenient to wear dark glasses.
Added: September 16, 2011 at 21:52 Marina Level: 13
Comment..
Your advice
Give advice..
Isn't this the problem you were looking for? Look at others under the tags visionophthalmologyhealth or create your own problem.
Drops for photophobia of eyes
If the cause of photophobia is hidden in an ophthalmological disease, then doctors usually prescribe drops to eliminate the symptoms:
- Antibacterial (“Levomycetin”, “Tobradex”);
- Anti-inflammatory (“Dexamethasone”, “Indokillir”);
- To moisturize the mucous membranes (“Oxial”, “Kationorm”);
- To narrow blood vessels (“Vizin”, “Okumetil”).
In addition to medications, it is recommended to regularly perform eye exercises and massage. If after five days therapy with drops does not produce results, it is necessary to adjust the treatment.
Traditional medicine for photophobia
Grandma's recipes should under no circumstances be an alternative to conservative therapy! They are used as one of the stages in complex treatment and to prevent the appearance of photophobia.
Eyebright erecta
The plant helps cope with photophobia and improves visual acuity. Take one teaspoon of herb and two hundred milliliters of water. Bring the broth to a boil, leave for three hours and strain. Use the resulting infusion for compresses (leave for half an hour), eye baths (it’s best to do them before bed) and instill three drops into each eye every day.
Chamomile with calendula
Take one teaspoon of dried flower and grind it. Add a glass of boiling water, leave for sixty minutes and strain. Use the solution as a bath three times a day. You can also drop the infusion into your eyes, two drops in each eye, or make a lotion out of it for the organ of vision.
Sea buckthorn
You will need two tablespoons of crushed orange berry pulp and 1 tsp. honey. For seven days, apply eye compresses in the morning and evening. Leave the lotions on for fifteen minutes.
Plantain
In a thermos, combine three hundred milliliters of boiling water and twenty grams of the plant. Leave for three hours, strain and rinse the affected eye morning and evening.
Possible complications
One of the most severe consequences that photophobia can provoke is the development of the disease into a chronic form and aggravation of the patient’s condition. In some cases, the disease causes complete loss of vision.
| In addition to the fact that a person’s quality of life is significantly reduced, the risk of developing a dangerous psychological illness called heliophobia increases. This is a panic fear of sunlight. |
Patients with this diagnosis, as well as those who have recovered from photophobia, experience stress and incredible emotional distress if they have to go outside during the day. On a subconscious level, they fear that sunlight will again cause pain and discomfort.
Heliophobia is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- Cardiopalmus;
- Tremor of the limbs;
- Arrhythmia;
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- Dizziness. In some cases, patients lose consciousness for a short period of time;
- Panic attack;
- Hysterics.
If intolerance to bright light appears, you should not hope that after a while the symptoms will go away. You need to immediately visit an ophthalmologist, because photophobia can be the first sign of serious destructive processes occurring in the body. Return to contents
Prevention
There are a number of recommendations that will help minimize the risk of photophobia. Monitor how much time your child spends on the computer. Even for training purposes, he should not sit in front of the monitor for a long time.
Normalize your sleep and rest patterns. You need to sleep at least eight hours, preferably going to bed at the same time. Walk more in the fresh air and balance your diet. Oxygen, vegetables and fruits will help build a protective barrier that will prevent the development of pathology.
From an early age, teach your child personal hygiene. Otherwise, pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate into the visual apparatus, causing a variety of ophthalmological diseases, including photophobia.
| In between working at the computer and in any free moment, do simple eye exercises, which will help relieve tension and relax the muscles of the visual apparatus. When going outside on a sunny day, do not forget to wear safety glasses. |
Causes of photophobia
Various factors can explain the causes of photophobia. There are cases in which short-term photophobia is quite normal. Everyone wants to squint their eyes; this happens mechanically, when the lighting becomes too bright, when the light suddenly illuminates the dark room. Mechanical damage to the eyes or a serious disorder can cause photophobia when there are no prerequisites for its onset, when there are no sudden changes in light. This is already a serious reason to contact an ophthalmologist.
Inflammation of the tissues of the conjunctiva and cornea can cause very unpleasant sensations if light enters the eye. Drug treatment can also lead to very significant negative effects, which will manifest itself in the form of photophobia. The functioning of the visual system is impaired, for example, measles, rubella, meningitis, this can be directly related to photophobia. It is also caused by our habits or poor lifestyle. The same constant loads, working at a computer, watching TV channels, cause a similar anomaly.