How does photophobia of the eyes manifest?
Photophobia is commonly understood as a painful reaction of the eyes upon direct contact with a source of natural or artificial light. The most pronounced symptoms of this pathological condition are closing of the eyelids and increased lacrimation. In addition, accompanying symptoms are often observed - pain, burning and itching. Sometimes photophobia of the eyes is accompanied by headache, nausea, vomiting, and in severe cases, even loss of consciousness. All of the above symptoms are typical for both children and adults. Discomfort occurs only with direct contact with a light source. When you are in a darkened room, it disappears.
Photophobia can be temporary or long-lasting. In the first case, it occurs due to exposure to external factors, for example, prolonged contact with ultraviolet rays or taking certain medications. This reaction usually goes away on its own, so the person does not require medical attention. If increased sensitivity of the eyes to light is observed for more than two days, we can talk about a long-term nature of the manifestation. In such a situation, you should consult a specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination to identify the cause of the pathology.
From a physiological point of view, photophobia is an excessive manifestation of the protective reaction of the eyes to exposure to a light source. In a normal state, when exposed to high-intensity light rays, the unconditioned reflex of involuntary squinting is triggered. Each person has his own threshold of permissible brightness, which the organs of vision can perceive. But in general, this indicator has an average statistical value. If the intensity of the light source exceeds the permissible norm, involuntary squinting of the eyes occurs, caused by blinding. This reaction is normal. In the case when the closure of the eyelids and increased lacrimation are observed at a normal level of brightness of the light source, we can talk about photophobia.
The appearance of such a reaction may be associated with a disruption in the functioning of the visual, nervous or endocrine system. Also, increased eye sensitivity to light occurs as a result of serious pathological conditions in the human body, including intoxication, an acute attack of glaucoma and migraine. Therefore, many are interested in photophobia: a symptom of what disease? To reliably answer this question, you need to take a general blood test and undergo a comprehensive examination.
In some cases, high eye sensitivity to light may be associated with a serious psychiatric illness such as heliophobia (fear of being in the sun). This reaction should not be confused with photophobia, since it has nothing to do with the functioning of the visual system. The cause of this pathological condition is associated with a malfunction of the human nervous system.
Signs of photophobia:
- Increased lacrimation;
- Involuntary squinting of the eyelids;
- Pain, itching, burning and stinging;
- In some situations - dizziness and headache;
- In severe cases - nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness.
Complications
Why is this painful manifestation dangerous? In addition to discomfort, psychological problems and constant stress from the inability to react normally to light, this pathology has much more negative consequences, which are caused by the course of various serious diseases caused by this pathology. Signs of photophobia, along with a host of accompanying symptoms, may indicate severe pathological processes in the body. And if they are not treated, everything can end very sadly.
For example, increased lacrimation may indicate the development of keratoconjunctivitis, a neurological process of the trigeminal nerve, or rabies. When the symptoms of photophobia are combined with a severe headache, this indicates the possible development of meningitis, migraine, encephalitis and a number of other infectious diseases.
When nausea and severe vomiting are added to photophobia, the doctor may be concerned about a developing brain abscess.
All of these diseases are very dangerous for a child. Their consequences may not only be difficult to respond to medical intervention, but also be irreversible. Therefore, if signs of photophobia appear, it is necessary to undergo a full examination by a specialist so as not to miss the onset of a serious problem, which can begin to slowly develop in a fragile body.
Photophobia of the eyes in an adult: why it occurs
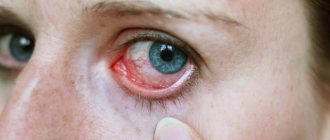
One of the most common causes of photophobia are various infectious, inflammatory and other diseases of the visual organs. Often people suffering from conjunctivitis (inflammation of the uvea), keratitis (inflammation of the cornea), and iritis (inflammation of the iris) turn to ophthalmologists with this problem.
In some cases, photophobia of the eyes in adults manifests itself due to adverse environmental influences, for example, with prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays reflected from snow. Also, photophobia can result from damage to the eyes from excessively bright light during welding work without protective glasses. Sometimes the occurrence of this reaction is associated with some common diseases, such as migraine, acute respiratory infections, influenza, and an acute attack of glaucoma may also be the cause.
People on forums often ask what serious disease symptom is photophobia. Experts say that this reaction may indicate problems with the thyroid gland or signal a tumor in the brain. The patient will be prescribed additional examinations, such as ultrasound, MRI or CT. The causes of photophobia are sometimes associated with damage to the visual organs of various types, including wearing incorrectly selected contact lenses or penetration of a foreign body. Sunburn, as well as ulcers, erosion and mechanical damage to the cornea can also cause involuntary squinting of the eyes when in direct contact with a light source.
What diseases does increased light sensitivity of the eyes indicate? The appearance of this reaction is often not associated with pathological processes. Sometimes constant drying of the cornea and increased visual stress also become the causes of photophobia. This is especially true for people who spend a long time in front of a computer monitor.
In rare cases, symptoms of photophobia occur in people due to the complete absence or insufficient amount of a special pigment in the body (melanin). At the same time, the eyes react too actively to any light source. In this case, the pathology is congenital. It should be noted that this form of sphetophobia is quite rare.
Photophobia can be a symptom of what disease?
- Various diseases of the organs of vision (inflammatory, infectious, etc.);
- Malfunctions of the nervous system;
- Pathologies of the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- General diseases (flu, acute respiratory infections, glaucoma);
- Hereditary diseases associated with insufficient melanin in the body.
Video
There can be many reasons when a baby begins to be afraid of daylight or artificial light. The real reason can only be identified by an experienced specialist during diagnosis.
- The described illness may be the result of mechanical damage to the eye, a foreign body entering the organ, or a consequence of a dangerous disease.
- In particular, photophobia occurs in children who have a congenital absence or deficiency of the melanin pigment.
- In addition, the disease manifests itself in pathologies of the membranes of the eye, tumors in the cornea of the organ.
- There are known cases of photophobia as a side effect of certain medications.
Photophobia in children
Increased sensitivity of the visual organs to light can occur in any person, regardless of age. Photophobia in children appears due to lack of sleep, excessive time spent at the computer, stress, as well as various pathologies of the visual organs. Children are more often susceptible to viral and infectious conjunctivitis and other diseases, so there is a risk of increased photosensitivity of the eyes. Sometimes incorrectly selected correction means can become a provoking factor. Therefore, it is important that the selection of optical products is carried out by a qualified ophthalmologist after conducting a comprehensive examination of the visual system.
Quite rarely, photophobia of the eyes in a child is associated with the so-called “pink disease”. This is an autoimmune disease accompanied by increased blood pressure, photophobia, increased sweating, anorexia, and pinking of the skin of the palms and soles with prolonged contact with a light source.
Prevention
To prevent photophobia and the diseases that cause it, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- periodic visits to an ophthalmologist with laboratory and instrumental tests to promptly identify and eliminate eye diseases;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases to prevent the formation of complications;
- avoiding visiting crowded places during an epidemic of viruses or infections that often appear in the autumn-winter period;
- removing dangerous objects that could injure a child’s eyes;
- Wearing sunglasses outdoors when exposed to strong winds.
Preventive measures will not eliminate the possibility of all ophthalmic diseases, but will significantly reduce the risk of their development. Parents should remember that photophobia can be a symptom of an ophthalmological or systemic disease, so not all conditions can be treated at home.
Diagnosis of photophobia of the eyes
If symptoms of photophobia persist for more than two days, you should seek medical help. Initially, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination of your vision organs in the office of an ophthalmologist. As a rule, it includes various diagnostic methods aimed at identifying the cause of the pathology: examination of the condition of the cornea, ophthalmoscopy, and others. If the specialist determines that the cause of photophobia is not related to a dysfunction of the visual system, the patient will be scheduled for further examination by a neurologist, who will most likely give a referral for an MRI or CT scan of the brain. In some cases, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and other examinations may be required. This approach is aimed at identifying the primary cause of photophobia. Only in this case can the patient be provided with qualified medical care to eliminate high sensitivity to light.
If it is impossible to eliminate the cause of the primary pathology, for example, with autoimmune thyroiditis, a person is recommended to make small adjustments to his daily life to prevent photophobia. On sunny days, direct contact with ultraviolet rays should be avoided. To do this, you should go outside wearing a wide-brimmed hat and safety glasses. These recommendations are also relevant if photophobia is in no way related to any pathological processes and is an individual feature of the human body.
If photophobia occurs temporarily, for example, due to a foreign body entering the eye, you should use a moisturizing ophthalmic solution, antiseptic or anti-inflammatory drops. This will help alleviate the symptoms somewhat. However, the use of medications is permissible only under the supervision of a physician.
Symptoms of photophobia for which you should consult a doctor:
- Increased lacrimation and pain in the eyes are observed even with low lighting levels;
- Vision becomes blurred when in contact with a light source;
- Discomfort persists for 2 or more days;
- Headaches and dizziness appear;
- There is a need to wear sunglasses indoors.
Treatment
Treatment methods depend on the cause of the condition. The most commonly used drugs and techniques are:
- removal of a foreign body using ophthalmic instruments and eye rinsing;
- antibacterial drugs in the form of drops, if the cause is an external infectious and inflammatory eye disease;
- antibacterial systemic drugs, if photophobia has developed due to an infectious disease of the body;
- antiviral agents in the form of tablets and eye drops;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of eye drops.
If the cause of the condition is a systemic disease, complex therapy will be needed to eliminate the risk of relapse.
When carrying out treatment, parents should remember that antibacterial drugs are applicable for no more than 7 days, after which time the bacteria develop resistance. Antiviral drugs can be used over a long course of therapy; they are not addictive.
How to prevent the appearance of photophobia?
To prevent the occurrence of increased eye sensitivity to light, doctors advise following a daily routine. It is important that sleep is stable and complete: at least 7 hours for adults and at least 8 hours for children. Daily walks in the fresh air are also recommended, preferably at least 1-1.5 hours a day.
Maintaining personal hygiene of the organs of vision is also an important factor in preventing the occurrence of photophobia. This will eliminate the risk of developing infectious and inflammatory processes in the eyes. Another important component of prevention is a balanced diet. It is important that a person receives the required amount of vitamins, macro- and microelements from food.
With increased visual stress, it is worth regularly performing simple eye exercises every 30-40 minutes of working at the computer. Builders, drivers and representatives of other professions who are often outdoors during the daytime need to wear sunglasses with a UV filter.
On the Ochkov.Net website you can profitably buy contact correction products to improve vision clarity for myopia, farsightedness and other refractive errors.
Symptoms
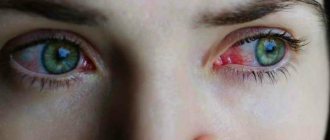
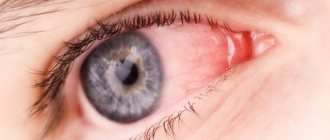
A person suffering from photophobia, when exposed to an illuminated space, squints, closes his eyes, and tries to protect his eyes from the light with his hands. When wearing sunglasses the situation improves slightly. Increased photosensitivity may be accompanied by additional symptoms, such as:
- Headache;
- Pupil dilation;
- Redness of the eyes;
- Feeling of “sand” or “stinging” in the eyes;
- Impaired visual acuity;
- Unclear outlines of objects.
If you increase sensitivity to light, you should not delay consulting a doctor, as this symptom may hide a malignant brain tumor that progresses quickly.